Application of "Green Principles " in the Field of Regional Technological Innovation:A State Intervention Perspective
Huang Yan,Zhao Shuliang
(School of Public Affairs,University of Science and Technology of China,Hefei 230026,China)
Abstract:Green technology innovation,which takes into account both innovation and environmental aims,has grown in importance as a regional response to systemic changes as the ecological needs of China's economic development become more and more apparent.How to secure and improve green patents is a crucial issue in regional development since they are the primary indication of the output of green technology innovation.State intervention in the technological innovation market is inextricably linked to it,and public policy is the primary tool used by local governments to do so.Based on this idea,this paper studies how the government influences green IP output through environmental policy and science and technology policy and explores the moderating role of science and technology policy.The panel data analysis of 29 provinces in China from 2009 to 2019 finds the following:command-and-control environmental policies and economic incentive environmental policies have different effects on green IP output;demand-side and environment-side science and technology policies affect green IP output;science and technology policies partially moderate the relationship between environmental policies and green IP output.The findings further confirm that the government is the core actor in the green IP system,and the government should continuously provide guidance,management,supervision,and policy improvement in the field of green technology innovation.By doing so,the government will continuously improve green IP output and implementation of green principles in the intellectual property system.
Keywords:green intellectual property output;environmental policy;science and technology policy;green principles;state intervention
1 Introduction
With changing economic development models,high-quality development has become the primary goal of economic development,while the ecological and environmental problems left behind by the past economic development model still need to be solved[1].The realistic demand for ecological transformation of China's economic development is increasingly prominent.In recent years,the central and local governments have continued to invest more resources in the field of sustainable development,and " green " has become the core concept of China's high-quality development.The Civil Code of the People's Republic of Chinaprovided the framework for the coordination of environmental conservation and economic development in China by encouraging civil subjects to consciously conserve resources and protect the environment[2].A significant application of the green principle in the field of innovation is green patent output.To foster new kinetic energy of economic development and support regional green intellectual property output,regional governments should fully rely on scientific and technological innovation.
By granting inventors temporary monopoly power over their innovations,the intellectual property system has effectively increased the innovation enthusiasm of all kinds of innovation subjects and played a prominent role in promoting the innovation-driven development strategy,which has received wide attention from governments at all levels.China's Green Intellectual Property system(Green IP)has become an important initiative to achieve long-term sustainable development in the country by combining the ecological needs of economic development and innovation development goals.With environmental protection and resource conservation as the primary objectives,the Green IP system aims to promote technological innovation[3],effectively guaranteeing a win-win situation for both technological progress and ecological civilization construction.Along with the development at the practical level,the academic community has been exploring the issues related to green IP for a while.Among such topics,green patents are the focus of research on green IP,and most studies use them as one of the indicators for measuring technological innovation or studying the improvement and development of green patent-related systems based on legal and policy perspectives[4-5].Green IP has been widely recognized as an important strategy for achieving sustainable development goals.Considering the multiple benefits of regional green IP system output on sustainable economic development and environmental protection,it is of great practical significance to accurately identify the driving factors of green patent output enhancement to promote the rapid enhancement of green IP and further improvement of China's IP protection system.
In the process of innovation,there are inevitable " failures ",for example,in a free competitive market environment,if the benefits of technological innovation of green patentees are lower than their costs,they may give up innovation based on profit considerations,leading to the prevalence of technological imitation,i.e.the phenomenon of " market failure "[6].To compensate for such failures,the government must make appropriate interventions.From the government's perspective,environmental policies promote eco-friendly development in the region,which can promote the " green " goal of green IP,and science and technology policies promote technological innovation and patent output,reflecting the " intellectual property " results of green IP.
The famous "Porter's hypothesis " suggests that the government can exert regulatory pressure on innovation projects to promote green technology innovation behavior by formulating appropriate environmental policies[7],thus promoting green IP output.Some scholars have raised doubts about the influence of environmental policies on green IP output,an influence not yet fully determined by academics.Therefore,from the government's perspective,correctly distinguishing the types of environmental policies and clarifying the role of environmental policies is vital for the correct use of environmental policy tools to promote regional development.Such knowledge is a prerequisite for scientific policymaking in the environmental field.
Both environmental policies and science and technology policies are important means of national intervention to promote the number of green patents in the region,but in the process of enhancement,different government policies do not operate independently and often interfere with each other.In regulatory development,different policies are often implemented together.Therefore,by linking different policy types and focusing on the interconnection and role of different drivers in green patent output enhancement,we can explore the necessity and means of government intervention in the regional green patent promotion.When faced with regulatory pressure from governmental environmental policies,regional innovators tend to respond by either allocating resources to combat pollution or developing technologies to save energy and reduce emissions.However,only the second method can produce green patents.When faced with the same environmental policies,then intra-regional innovation projects may make different choices depending on the differences in R&D resources at the time.Innovative projects with stronger R&D strength and sufficient R&D resources can make timely technological innovation even in the face of environmental policies and avoid the lack of legality through product innovation and process innovation.Science and technology policy is an important supplement to R&D resources.Such policy can guarantee the R&D environment from various aspects such as financial,and human resources through financial subsidies,training of scientific and technological talents,and public service support,thus increasing the speed of technological innovation in response to environmental policies and promoting the output and rapid transformation of green intellectual property.In summary,environmental policies and science and technology policies do not play isolated roles in the process of improving green IP output,and science and technology policies can jointly influence regional green IP output by affecting the response speed of regional innovation projects to environmental policies.
Based on the above analysis,this paper explores the application of the " green principle " in the field of regional technological innovation and how the government can promote the application of the " green principle " through appropriate state intervention based on the legal perspective of the " green principle " and " state intervention ",combined with empirical analysis and provincial panel data,to clarify the role of the government.
2 Research on the Necessity of the Application of Green Principles in the Field of Regional Technological Innovation
2.1 The Basic Meaning of the Green Principle
The green principle is one of the basic principles established by civil law,which is in line with the overall layout of China's current development of the five-in-one and the concept of green development."Green " is the core concept of the green principle,and this study adopts Professor Xu Guodong's definition of green,which means vitality and ecology,and people need to consider the bearing capacity and recovery capacity of resources when engaging in production activities,to guarantee the continuous source of resources so that society can develop continuously.The resources here should not only be natural resources but also include policies,time,patent rights,etc[8].On this basis,some scholars conclude that the green principle is a basic civil law principle established with the core concept of protecting the environment and conserving resources in order to protect the basis of civil activities[9].The core of the green principle is to emphasize the obligation of civil subjects to protect the environment[10],which also shows that the green principle has a wide range of constraints.Therefore,studying the application of green principles in various fields is in line with the basic demand for ecological improvement in China's economic development.
2.2 The Basic Meaning of Green Patent and Green Technology
There is no uniform standard for the definition of green technology.The United Nations,the Japanese Patent Office,and the European Patent Office use a generalized definition and consider green patents to be environmentally friendly technology;while the United States and Korea,and other countries have an enumerated definition of green technology,which is green technology if it meets the relevant technical standards.Generally speaking,we can consider that any technology that is conducive to the improvement of the ecological environment,helps to reduce the emission of harmful substances,and helps to save resources is green,which is also the most significant feature of green technology compared with ordinary technology.The research and development and application of green technology includes the concern for the environment and tries to achieve the harmonious development of economic development and environment.Because of the obvious " double externality " of green technology,the benefits brought by technological innovation are not only enjoyed by the inventor but also have certain social and environmental benefits.Therefore,it is necessary to protect green technology and green knowledge,so as to promote the development of green innovation.The more effective way to protect green technology with the attributes of public goods is to patent green technology,which can only be better protected if it is attached to products or exists in the form of intangible property.
There are also some differences in the definition of green patent.Some scholars believe that a green patent follows the patenting of green technology.Other scholars believe that any patent that is beneficial to the environment can be called a green patent.A green invention patent is essentially a patent for an invention,but with obvious " green " characteristics,and in addition to the novelty,creativity,and practicality that a patent should have,it also has green attributes,and green examination is required in the process of patent acquisition.China's construction of a green patent system,related laws,and regulations,as well as a financial and fiscal incentive system,are not enough to promote green technologies and inventions,and the relevant government procurement and public demand for green consumption are not strong enough to pull green innovation.Therefore,the relationship between the relevant policies and measures introduced by the government and green technology innovation needs to be explored.The goal of green patents is to prevent the abuse of rights,to restrict the arbitrary use of intellectual property rights such as green technology patents by others,and more importantly,to promote the output and transformation of green intellectual property rights,to protect the ecological environment more efficiently,to promote public welfare,and to meet the public demand for environmental protection and other public interests[11].
2.3 The Necessity of Applying Green Principles in the Field of Regional Technological Innovation
Innovation is the core tool for coordinating economic development and environmental friendliness.Technological innovation is the core technical support for product production and production process,which directly affects the production process of green products and how innovation subjects use resources and discharge waste.Ecologically friendly and innovation-led is the basic direction of China's economic and social development in the new era.However,due to the geographical location and natural resource endowment differences of each region in China,the unbalanced regional development characteristics,which also led to the regional economic development of each region can not " walk in unison ".How to effectively promote each region to break the resource and environmental constraints,with innovation to lead high-quality development has become a new challenge in the regional economic development.The core concept of the green principle,which emphasizes that civil subjects pay attention to environmental improvement and resource conservation in civil activities,is consistent with the ecological development demands in the current development of regional technological innovation,and is in line with the development goals of regional efforts to improve technological innovation,continuously improve the ecological environment,and strive to enhance the quantity and quality of green patents.Studying how technological innovation can better link the footsteps of ecologization in the current context,guided by green principles and relying on innovation,to take a dominant advantage in international competition,is not only of great significance to regional development but also in line with the economic trend of high-quality development in China.
3 Impact of Policy Intervention on Regional Green Patent Enhancement
3.1 The Need for State Intervention in the Field of Technological Innovation
"State intervention " is a useful complement to market failure,which refers to the intervention of the state,mainly at all levels of government,in the market economy through administrative coercion or economic instruments.The proposal of state intervention has aroused widespread discussion in academic circles,and scholars have engaged in heated debates on whether it is necessary for the government to intervene in the free development of the economy.State intervention is mainly carried out through decision-making,regulation,supervision,guidance,and other ways or means[12].There are market failures,and the same is true in the field of technological innovation.Market failure phenomenon appears along with the market,and it also accompanies the market in the field of intellectual property.Every step from the laboratory to the market may inevitably be accompanied by market failure[13].When failure threatens,it is necessary to resort to government intervention,and the most effective method of government intervention is to formulate reasonable policies for control.
3.2 Environmental Policy and Green IP Output Enhancement
The promotion of green patents shows the impact of the government's involvement,and regional governments are one of the leading advocates for the implementation of the " green principle " in the area of technical innovation.Provincial governments promote environmental regulation of regional innovation projects through administrative coercion and market incentives,thus promoting green IP output enhancement.Based on the perspective of regional governments,environmental policies can be divided into command-and-control and economic incentive instruments.The command-and-control environmental policy refers to the government's implementation of a series of regulations,policies,and codes of conduct to directly or indirectly control the production and operation activities of production entities in order to achieve eco-friendliness and resource conservation.Command-and-control environmental policies can enhance the output of innovation projects,and properly designed environmental policies can positively impact technological innovation and promote industrial transformation when a certain intensity is reached[14].Therefore,from a dynamic,long-term perspective,when environmental policies exert mandatory pressure on innovation projects on environmental issues,innovation projects tend to focus on methods such as introducing new technologies and developing new processes to avoid government-imposed penalties and warnings,thus overcoming organizational inertia,stimulating creative thinking,offsetting compliance costs through innovation gains,and improving organizational competitiveness.
Since a lack of government regulation and transparency of information disclosure can weaken the effect of command-and-control environmental regulation[15],the government introduces economic incentive environmental policies using command-and-control policies.Economic incentive environmental policy is the sum of government policies that guide innovative projects to take the initiative to reduce pollution emissions through market instruments,such as prices and taxes.Economic incentive environmental policy is based on market instruments and drives the green IP output of innovation projects through two mechanisms:" pushing " and " encouraging ".On the one hand,the government pushes innovation projects to improve green IP output through environmental taxation and other policy tools.On the other hand,the encouragement policy is based on the market mechanism of " pushing " and " encouraging " to encourage innovation projects to improve their green IP output.In contrast,an incentive-based policy promotes innovation in environmental protection and resource use by giving a resource preference to innovative agents that perform well in environmental protection and resource use,by replenishing their R&D resources through market means,and by stimulating their environmental technology innovation[16].Based on this,this paper proposes research hypothesis 1.
H1:Environmental policies positively influence regional green IP output enhancement.
H1a:Command-and-control environmental policies positively influence regional green IP output enhancement.
H1b:Economic incentive environmental policies positively influence regional green IP output enhancement.
3.3 Science and Technology Policy and Regional Green IP Output Enhancement
Science and technology policy is the main policy instrument for government intervention in regional IP development.Science and technology policy constructs a policy framework for promoting regional IP development through three dimensions-supply,demand,and the environment-and provides strong support for the R&D and innovation activities of innovation projects.The government plays an important role in industrial R&D activities by attracting innovation projects to increase technological investment and cultivate competitive advantages through science and technology policies[17].
Supply-oriented science and technology policies provide regional innovation projects with policy support required for IP output by introducing resource-securing policies,and the main types of policies are science and technology talent training,financial subsidies,infrastructure construction,and public service support.Among them,government financial subsidies,as an important tool of science and technology policy,are widely used by the government.As an additional income for innovation projects,government subsidies can be used to supplement the R&D resources of innovation projects,thus effectively promoting IP output[18].It is worth paying attention to the fact that government financial subsidies are not a universal policy and are selective,and not all innovation projects can obtain financial subsidies.Obtaining financial subsidies represents government support to a certain extent,and in order to obtain financial subsidies,innovation projects are required to keep close to the requirements of government financial subsidy type firms,which will also stimulate innovation enthusiasm of innovation projects to a certain extent and promote intellectual property output[19].Human resources are the most dynamic element in regional innovation,and regional innovation is inseparable from the support of a large number of scientific and technological talents,and the government is inseparable from the cultivation of scientific and technological talents[20].Through policy means,the government continuously promotes the integration of schools and firms,and the cultivation of more talents with cutting-edge innovation ability through universities,firms,and society is the inexhaustible driving force to promote regional innovation.Public services and infrastructures,on the other hand,provide field support for innovative projects.Based on this,supply-oriented science and technology policy provides resource support for regional innovation activities from finance,and people,creating good resource conditions for regional technological innovation activities,including green intellectual property output.
Demand-oriented science and technology policy pulls IP output by increasing public or private demand,such as stimulating innovation projects to market their innovation output faster through science and technology achievement transformation policy and government public procurement.Among them,the government can reduce the market uncertainty in the pre-innovation stage of product innovation by giving priority to the procurement of products with independent innovation in the region and providing guarantees for the innovation activities of innovation projects,thus promoting green IP output[13].At the same time,government procurement can guarantee that the IP results can quickly obtain economic benefits after they are put into the market,thus ensuring the continuity of R&D activities[21].The transformation of technological achievements refers to the transformation of technological innovation into marketable products,which is the basis for new products and even new industries[22],and national policies are considered to have a strong influence on technology transfer,which can encourage and facilitate technology transfer and appropriate policies for the transformation of technological achievements are important drivers of regional technological innovation[23].Trade control policies refer to regional governments'efforts to promote the import and export of innovations in the region by introducing control policies,which indirectly affect the enhancement of intellectual property output.
Environmental-oriented science and technology policies are a combination of policies promulgated by the regional government to optimize the institutional environment for innovation activities conducive to improving the external innovation environment of innovation projects.Environmentally oriented science and technology policies are divided into six main categories[24].Among them,goal planning refers to the regional government agencies'efforts to set feasible development goals in order to promote innovation,guide the strategic planning of innovation projects,and indirectly promote the occurrence of innovative behavior.Similar to government financial subsidies,financial services can help regional innovation projects obtain financial support more conveniently by improving the financing environment of innovation projects,providing financial security for their R&D activities,and promoting intellectual property output.Tax incentives are similar to financial subsidies,which help alleviate the problem of R&D capital shortage of innovation projects and greatly reduce the externalities of technological innovation[25].The external openness policy improves innovation awareness and enhances innovation capability by improving the environment of external communication for innovation projects.The intellectual property policy,on the other hand,protects the patent rights and intellectual property rights of innovation projects by fighting against infringement,avoiding the reduction of innovation motivation of innovation projects due to the ease of imitation of innovation activities,and inhibiting the enhancement of regional intellectual property output.Regulatory control is the most common type of regulatory science and technology policy,which regulates the behavior of regional innovation projects by formulating strict laws and regulations related to innovation or industry implementation standards to ensure a stable institutional environment for innovative R&D activities.In summary,we can find that science and technology policies actively contribute to improving regional green IP output through various policy tools such as supply-push,demandpull,and innovation environment construction.Accordingly,this paper proposes research hypothesis 2.
H2:Science and technology policies positively influence regional green IP output enhancement.
H2a:Supply-oriented science and technology policies positively influence regional green IP output enhancement.
H2b:Demand-oriented science and technology policies positively influence the regional green IP output enhancement.
H2c:Environmental-oriented science and technology policies positively influence the improvement of regional green IP output.
3.4 The Moderating Role of Science and Technology Policy
When different regions face the same environmental policy,their regional green IP output will be significantly different,mainly because their resource endowment is different,and science and technology policy is the main policy tool for innovation agents in the region to obtain resources.Regional governments participate in resource allocation through financial subsidies,tax subsidies,and other science and technology policies,which makes the allocation of financial and other resources inevitably political.Therefore,science and technology policies can not only influence regional green IP output by themselves but also regulate the relationship between environmental policies and regional green IP output by influencing the allocation of resource factors.
As an exogenous variable,environmental policy wants to fully play its driving role in regional green IP output,which requires relying on the perception and response speed of regional innovation projects to the policies.Some scholars have noticed that even under the same degree of command-and-control environmental policy pressure,different organizations react and perform differently in response[26].When faced with the command-control environmental policies of regional governments,the innovation projects that enjoy the support of supply-oriented science and technology policy can often take quick actions due to the full support of the policies.This allows them to promptly control pollution and improve the output of green intellectual property rights in the production process and products to avoid administrative penalties.Secondly,when facing the command-and-control environmental policies of regional governments,regions enjoying more demand-oriented science and technology policies can promote the transformation of green IP output results as soon as possible by accelerating the process of transformation of scientific and technological achievements,while government procurement opens the first door for the results to market.Finally,when faced with the regional government's command-and-control environmental policy,regions enjoying more environmental-oriented science and technology policies can adopt green technology innovation behaviors in a more timely manner and promote IP output because they have an excellent innovation environment.
The response degree of innovation projects to economic incentive environmental policy reflects the degree to which those projects actively assume social responsibility.Competitive advantage theory suggests that balancing social responsibility and economic benefits can create new resources,in particular,reputation benefits,for innovation projects.An innovation project enjoying regional science and technology policies is equivalent to the government implicitly guaranteeing it.Such innovation projects often have higher industry visibility,are supervised by more stakeholders,and are regarded as benchmarks in the industry.Firms with such projects tend to show a higher willingness to increase green intellectual property output,and they assume a certain social responsibility for the government[27].In terms of the " push " mechanism of economic incentive environmental policies,science and technology policies are an important supplement to the R&D resources for innovation projects in the region.When innovation projects face the lack of funding caused by economic incentives and environmental policies,it is easier to obtain innovation resources support to make up for the lack of internal research and development[28].In terms of the " encouragement " mechanism of economic incentive environmental policies,when the innovation projects in the region enjoy the support of government science and technology policies,this boosts the social image of the firms.They tend to actively strive for various government policy support measures to continuously improve their industry visibility and highlight their legitimacy.In addition,when faced with the same " encouragement ",innovation projects enjoying science and technology policies will attract more public and media attention due to their high industry visibility,which also forces innovation projects to improve their resource utilization efficiency.Based on the above analysis,this paper proposes research hypothesis 3.
H3:Science and technology policy positively moderates the relationship between environmental policy and regional green IP output.
H3a:Supply-oriented science and technology policies positively moderate the relationship between commandand-control environmental regulation policy and regional green IP output.
H3b:Demand-oriented science and technology policies positively moderate the relationship between command-and-control environmental regulation policy and regional green IP output.
H3c:Environmental-oriented science and technology policies positively moderate the relationship between command-and-control environmental regulation policy and regional green IP output.
H3d:Supply-oriented science and technology policies positively moderate the relationship between economic incentive environmental regulation policy and regional green IP output.
H3e:Demand-oriented science and technology policies positively moderate the relationship between economic incentive environmental regulation policy and regional green IP output.
H3f:Environmental-oriented science and technology policies positively moderate the relationship between economic incentive environmental regulation policy and regional green IP output.
4 Empirical Analysis of the Impact of Policy Intervention on Regional Green Patent Enhancement
4.1 Data and Variable
This study uses panel data for 29 provinces in China during 2009-2019.To explore the impact of government policy intervention in each province on regional green patent output,as well as the moderating effect of science and technology policies on the relationship between environmental policies and regional green IP output.The research sample data were mainly obtained from the China Statistical Yearbook,China City Statistical Yearbook,China Science and Technology Statistical Yearbook,and China Marketization Index Database.The original data were collated,and data from Tibet,Hainan,Hong Kong,Macao,Taiwan,and other regions with missing data were screened out,resulting in panel data containing 319 observation values,with specific variable measures as follows.
Dependent variable:Green Intellectual Property Output(GIP):Patents are a common and easily available indicator for measuring innovation indicators[29]and the most representative indicator of intellectual property output.Therefore,in this paper,the number of regional green invention patents is chosen to measure regional IP output.
Independent variables:There are two independent variables in this study,both of which are policy dimension variables.With reference to the measurement of proxy variables,representative policy indicators in this policy area are selected as proxies.
Command-and-control Environmental Policy(CEP):Command-and-control environmental policy reflects compulsory environmental regulation pressure from the government.In using this variable,we refer to the study of Yuan[30].The strength of command-and-control environmental policy directly affects the regional environmental pollution level.In this paper,we choose inter-provincial level data of three waste emissions to measure the intensity of environmental policies in each province by calculating their composite scores through the entropy method.Since the statistical results of the relevant raw data were not released in the final 2017 statistical yearbook,the calculation of environmental policies does not include 2017.For the panel data with missing intermediate data,the treatment of other scholars is referred to and interpolated to make up for the final environmental policy regulation intensity indicators of the 29 provinces during 2010-2019.
Economic Incentive Environmental Policy(EEP):Emission fees are the most common economic incentive environmental regulation instrument in China,and this study selects regional emission fee revenue as a measure of economic incentive environmental policy by referring to the study of other scholars.This variable is finally chosen to use data from 2010-2018 because data from some provinces are missing and cannot be determined by other means.
Supply-oriented Science and Technology Policy(STP):Financial subsidies are one of the most important forms of government support for the R&D activities of innovation projects,and the government compensates for the plight of insufficient R&D resources for innovation projects in the form of subsidies,which is conducive to innovative behavior.In this study,we measure the government's financial subsidies as the percentage of government funds invested in the R&D of firms.
Demand-oriented Science and Technology Policy(DTP):The government's science and technology results transformation policy can significantly improve the efficiency of that transformation by improving the environment.Innovative R&D results eventually enter into production activities through trading activities in the technology market to realize results on the ground.Therefore,with respect to measuring the transformation of scientific and technological achievements,this paper refers to the study of Zhang and Guo[31]to choose the technology market turnover as the proxy variable for demand-oriented science and technology policy.
Environmental-oriented Science and Technology Policy(ETP):Intellectual property protection(IPP)plays a crucial role in encouraging innovation,promoting technological progress,and stimulating economic growth.A good IPR protection environment can effectively promote regional technological innovation activities,and this study chooses patent grant/GDP to measure the regional IPR protection index to exclude the influence of economic level.
Moderating variable:CEP and EEP are used as moderating variables.
Control variables:Because green IP output is affected by many factors,such as regional economic development status and urbanization level,the following variables are selected as control variables in this paper.(1)Per capita income(PI):The regional per capita income in this study is expressed by regional per capita GDP.(2)Foreign direct investment(FDI).Foreign investment can bring external innovation resources such as capital,technology,and management experience to regional innovation projects,positively affecting regional green IP output.At the same time,FDI may also bring an influx of polluting industries(i.e.,the " pollution paradise " effect),which will negatively affect the regional ecological environment and the output of regional green intellectual property,so the scale of FDI is closely related to the level of regional green IP output.In this paper,the proportion of foreign direct investment in regional GDP is used to measure FDI.(3)Population concentration degree(PD):The population density of municipal districts reflects the influence of the urban population concentration.
4.2 Correlation Analysis and Hypothesis Testing
This study uses SPSS 26.0 statistical analysis software to conduct Pearson correlation analysis for all variables.Table 1 shows the specific results.
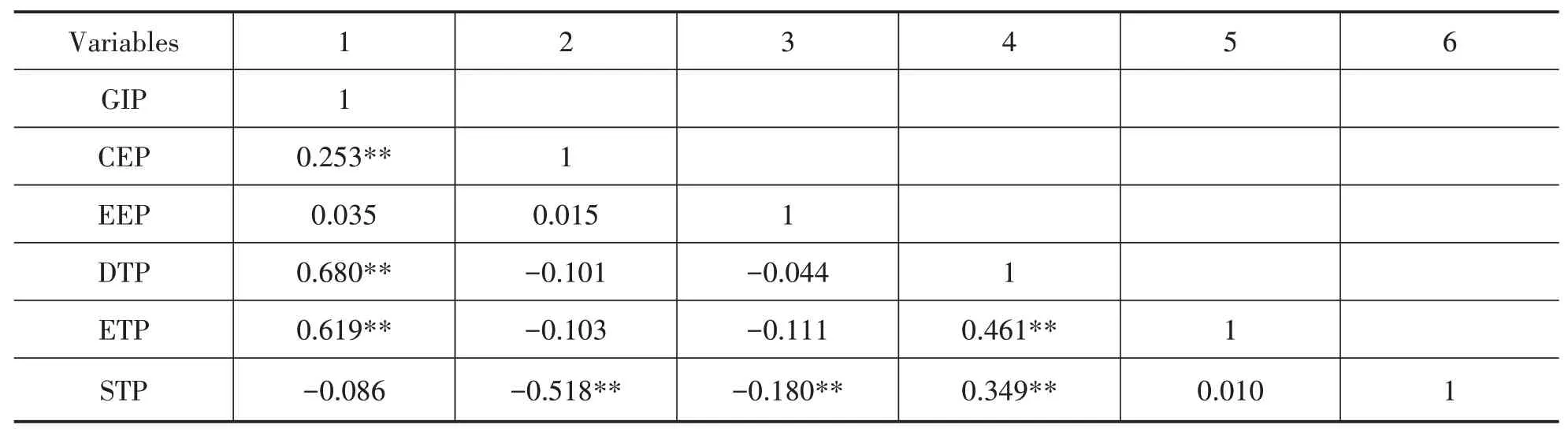
Table 1 Correlation Analysis
The results regarding the research hypotheses in this paper are shown in Table 2.In this paper,after decentering the independent and moderating variables,the regression equations are gradually added to prevent the generation of multicollinearity,and multiple cross-terms are introduced to apply the multilayer regression method for hypothesis testing.In each model in Table 2,the VIF values are much less than 10,indicating that the problem of multicollinearity can be excluded.
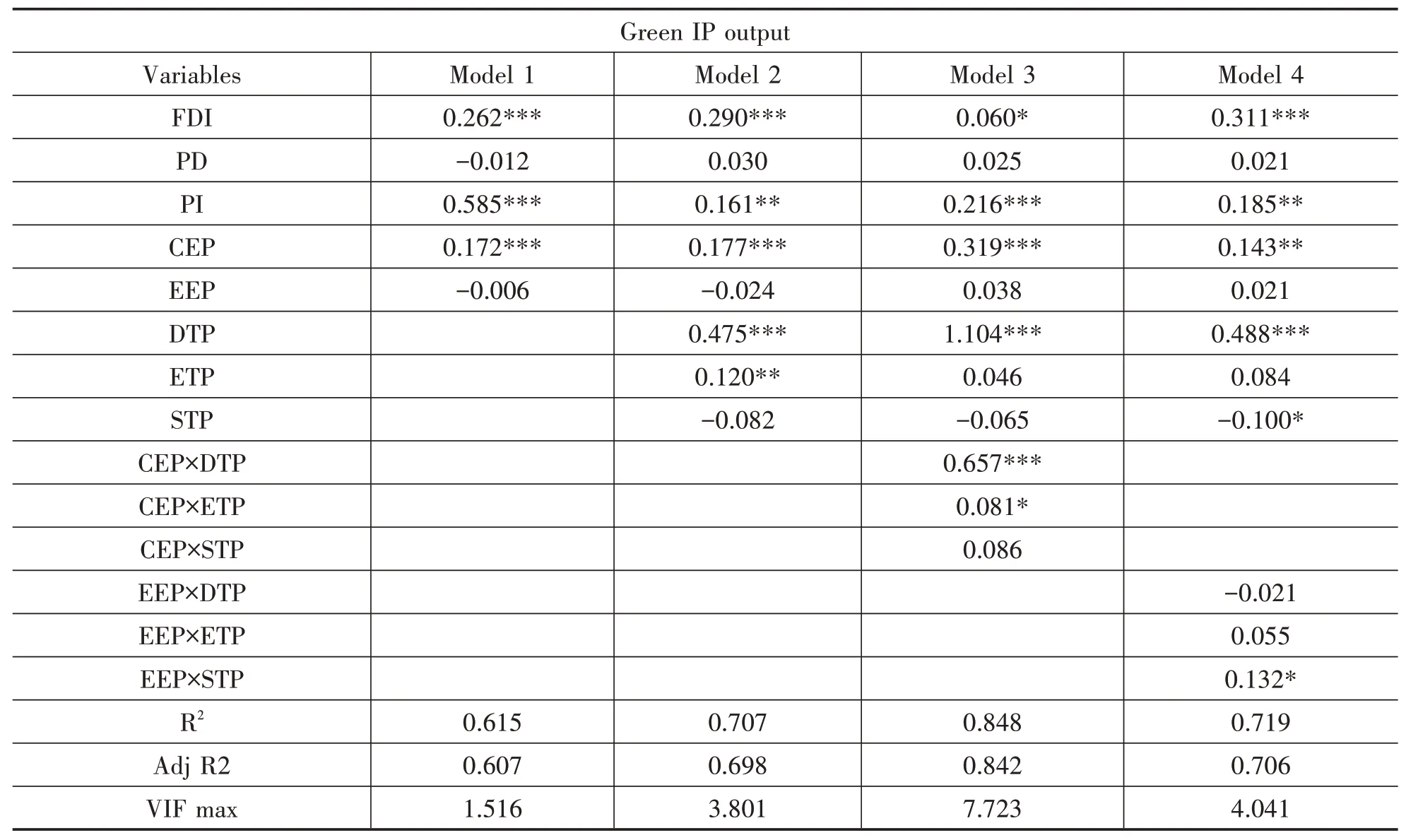
Table 2 Multilevel Regression Results
4.3 Empirical Findings and Discussion
Through the empirical analysis of the panel data of 29 provinces in China,this study draws the following conclusions.
Conclusion 1:Environmental policies partially affect regional green IP output.First,command-and-control environmental policies can significantly and positively influence regional green IP output.This finding is consistent with the mainstream findings and confirms that the government can increase the level of green IP output through administrative coercion.The institutional theory suggests that the government's environmental regulations and policies exert compulsory pressure on regional innovation projects.In the face of harsh environmental policies from the government,regional innovation projects must improve production processes and introduce new technologies to avoid penalties and pursue benefits.From a realistic point of view,in the future,driven by the goal of carbon peaking and carbon neutrality,regional governments will adopt more severe administrative and mandatory environmental protection measures to force regional innovators to improve their production technologies and reduce pollution emissions.Therefore,under the stimulation of both penalty avoidance and profit-seeking,regional innovators will carry out " greening " activities,thus promoting the improvement of regional green IP output.This view is also confirmed by the fact that command-and-control environmental policies positively influence regional green IP output.Second,economic incentive environmental policies have no significant impact on regional green IP output,supporting the " cost of compliance " hypothesis.As a typical " push " type of economic incentive policy,which upholds the " polluter pays " principle,an emission fee adds cost to innovation projects,but it also raises the manufacturers'awareness of environmental protection and reduces pollutant emissions because they invest in clean production equipment.The economic incentives are based on the " polluter pays " principle.The high cost of investment in transformation causes crowding out of production factors and investment in innovation,resulting in a decrease in investment in innovation.Therefore,although the emission fee policy improves the green awareness of innovation projects to a certain extent,it also increases the production cost of innovation projects,and the " innovation compensation " cannot fully cover the loss of R&D cost,so the economic incentive environmental policy has no significant positive impact on regional green IP output.However,it is worth noting that the emission fee policy was officially changed to an environmental protection tax only in 2018,and excessive flexibility of regional governments in the operation of the emission fee has appeared in the past;this situation cannot give full play to the " innovation compensation " effect of economic incentive environmental policies on regional green IP output.
Conclusion 2:Science and technology policies partially affect regional green patents output.First,supply-oriented science and technology policy has no significant impact on regional green IP output,which indicates that that type of policy,a kind of resource-supply science and technology policy,has a certain degree of selectivity.That is,only some innovation projects in the region can enjoy the support of supply-oriented science and technology policy,which may generate rent-seeking behavior in the process and reduce the resource utilization efficiency of the support resources from the government.However,the supply-oriented science and technology policy supports some innovation projects in the region,and the supported behavior is all regional technological innovation,not just green technology innovation.Compared with other technological innovation behaviors,the primary goal of green technological innovation is ecological environment improvement and resource utilization efficiency improvement rather than rapid improvement of economic efficiency.To continuously enjoy the supply-oriented science and technology policy,innovation projects will prefer to choose other technological innovation behaviors to maintain high performance and highlight their innovation results while continuing their enjoyment of the supply-oriented policy.Second,demand-oriented science and technology policies can significantly and positively influence regional green IP output,which is consistent with the mainstream findings and confirms that the government can improve regional green IP output through demand-oriented science and technology policy tools.Finally,environment-based science and technology policies significantly affect regional green IP output,indicating that a good S&T innovation environment is an important support for green IP output.
Conclusion 3:Science and technology policy partially moderates the relationship between command-and-control environmental policy and regional green IP output.First,supply-oriented S&T policy does not significantly moderate the relationship between command-and-control environmental policy and regional green IP output,which indicates that when faced with environmental coercion from the government,innovation projects are more likely to invest their innovation resources in other technological innovation areas even if they enjoy supply-oriented S&T policy supplements.Second,demand-oriented science and technology policy positively moderates the relationship between command-and-control environmental policy and regional green IP output.This finding confirms that demand-oriented science and technology policy can improve how quickly regional environmental projects respond to government policies and regulations by supporting the R&D of regional innovation projects.Finally,Environmentaloriented science and technology policy significantly moderates the relationship between command-and-control environmental policy and regional green IP output,indicating that the regional government can improve the R&D speed and efficiency of innovative projects by creating a favorable innovation environment.
Conclusion 4:Science and technology policy partially moderates the relationship between economic incentive environmental policy and regional green IP output.First,supply-oriented science and technology policies significantly moderate the relationship between economic incentive environmental policies and regional green IP output,which indicates that in the market environment,resource tilting from the government can effectively compensate for the lack of resources for R&D projects.Second,demand-oriented science and technology policies do not significantly moderate the relationship between economic incentive environmental policies and regional green IP output,which indicates that economic incentive environmental policies encourage more eco-friendly behaviors than command-and-control environmental policies,and demand-oriented policies such as government procurement of green products can greatly reduce market uncertainty for innovation projects that have already produced green products in large quantities.However,both types of policies do not necessarily encourage green IP output by innovation projects that do not yet produce green products.Finally,environmental science and technology policies do not significantly regulate the relationship between economic incentive environmental policies and regional green intellectual property output,i.e.,regardless of the level of intellectual property protection,the emission fee standard treats innovators in different regions equally,and the current economic incentive policies such as environmental protection tax are becoming more and more complex and standardized,making them difficult to influence.
5 Analysis of the Government's Role in Regional Green IP Output Enhancement
5.1 Promoter of Green IP Output
The promotion of regional green IP output is inseparable from the guidance of multiple levels of government,which promote green IP output through environmental policies and science and technology policies through administrative coercion and resource supply.However,the implementation effect of public policy is positively related to the cooperation of policy projects.If the policy projects have a strong rejection mentality and weak obedience to the policy,this will not only increase the cost of policy implementation but also greatly reduce the effectiveness of the policy.Education and publicity are the main ways to improve policy compliance.When promoting science and technology policy and environmental regulation policy,regional governments should actively strengthen education for those involved in innovation projects and the public before policy planning and during policy implementation.In this way,policy initiatives can leverage the important value of environmental improvement and science and technology innovation known through education and policy publicity,and promote public understanding and approval,so that policy implementation can get more the outcome.In this way,the implementation of the policy will be twice as successful.At the same time,the government should take the lead and pay more attention to the field of green IP,stimulate the output of green IP by setting up incentive mechanisms,and improve the speed of green IP review through policy measures,to create a favorable external environment for the output of green IP.
5.2 Guide of the Green Principles
The government can effectively influence regional green technological innovation by formulating reasonable environmental policies as well as science and technology policies.The government influences the application of green principles in the field of regional technological innovation through state intervention.The implementation of regional policies is not single,but many policies are often intertwined to form a policy environment.To reflect the advantages of green principles and improve the quantity and quality of green patents,we need to pay full attention to the regional policy environment to promote the output of green IP results.As far as environmental policies are concerned,the mechanism of environmental policies on regional green IP output is mainly realized through the mechanism of " innovation compensation ",so long-term planning of environmental policies is needed.At the same time,the impact of different types of environmental policies on the output of regional green IP differs.Regional governments should correctly distinguish environmental policy tools and skillfully apply environmental policies in accordance with the socio-economic conditions and the current situation of environmental pollution in the region.At the present stage,the driving effect of command-and-control environmental policies on regional green IP output is becoming more obvious,so the administrative coercive power of the government should be given full play to enhance the driving force of command-and-control environmental policies on regional green IP output.With the continuous improvement of regional market mechanisms,economic incentive-type environmental policies should be used well in combination with regional economic and social characteristics.
As far as science and technology policies are concerned,there are many different kinds of science and technology policies,and regional governments should pay attention to the positive impact of demand-based science and technology policies on regional green IP output when conducting policy planning,and strive to improve the policy effectiveness of demand-based science and technology policies.They should correctly recognize the unique value of green patents in environmental protection and provide more support and assistance to enterprises and individuals in green technology innovation.Government public procurement is one of the core policy types in demand-based science and technology policy.The government is the purchaser of green products by purchasing green patented products with green connotations in the region.Green procurement by the government can reduce the uncertainty of green patented products entering the market and help promote the popularization of green technology.In recent years,governments at all levels have been strengthening government green procurement,and policy documents such as the Notice on Adjusting and Optimizing the Implementation Mechanism of Government Procurement of Energysaving Products and Environmental Labeling Products have been issued one after another,so regional governments should make good use of government green procurement as a demand-based science and technology policy to stimulate green patent output.The policy of transformation of scientific and technological achievements is the next step for green intellectual property output.The government should implement scientific policies in the field of transformation of scientific and technological achievements,continuously improve the transformation rate of scientific and technological achievements of green patents,and help green intellectual property output move from the laboratory to the market.
Secondly,we should pay attention to the role of environment-based science and technology policies and create a suitable environment for innovation for technological innovation subjects,such as reasonable target planning that can guide the production and operation activities of regional innovation subjects at the strategic level."Green principles " should be embedded in the regional development target plan as the core guiding idea.It is worth noting that policy resources are limited,which requires policy implementers to allocate policy resources reasonably.The policy planning of science and technology policies should not only consider the role of a single policy,but also the combination of different science and technology policies,and constantly adjust the proportion and priority of resource input.
5.3 Perfector of Green Patent System
First and foremost,the " green principles " should be viewed as the legal value coordinates of legislation in the area of technological innovation,with the aim of speeding up the promotion and application of advanced green technology through the fine-tuning of specific regulations to fulfill the legislative goal of environmental protection.On the one hand,it is important for municipal legislation to have a clear aim.In order to better play the role of legislative activities in promoting the improvement of the green intellectual property system,local governments should clearly protect and improve the ecological environment,prevent pollution,promote the output of green intellectual property,and strengthen the construction of ecological civilization when formulating local regulations.On the other hand,we ought to concentrate on how the law is put into practice.Incorporating local growth,implementing a green intellectual property system,and strengthening the law's enforcement capabilities should all be priorities in municipal legislation.
Second,by enhancing the current patent system,the " green " component of technological innovation is boosted.The " green principle " is stressed in the patent system.To increase the number of green patents issued,it is important to properly lengthen the patent term of these patents in order to better protect the patentees'rights and give them access to higher monopoly license fees(Xiao Xia,Research on Legal Issues of Green Patents).The second is to keep enhancing the green patent examination system,defining the standards for the examination,and streamlining the examination processes.Green patents are clearly superior to other types of patents in terms of their positive environmental externalities,and hastening their market introduction is beneficial for both economic growth and environmental improvement.First of all,China's patent law makes it very plain that ideas and creations that contravene national laws,social morality,or the public interest,as well as technological advancements that negatively impact the environment,cannot be granted patents.To split green patents in the patent system.Secondly,it is required to establish precise criteria for differentiating between general and green patents.it is necessary to set up a fast examination channel for green patents in the patent examination,so as to speed up the time for green technological innovation to enter the market and optimize the examination procedure.
5.4 Supervisor of the Implementation of Green IP Policies
Policy resources are limited and scarce,which requires policy implementers to allocate policy resources reasonably.In the process of promoting green technology innovation,the government is not only the allocator of resources but also the supervisor of the use of resources.To guarantee the output and transformation of green patents,the government will inevitably invest more funds and human resources in green IPR.In the process of using the funds,the government should function as a supervisor and focus on improving the utilization rate of resources to avoid wasting resources.To obtain the green resources from the government,innovation projects may carry out strategic innovation by " greening " and even generate corrupt behaviors such as " rent-seeking " in the process,which further requires the government to play a supervisory role.This further requires the government,through its regulatory function,not to be absent in the whole chain of the implementation of the green IP system.
6 Conclusions
The " green principle " in civil law is an important element of institutional guarantee for the long-term sustainable development of China's economy,and the application of the green principle in the field of regional technological innovation is not only the rightful realization of China's ecological civilization construction goals but also a necessary part of promoting China's innovation-driven development strategy.Regional governments can effectively enhance regional green patent output and promote regional green technology innovation through appropriate state intervention means and public policies such as environmental policies and science and technology policies.Through education and propaganda,resource inclination to guide green intellectual property output,optimize the green patent system by improving the top-level institutional arrangement,strengthen the supervision function by improving the transparency of the use of funds in the field of green technology innovation,participate in the green patent system through green procurement and other means,and make the green patent system continuously renew a new era of vitality by continuously improving relevant policies.
- 科技與法律的其它文章
- “商標(biāo)護(hù)城河”理念的泛化認(rèn)知局限與糾偏
- 司法區(qū)塊鏈的數(shù)智邏輯與訴訟規(guī)訓(xùn)
——以《人民法院在線運(yùn)行規(guī)則》展開 - 論鼓勵創(chuàng)新作為《反壟斷法》立法目的
- Analysis of the Criteria for Judging Unfair Competition in Data Crawling
- Interest Balancing Model of Separate Consent to Personal Information
- 從管理到服務(wù):知識產(chǎn)權(quán)糾紛調(diào)解機(jī)制的模式重塑

