Ontology:Footstone for Strong Artificial Intelligence
Xiaolin Yang,Zhe Wang ,Hongjie Pan ,Yan Zhu
1Department of Biomedical Engineering,Institute of Basic Medical Sciences,Chinese Academy of Medical Sciences,Beijing,100730 China
2Research Division of Knowledge Organization and Standardization,Institute of Information on Traditional Chinese Medicine,Chinese Academy of Chinese Medical Sciences,Beijing,100700 China
Key words:ontology;artificial intelligence;biomedicine;big data
Abstract In the past ten years,the application of artificial intelligence (AI) in biomedicine has increased rapidly,which roots in the rapid growth of biomedicine data,the improvement of computing performance,and the development of deep learning methods.At present,there are great difficulties in front of AI for solving complex and comprehensive medical problems.Ontology can play an important role in how to make machines have stronger intelligence and has wider applications in the medical field.By using ontologies,(meta) data can be standardized so that data quality is improved and more data analysis methods can be introduced,data integration can be supported by the semantics relationships which are specified in ontologies,and effective logic expression in nature language can be better understood by machine.This can be a pathway to stronger AI.Under this circumstance,the Chinese Conference on Biomedical Ontology and Terminology was held in Beijing in autumn 2019,with the theme“Making Machine Understand Data”.The success of this conference further improves the development of ontology in the field of biomedical information in China,and will promote the integration of Chinese ontology research and application with the international standards and the findability,accessibility,interoperability,and reusability(FAIR) Data Principle.
IT has been over 60 years since the introduction of artificial intelligence (AI) into the computer field as an extremely creative scientific task.Initially,scientists aimed to design a machine which could think,learn and infer like human beings.After its rise and fall over several decades,we are now privileged to witness the application of AI in people's daily lives.At present,face scan payment and voice recognition are commonly employed,whilst driverless technology will soon become mature within the next ten years.However,it seemed that AI has not realized the original conception proposed more than 60 years ago.Can AI fulfil tasks like human beings? A recent hot topic is the failure of IBM's medical supercomputer Watson at MD Anderson Cancer Center,indicating a huge gap between AI and human beings in terms of efficiency and effectiveness when resolving complex issues.
Narrow AI vs.General AI
AI can be divided into various levels according to its“intelligence ability”.The first level is called narrow AI,or weak AI,1which aims at problems of specific areas,such as image recognition,voice recognition and intellectual games.With the accumulation of mass data and the rapid decline of calculation and storage costs,machine learning has achieved significant successes represented by deep learning,surpassing human beings in certain areas.However,the above type of AI remains quite far-off from the initial conception,as it cannot even adapt to new environment,not to mention thinking,learning and inferring like human beings.The high-level“human resemblance”that we expect from AI is known as general AI,or strong AI.1At present,deep learning,as the most representative method in the narrow AI field,is still based on the probability model.It establishes the mapping relationship between input samples and a specific output mode through the training process and applies it to the test samples to realize classified prediction.The corresponding results are hard to explain,do not integrate with the background knowledge,and cannot dynamically respond to environmental changes.From this perspective,it is therefore easy to understand why Watson Project Director,Dr.Lynda Chin at MD Anderson Cancer Center,stated that“making the computer understand a medical record is much harder than anyone can imagine”,even though the supercomputer in Watson Project has collected over 1,500,000 pages of literatures about cancer.2
Introducing background knowledge (prior knowledge) into the AI system is essential for the improvement of its intelligence level.Ontology,originated from contemporary computer science and information science,is a novel and effective knowledge organization method.It can provide a common understanding about domain knowledge through standardizing the concept,attribute and definition as well as the relationships between entities in a specific field.Figure 1 shows the expression a common disease,influenza (DOID_8469),in human disease ontology (DO).3Its core framework is based on the phylogenetic classification relationship established with“is a”.It can be observed that influenza is both a respiratory system disease and a viral infectious disease,which can be divided into two subclasses,i.e.swine influenza and avian influenza.Meanwhile,the correlation of“l(fā)ocated in”indicates that influenza mainly invades the respiratory system,whilst the correlation of“has material basis in”suggests that this disease can be caused by three different viruses,namely influenza virus A,B and C.At present,the general ontology language is Web Ontology Language(OWL),4which has a strong semantic expression logic and supports inference based on first-order logic.
Ontology makes AI more effective and meaningful
Ontology improves the performance of AI in multiple aspects.
First,standardized annotation of data and metadata can be realizedviaterms contained in ontology,thereby enhancing data quality.On this basis,the semantic relation in ontology can be utilized to carry out effective data analysis with other methods to escalate the performance of machine learning.The functional interpretation of gene ontology (GO)5for genomic sequencing is the most successful application in this respect.Through standardized annotation for molecular functions of gene and its products,biological process of participation,and cellular localizationviaontology,it is possible to further speculate the occurrence mechanism of diseases,discover new functions of gene,and explore possible biomarkers.6
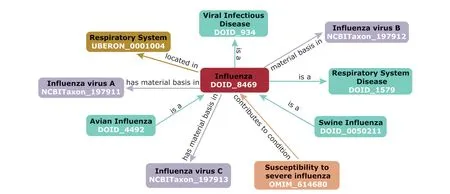
Figure 1.Expression of influenza in human disease ontology.
Second,ontology can support data integration at the semantic level,thereby expanding the application of AI.At present,Open Biological &Biomedical Ontologies Foundry (OBO Foundry)7is devoted to develope specific domain ontology under the framework of top-level ontology-basic formal ontology (BFO).8Different types of biomedical data apply these domain ontologies for annotation and management,which are then integrated through the common top-level ontology structure.In order to realize data integration at the semantic level,it is necessary that the domain ontology possesses abundant synonymy and near-synonymy semantic relations.In fact,in the field of AI,the difficulty of data integration is significantly underestimated.When identifying reasons for the failure of IBM's Watson Plan,the frequently mentioned is the ineffective data integration between systems.9
Third,ontology helps delivering accurate logical expressions of natural language.Human knowledge accumulated thus far mainly exists in the form of natural language.The conversion of this form into one that is comprehensible by computer will greatly facilitates its extensive application.For example,in the field of clinical decision making,attempts have been made to establish a knowledge base of clinical guidelines expressed by OWLviathe general ontology framework.On this basis,the decision-making software can combine the patient data in the electronic medical records with the knowledge base to determine the optimal treatment plan.10
Fourth,the combination of machine learning and interference with ontology is an important step towards general artificial intelligence.Currently,multiple domestic and international studies have combined deep learning with ontology for knowledge inference,which have presented results superior to those of logical reasoning.Alternatively,the application of ontology also improves the intelligibility of machine learning(deep learning) results.11
In the past decade,basic deep learning methods supported by large-scale data accumulation and largescale calculation ability have become mature,with clear future of sustainable development in fields with specific-defined tasks and sufficient data.However,in the biomedical domain,despite rapid data accumulation,the existing application effect of AI is still poor owing to problem sensitivity,numerous influence factors,data correlation complexity and data form diversity.On the contrary,ontology has unique advantages in the aspects of enhancing data quality,enriching the semantic relation of data,and establishing logical expression of knowledge,making it the footstone for future development of AI.
CCBOT promotes the development of ontology in China
To further improve the application and research of ontology in biomedical information field of China,Chinese Conference on Biomedical Ontology and Terminology 2019 (CCBOT 2019)12was held on October 28-30,2019 in Beijing.The conference was hosted by the National Population Health Data Center (NPHDC)13at Chinese Academy of Medical Sciences.The theme of this conference is“Making Machine Understand Data”.Professor Ba Denian,academician of Chinese Academy Engineering,along with more than ten domain experts at home and abroad,presented at the conference.
The conference focused on the application of ontology in data analysis and data management.The important roles of FAIR (findability,accessibility,interoperability,and reusability) Data Principles,14and ontology,as well as the application prospects of medical ontology in the area of population health were introduced.
During the academic exchange session,Dr.Robert Hoehndorf from the King Abdullah University of Science and Technology gave presentation on ontology-based data analysis in biomedical sciences.He shared his experiences in how to better apply ontology to search and optimize machine learning algorithms,and how to support scientific discovery,analysis of biomedical sciences,and data evaluation using ontology.Dr.Michel Dumontier,professor of the Institute of Data Science Maastricht University,introduced the application of FAIR Data Principles in terminology standardization,including how to solve problems such as format incompatibility,vocabulary overlapping and incompleteness,unclear license and access point isomerism through FAIR Data Principles,as well as how the semantic technology of FAIR Data Principles facilitate the exploration of biomedical knowledge more effectively and concisely.In addition,Dr.Yongqun He,the associated professor from the Medical School University of Michigan,presented on the knowledge and data standardization,integration and analysis in the community-based Ontology of Host-Microbiome Interactions (OHMI) project,in which he demonstrated the specific application of ontology in biomedicine.
Through the conference,attendees learned the most recent progress of research and application in ontology worldwide.Moreover,the up-to-date development of ontology in biomedicine in China was delivered.The conference provided a platform for international communication and collaboration of research and application in domain of the ontology.It will promote the integration of the ontology in biomedical field of China with the international standards,and facilitate further development of biomedical big data in China.Meanwhile,the friendship between Chinese and international researchers in the field has been established through the conference.It is noted that the Biomedical Ontology Committee of International Society for Biological Computing has promised to cooperate with National Population and Health Science Data Center of China to launch training program specifically for ontology application in biological medicine to technically support the progress of ontology in China.
Conflict of interest statement
All authors declared no conflicting interests.
 Chinese Medical Sciences Journal2019年4期
Chinese Medical Sciences Journal2019年4期
- Chinese Medical Sciences Journal的其它文章
- Bevacizumab Combined with Icotinib Overcomes Osimertinib Resistance in a Patient of Non-Small Cell Lung Cancer
- An Optimized Protocol of Azoxymethane-Dextran Sodium Sulfate Induced Colorectal Tumor Model in Mice
- Antagonistic Effects of N-acetylcysteine on Mitogenactivated Protein Kinase Pathway Activation,Oxidative Stress and Inflammatory Responses in Rats with PM2.5Induced Lung Injuries
- Physiological Variables Associated with the Development of Acute Mountain Sickness
- A Single-center Retrospective Cohort Study on Cesarean Section under General Anesthesia
- Expression of PD1 and BTLA on the CD8+ T Cell and γδT Cell Subsets in Peripheral Blood of Non-Small Cell Lung Cancer Patients
