Predicting the Potential Distribution of Rubia cordifolia L. in China
Wei QIN, Suping JIANG, Xueke ZHANG, Dingkang CHEN, Shoujin LIU,2*, Daiyin PENG,2
1. Anhui University of Traditional Chinese Medicine, Hefei 230038, China; 2. Institute of Traditional Chinese Medicine Resources Protection and Development, Anhui Academy of Chinese Medicine, Hefei 230038, China; 3. State Key Laboratory of Phytochemistry and Plant Resources in West China, Kunming Institute of Botany, Chinese Academy of Sciences, Kunming 530100, China
Abstract [Objectives] We intend to conduct a study to predict habitat suitability and geographic distribution of Rubia cordifolia L., to find the most suitable ecological environment for its growth, and to provide a theoretical basis for the development and cultivation of R. cordifolia L. industry. [Methods] Based on the environmental factors and the occurrence data, we predicted the potential geographic distribution of R. cordifolia L. in China by combining the MaxEnt model and ArcGIS. [Results] The training set and test set AUC were respectively 0.963 and 0.946, indicating that the MaxEnt model predicted well. The wettest monthly precipitation, precipitation in July, precipitation of driest season, and average monthly temperature in September and April were the dominant environmental factors affecting the distribution of R. cordifolia L. The highly habitable areas were mainly concentrated in central, eastern and northern China. [Conclusions] The results of this study can be used as a reference for the development of R. cordifolia L. industry in related areas.
Key words Rubia cordifolia L., MaxEnt, Habitat suitability, Arcgis
1 Introduction
From 2000-2003, 10.6 million children under 5 years of age died each year worldwide, of which diarrhea accounted for 18%, and pediatric acute diarrhea was the second leading cause of death among children under 5 years old. Especially in developing countries in Africa, where the prevalence of diarrheal diseases is high, the mortality rate is much higher than that in other countries. In China, the above-ground parts ofRubiacordifoliaL. have been traditionally used to treat acute pediatric diarrhea with good efficacy and no significant adverse effects. The dried roots and rhizomes ofR.cordifoliaL. have various pharmacological activities such as anti-inflammatory, anti-cancer, antioxidant, hemostatic and antibacterial. It is widely distributed in China, but there are not many areas with large scale production, and the supply is mostly wild. In addition, the recovery ability of this species is extremely weak, and the artificial cultivation technology is still immature.
R.cordifoliaL. is a perennial climbing vine that belongs to the Rubiaceae family with quadrangular, barbed stems. The leaves are in whorls of four, mostly ovate. It is widely distributed in southern Europe, Africa and Asia.R.cordifoliaL. has a long history of application in China and India[1-4]. Its roots and rhizomes are not only an important source of red dye, but also a good medicine for cooling the blood, stopping bleeding and dispelling blood stasis. Aqueous decoction of the above-ground parts ofR.cordifoliaL. has been used to treat acute diarrhea in children with remarkable efficacy and no toxic side effects. Its active ingredients have various pharmacological activities such as anti-inflammatory, anti-cancer, antioxidant, hemostatic, and antibacterial[5-11]. In China,R.cordifoliaL. is mainly produced in Anhui, Shanxi, Henan, Shandong and Hubei, among which Shanxi and Henan have the largest production and best quality.
In recent years, habitat for species has been gradually lost with growing population numbers and demand for land from urbanization. Habitat loss is the main reason for species endangerment, species extinction and biodiversity loss[12-13]. Climate change and land use change, may shrink, degrade or destroy the habitats of wild animals and plants[14-15]. Habitat loss affects the spatial pattern of residual habitat and induces microclimatic change and habitat fragmentation[16]. Therefore, the potential distribution prediction and habitat simulation ofR.cordifoliaL. are of great significance for the conservation and development of its resources. In this study, we collected information on the latitude and longitude of the sampling sites ofR.cordifoliaL., combined with climate, topography, soil and other relevant environmental factors, and used the MaxEnt model to analyze the habitat suitability ofR.cordifoliaL. in order to study its potential distribution area in China.
The commonly used ecological niche models for predicting the potential distribution of species are GARP[17], Bioclim[18], Domain[19], ENFA[20], and MaxEnt. In comparison, the MaxEnt model has higher accuracy and better prediction results with a smaller sample size[21-24]. It has been widely used in biogeography[25-28], invasive warning[29-32], disease transmission and pathways[33-36], and prediction of the potential geographic distribution of species[37-38].
2 Materials and methods
2.1 Species dataThrough the Chinese Virtual Herbarium (CVH) (http://www.cvh.org.en/en/cms/) and the China Nature Reserve Resource Platform (http://www.papc.cn/), 3 361 occurrence data ofR.cordifoliaL. were selected in the last 30 years. To ensure full representation of the environmental conditions associated with each species and to counter any sampling bias, China scale occurrence data was obtained from the GBIF data portal (http://data.gbif.org). After aggregating all the data, duplicate, fuzzy and adjacent records were removed in strict accordance with MaxEnt requirements, and finally 263 valid data were retained for model construction (Fig.1).
2.2 Ecological factors and related geographic information dataThe climatic type data and ecological factors related to the distribution of traditional Chinese medicine resources were obtained from the Spatial Information Network Database of Traditional Chinese Medicine (TANET). The ecological factors included precipitation, sunshine, climate, soil, topography and vegetation type. The climatic type data included 12 months’ precipitation and average temperature, and 19 integrated climatic factors (Table 1).
Six soil type data, one vegetation type data and three topographic data (altitude, slope and aspect) were selected. Soil type data included the following: soil cation exchange capacity (trylzjhnl), soil sand content (trhsl), soil clay content (trhndl), soil subclass (sym90), soil effective water content class (tryxshldj), organic carbon content (yjthl).
The 1∶4 million maps of China and the administrative divisions of China used in the experiment were downloaded from the National Geographic Information System (NGIS).
2.3 Modelling method and statistical analysisThe version of MaxEnt software is 3.3.3; analysis and mapping software is the GIS platform ArcMap10.7 developed by ESRI. MaxEnt theory holds that under known conditions, the thing with the greatest entropy is closest to its true state. That is, species will spread as much as possible under unconstrained conditions and approach uniform distribution[39]. Based on this theory, the habitat of the target species can be evaluated and predicted by the actual distribution points of the species and the environmental factors in the study area. Selection of 25% of the occurrence data as test data, the maximum number of iterations was 106, and the response curve and ROC curve were set, the model was fitted using MaxEnt built-in cross-validation using 10 folds. Jackknife method was used to analyze the weights of each ecological factor in influencing the habitat suitability ofR.cordifoliaL.
3 Results
3.1 Model performanceThe model accuracy is evaluated by the ROC curve and the area under the curve (AUC). Fig.2A shows the ROC curve of the initial model, the AUC of the training set is 0.973, and the AUC of the test set is 0.957. Fig.2B shows the ROC curve of the final model, and the result shows that the mean AUC of 10 repetitions is 0.972, indicating that the MaxEnt model has high accuracy and reliability[40].
3.2 Dominant environmental factor analysisThe MaxEnt model was used to calculate the weights of different ecological factors in the habitat ofR.cordifoliaL., and the following were identified as the main ecological factors affecting its distribution: wettest monthly precipitation, monthly precipitation in July, average monthly air temperature in March, average monthly air temperature in September, average monthly air temperature in April, vegetation type and precipitation in the driest season. Environmental factors with a contribution of more than 1.8% (Table 2) have a cumulative contribution of 90.1%.
The results of the Jackknife test are shown in Fig.3. Taking into account the results of MaxEnt modeling and the Jackknife test, the wettest monthly precipitation, monthly precipitation in July, average monthly temperature in September and April, and rainfall in the driest season were identified as the dominant environmental factors affecting the potential distribution ofR.cordifoliaL.
3.3 Potential distribution area analysisHabitat suitability was re-classified by Arcgis software from MaxEnt, and the suitability zoning map (Fig.4) was obtained, which was divided into four categories: unsuitable area (P<0.05), lowly suitable area (0.05≤P<0.25), moderately suitable area (0.25≤P<0.5) and highly suitable area (P≥0.5). The white zone represents the unsuitable area, green zone represents the lowly suitable area, yellow zone represents the moderately suitable area, and red zone represents the highly suitable area. According to the distribution map of the potential distribution range of Chinese regional psyllium, its distribution areas were mainly concentrated in North, Central, East, South and Southwest China. It can be seen that the population ofR.cordifoliaL. has expanded significantly in the context of climate warming, and its geographic distribution has gradually spread northward. Therefore, it is extremely important to study the influence of climatic factors on the distribution ofR.cordifoliaL.
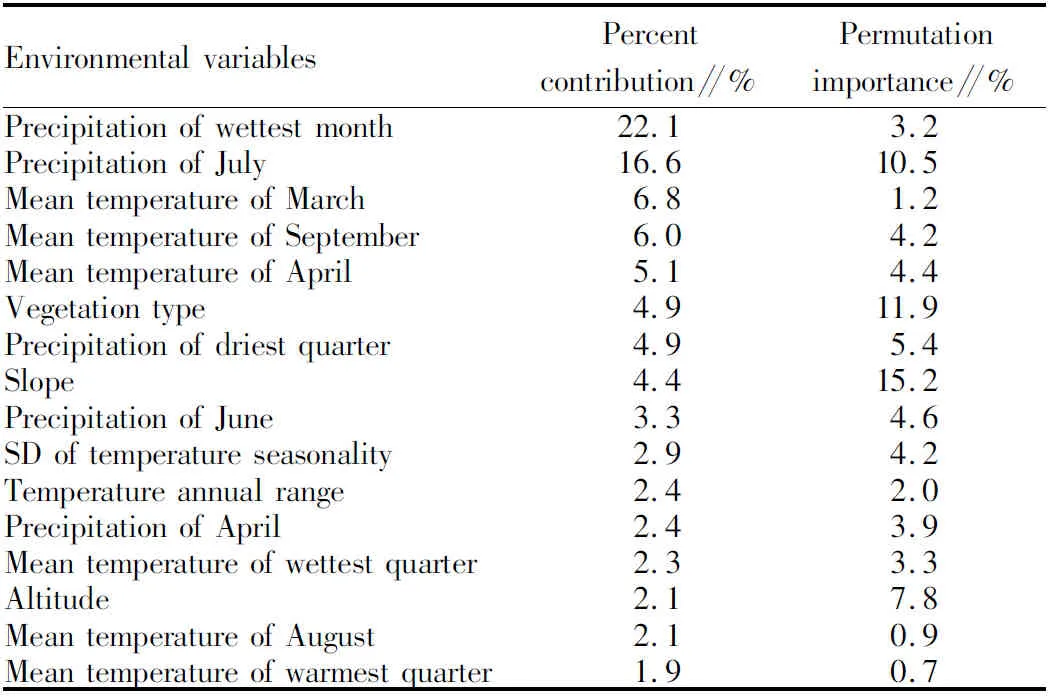
Table 2 Percent contribution and cumulative contribution of the environmental variables to the Maxent model
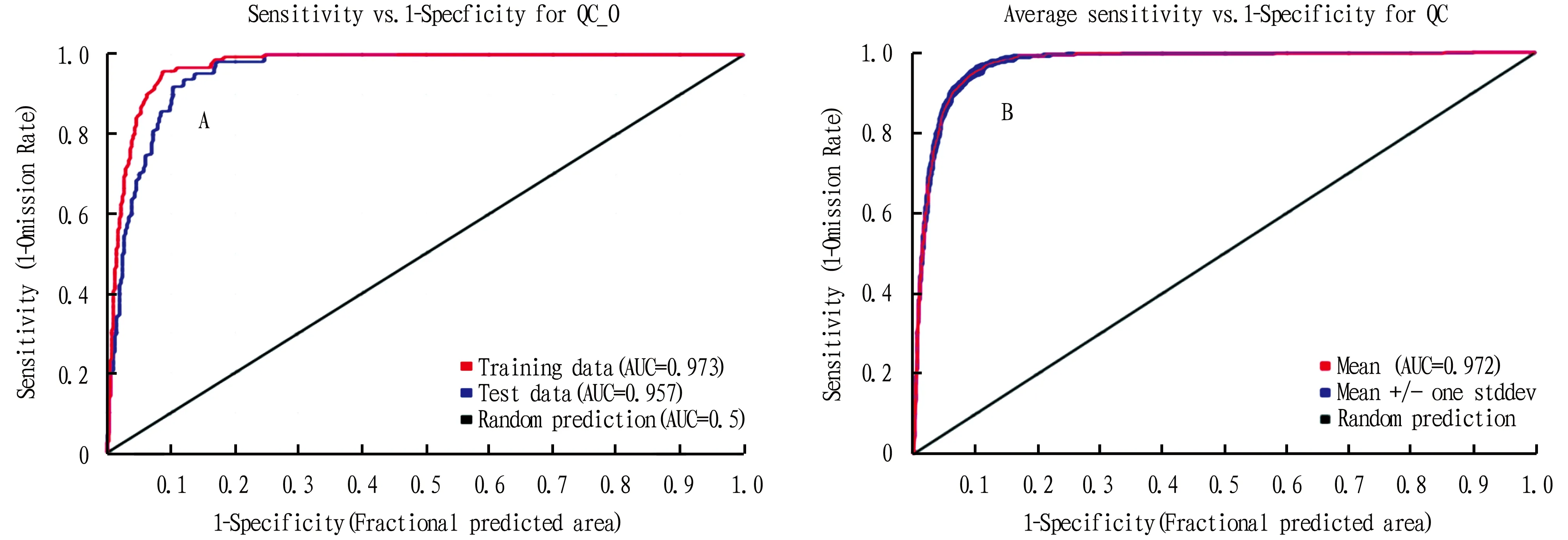
Fig.2 ROC curve and AUC values for the initial model (A) and the final model (B)
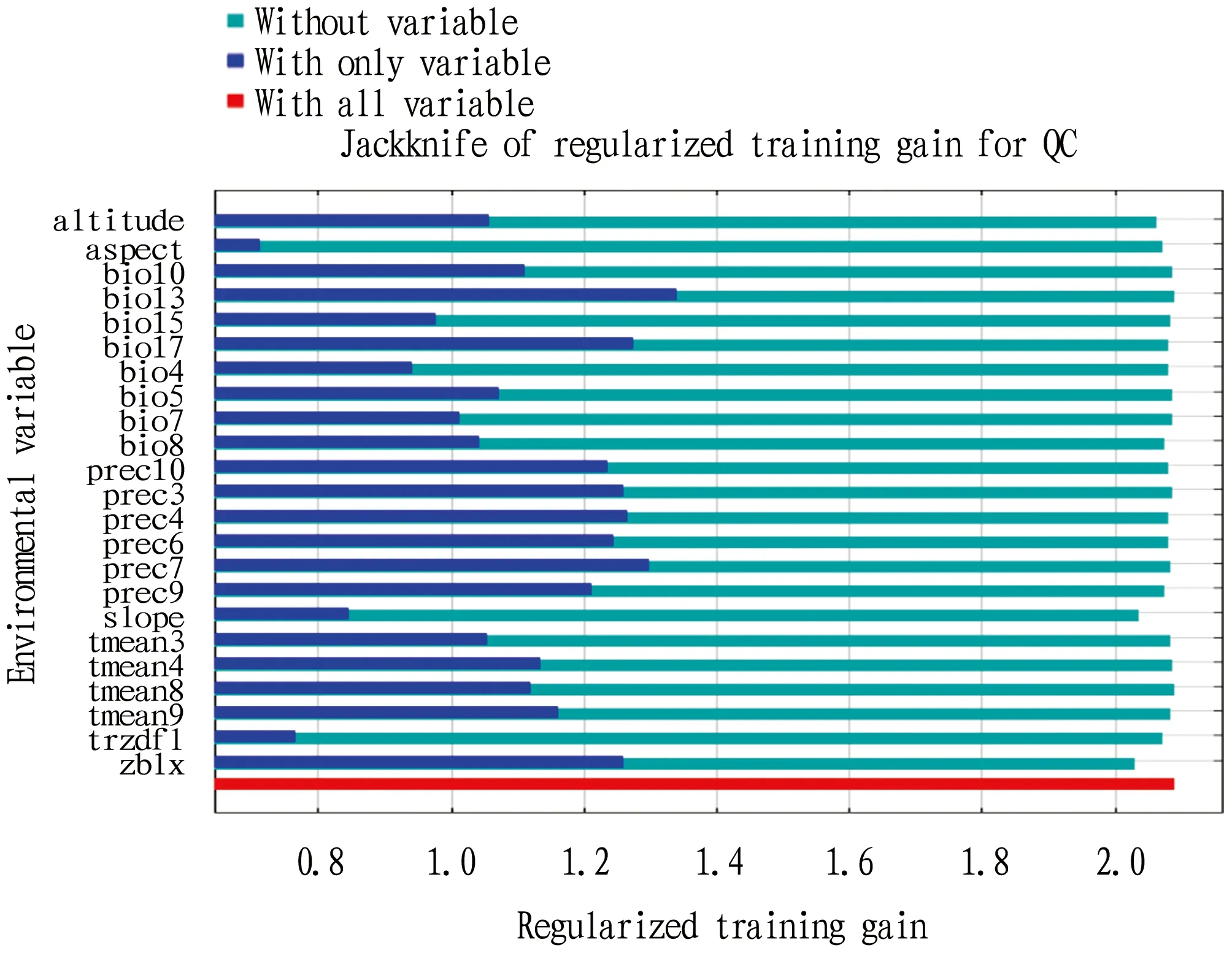
Fig.3 Jackknife test for variable importance in the Rubia Cordifolia L. distribution: values shown are averages over 10 replicate runs
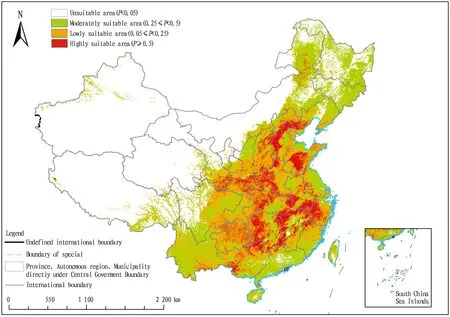
Fig.4 Probability of the potential distribution ofRubiacordifoliaL. in China based on the MaxEnt model
3.4 Impact of environmental factors on areas of potential distribution
3.4.1Rainfall. Precipitation in the driest season, wettest month and July month all has a great influence on the distribution ofR.cordifoliaL., and the total weight of precipitation in all ecological factors is 49.3%. As shown in Fig.5, when the precipitation in the driest season is less than 8 mm, the probability of normal growth ofR.cordifoliaL. is less than 0.33. With the increase of precipitation, the habitat suitability gradually increases. When the wettest monthly precipitation is less than 100 mm, the habitat suitability is less than 0.33. With the increase of precipitation, the probability of habitat suitability increases rapidly, and reaches the maximum at 260 mm, if the precipitation continues to increase, the suitability decreases.
The optimum value of monthly precipitation in July is between 175-198 mm. When the precipitation is greater than 290 mm, the suitability decreases rapidly.
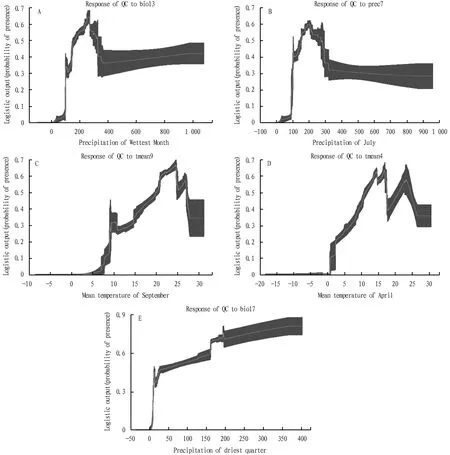
Note: A. BIO13; B. prec7; C. tmean9; D. tmean4; E. BIO17.
3.4.2Temperature. Temperature has a weight of 29.5% on the distribution ofR.cordifoliaL. When the average temperature in September reached 7.8 ℃, the temperature required for the survival of the grass was basically met, and the probability of habitability reached the maximum at 24.5 ℃, which was the most suitable temperature for the growth of the grass. If the temperature continues to rise, the habitability will decrease.
When the average temperature of April reaches 6.5 ℃, the temperature conditions gradually meet the survival requirement ofR.cordifoliaL., and the probability of habitability reaches the maximum at 13.6 ℃. This is also consistent with the characteristics ofR.cordifoliaL. which likes cool and moist.
4 Conclusions
Based on the MaxEnt model and ArcGIS, combined with environmental data, this study predicted the geographic distribution of the medicinal plantR.cordifoliaL. in China. The data sources ofR.cordifoliaL. in this study were mainly the literature, the Chinese Virtual Herbarium (CVH) (http://www.cvh.org.en/en/cms/), the Chinese Nature Reserve Resource Platform (http://www.papc.cn/) and GBIF data portal (http://data.gbif.org). The latitude and longitude of some data were obtained by positioning software, so there was some geographical error. The fundamental niche is the maximum ecological niche occupied by a species under the most ideal living conditions. The ecological niche model only analyzed the effects of abiotic factors on species distribution, which indicated that the model predicted a wider ecological niche than the actual ecological niche occupied by species. Therefore, the results of this study have some limitations and shortcomings.
In summary, the results of this study provide a comprehensive study of the resource distribution zonation and ecological environment factors ofR.cordifoliaL., determine the ecological environment affecting the growth ofR.cordifoliaL. using the MaxEnt model, divide and distribute the growth of the species using ecological factors, and find the most suitable ecological environment for its growth, which provides a theoretical basis for the development and cultivation of the industry. In the next step, we will explore whether the most suitable ecological environment for the growth ofR.cordifoliaL. is suitable for the accumulation of active ingredients. The results of this study can be used as a reference for the development ofR.cordifoliaL. industry in related areas.
- Medicinal Plant的其它文章
- Advances in Research of Pharmacological Activities of Resveratrol
- Determination of Enantiomers in ET-26-HCl by Ultra Performance Convergence Chromatography
- In vitro Pharmacological Activity of Chromenes in Disk of Helianthus annuus
- Experimental Study on Key Techniques for Indoor Cultivation of Sprout Vegetables in Families
- Advances in Research of Toxic Traditional Chinese Medicines in the Treatment of Malignant Tumors
- Optimization of Extraction Process of Polysaccharides from Actinidia arguta (Sieb. & Zucc.) Planch. ex Miq.

