Expression of gastrin and cholecystokinin B receptor in Lateolabrax maculatus
Tingwen Cui, Jiqi Wng, Zhongjun Hu, Xiowu Chen
a Shanghai Ocean University, National Experimental Science and Education Demonstration Center for Fishery Science, Shanghai, 201306, China
b Shanghai Ocean University, Shanghai Collaborative Innovation Center for Aquatic Animal Genetics and Breeding, Shanghai, 201306, China
Keywords:Lateolabrax maculatus Gastrin Cholecystokinin B receptor
A B S T R A C T Gastrin (gas) is a peptide hormone that stimulates gastric acid secretion by gastric parietal cells and stimulates gastric motility.The cholecystokinin B receptor (cckbr) can act as a receptor for gastrin, conveying regulatory information on gastrin, but there are fewer studies on its function in fish.The Lateolabrax maculatus is one of the marine aquaculture species in China, it widely distribute in coastal areas.In the study, we cloned the genes of Lateolabrax maculatus gastrin (Lm-gas) and Lateolabrax maculatus cholecystokinin B receptor (Lm-cckbr).The results showed that the full-length gene of Lm-gas is 638bp and the carboxy-terminal conserved domain (DFGRR)is the core functional domain of gastrin protein.The Lm-cckbr gene has a total nucleotide sequence of 2066 bp,and the open reading frame encodes a total of 453 amino acids.The result of protein sequence alignment showed that the similarity between Lm-cckbr protein and other different species was 50.11%–89.67%.The PCR results showed that Lm-gas and Lm-cckbr were expressed in brain and stomach.Further localization by immunehistochemical staining showed that Lm-gas protein was located in the mucosal layer of the gastric wall, but the expression signal was weak in the brain.Hunger causeed a significant decrease in these two genes.The results provided basic research data for further study on the function of Lm-gas and its recepter Lm-cckbr in the in the central nervous system and digestive system of Lateolabrax maculatus.
1.Introduction
Gastrin is an important gastrointestinal hormone, which exists widely in mammals, amphibians, birds and fish.Gastrin can stimulate gastric parietal cells to secrete gastric acid and propepsin, increase gastrointestinal motility and stimulate gastrointestinal mucosal growth(Guilloteau et al., 2006; Koh & Chen, 2000).Human gastrin is produced by G cells of gastric antrum and duodenum (Modvig et al., 2020), the mature gastrin obtained by enzyme digestion and processing has a relatively conserved carboxy-terminal sequence with high similarity among vertebrates.The gastrin family includes gastrin, cholecystokinin and frog skin peptide.Phylogenetic analysis shows that although they share a common ancestor, the former two genes are more closely related.(Vigna, 2000).Structurally, the three have four amino acid sequences at the carboxyl end, namely tryptophan-methionine-aspartic acid--phenylalanine, and a sulfated tyrosine residue.
There are two kinds of cck receptors of cckar and cckbr in vertebrate,both receptor subtypes are members of the seven transmembrane G protein coupled receptor family, with approximately 50% amino acid identity (Yu & Smagghe, 2014).The amino acid sequence alignment of the two showed high similarity, and the phylogenetic tree showed that Cckar and Cckbr shared a common ancestor, which suggested that they had a certain degree of functional similarity.However, there are obvious evolutionary divisions in vertebrates, and there are also differences in tissue distribution and priority binding ligands between them (Rathore et al., 2013).Cckar mainly exists in the gastrointestinal tract.It can preferentially recognize sulfated CCK and was used as a specific receptor.For mammals, Cckbr is mainly distributed in the central nervous system, mainly in the neocortex and marginal structures.In the peripheral structure, the cckbr is strictly limited to the stomach (Nishimura et al., 2015) and can bind gastrin, so Cckbr can be used as a gastrin receptor (Lindstrom et al., 2001).
Lateolabrax maculatus, as an important marine economic animal in China, is a species distributing in coastal and estuarine areas.Adult fish also could be feed on shrimp, crabs and small fish in freshwater waters(Hong et al., 2012).In intensive culture, artificial feed culture can be achieved onLateolabrax maculatus, and changes in food nutrient sources have multifaceted effects onLateolabrax maculatusgrowth.The digestivephysiology ofLateolabrax maculatusis an area of great concern.According to the results of genomic sequencing (Shao et al., 2018) and transcriptome sequencing (Wang et al., 2017) completed in the same period, we obtained gastrin and its receptor genes by homologous alignment and analyzed their structural characteristics and tissue expression in the hope of providing basic data for endocrine regulation in the fish digestive system.
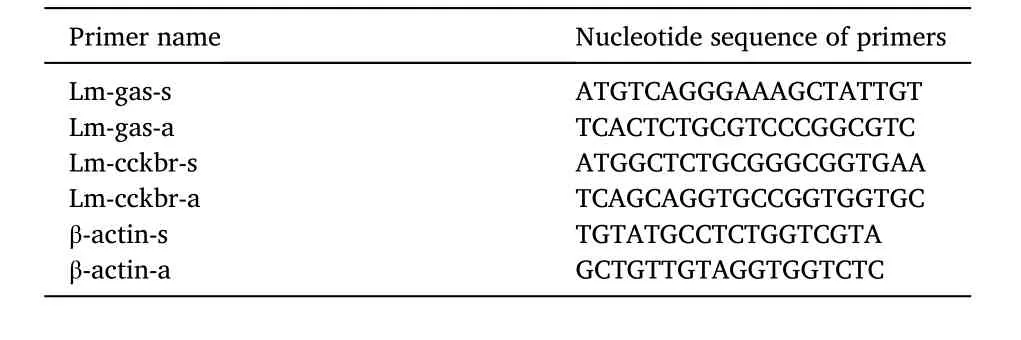
Table 1 Primer sequences used for gene cloning.
2.Materials and methods
2.1. Ethics statement
The collection and handling of the animals in the study was approved by Shanghai Ocean University’s animal care and use committee.For sampling, all fish were anesthetized using MS-222 to minimize suffering.
2.2. Fish
All experimental animal protocols in this study were reviewed and approved by the Regulations for the Administration of Affairs Concerning Experimental Animals approved and authorized by the State Council of the People’s Republic of China and the Animal Ethics Committee of Shanghai Ocean University (2016NO.4).Fish were sacrificed,and all efforts were exerted to minimize suffering.The experimentalLateolabrax maculatuscame from the Binhai Culture farm of Shanghai Ocean University and is a freshwater domesticated population.Its body weight ranged from 180 to 220g, and the culture water temperature is 25 ± 2?C.Fresh minced fish was fed twice a day regularly.The experimental group included 6 individuals with normal body color and healthy fish body.Fish in the starvation group did not feed for three days.SixLateolabrax maculatuswere dissected, the tissues (brain, gill,stomach, intestine, liver, kidney, testis and ovary) were frozen at 80?C.
2.3. Gene cloning and quantative PCR
The total RNA was extracted from the collected tissues according to the instructions of TrizolReagent (Invitrogen) instructions, and the total RNA was inverted into the first chain cDNA by PrimeScriptTMRT reagent Kit with gDNA Eraser (Takara).The gastrin mRNA sequences of human,medaka, flounder and tilapia were obtained and compared from NCBI database.According to the conservative region, referring to our genome sequencing (Shao et al., 2018) and transcriptome sequencing (Wang et al., 2017), the specific primer sequences of Lm-gas and Lm-cckbr were designed by using primer design software Primer Premier 6.0.The beta-actin was used as internal reference gene.The sequence of primers is shown in Table 1.After gene cloning and sequencing, the confirmed Lm-gas and Lm-cckbr gene sequences were analyzed by bioinformatics,and the amino acid sequence was predicted by sequence manipulation toolbox (http://www.detaibio.com/sms2/index.html).And we predicted the position and cutting site of the signal peptide in the amino acid sequence through SignalP 4.0 Server (http://www.cbs.dtu.dk/se rvices/SignalP-4.0/).The amino acid sequences of gastrin and cholecystokinin B receptor (Lm-cckbr) of different species were compared by Jalview 2.10.5 software, and the phylogenetic tree of gastrin in different vertebrates was established by MEGA 7.0.26 software.Quantitative PCR was performed using a SYBR Green Q-PCR Supermix kit (Invitrogen),the β-actin gene served as an internal reference, three technical replicates were set for each cDNA sample, and three biological replicates were set for each tissue.The data of expression level were calculated by Relative quantification was calculated by the 2- ΔΔCT method(Livak &Schmittgen, 2001).Comparisons between groups were uesed by one-way analysis of variance and Tukey test for the statistically distinct groups.Differences with two-sided P < 0.05 were considered to be statistically significant.
2.4. Immunohistochemical staining
The specific immunohistochemical experiment refers to the previous work (Wu et al., 2017).The tissues such as brain, stomach and intestine ofLateolabrax maculatuswere fixed overnight in Bonn’s solution, and the routine paraffin sections were prepared, dewaxed to water, and incubated with 3% H2O2at room temperature for 10 min to eliminate the activity of endogenous peroxidase.After soaking in distilled water and PBS buffer (PH7.2) for 5 min, 10 min was sealed by goat serum at room temperature.The first antibody was incubated for 2 h (37?C), followed the biotinylated second antibody (all sheep anti-rabbit IgG antiserum)incubation of 15 min at room temperature, DAB coloration, dehydration transparent.In the negative control group, PBS was used instead of primary antibody, and the tissue was observed by Nikon DS-Ri2 microscope and the stained area was selected to take pictures.Gastrin first antibody (No.ZA-0115) was purchased from Beijing Zhongshan Jinqiao Biological Co., Ltd.
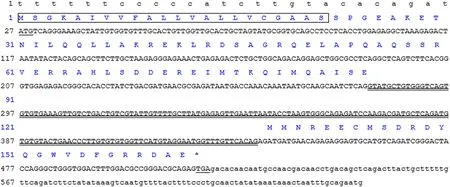
Fig.1.Nucleotide sequence of Lm-gas gene and its predicted protein sequence The start codon (ATG) and stop codon (TGA) are underlined.Double-underline is used to mark the intron; Amino acid sequence predicted by two exons was showed in capital blue letters.The box is used to indicate the signal peptide of Lm-gas protein.
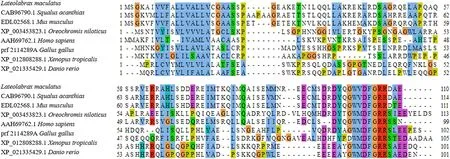
Fig.2.Multiple sequences alignment of gastrin homologous protein from different species.Different colors represent the difference in amino acid similarity at this site.A vertical column of amino acids with the same or similar color indicates that it is a conserved site in different homologous protein.

Fig.3.Phylogenomic analysis of gastrin in several different vertebrate.Bootstrap resampling (100 replicates) was used to indicate the confidence in the sequence clusters obtained.The name of each branch is represented by its scientific name and species name.
3.Results
3.1. Sequence analysis of Lm-gas gene
The full-length of Lm-gas gene was 638bp which contains two exons.It encoded a total of 110 amino acids.The N-terminal signal peptide was composed of 22 amino acids (Fig.1).The relative molecular weight of Lm-gas is 12.37 kD, and the theoretical isoelectric point was 5.46.The results also showed that there were great differences in gastrin amino acid sequences among different species, but there was a conservative region composed of 5 amino acid (DFGRR) at the carboxyl terminal.Although gastrin was highly conserved in the C-terminal of fish, there was still a slight difference between the white spot horn shark belonging to chondroid fish and other bony fish.Compared with other species, the ninth amino acid at the carboxyl terminal of teleost fish was valine, and the other was methionine (Fig.2).
According to the phylogenetic analysis, Lm-gas was closer to the homologs from flounder and tilapia.Bony fish, cartilaginous fish, reptiles, birds and mammals gather in different groups.In bony fish, the genetic distance betweenLateolabrax maculatusgastrin and Japanese flounder was closer, followed by tilapia, and the lower similarity relationship with zebrafish (Fig.3).
3.2. Sequence analysis of Lm-cckbr gene
The nucleotide sequence of Lm-cckbr cDNA was 2066 bp.The complete open reading frame of the Lm-cckbr encodes 453 amino acids and has a signal peptide composed of 24 amino acids at the N-terminal(Fig.4).

Fig.4.The Nucleotide sequence and its protein sequence of Lm-cckbr cDNA.Underlines are used to mark the initiation codon (ATG); The signal peptide of Lm-cckbr protein is boxed.
The amino acid sequences of Lm-cckbr ofLateolabrax maculatuswere compared with those ofPagrus major,Gasterosteus aculeatus,Paralichthys olivaceus,Rattus norvegicus,Gallus gallusandHomo sapiens.The results showed that more than 40% amino acid of cckbr were consistent.All kinds of species were ranked from high to low according to the degree of similarity, among which the similarity between Lm-cckbr protein sequence andPagrus majorwas the highest, which was 89.67% (Fig.5).
3.3. Expression of Lm-gas and Lm-cckbr genes
Immunohistochemical staining showed that gastrin cells were localized in the gastric mucosal layer, were all in a single-cell distribution, varied in morphology, and exhibited a thin rod, spindle, or cone shape, probably arising from the angle observed In brain, the positive reaction of gastrin was very weak, possibly because the cells expressing gastrin were in a small aggregation area.RT-PCR results showed that although Lm-gas was expressed in both brain and stomach.Importantly,the expression levels of Lm-gas and Lm-cckbr were significantly decreased after starvation stress (Fig.6).
4.Discussion

Fig.5.Comparison of amino acid sequences of Cckbr homologous protein in different species.A vertical column of amino acids with the same or similar color indicates that it is a conserved site in different homologous protein.
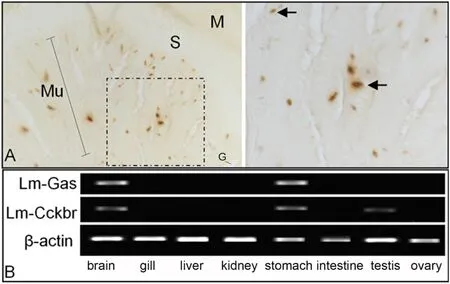
Fig.6.The expression of Lm-gas and Lm-cckbr in different tissues.A.The results of immunohistochemical staining of Lm-gas in the stomach and the right image is a partial enlargement of the dotted box on the left; S: submucosa; Mu: mucosa; M: muscular layer; G: gastral cavity.B.RT-PCR analysis of Lm-gas and Lm-cckbr expression in eight different tissues.
Gastrin and cholecystokinin form a highly related polypeptide family and become a typical hormone regulation system.They have a common short carboxyl terminal peptide sequence (Zeng et al., 2020).In chordate, there is an ecdysozoan sulfakinin signaling system and gastrin/cholecystokin are homologous.It can be seen that it is of great importance in animals (Bloom et al., 2019).The starfish (Echinodermata), two neuropeptides (ArSK/CCK1, ArSK/CCK2) determined from the antecedent protein ArSK/CCKP act as ligands for an SK/CCK-type receptor and these peptides/proteins are communicated within the apprehensive framework, stomach related framework, tube feet, and body divider(Tinoco et al., 2021).In teleost, two independent cholecystokinin and gastrin-like peptides found in dogfish sharks are called the ancestors of cholecystokinin and gastrin in fish and higher vertebrates (Baldwin et al., 2010; Vigna, 2000).According to the gene data of vertebrates in GenBank database, including mammals, birds,reptiles, amphibians and fish, the length of gastrin proteins is 104 ±11.9 amino acid (aa) and the number of exons was 2 ±0.84.The gastrin gene ofLateolabrax maculatusalso has two exons and one intron, so there is insignificant difference in gene structure and protein size, indicating that it is relatively stable in animal evolution.In contrast, the protein length of cckbr in vertebrates is 442 ±60.6 aa, and the number of exons is 5 ±2.33, there are some differences in the length of homologous genes(Sayers and Karsch-Mizrachi, 2016).
The conservation of gastrin protein molecules enables its antibodies to be immunocytographically localized in different species (Zhang &Wang, 2002).The gastrin cells of stomachless fish ofCtenopharyngodon idellus,Mylopharyngodon piceusandHypophthalmichthys molitrixhave high density and various shapes between the epithelium of foregut mucosa.The cells are slightly enlarged and the shape is longer and can contact with adjacent cells or basement membrane (Pan et al., 2000).In comparison, the gastrin cells of fish with stomach structure are more widely distributed in the digestive system, but the gastrin cells of most fish with stomach are still mainly in the intestine.While the gastrin cells ofMugil cephalusare located in the intestinal mucosa and distributed in stomach, small intestine, midgut and hindgut (Fang et al., 2002).On the other hand, the gastrin cells ofMonopterus albuswere distributed between esophageal stratified flat epithelium and goblet cells, and a few were also found in the cardia of the stomach (Fang et al., 2003).In contrast, the expression of gastrin is strictly limited to the stomach and small intestine in chicken, and in the pylorus of primitive mammals(Reid & Dunn, 2018).In this study, it is found that gastrin cells are mainly distributed in the stomach ofLateolabrax maculatus, but the gastrin gene is expressed in both stomach and brain.Therefore, some of the differences in different research results may come from different experimental methods and animal physiological states.
In human, gastrin plays an important role in promoting nutrition absorption and growth of gastric mucosa (Kasacka et al., 2012).The main targets are gastric parietal cells and intestinal chromaffin cells.The peptides originally synthesized by gastrin in cells are progastrin and are processed and modified by endonuclease after translation to form a peptide family of gastrins with the same carboxyl terminal.Among them, there are three main forms of circulation in tissue and blood,gastrin-34 (large gastrin), which has 34 amino acid sequences, which can be detected in the stomach; the smallest peptide (gastrin-14) also has complete biological activity and strong binding ability to cckbr; in addition, progastrin can also form gastrin-17, also known as small gastrin, which is secreted by the intestinal tract (Varro & Ardill, 2003).Gastrin peptides in the blood can also be synthesized in a small amounts in brain, neurons, pituitary, intestinal tract and pancreas (Smith &Morton, 2010).The biological activity of gastrin is retained in the five C-terminal amino acids of gastrin, which is called pentapeptide gastrin.The five C-terminal amino acids of gastrin and cholecystokinin are the same, indicating that they have partially overlapping biological functions.Cckbr is a member of the G protein-coupled receptor family, which binds gastrin preferentially and is also one of the cholecystokinin receptors.Gastrin binding receptor stimulates the increase of intracellular calcium, which leads to the activation of protein kinase C and the hydrolysis of inositol phosphate (Dimaline & Varro, 2014).It has been found that Cckbr mRNA can be expressed in normal human brain and stomach, especially in gastric fundus mucosa and cerebral cortex (Ito et al., 1993).Similarly, Cckbr is also expressed in the brain and stomach of theLateolabrax maculatus.
CRediT authorship contribution statement
Tingwen Cui:Conceptualization, Methodology, Software Priya Singh, Data curation, Writing – original draft.Jiaqi Wang:Investigation, Resources.Zhongjun Hu:Visualization, Investigation.Xiaowu Chen:Supervision, Writing – review & editing.
Acknowledgement
This project was supported by the National Key Research and Development Program of China (2017YFC0506003), Blue Granary Science and Technology Innovation Project, and Shanghai Collaborative Innovation Center of Animal Genetics and Breeding (ZF1206).
 Aquaculture and Fisheries2023年5期
Aquaculture and Fisheries2023年5期
- Aquaculture and Fisheries的其它文章
- The effectiveness of light emitting diode (LED) lamps in the offshore purse seine fishery in Vietnam
- Effects of dietary phosphorus level on growth, body composition, liver histology and lipid metabolism of spotted seabass (Lateolabrax maculatus)reared in freshwater
- Immunomolecular response of CD4+, CD8+, TNF-α and IFN-γ in Myxobolus-infected koi (Cyprinus carpio) treated with probiotics
- Effects of transport stress on immune response, physiological state, and WSSV concentration in the red swamp crayfish Procambarus clarkii
- The first draft genome assembly and data analysis of the Malaysian mahseer(Tor tambroides)
- The competitiveness of China’s seaweed products in the international market from 2002 to 2017
