Optimization of Extraction Process of Polysaccharides from Actinidia arguta (Sieb. & Zucc.) Planch. ex Miq.
Xiaohui LI, Lihua MA, Lidong YIN, Tao LUO
Liaoning Institute of Science and Technology, Benxi 117004, China
Abstract [Objectives] To optimize the extraction process of polysaccharides from Actinidia arguta (Sieb. & Zucc.) Planch. ex Miq. [Methods] On the basis of single-factor tests, an orthogonal test was conducted with solid/liquid ratio, ultrasonic temperature, ultrasonic time and ultrasonic power as influencing factors. [Results] The optimal extraction process was as follows: solid/liquid ratio 1∶15 (g/mL), ultrasonic temperature 50 ℃, ultrasonic time 50 min and ultrasonic power 90 W. Under the optimal extraction conditions, the extraction rate of polysaccharides reached 2.05%. [Conclusions] The method is simple and feasible, and can be used to optimize the extraction process of polysaccharides in A. arguta, in order to provide a theoretical basis for the further development and utilization of related resources.
Key words Actinidia arguta (Sieb. & Zucc.) Planch. ex Miq., Polysaccharide, Extraction process
1 Introduction
Actinidiaarguta(Sieb. & Zucc.) Planch. ex Miq. (Actinidiaceae:Actinidia) is a deciduous vine plant, also called "soft date" and "kiwiberry". The fresh fruit is edible and can also be used for medicinal purposes, with high value. In addition to being rich in vitamin C, it also contains many active ingredients such as flavonoids, polysaccharides, alkaloids and saponins[1]. Research results show thatA.argutahas obvious effects in preventing and treating heart disease, protecting liver, reducing fat, and preventing and treating diabetes and cancer[2]. Pharmacological research shows that the pharmacological effects ofA.argutaare closely related to its flavonoids, polysaccharides and other ingredients[3-4]. At present, the research on extraction of polysaccharides inA.argutamostly focuses on single indices, and thus the pros and cons of the extraction process cannot be well evaluated. To this end, in this experiment, the extraction process of polysaccharides inA.argutawas optimized, with a view to providing a certain theoretical basis for the in-depth development and utilization ofA.arguta.
2 Materials
UV-Vis spectrophotometer (Beijing Puxi General Instrument Co., Ltd.); AR224CN electronic balance [Ohaus Instruments (Shanghai) Co., Ltd.]; three-frequency band CNC ultrasonic cleaner (Zhengzhou Shengyuan Instrument Co., Ltd.); centrifuge (Shanghai Lu Xiangyi Centrifuge Instrument Co., Ltd.); SY-5000 rotary evaporator (Shanghai Xiande Experimental Instrument Co., Ltd.).
A.argutawas picked in Benxi City, Liaoning Province, and identified by Professor Ge Huiqi of Liaoning Institute of Science and Technology.
3 Methods
3.1 PretreatmentAfter removing impurities and cleaning, freshA.argutawas pre-refrigerated for 12 h, cut into thin slices in a semi-melted state, dried in a constant temperature oven to constant weight, crushed and passed through a 40-mesh sieve for use.
3.2 Determination of polysaccharides and drawing of standard curveThe content of polysaccharides was determined with 5% phenol-sulfuric acid method[5]. An accurate amount (20 mg) of glucose was dissolved in water to 100 mL. Different volume (2.0, 4.0, 6.0, 8.0 and 10.0 mL) of the glucose liquid prepared foregoing was diluted to 100 mL, respectively. An accurate volume (2 mL) of each of the glucose diluents was transferred into a test tube, added with 1.0 mL of 5% phenol solution and 5.0 mL of concentrated sulfuric acid, shaken well, bathed in boiling water for 15 min, bathed in cold water for 5 min, and measured at 490 nm, respectively. Taking absorbanceAas the ordinate and glucose concentrationCas the abscissa, standard curve was drawn, and regression equation (A=0.018 4C+0.018 1,r=0.999 2) was obtained.
3.3 Preparation of polysaccharides test solutionA certain amount (5 g) of powder ofA.argutawas ultrasonicated for a certain period of time, and the extract was recovered and concentrated to 1/10 of the original volume, added with 10 times the volume of ethanol, let stand for 12 h, centrifuged, and dried. A certain amount of the powder obtained was dissolved in hot water ultrasonically to 100 mL, and 1.0 mL of the supernatant was sampled for determination of polysaccharides content.
3.4 Single-factor tests of extraction processOther factors were fixed, and the influence of solid/liquid ratio, ultrasonic time, ultrasonic temperature and ultrasonic power on the extraction rate of polysaccharides inA.argutawas investigated. The results are shown in Fig.1. When the ultrasonic time, ultrasonic power and ultrasonic temperature were fixed at 30 min, 70 W and 40 ℃, the content of polysaccharides increased first and then decreased with the increase in solid/liquid ratio, highest at 1∶20 g/mL and lowest at 1∶10 g/mL, and therefore, the solid/liquid ratio should be within the range of 1∶15-1∶25 g/mL. When the solid/liquid ratio, ultrasonic power and ultrasonic temperature were fixed at 1∶15 g/mL, 70 W and 40 ℃, respectively, the content of polysaccharides first increased slowly and then decreased with the extension of ultrasonic time, and therefore, the ultrasonic time should be within 30-50 min. When the solid/liquid ratio, ultrasonic time and ultrasonic power were fixed at 1∶15 g/mL, 30 min and 70 W, the content of polysaccharides increased first and then decreased with the increase of ultrasonic temperature, and so the ultrasonic temperature should be within 40-60 ℃. When the solid/liquid ratio, ultrasonic time and ultrasonic temperature were fixed at 1∶15 g/mL, 30 min and 40 ℃, the content of polysaccharides increased first and then remained unchanged with the increase of ultrasonic power, and therefore, the ultrasonic power should be determined within 60-80 W.
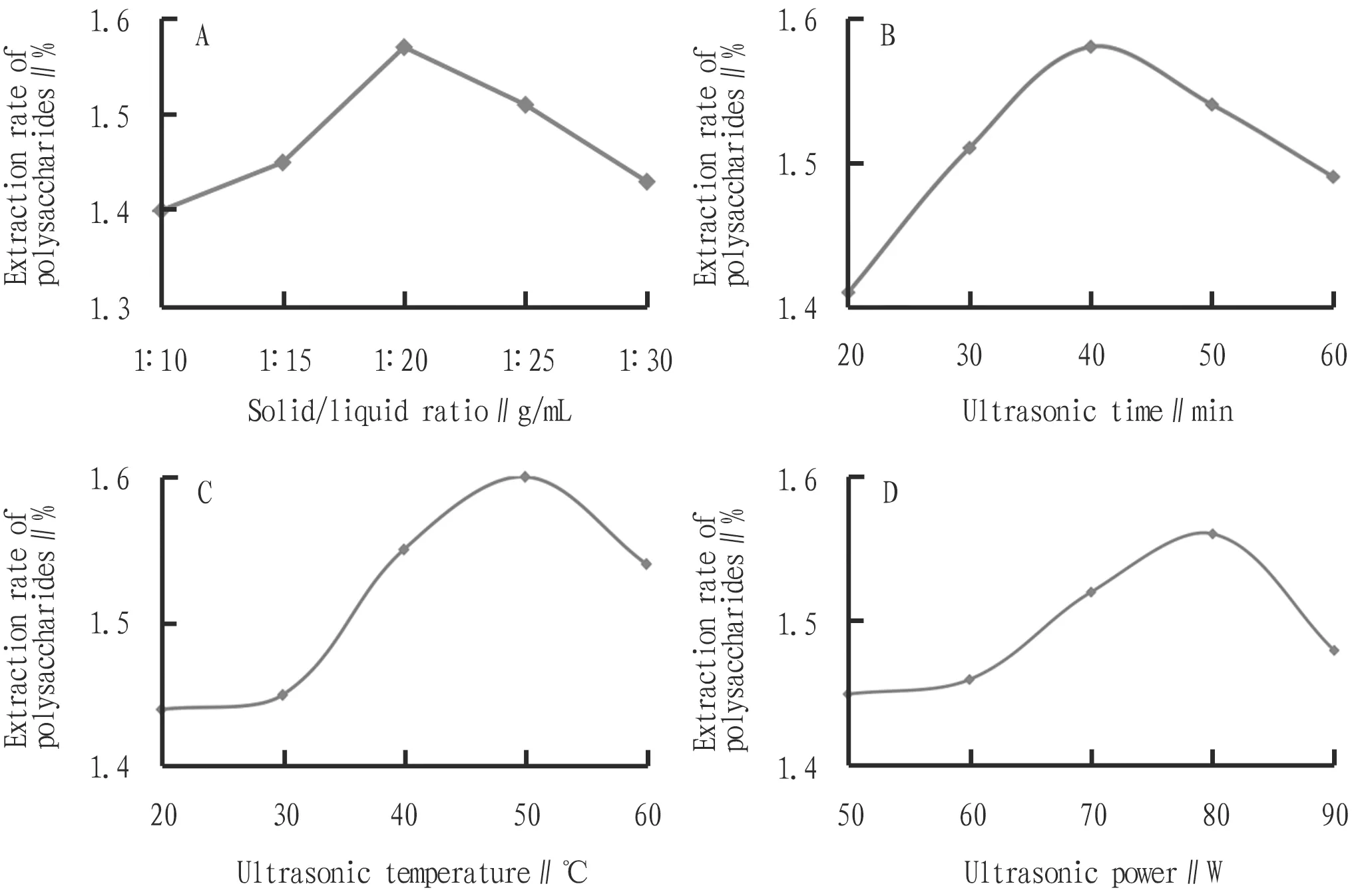
Note: A. solid/liquid ratio; B. ultrasonic time; C. ultrasonic temperature; D. ultrasonic power.
3.5 Optimization of extraction process for polysaccharides
On the basis of single-factor tests, an L9(34) orthogonal test was conducted to optimize the extraction process of polysaccharides inA.arguta. The factors and levels of the orthogonal design are shown in Table 1. The test results are shown in Table 2.
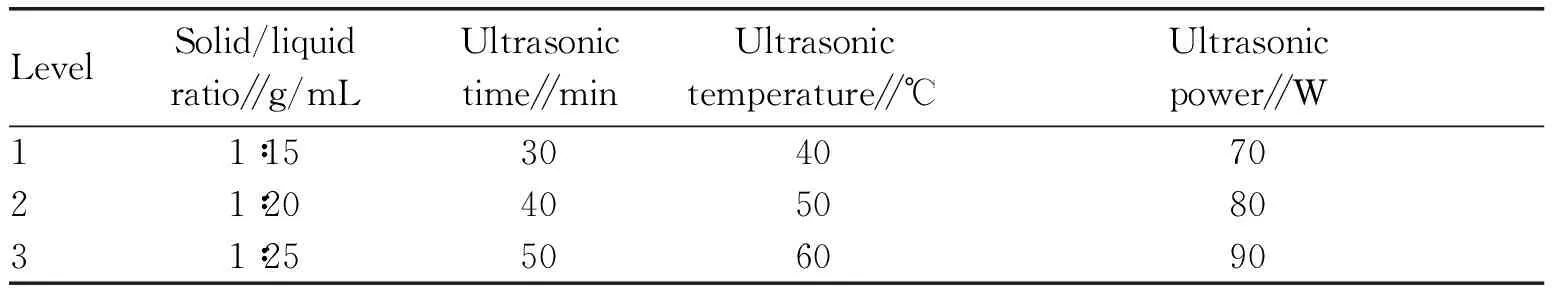
Table 1 Factors and levels of orthogonal test for optimizing extraction process of polysaccharides in Actinidia arguta (Sieb. & Zucc.) Planch. ex Miq.
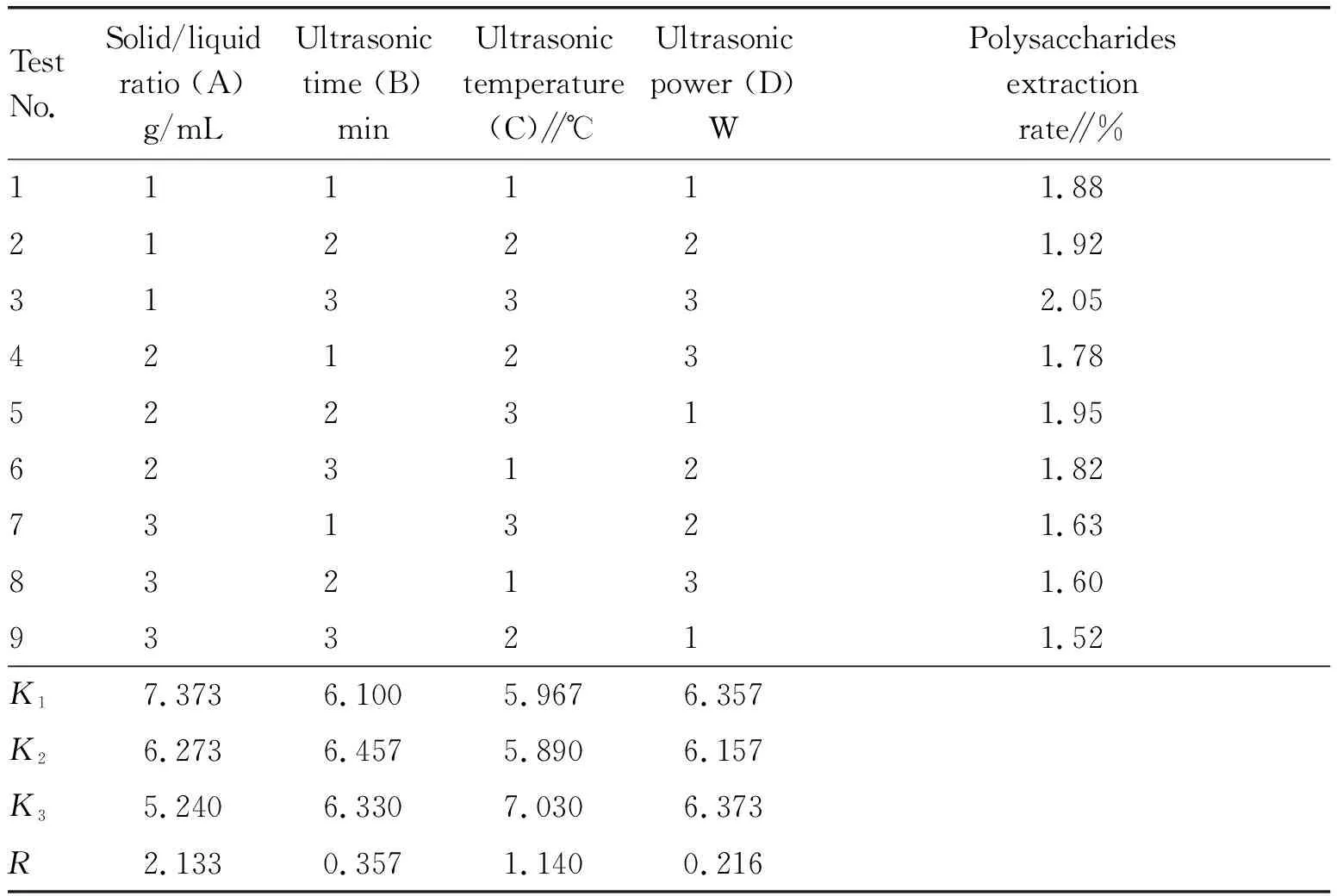
Table 2 Results of orthogonal test for optimizing extraction process of polysaccharides in Actinidia arguta (Sieb. & Zucc.) Planch. ex Miq. (n=3)
In terms ofRvalue, it could be concluded that the influencing intensity of different factors ranked as A>C>B>D, that is, solid/liquid ratio>ultrasonic temperature>ultrasonic time>ultrasonic power. The optimal combination of the influencing factors was A1B2C3D3, that is, solid/liquid ratio 1∶15 g/mL, ultrasonic temperature 50 ℃, ultrasonic time 50 min and ultrasonic power 90 W. As the influence of ultrasonic power (D) on the extraction rate of polysaccharides inA.argutawas little, it was used as an error item in the analysis of variance table. As shown in Table 3, solid/liquid ratio and ultrasonic temperature have a significant effect on the extraction rate of polysaccharides inA.arguta, with statistical significance.
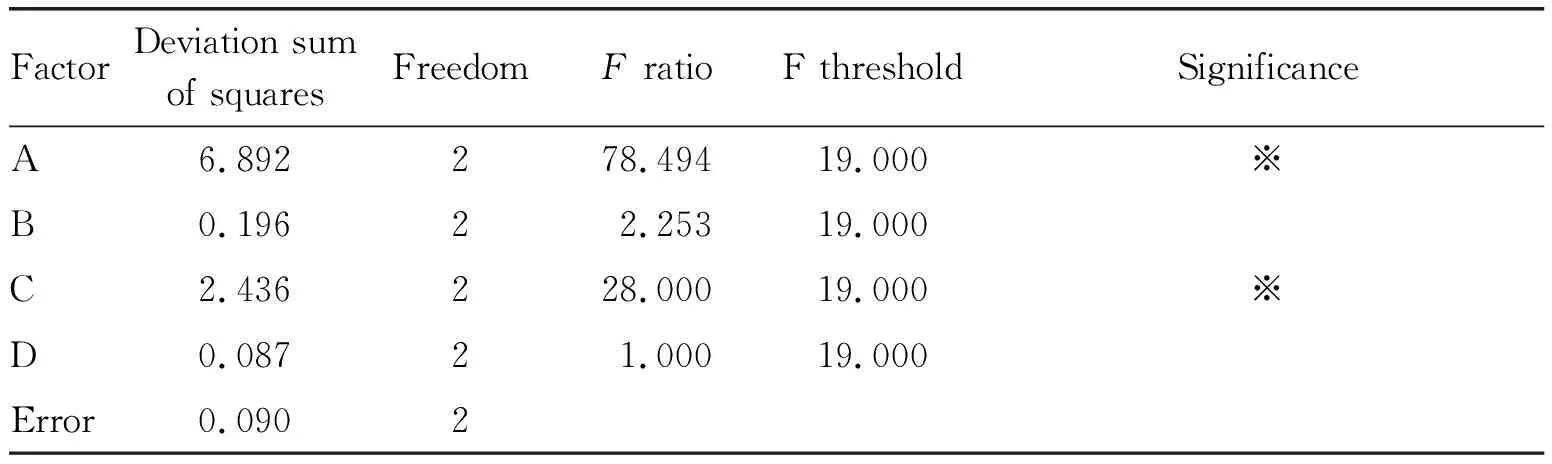
Table 3 Variance analysis of results of orthogonal test for optimizing extraction process of polysaccharides in Actinidia arguta (Sieb. & Zucc.) Planch. ex Miq.
4 Conclusions
Due to extremely high nutrition, and health care and medicinal functions,A.argutahas attracted more and more attention. Liaoning has now become China’s largest industrial base ofA.arguta. At the same time,A.argutais also the main economic species promoted by agriculture in Liaoning Province. As the industry continues to develop, the existing problems have become increasingly prominent. For example, the effective use of theA.arguta
resources is still insufficient; and most of the existing products are processed simply and roughly, with low economic added value; and new varieties with market competitiveness are lacked. Therefore, the development of high value-added, new functional health products and medicines is extremely urgent.
The optimal extraction process concluded by this study is as follows: solid/liquid ratio 1∶15 g/mL, ultrasonic temperature 50 ℃, ultrasonic time 50 min and ultrasonic power 90 W. Under the optimal extraction conditions, the extraction rate of polysaccharides was 2.05%. The extraction process of polysaccharides inA.argutaestablished in this experiment is simple and accurate, and can provide a certain theoretical basis for the in-depth development and utilization ofA.arguta.
- Medicinal Plant的其它文章
- Advances in Research of Pharmacological Activities of Resveratrol
- GC-MS Analysis of Volatile Oils in Mango Leaves from Different Producing Areas
- In vitro Pharmacological Activity of Chromenes in Disk of Helianthus annuus
- Experimental Study on Key Techniques for Indoor Cultivation of Sprout Vegetables in Families
- Advances in Research of Toxic Traditional Chinese Medicines in the Treatment of Malignant Tumors
- Determination of Enantiomers in ET-26-HCl by Ultra Performance Convergence Chromatography

