Serum Levels of Interleukin-1 Beta, Interleukin-6 and Melatonin over Summer and Winter in Kidney Deficiency Syndrome in Bizheng Rats△
Miao Zhang, Tong Wang, Huai-min Chen, Yan-qin Chen, Yang-chun Deng, and Ya-tian Li
School of Basic Medical Sciences, Beijing University of Chinese Medicine, Beijing 100029, China
BIZHENG is an immune system disease which belongs to rheumatoid arthritis (RA) in western medicine.1Interleukin-1 beta (IL-1β) and interleukin-6 (IL-6) play a key role in the pathogenesis of RA. These 2 kinds of cytokines are closely related to the climatic change, especially in winter, which is usually accompanied with the rhythm of melatonin (MT). MT is a kind of amine hormones produced by pineal gland, which is mostly influenced by light. This kind of biological rhythm becomes the new target linking human body condition with the change of seasons. So the relationship between RA and the level of IL-1β, IL-6 and MT is worthy of further exploration. In this study, directed by the entirety control ideology of “correspondence between human and nature” and the concept of “kidney corresponding with winter” in traditional Chinese medicine, we observed the changes of the serum levels of IL-1β, IL-6, and MT in Bizheng rat model during summer and winter, analyzed the relationship between IL-1β, IL-6, MT and the pathogenesis of RA, aiming to provide experimental and theoretical basis for the chronotherapy of RA.
MATERIALS AND METHODS
Materials
One hundred and sixty Sprague-Dawley (SD) rats aged 7-8 weeks were purchased from the Weitong Lihua Experimental Animal Technology Co., Ltd. (Beijing, China). All the animals were delivered 56 days before midsummer or midwinter. The average weight of female rats was 150±10 g and that of male rats was 170±10 g. The room temperature range was 25°C±5°C in summer and 17°C± 5°C in winter. The rats were provided with standard chow and drinking water freely.
10% Chloralic hydras solution, iodophor, 75% alcohol, IL-1β (HY-075) radio immunity kit, IL-6β (HY-078) radio immunity kit, and melatonin (HY-104) radio immunity kit were all purchased from Huaying Biological Technology Research Laboratory (Beijing, China).
Animal groups and experiment procedures
A total of 80 SD rats were randomly divided into 4 groups in summer or in winter: normal group (n=20), collagen-induced arthritis (CIA) model group (n=20), operation group (n=20), and sham-operation group (n=20). There were 10 male rats and 10 female rats in each group.
In the normal group, no specific treatment was conducted. In the CIA model group, each rat was injected with 0.2 ml emulsion (collagen: 200 μg) subcutaneously at the base of the tail. The needle was inserted 2 cm from the base of the tail until the tip of the needle was 0.5 cm from the base. Every time the needle was slowly pulled out to prevent leakage of emulsion. In the first 7 days after injection, each rat was injected with 0.1 ml CII emulsion (collagen: 100 μg) subcutaneously at the base of the tail to excite the immune response.2,3
In the operation group, the rats were anesthetized with 10% chloral hydrate (0.3-0.35 ml/100g) by intraperitoneal injection. Skin preparation, sterilization and incision on the skin of the head were performed sequentially. The skull was cut with a round dental drill in lambdoid and sagittal lines. The pineal gland was extracted by ophthalmic forceps. Debridement, clearance with a little amount of penicillin solution, skin suture, and disinfection were performed. Penicillin was injected for 3 days to prevent infection. Seven days after the first operation, testectomy was operated for male rats and oophorectomy was operated for female rats. The rats were anesthetized with 10% chloral hydrate (0.3-0.35 ml/100g) by intraperitoneal injection. In testectomy, the incision was made along the scrotum septum, and then the vessels of testis and epididymis were ligated. The distal end of testis was lifted and extracted. The other testis was also extracted. In oophorectomy, the incision was located 2 horizontal fingers (2 cm) away from the inferior border of the rib and 1 vertical finger near the vertebral (next to the erector spinae). The size of the longitudinal incision was about 0.5-1.0 cm. The subcutaneous tissue and muscle were separated and the abdominal cavity was exposed. A carmine cauliflower ovary was found along the red earthworm segment of the white shiny adipose tissue. The ovarian tissue were ligated and extracted before the abdominal cavity was closed. The other ovary was extracted in the same manner. Skin suture, disinfection and clearing with penicillin solution were performed. After that, the operated rats were immunized with the same method as in the CIA model group.
In the sham-operation group, the rats were operated to ligature the sagittal sinus instead of extracting the pineal gland. Penicillin was injected for 3 days to prevent infection. 7 days after the first operation, an incision was made on each side of the spine to expose the kidney. Then skin suture, disinfection and clearing with penicillin solution were performed. After that, the rats were immunized with the same method as in the CIA model group.
Measurement of IL-1β, IL-6, and MT
The rats were continuously fed about 3 weeks to the midsummer or midwinter after the second collagen injection. Blood samples (5 ml) were taken from the abdominal aorta at 8:00 pm and centrifuged at 2000 r/min for 20 minutes. The supernatant was drew carefully and centrifuged for another 10 minutes at the same speed. At last, the serums were collected and stored in -80°C refrigerator. The levels of IL-1β, IL-6, and MT were determined by radioimmunoassay according to the manufacturer’s instructions.
Statistical analysi s
Statistical analyses were performed using SPSS 17.0 software. All data were expressed as means±SD. Data in normal distribution were compared using one-way analysis of variance (ANOVA) followed by Student-Newman-Keuls (SNK) test, and data in abnormal distribution were compared using non-parametric test. The differences between winter and summer were analyzed using Student’s t test. P <0.05 was considered statistically significant.
RESULTS
Serum levels of IL-1β among different groups in summer and winter
Compared with the normal group, the level of IL-1β increased in the CIA model group, the operation group and the sham-operation group both in summer and in winter (summer, P=0.008, P<0.01, P=0.012; winter, P=0.019, P<0.01, P=0.027) (Table 1). The level of IL-1β in the operation group was higher in winter than in summer, but with no statistically significant difference (P=0.844). The levels of IL-1β in the CIA model group and the sham-operation group were significantly higher in winter than in summer (P=0.048, 0.014).
Serum levels of IL-6 among different groups in summer and winter
Compared with the normal group, the level of IL-6 increased in the CIA model group, the operation group and the sham-operation group both in summer and in winter (summer, P=0.028, P<0.01, P=0.024; winter, P=0.006, P<0.01, P=0.008) (Table 2). There was no statistically significant difference in IL-6 level in the operation group between summer and winter (P=0.679). The levels of IL-6 in both the CIA model group and the sham-operation group were significantly higher in winter than in summer (P=0.039, 0.046).
Serum levels of MT among different groups in summer and in winter
The serum levels of MT were higher in the CIA model group and sham-operation group than in the normal group both in summer and in winter (summer, P=0.002, P=0.003; winter, P=0.008, P=0.007) (Table 3). The serum level of MT in the operation group was significantly lower than that in the normal group in both summer and winter (P=0.023, 0.003), but the level showed no significant difference between summer and winter (P=0.947). The levels of MT in the normal group, the CIA model group and the sham-operation group were significantly higher in winter than in summer (P=0.026, 0.048, 0.020) (Table 3).
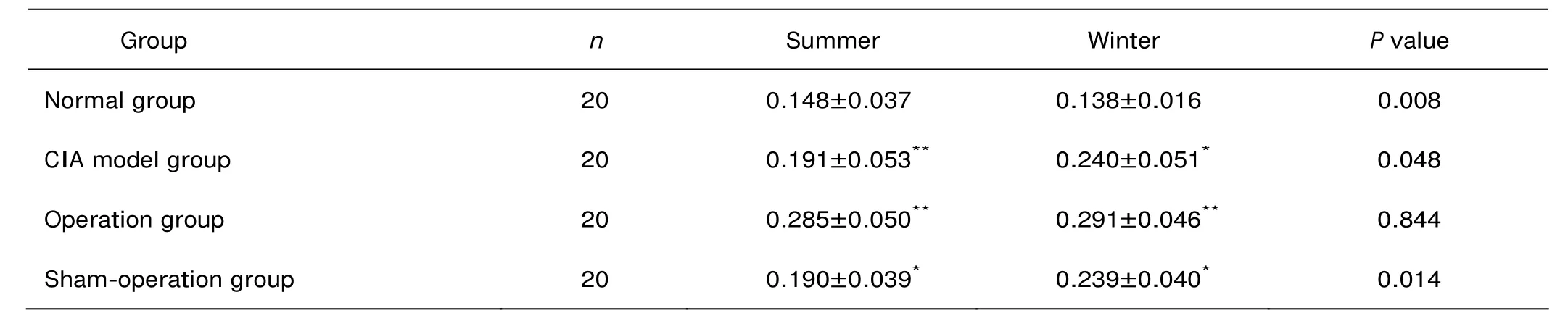
Table 1. Changes in serum levels of interleukin (IL)-1β among four groups in summer and winter (μg/L)§

Table 2. Changes in serum levels of IL-6 among four groups in summer and winter (ng/L)§

Table 3. Changes in serum levels of melatonin among four groups in summer and winter (ng/L)§
DISCUSSION
From the result of measurements of cytokines IL-1β, IL-6 in summer and winter in the present study, we observed that the levels of IL-1β and IL-6 in the CIA model group and the sham-operation group in winter are significantly higher than those in summer. Compared with the levels in summer, the level of IL-1β in the operation group in winter increased slightly and the level of IL-6 declined, neither of which showed statistically significant differnce. It could be said that the concentrations of IL-1β and IL-6 in rat serum presented a tendency of rising in winter and reducing in summer, which corresponds with the “kidney correlated with winter” theory in traditional Chinese medicine. Jiang et al4reported that there was a tendency of obviously lower level in the sex hormone in hypothalamus-hypophysis-testis axial in winter, similar to the reproductive function which coordinates with the function of kidney sense winter and works on hibernation and conservation.5
The drop of sex hormone level cause more severe reaction in patients suffering Bizheng in winter than in summer, followed by the increase of cytokine IL-1β and IL-6. The reason why the cytokines in Bizheng group were not significantly influenced by season is related to the design of animal model. The model of deficiency in the operation group was established by removing pineal gland through surgery. Although the deficiency of kidney is considered to be exacerbated and cause more severe reaction in Bizheng in winter, the removal of pineal gland caused the loss of season regulator and decreased the excretion of MT in rats, which possibly lead to the loss of seasonal adjustment on sexual gland. Therefore, there was no significant inter-season difference in the operation group. As to the other two groups with pineal gland, namely the CIA model group and the sham-operation group, the seasonal differences were statistically significant. These findings suggest the relationship between the change of seasons and pineal gland.
RA is a kind of autoimmune disease.6MT has anti-infla- mmatory and immune regulating effect to autoimmune disease.7It also has a close relationship with sexual gland and can adjust the maturity and cyclical activities of sexual gland during the growth and aging process. The concentration of MT in serum varied among the 4 groups in this study: compared with the normal group, the MT level rose significantly in the CIA model group and sham-operation group. The MT level in the operation group was significantly lower than those in the other 3 groups. The difference may be related with the establishment of animal model. The CIA model was induced by collagen injection, resembling RA. The sham-operation group, while had incisions at the skull, was not treated with removal of pineal gland and sexual gland, so the stimulation was just mechanical and no material damage happened. The rise of MT level in serum in the CIA model group and sham-operation group might derive from the anti-inflammatory effect of MT. When organism engenders inflammatory reaction, the pineal gland secretes massive MT to depress the inflammation. Therefore, the serum levels of MT had the tendency to rise in the CIA model group and the sham- operation group. Meanwhile, the rise of MT depresses the sexual gland (sex hormone), causes the decrease in excretion of sex hormone, leading to the exacerbation of RA reaction and forming a vicious circle. The pineal gland and sexual gland were removed in the operation group, which destroyed the important carrier of the composition of MT. That causes the decrease of MT secretion and immune function. Although MT exists in other organs and systems as well, the content is extremely low that it could not make compensation for the loss of pineal gland. If the level of MT decreases, it could exacerbate and deteriorate RA indirectly.
MT has special biological rhythmicity. The main reactor organ of this rhythmicity is pineal gland, which adjusts the level of MT secretion by light change. The difference of the season was not only about climate but also characterized by the intensity and length of sunlight. The change of the light is also the main influence factor of the composition and secretion of MT.8Based on the MT level measured in summer and winter, it was pointed out that there were differences in MT content in different seasons. The serum level of MT in the CIA model group, the sham-operation group and normal group in winter significantly increased than in summer (all P<0.05). In contrast, there was no significant difference in MT level in the operation group between summer and winter. The secretion of pineal gland coordinates the biological rhythm to the natural environment, conforming to the holistic view in traditional Chinese medicine and the theory of relevant adaptation of human body to natural environment. As to the depressing effect on the sexual gland by MT, it displays a tendency of being stronger in winter and weaker in summer, adding to the time theory of “kidney corresponding with winter” in traditional Chinese medicine. That could also be a piece of objective evidence to prove the effectiveness of establishing renal deficiency by removing the sexual gland.
In conclusion, based on the serum levels of IL-1β, IL-6, and MT of rats in summer and winter, we proved the relationship of Bizheng and season-related pineal gland hormone (i.e. MT) with cytokines, which could provide new basis and evidence for further study of the pathogenesis and clinic treatment of RA.
1. Wu MY. Regular pattern study on inpatient of rheumatoid arthritis in our hospital in the past five years. Guangzhou University of Chinese Medicine 2007 master degree thesis, 2010:19.
2. Liu P, Wang T, Guo XZ. Study on kidney adjustment system in entirety according to three level of methodology. World J Integ Trad West Med 2009; 4:893-4, 902.
3. Wang Y, Zhao HY, Liu MJ, et al. Establishment of a rat model of rheumatoid arthritis with kidney deficiency syndrome. J Chin Integ Med 2011; 9:973-81.
4. Jiang XQ, Han ZJ, Mei XD. Application study on the regulating action of immune system by melatonin cell and molecular immunology journal. Chin J Cell Mol Immunol 2007; 23:1091-3.
5. Zhang JT. Basic study and clinical application on melatonin. Beijing: Chemical Industry Press; 2005 .p. 29.
6. Zhang MQ, Guo XZ, Liu XY, et al. Discuss on the integrality and rhythmicity. Liaoning J Trad Chin Med 2007; 34:585-6.
7. Lu QS, Guo XZ. Laboratory study on kidney correlated with winter in TCM. J Beijing Univ Trad Chin Med 2001; 24:27-8.
8. Zhu CT, Wu CY. Principles and research ideas for study of standardization of traditional Chinese medicine kidney system syndromes. J Nanjing Univ Trad Chin Med 2005; 21:8-10.
 Chinese Medical Sciences Journal2014年2期
Chinese Medical Sciences Journal2014年2期
- Chinese Medical Sciences Journal的其它文章
- Minimally Invasive Perventricular Device Closure of Ventricular Septal Defect: a Comparative Study in 80 Patients
- Expression of Peptidylarginine Deiminase 4 and Protein Tyrosine Phosphatase Nonreceptor Type 22 in the Synovium of Collagen-Induced Arthritis Rats△
- Lipocalin-2 Test in Distinguishing Acute Lung Injury Cases from Septic Mice Without Acute Lung Injury△
- False Human Immunodeficiency Virus Test Results Associated with Rheumatoid Factors in Rheumatoid Arthritis△
- Arachnoiditis Ossificans of Lumbosacral Spine: a Case Report and Literature Review
- Ketamine Abuse-Induced Obstructive Nephropathy and Kidney Injury
