Antagonistic Effects of N-acetylcysteine on Mitogenactivated Protein Kinase Pathway Activation,Oxidative Stress and Inflammatory Responses in Rats with PM2.5Induced Lung Injuries
Fen Ping,Qin Cao,Hua Lin,Shuzhi Han
Department of Respiratory Medicine,Hebei General Hospital,Shijiazhuang,050051 China
Key words:fine particulate matter (PM2.5);N-acetylcysteine;mitogen-activated protein kinases;oxidative stress;inflammatory response;rats
Objective To evaluate the antagonistic effects of N-acetylcysteine (NAC) on mitogen-activated protein kinases(MAPK) pathway activation,oxidative stress and inflammatory responses in rats with lung injury induced by fine particulate matter (PM2.5).Methods Forty eight male Wistar rats were randomly divided into six groups:blank control group (C1),water drip control group (C2),PM2.5exposed group (P),low-dose NAC treated and PM2.5exposed group (L),middle-dose NAC treated and PM2.5exposed group (M),and high-dose NAC treated and PM2.5exposed group(H).PM2.5suspension (7.5 mg/kg) was administered tracheally once a week for four times.NAC of 125 mg/kg,250 mg/kg and 500 mg/kg was delivered intragastrically to L,M and H group respectively by gavage (10 ml/kg)for six days before PM2.5exposure.The histopathological changes and human mucin 5 subtype AC (MUC5AC)content in lung tissue of rats were evaluated.We investigated IL-6 in serum and bronchoalveolar lavage fluid (BALF)by Enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay (ELISA),MUC5AC in lung tissue homogenate by ELISA,glutathione peroxidase (GSH-PX) in serum and BALF by spectrophotometry,and the expression of p-ERK1/2,p-JNK1/2 and p-p38 proteins by Western blot.All the measurements were analyzed and compared statistically.Results Lung tissue of rats exposed to PM2.5showed histological destruction and increased mucus secretion of bronchial epithelial cells.Rats receiving NAC treatment showed less histological destruction and mucus secretion.Of P,L,M and H group,MUC5AC in lung tissue,IL-6 in serum and BALF were higher than controls (C1 and C2) (all P<0.05),with the highest levels found in the P group and a decreasing trend with increase of NAC dose.The activity of GSH-PX in serum and BALF of PM2.5exposed rats (P,L,M and H) was lower than that of controls(all P<0.05),with higher activities found in NAC treated rats (L,M,and H),and an increasing trend with increase of NAC dose.The expressions of p-ERK1/2,p-JNK1/2 and p-p38 proteins in PM2.5exposed lung tissue(P,L,M and H) was higher than controls (all P<0.05),with decreased levels and dose dependent downregulation found in NAC treated rats.Conclusion NAC can antagonize major MAPK pathway activation,lung oxidative stress and inflammatory injury induced by PM2.5in rats.
PM2.5refers to environmental fine particulate matter with an aerodynamic diameter of 2.5 μm or less,which is the main component of fog and haze.As one of the important barriers in organisms,respiratory system plays a significant role in preventing organism from harm caused by PM2.5.
Lung inflammatory response and oxidative stress occur earliest upon air pollution,which may promote changes in coagulation system,cardiovascular system,systemic inflammatory response and oxidative stress.1PM2.5has complex components.When exposed to particulates,the organic and metal components can produce oxygen free radicals,causing direct damage to organism.In addition,a series of intracellular reactions(kinase cascade activation,transcription factor activation,inflammatory mediator release) can be activated,resulting in cell damage or apoptosis.2The mechanisms of oxidative stress and inflammatory injury play a core role in multiple injuries.Antagonistic drugs based on these mechanisms may provide a protective effect on preventing organisms from harms caused by PM2.5air pollution.
Foreign studies found that antioxidant-rich food and drink have certain effects on preventing PM2.5and protecting cardiovascular health.3Animal experimental studies found that early treatment for PM2.5exposed rats with vitamin E and ω-3 polyunsaturated fatty acid can improve antioxidant activity and reduce production of inflammatory cytokines in rats.4Some bacterial products,viruses,environmental pollutants and inflammatory cytokines can cause airway mucus hypersecretion.MUC5AC is a specific marker of pulmonary airway goblet cells and the most important component of airway mucus.5Mitogen activated protein kinases (MAPK)pathway is one of the important signal transduction systemsin vivo,which is activatedviathree-kinase cascade.MAPK subfamily includes extracellular signal-regulated protein kinases (ERK1/2),c-Jun NH2-terminal kinases (JNK1/2) and p38,which are involved in cell proliferation,differentiation,apoptosis and inflammation,and are activated by dual phosphorylation on threonine and tyrosine.Experimental studies found that PM2.5can increase reactive oxygen species in cardiomyocytes to reduce survival and increase apoptosis,upregulate the expression of phosphorylated MAPK,i.e.p-ERK1/2,p-JNK1/2 and p-p38.MAPK signaling pathway is expected to be the target of clinical treatment of PM2.5-induced myocardial injury.6Polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons (PAHs) in urban particulate pollutants induce JNK activation in hepatocarcinoma cells.7
N-acetylcysteine (NAC) is commonly used as an expectorant drug in respiratory department.It contains a free thiol group which can directly react with electrophilic oxidizing groups playing the role of antioxidant.This study investigated the impact of PM2.5exposure on inflammatory response,oxidative stress,mucus secretion and major MAPK pathway activation in serum and lung tissues of rats treated by NAC,in order to observe the effects of NAC at different dose on major MAPK pathway activation,oxidative stress and inflammatory injury in lungs.We hope this work can provide a theoretical basis for prevention and treatment of PM2.5induced lung injury.
MATERIALS AND METHODS
Preparation of PM2.5 suspension
PM2.5particulates which contain organic carbon (OC),elemental carbon (EC),nitrate,sulfate,ammonium,and sodium were provided by Hebei Provincial Environmental Monitoring Center.To prepare PM2.5suspension,we conducted autoclaved sterilization before use,suspended in sterile water at a concentration of 7.5 mg/ml,and mixed up by ultrasonic oscillation.
Grouping and administrations
We randomly divided 48 male Wistar rats (provided by the Experimental Animal Center of Hebei Medical University,180-200 g each) into six groups:two control groups [blank control group (C1),drip control group(C2)],four treatment groups [PM2.5group (P),lowdose NAC group (L),middle-dose NAC group (M),highdose NAC group (H) ].C1 received no treatments at all.C2 were instilled sterile water (1 ml/kg) tracheally once a week for four times.P were instilled PM2.5suspension (7.5 mg/kg) tracheally once a week for four times.L,M and H were intragastrically administrated NAC aqueous solution (10 ml/kg,freshly prepared,Fluimucil,Zambon,produced by Hainan Zambon Pharmaceutical Co.,Ltd) of 125 mg/kg,250 mg/kg,500 mg/kg respectively for six days,followed by tracheally instillation of PM2.5suspension on the seventh day.The procedures were repeated three times.
Collection of samples
Twenty four hours after the last intra-tracheal instillation,we performed intra-peritoneal injection of 10%chloral hydrate (3 ml/kg) to make anesthesia.Blood samples were collected from femoral artery.Bronchoalveolar lavage fluid (BALF) was obtained through bronchoalveolar lavage of left lung.Lower lobe of right lung was fixed with formaldehyde solution,embedded in paraffin,sliced,stained with hematoxylin-eosin (HE) and AB-PAS,and observed under light microscope.The rest of right lung was prepared for tissue homogenate.
Detection of protein expression in lung tissues with western blot method
Appropriate amount of lung tissue was weighed,mixed with cell lysis solution,protease inhibitor and phosphatase inhibitor,then was quickly cut into pieces and homogenized.The above operations were carried out on ice.Homogenate was centrifuged and the supernatant was absorbed and measured for protein concentration with bicinchoninic acid (BCA) method.With loading buffer added,it was heated for 5 min at 95°C to denature protein.Samples with extracted protein were packaged and preserved at -80°C.SDS-polyacrylamide gel electrophoresis (SDS-PAGE) method was used for separating protein by electrophoresis,which stopped when bromophenol blue indicator move to the bottom of separation gel.Membrane was transferred at constant current of 200 mA for 1.5 h,blocked with skim milk powder.After washing with TBST washing buffer,bovine serum albumin (BSA) diluted primary antibody was added to incubate overnight at 4°C(P-Erk1/2,1:2000 dilution;p-JNK1/2,1:1000 dilution;p-p38MAPK,1:1000 dilution).After washing membrane,mixing with secondary antibody,incubating for 1.5 h,we washed it and mixed it with luminescence liquid for photographic analysis.
Measurements of IL-6,BALF,MUC5AC and GSH-PX
The IL-6 level of serum and BALF and MUC5AC content of lung tissue homogenate were detected by ELISA .The levels of glutathione peroxidase (GSH-PX) in serum and BALF were detected by spectrophotometry.The operations were carried out following the instructions strictly.
Statistical analysis
Statistical analysis was performed using SPSS software(version 21.0).Measurement data with normal distribution were presented as means and standard deviation.When normal distribution and homogeneity of variance were satisfied simultaneously,one-way analysis of variance was performed for comparisons among multi-groups,and Student-Newman-Keuls (SNK) test was used to compare between two groups.P<0.05 was considered statistically significant.
RESULTS
Changes of lung tissue
Histological changes of lung tissue
Microscopic observation showed that there was no obvious difference in pathology of lung tissue between C1 and C2 group.Lung tissues of P group and treatment groups were destructed,presenting alveolar septum thickening,alveolar cavity deformation,infiltration of peripheral inflammatory cells,interstitial edema and congestion of blood capillary.Lung tissues in P group presented the most severely destructed changes;of the NAC treated groups,with the increase of NAC dose,the degree of histological destruction reduced(Figure 1).
Mucus secretion in lung tissue
Small amount of mucus was observed in lung tissue of rats in C1 and C2 group.Rats exposed to PM2.5(P group) presented remarkable increase of blue-stained mucus in bronchial epithelial cells.With the increase of NAC dose,positive-staining substances in L,M and H group decreased,indicating gradually reduced mucus secretion (Figure 2).
Effects of NAC on MUC5AC in lung tissue of rats
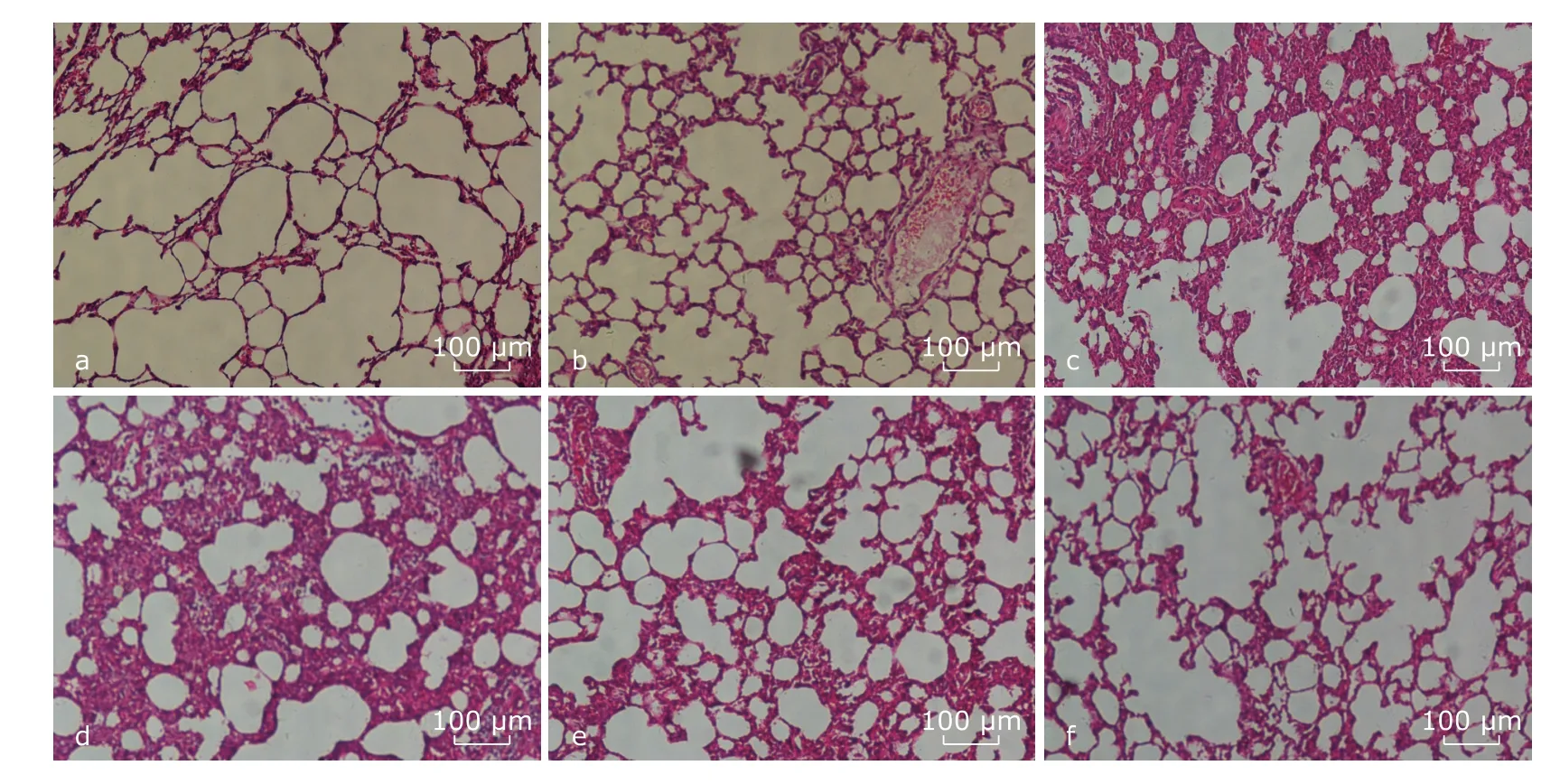
Figure 1.Pathological findings in lung tissue of rats under light microscope (HE staining,100 ×).
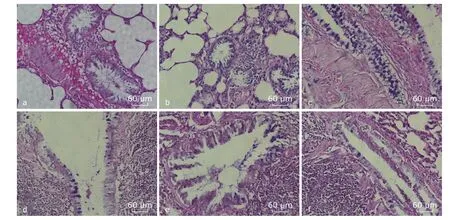
Figure 2.Pathological findings of mucus observed in lung tissue of rats under light microscope (AB-PAS staining,200 ×).
The contents of MUC5AC in lung tissue of L,M and H were lower than that of P group (allP<0.05) in a dose-dependent manner,and the difference in the MUC5AC of lung tissue among P,L,M and H group was statistically significant (P<0.05) (Table 1).The content of MUC5AC in lung tissue of C1 and C2 group were significantly lower than that of P,L,M and H group (allP<0.05),with no significant difference between each other.
Effect of NAC on IL-6 and GSH-PX in serum and BALF of rats
In serum and BALF of rats exposed to PM2.5by intra-tracheal instillation,the activity of GSH-PX was found lower and IL-6 level was found higher than that of C1 and C2 (allP<0.05).Among PM2.5exposed rats,rats with NAC treatment(L,M,and H group) showed decreased IL-6 and increased GSH-PX activity in serum and BALF,compared with rats in P group (allP<0.05).With the increase of NAC dose,IL-6 level was on downtrend and GSH-PX activity was on uptrend(allP<0.05) (Table 1).
Effect of NAC on expression of p-ERK1/2,p-JNK1/2 and p-p38 proteins in lung tissue of rats
The expressions of p-ERK1/2,p-JNK1/2 and p-p38proteins in lung tissue of rats with PM2.5 exposure (P,L,M and H) were significantly higher than those of C1 and C2 (allP<0.05).Of rats with NAC treatment (L,M and H group),the expression of p-ERK1/2,p-JNK1/2 and p-p38 proteins in lung tissue decreased compared with rats in P group,and the decreases were dose-dependent (allP<0.05) (Table 2,Figure 3).
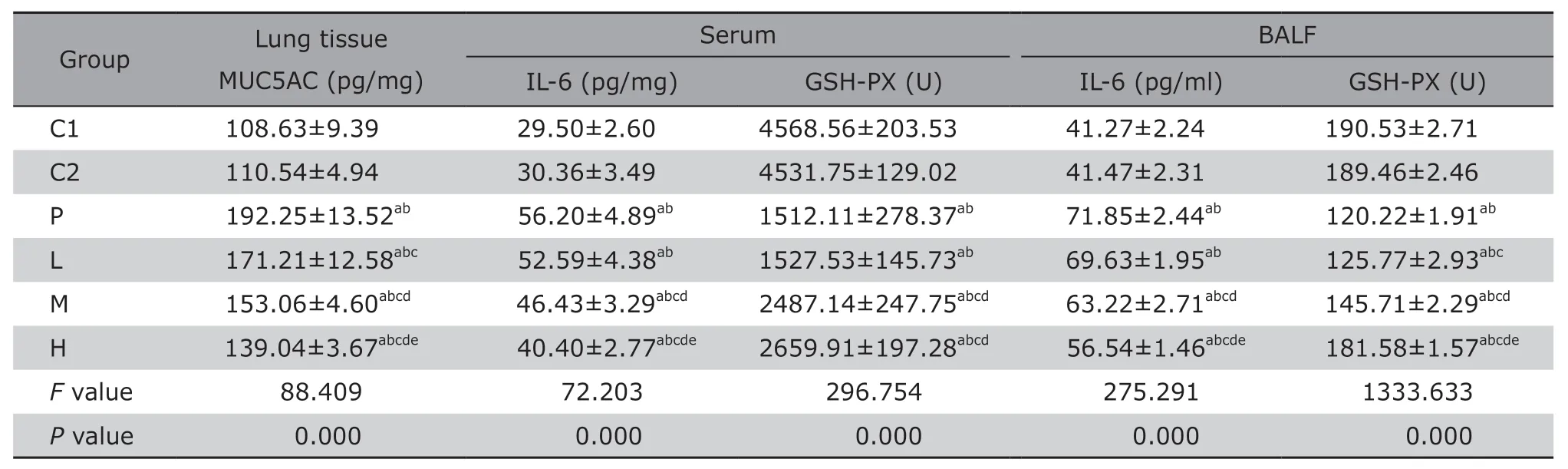
Table 1.MUC5AC in lung tissue,IL-6 of inflammatory response and oxidative stress in serum and BALF of rats (n=8)§
DISCUSSIONS
Air pollution of PM2.5harms human health.Many researchers are studying its toxicity characteristics and harm mechanisms.Studies found that PM2.5exposure increased respiratory and cardiovascular diseasemortalities and all-cause mortalities.8Particulate air pollution attributable mortality is up to 16.2% of total mortality of Chinese population,ranking the fourth in 67 risk factors for death of Chinese.9
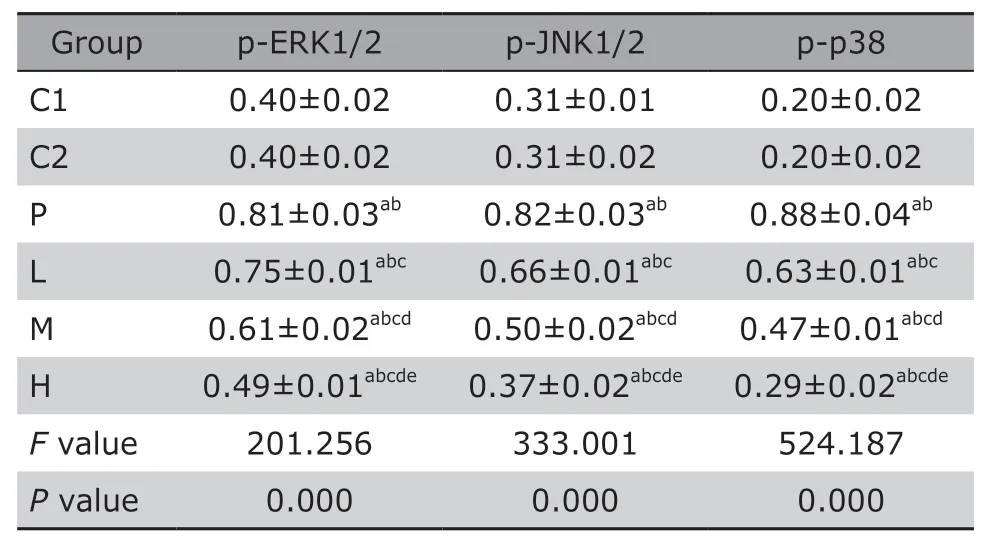
Table 2.Comparison of relative values of p-ERK1/2,p-JNK1/2 and p-p38 expressions in lung tissues of rats among and between each group (n=8)§
Animal experiments with PM2.5exposed rats showed that PM2.5caused pulmonary congestion,inflammatory cell infiltration,and increase of inflammatory cells in BALF.Intra-tracheal instillation of high-concentration PM2.5could cause oxidative stress and increase proinflammatory mediators like TNF-α and IL-6 in lung tissues.10IL-6 is a marker of systemic inflammatory response,which can stimulate liver cells to produce acute-phase proteins and stimulate bone marrow to increase white blood cells and platelets in blood circulation.In this study,the IL-6 in serum and BALF of rats exposed to PM2.5by intra-tracheal instillation were higher than that of rats without PM2.5exposure,indicating exposure to PM2.5stimulated production of inflammatory response in rats.IL-6 level of BALF was higher than that of serum in the same group of rats,suggesting that lung inflammatory injury occurred earlier than systematic changes after exposure to PM2.5.However,the numerical difference may be also due to the differences in bronchoalveolar lavage techniques.
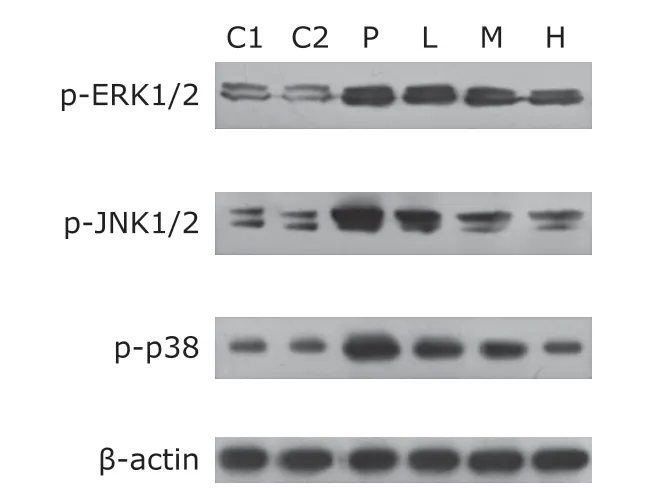
Figure 3.Expression of p-ERK1/2,p-JNK1/2 and p-p38 in lung tissue of each group by Western blot method.
Tissue inflammatory response is often accompanied with oxidative stress,which induces release of reactive oxygen species and results in tissue damage.11Study found that PM2.5exposure increased inflammatory factors in BALF while decreased antioxidant enzyme GSH-PX and superoxide dismutase (SOD) activity in lung tissues.12Studies have shown that for human bronchial epithelial cells,PM2.5exposure decreases cell activity,increases reactive oxygen species,destructs mitochondrial morphology,reduces gene expression,and improves oxidase and inflammatory cytokine expression.Vitamin C and quercetin,the antioxidant nutrients prevalent in fruits and vegetables,can antagonize PM2.5-induced oxidative damage.13NAC,as nucleophile and thiol donor,has antagonistic effect on toxicants.14NAC protects tissues from damage by reacting with hydroxyl radicals and producing glutathione.Aliet al.found that NAC can reduce hepatic inflammatory response,increase hepatic antioxidant enzyme activity and protect against diclofenac acid-induced hepatotoxicity in rats.15The current study showed that NAC can increase the antioxidant capacity of rats,reduce inflammatory response,and partially antagonize PM2.5toxic effect within a certain dose range.
MUC5AC is the main component of airway mucus.In physiological conditions,mucus secretion can protect respiratory tract from foreign bodies.Excessive mucus secretion is related to chronic obstructive pulmonary disease,asthma and other respiratory diseases.In vivoandin vitroexperiments have demonstrated that proinflammatory cytokines,growth factors,neutrophil and eosinophil products,bacterial virus products and environmental toxic substances can induce MUC5AC expression in airway epithelial cells.16Iwanagaet al.found that urban particulates increased the expression of MUC5AC and IL-8 in bronchial epithelial cells of normal children and asthmatic children.17In this study,the intra-tracheal instillation of PM2.5increased MUC5AC content in lung tissue of rats,and the NAC treatment had reduction effect on it;with increase of NAC dose,the MUC5AC decreased.This result suggested that PM2.5exposure increased mucus secretion,after NAC treatment,PM2.5-induced mucus secretion decreased,which might be caused by reduction of oxidative stress.However,the content of MUC5AC of high dose NAC treated rats was still higher than that of rats without PM2.5exposures,indicating that NAC may not antagonize all PM2.5-induced injuries and there are multiple pathogenic mechanisms.
MAPK pathways are prevalent in organisms.The expressions of p-ERK1/2,p-JNK1/2 and p-p38 are through the activation of major MAPK subfamily members such as ERK1/2,JNK1/2 and p38 by phosphorylation.ERK signaling pathway plays an important role in acute lung injury.ERK inhibitors reduce lipopolysaccharide induced pulmonary neutrophil recruitment and release of inflammatory cytokines in BALF.18JNK and p38 pathway activation leads to stress response,growth arrest,and apoptosis.19Studies found that diesel engine exhaust particulates can activate signaling pathways (ERK1/2,JNK1/2) in mouse tracheal allograft and induce acid mucus production,vacuolization and apoptosis,and thus lead to airway diseases.20Research on mechanisms has demonstrated that inflammatory factors IL-1β and TNF-α mediate the expression of MUC5AC gene in human nasal epithelial cellsviaERK1/2 and p38 MAPK activation and downstream signaling pathway,which provides a theoretical basis for airway mucus hyper-secretion induced by inflammatory response.21PM exposure significantly enhanced the airway inflammatory response through MAPK(ERK,JNK,p38 MAPK) and downstream NF-kB signaling pathways.22In this study,we found the intra-tracheal instillation of PM2.5 increased the protein expression of p-ERK1/2,p-JNK1/2 and p-p38 in lung tissues and activated MAPK pathways.After NAC treatment,phosphorylated protein expression in PM2.5exposed rats decreased.Within the experimental dose scope,the higher of NAC dose,the more remarkable decrease of protein expression,which indicated that NAC could partially antagonize major MAPK pathway activation caused by PM2.5.
In conclusion,PM2.5leads to lung injury through multiple mechanisms which interact or influence each otherviainflammation and oxidative stress.NAC can antagonize major MAPK pathway activation,oxidative stress,and inflammatory injury in rats with lung injury induced by PM2.5.
Conflict of interests statement
All authors in this article declared no conflicting interests.
 Chinese Medical Sciences Journal2019年4期
Chinese Medical Sciences Journal2019年4期
- Chinese Medical Sciences Journal的其它文章
- Bevacizumab Combined with Icotinib Overcomes Osimertinib Resistance in a Patient of Non-Small Cell Lung Cancer
- An Optimized Protocol of Azoxymethane-Dextran Sodium Sulfate Induced Colorectal Tumor Model in Mice
- Ontology:Footstone for Strong Artificial Intelligence
- Physiological Variables Associated with the Development of Acute Mountain Sickness
- A Single-center Retrospective Cohort Study on Cesarean Section under General Anesthesia
- Expression of PD1 and BTLA on the CD8+ T Cell and γδT Cell Subsets in Peripheral Blood of Non-Small Cell Lung Cancer Patients
