Multi-slice spiral computed tomography in diagnosing unstable pelvic fractures in elderly and effect of less invasive stabilization
lNTRODUCTlON
The pelvis is an important structure that connects the upper and lower parts of the body and is rich in large blood vessels, nerves, and other important organs. The pelvis of a normal adult comprises the left and right hip bones, sacrum, coccyx, and other bones. Ligaments between bones form joints with a small range of activity. With age, bone loss can lead to changes in the mechanics of bones, which are more fragile than those of younger people[1]. Pelvic fractures often occur during high-energy traumas. In elderly individuals, the ability of the bone to resist rotation and compression is insufficient owing to osteopenia, and minor violent stimulation can cause fractures[2]. Pimelosis of the yellow marrow in the sacral wing of the elderly leads to greater bone loss in this area, whereas the sacrum has a relatively large bone mass[3]. In elderly patients with pelvic fractures, fracture lines are often found on the sacral wing, mainly in cases of lateral compression of incomplete fractures[4]. The absorption of X-rays differs for different tissue structures, forming chiaroscuro images. Studies have shown that X-ray examinations are prone to misdiagnosis owing to the complex structure of the pelvis and affected by various factors[5]. The pelvic ring consists of the ilium, pubis, ischium, and sacrum. When the sacrum is fractured, bone continuity is interrupted, which can cause separation and dislocation of the cortical bone. Since the pelvic ring is an overlapping structure, radiographic examinations are prone to misdiagnosis. Studies have shown that 16-slice computed tomography (CT) can be used to observe the internal structure of the bone, which can increase the detection rate of occult sacral fractures[6]. Multi-slice spiral CT can produce three-dimensional (3D) images using 3D reconstruction technology, leading to a clear observation of the 3D space of the bone fracture. Raniga
[7] reported that multi-slice spiral CT had a higher detection rate of bone fractures than thin-slice CT and could directly observe the fracture degree and shape. Unstable pelvic fractures in the elderly are mainly treated with open surgery. Simple incomplete sacral wing fractures are commonly treated with sacroplasty. Non-displaced sacral fractures are often treated using percutaneous sacroiliac screws. Anterior ring fractures of the pelvis are often fixated with retrograde screws from the pubic tubercle to the iliac crest through the symphysis pubis[8,9]. This study aimed to investigate the application value of multi-slice spiral CT in the diagnosis of unstable pelvic fractures in the elderly and the efficacy of minimally invasive internal fixation with hollow tension screws to provide a valuable reference for clinical practice.
MATERlALS AND METHODS
Clinical data
A total of 86 patients with unstable pelvic fractures between March 2016 and March 2019 were enrolled in this study. The inclusion criteria were as follows: (1) Age 65-85 years; (2) within 2 wk after the injury; and (3) meeting the diagnostic criteria for unstable pelvic fractures in “Practical Bone Science” (3
edition). The exclusion criteria were as follows: (1) Severe cardiovascular or hepatorenal dysfunction; (2) unsuitable for surgery; and (3) mental health condition. A total of 86 subjects (50 men, 36 women) were studied. According to the Tile classification, 11 cases were type B1, 66 were type B2, four were type B3, and five were type C1. The mean patient age was 75.86 ± 3.42 years (range, 68-82 years). The average injury time was 5.24 ± 1.23 days prior. There were 39 cases of traffic accidents, 30 cases of high fall injuries, 13 cases of heavy object bruise injuries, and four cases of crush injuries. Written informed consent was obtained from all patients.
Methods
All patients were first subjected to supracondylar femoral traction. Once the vital signs and hemodynamic indicators were stable, pelvic radiography and multi-slice spiral CT were performed to observe the fracture and perform 3D surgical simulation. Pain was assessed using a visual analog scale (VAS).
Gerhard Mueller discusses cannibalism in his criminological analysis of the tale. He cannot find laws concerning cannibalism and its punishment in Europe during the Middle Ages. However, he finds it interesting that cannibalism appears often in fairy tales such as this one. He states that in the minds of the people, cannibalism lived on, if only as a nightmare (Mueller 1986).
‘Are you the girl,’ he said, turning his eyes away as he spoke38, ‘a(chǎn)re you the girl who has a room in the furthest corner of the inner court of the farmhouse46?’
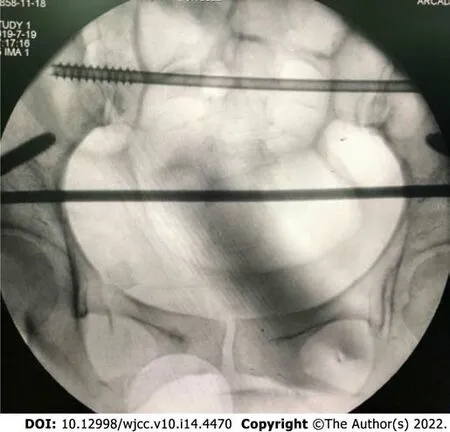
A 64 × 128-slice LightSpeed spiral CT (Siemens) was used. The patient was placed in the supine position, and cross-sectional thin-slice scanning was performed. The scanning conditions were 0.625-mm thickness, 0.625-mm layer spacing, 500 mA tube current, and 120 kV tube voltage (Figure 2). Multi-plane reconstruction, volume rendering, and maximum intensity projection were performed on the original image data to create the multi-plane 3D reconstruction images. The diagnoses were recorded.

Two radiologists and orthopedists with more than 5 years of clinical experience analyzed the obtained X-ray and CT 3D reconstruction images. After basic or complete reduction of the pelvic vertical displacement, which was determined using 3D reconstruction images, minimally invasive internal fixation with a hollow tension screw was performed. The inner fixing apparatus was provided by the Xiamen Dabo Company. Patients were divided into two groups [study group (
= 58) and control group (
= 28)] according to whether the 3D surgical simulation was performed before surgery (Figure 3).

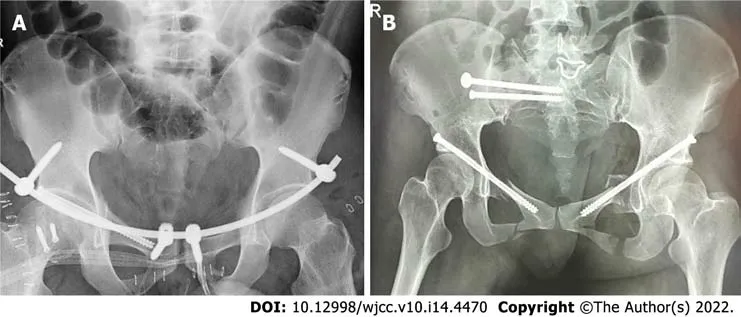
Minimally invasive fixation with a hollow tension screw was performed as follows: (1) anterior ring fixation: internal fixation of the percutaneous hollow tension screw was performed. The patient was placed in a supine position with lower limb traction. A guide needle was inserted into the iliac crest. Under C-arm fluoroscopy, with the obturator in the oblique position, the pelvic inlet and outlet were used to determine needle direction and position. Subsequently, the skin was cut longitudinally, with the anterior superior iliac spine as the midpoint, and the muscles were bluntly separated to the anterior superior iliac spine. The internal and external iliac plates were separated with a periosteum stripper, and the curvature of the subcutaneous rod was adjusted according to the patient’s abdominal type and subcutaneous fat thickness. The adjusted subcutaneous rod was placed from the incision on one side of the anterior superior iliac spine to the contralateral screw through the bikini area formed between the lower abdomen and groin. Bilateral screws were connected to complete the traction reduction, and the nut was tightened. The reduction was observed under C-arm fluoroscopy, and the excess rod was cut after its confirmation. And (2) Posterior ring fixation: Percutaneous sacroiliac tension screw internal fixation was performed. The patient was placed in the prone position with lower limb traction. The guide needle was inserted into two transverse fingers outside the posterior superior iliac spine and two transverse fingers above the greater sciatic notch. C-arm fluoroscopy of the pelvis in the anteroposterior, inlet, outlet, and lateral positions was used to determine the direction and position of the needle, which was inserted into the anterior 1/3 of the S1 vertebra at a 20° ventral incline and 20° cephalic incline. Carm fluoroscopy was used to reconfirm the angle and position, followed by placement of the hollow nail with a washer along the guide needle and tightening after confirmation under C-arm fluoroscopy. All patients received routine anti-infection treatment after surgery and were instructed by a physical therapist to start improving the lower limb muscle strength upon awakening (Figure 4).
Observation
Once clear of the stable the young man sprang on his back and galloped11 off, calling over his shoulder, Hi! dragon! dragon! if anyone asks you what has become of your horse, you can say that I have got him! But the king said, The flying horse is all very well, but I want something more
58. They lived happily ever afterward: The Grimms changed the story considerably138 to try to justify139 the father s redemption and ability to live happily ever after. However, many critics, such as Hans Dieckmann, find the ending disturbing and even unethical. The father, who was too weak to resist the evil suggestion of his wife and with her abandoned the children in the forest, is not only not punished for his highly immoral140 way of acting141 but even gets to enjoy the treasures the children bring back (Dieckmann 1986). Also note that part of their happiness centers on their acquisition of material wealth.Return to place in story.
Determination criteria
Type A was a stable but slightly displaced fracture; type A1 was a fracture with an intact pelvic ring; type A2 was a stable and less displaced fracture; type A3 was a transverse fracture of the sacrococcyx not affecting the pelvic ring; type B was a rotationally unstable and vertically stable fracture; type B1 involved anteroposterior compression or external rotation force on the pelvis, resulting in the separation of the pubic symphysis fracture; type B2 was a pelvic lateral extrusion injury or hip bone rotation injury; type B3 was a bilateral rotatory instability fracture; type C was an unstable pelvic fracture in both rotation and vertical directions; type C1 was unilateral posterior ring injury; type C2 was bilateral posterior ring injury; and type C3 was a bilateral C type fracture. The VAS score was 0-10, and the pain was aggravated from lower to higher scores (0, none; 1-3, mild; 4-6, moderate; 7-10, severe). The Matta score was used to examine the postoperative reduction effect; the total score was 18 points (18, excellent; 15-17, good; and < 15, poor), and the total effective points were the sum of excellent and good. The Majeed score was used to assess postoperative functional recovery, with a total possible score of 100 (85-100, excellent; 70-84, good; and < 69, poor).
Statistical analysis
Statistical analyses were performed using SPSS 20.0. Measurement data are expressed as mean ± SD. A paired t-test was used to examine normally distributed data, while the
test was used to examine nonnormally distributed data. Enumeration data are expressed as frequency (%) and were examined by the
test. Statistical significance was set at
< 0.05.
RESULTS
Detection of fracture site by different methods
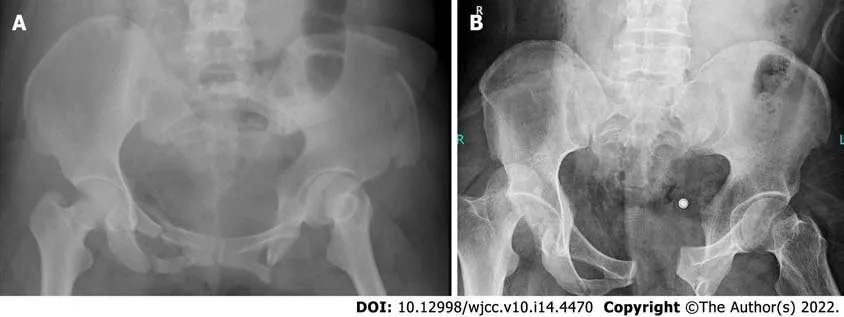
All patients were surgically diagnosed with pelvic instability fractures, including 10 with pubic symphysis, 19 with iliac wing, 36 with sacroiliac periarticular, and 21 with sacral fractures. The diagnostic coincidence rates of the X-rays were 40.00%, 36.84%, 30.56%, and 33.33% for them, respectively, whereas the rates of CT reconstruction were 100.00%, 100.00%, 97.22%, and 90.48%, respectively (Table 1).
A digital X-ray imaging system (Siemens Company, Germany) was used. The patient was placed in the supine position in which the median sagittal plane was perpendicular to the bed’s surface and coincided with the midline. The upper aperture was 2 cm beyond the iliac crest and 3 cm beyond the lower edge of the symphysis pubis, while the bulb was 100 cm away from the plate detector with a tube current of 200 mA, tube voltage of 80 kV, and exposure time of 160 ms. The diagnosis was recorded (Figure 1).

Tile classification
The guiding significance of multi-slice spiral CT for the diagnosis, classification, and treatment of unstable pelvic fractures in the elderly is high. Preoperative 3D reconstruction is effective for shortening the operation time and promoting postinjury and fracture healing. Minimally invasive internal fixation can effectively reduce pain and promote functional recovery of fracture sites.
Postoperative condition
The wound healing, fracture healing, and hospitalization times were significantly shorter in the study group than in the control group (
< 0.05) (Table 3).
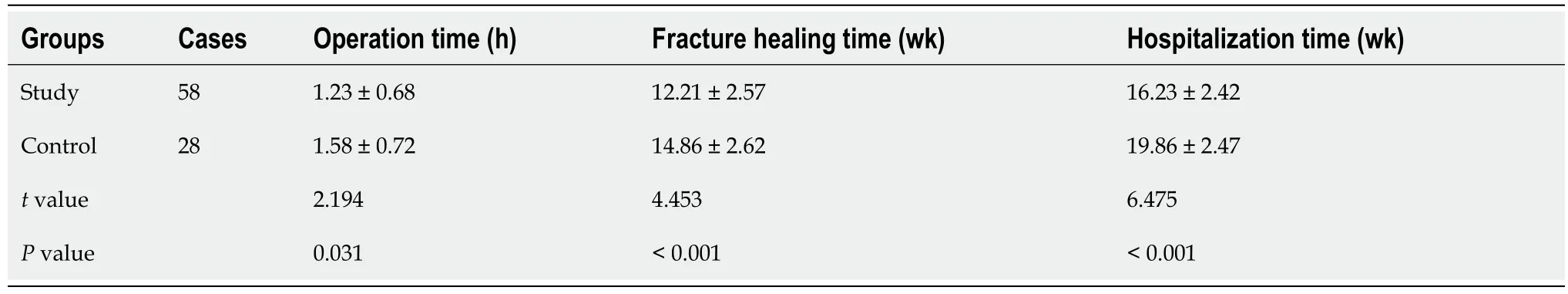
VAS scores
The mean postoperative VAS scores in both groups were lower than the preoperative scores, and the mean postoperative VAS score in the study group was lower than that in the control group (
< 0.05) (Table 4).
Above all, multi-slice spiral CT has high guiding significance for the diagnosis, classification, and treatment of unstable pelvic fractures in elderly individuals. Preoperative 3D reconstruction can effectively shorten the operation time of patients and promote post-injury and fracture healing. Minimally invasive internal fixation can effectively reduce pain and promote functional recovery of fracture sites, making it worthy of clinical application.
Then the Princess was compelled by her thirst to get down, and bending over the flowing water she cried and said: Oh! heaven, what am I to do? and the three drops of blood replied: If your mother only knew, Her heart would surely break in two
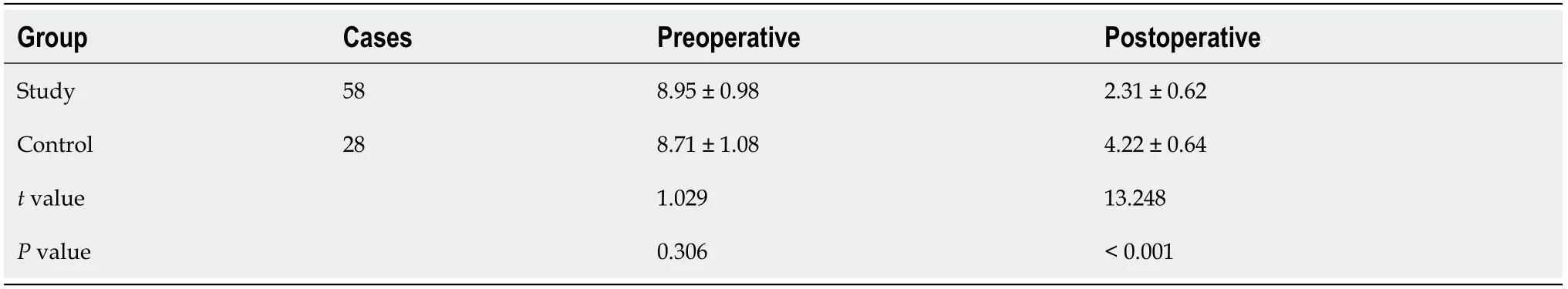
Postoperative fracture reduction
The total postoperative reduction rate was significantly higher in the study group than in the control group (
< 0.05) (Table 5).
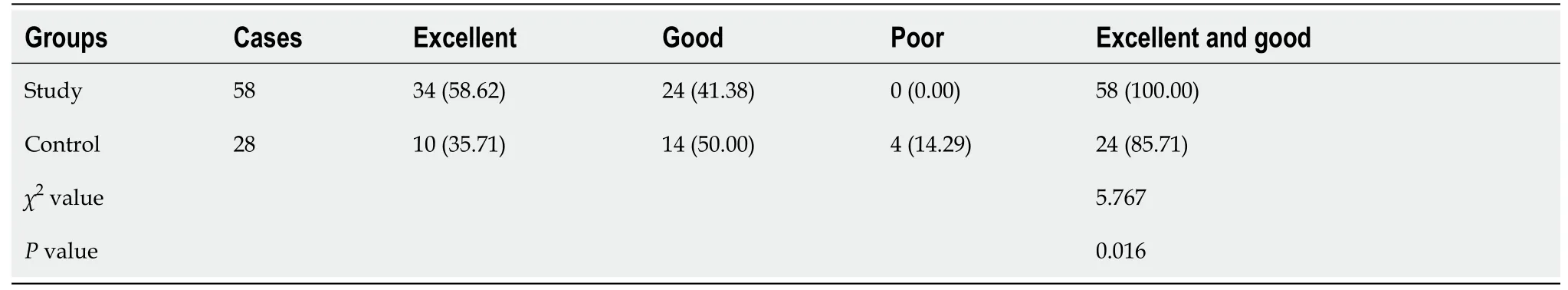
Postoperative poor internal fixation
This study investigated the value of multi-slice spiral CT 3D reconstruction in the diagnosis and treatment of unstable pelvic fractures in the elderly.
Learn and know, O young man! that I am King Janangir of Babylon, and that once I had army and servants, family and treasure; untold20 wealth and belongings21
After the old man had bowed politely and taken farewell of them the eldest brother said to the rest, I will go in search of the water of life, and the talking bird, and the tree of beauty
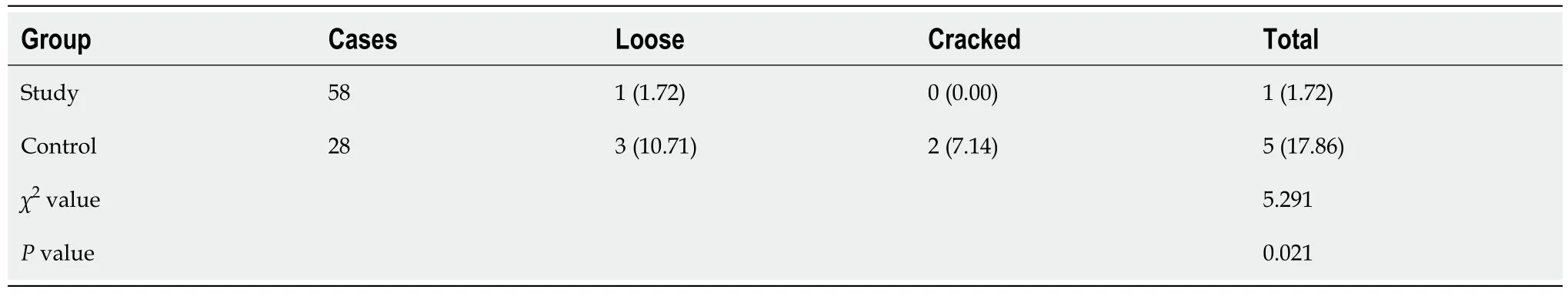
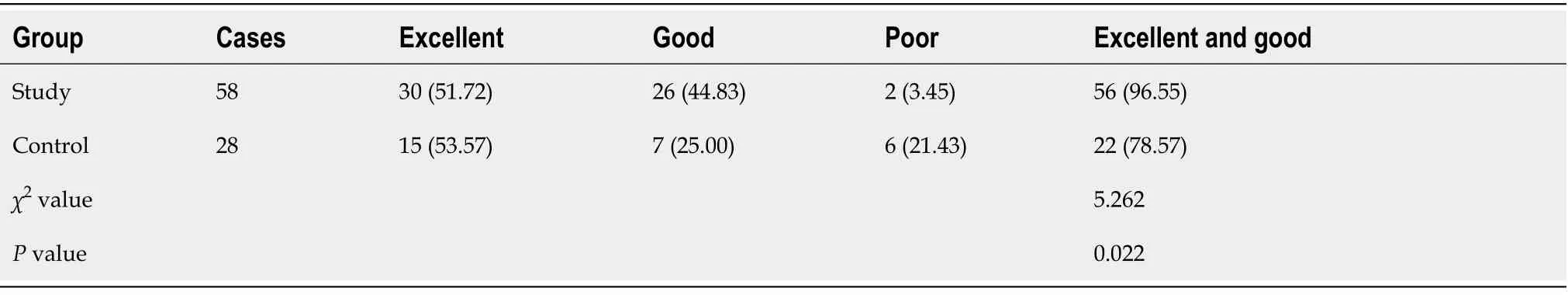
Postoperative functional recovery
All patients were followed up until March 2019. The total excellent and good rates of postoperative functional recovery were significantly higher in the study group than those in the control group (
< 0.05) (Table 7).
DlSCUSSlON
Bone can be divided into dense and cancellous. Dense bone gradually thins with age, while the number of bone trabeculae in the cancellous bone decreases and it thins, leading to osteoporosis characterized by decreased bone mass per unit volume or changes in bone microstructure[10]. The decrease in estrogen levels during menopause accelerates calcium loss from the bones. Osteoporotic fractures are common complications of osteoporosis[11]. Under normal circumstances, pelvic fractures are caused by highenergy trauma, but when the bone is loose in the pelvis, low-energy impact can also cause pelvic fractures[12]. Elderly patients are less sensitive to pain than young people; thus, they may easily ignore low-energy trauma. When a fracture occurs, the symptoms are not obvious and clinical misdiagnosis is possible[13]. At the same time, because of low bone density, X-ray image resolution can be affected, which can also lead to misdiagnosis and delayed treatment of patients with concealed fractures, such as posterior ring fractures of the sacral wing[14]. Multi-slice spiral CT can construct 3D images, allowing physicians to observe the fracture site from multiple angles and providing more information for treatment through simulated surgical reduction[15].
This study demonstrated that the diagnostic coincidence rates of CT reconstruction were 100.00%, 100.00%, 97.22%, and 90.48% for the pubic symphysis, iliac wing, sacroiliac periarticular, and sacral fractures, respectively, significantly higher than those of the X-rays. The 3D image constructed by multislice spiral CT can compensate for the poor image affected by bone density on the X-ray, remove excess muscle tissue, and present the 3D whole pelvic structure. Diagnostic accuracy can be significantly improved through clear observation of the fracture site, reducing the occurrence of misdiagnosis. The 3D reconstruction images were used to classify fractures, and the coincidence rate of CT reconstruction for all types of clinical pelvic fractures was 100%. In contrast, there were 11 cases of misdiagnosis by radiography for a total coincidence rate of 87.21%, indicating that multi-slice spiral CT is clinically significant for the preoperative classification of pelvic fractures. Simultaneously, surgical reduction of fractures was simulated using 3D reconstruction technology, and the length, size, position, and direction of the internal fixation were determined preoperatively.
The study showed that the operative, fracture healing, and hospitalization times were significantly shortened by the preoperative simulation. Meanwhile, patients with minimally invasive hollow tension screw internal fixation had fewer wounds and pain, good postoperative reduction and functional recovery, and a lower incidence of poor internal fixation. The clinical outcomes were remarkable. Due to the small sample size and the fact that the included types were mainly pubic symphysis, iliac wing, sacroiliac joint, and sacral fractures, it is necessary to further expand the sample size and conduct research that includes patients with other pelvic bones.
25. Naughty children: Note the stepmother s defense82 mechanism83 of blaming the children for their absence to avoid her own incrimination. The stepmother is continually abusive in her language towards the children, calling them naughty, donkeys, fools, and lie-abeds. The Grimms added most of this language to intensify84 her nasty character.Return to place in story.
CONCLUSlON
Multi-slice spiral CT has a high guiding significance for the diagnosis, classification, and treatment of unstable pelvic fractures in the elderly. Preoperative 3D reconstruction can effectively shorten the operation time and promote postinjury and fracture healing. Minimally invasive internal fixation is effective in reducing pain and promoting functional recovery of fracture sites, and is worthy of clinical application.
28.Put out the light a man came and lay down beside her: Note that the heroine is not asked to sleep with a beast, but a man. While animal bridegroom stories are abundant around the world, the maiden often finds herself sleeping with a human male in her marriage bed.
ARTlCLE HlGHLlGHTS
Research background
Bone loss can lead to changes in bone mechanics with age, and older people have more fragile pelvises than younger people. Multi-slice spiral computed tomography (CT) uses three-dimensional (3D) reconstruction technology to generate 3D images, so that the 3D space of fractures can be clearly observed, and the detection rate of fractures is higher.
Research motivation
The total incidence of poor internal fixation was significantly lower in the study group than that in the control group (
< 0.05) (Table 6).
Research objectives
The study aimed to investigate the clinical value of multi-slice spiral CT 3D reconstruction in the diagnosis of unstable pelvic fractures in the elderly and the effect of less invasive stabilization.
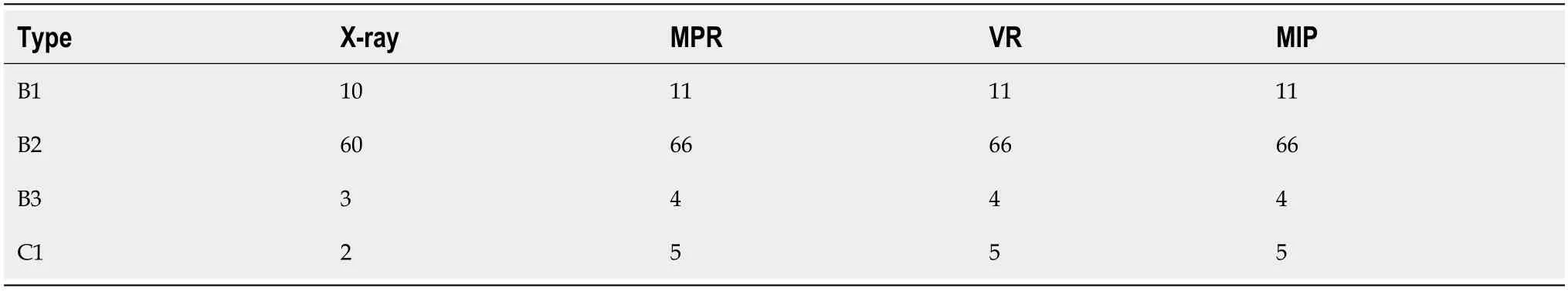
The VAS score was again determined at 24 h postoperative. Radiography and multi-slice spiral CT scans of the pelvis were performed again 3 mo after surgery to observe the reduction of the pelvis (Figure 5), and the postoperative reduction was evaluated using the Matta scoring criteria. Functional recovery was evaluated using the Majeed score at 1 year postoperative.
Research methods
A total of 86 inpatients with unstable pelvic fractures underwent pelvic X-ray and multi-row spiral CT scanning from March 2016 to March 2019. The detection rates of fracture location and classification by X-ray and CT reconstruction were compared. Postoperative reduction, wound healing time, fracture healing time, hospitalization time, visual analog scale (VAS) score, poor internal fixation, and functional recovery were compared between groups the presence or absence of preoperative 3D reconstruction.
Research results
The coincidence rate of CT reconstruction in the clinical classification of pelvic fractures was 100%. The overall excellent and good rate of postoperative reduction and the overall functional recovery rate of the study group with preoperative 3D reconstruction were significantly higher than those of the control group. The wound healing time, fracture healing time, hospital stay, VAS score, and the total incidence of postoperative poor internal fixation were significantly lower in the study group than those in the control group.
Research conclusions
The coincidence rate of CT reconstruction for all types of pelvic fractures in the clinical classification was 100%, whereas there were 11 cases of misdiagnosis by X-ray for a coincidence rate of 87.21% (Table 2).
Research perspectives
Multi-slice spiral CT can play a role in the diagnosis and treatment of unstable pelvic fractures in the elderly.
Rather than look at helplessly her two babies die in succession, the female eagle thought she should do something. She pulled apart her own chest with the sharp beaks5, the feathers that fell off her body being blowed here and there by the icy wind. With feeble strength, she told her last baby who was still at the verge6 of death: Eat me… . Outside, the male eagle, who stood for a long time keeping close watch on the food, shook out the snow accumulated in her wings. After making a yowl, he made his best efforts to unfold two wings, flinging into the sky. He overlooked the land, which was still a vast expanse of whiteness. Suddenly, a leaden object jumped into his eyes.
FOOTNOTES
Huang JG designs topics and writes articles; Zhang ZY collects patient case information; Li L organizes examination results; Liu GB statistically analyzes experimental results; Li X is responsible for research progress, article writing and revision.
This study was approved by the Institutional Review Board of Sanya Hospital of Traditional Chinese Medicine.
Once upon a time...There was a pig who lived with her three children on a large, comfortable, old-fashioned farmyard. The eldest1 of the little pigs was called Browny, the second Whitey, and the youngest and best looking Blacky. Now Browny was a very dirty little pig, and I am sorry to say spent most of his time rolling and wallowing about in the mud. He was never so happy as on a wet day, when the mud in the farmyard got soft, and thick, and slab2. Then he would steal away from his mother s side, and finding the muddiest place in the yard, would roll about in it and thoroughly3 enjoy himself. His mother often found fault with him for this, and would shake her head sadly and say: Ah, Browny! some day you will be sorry that you did not obey your old mother. But no words of advice or warning could cure Browny of his bad habits.
All patients provided informed consent.
All authors declare no conflict of interest.
The date that support the findings of this study are available from the corresponding author upon reasonable request.
This article is an open-access article that was selected by an in-house editor and fully peer-reviewed by external reviewers. It is distributed in accordance with the Creative Commons Attribution NonCommercial (CC BYNC 4.0) license, which permits others to distribute, remix, adapt, build upon this work non-commercially, and license their derivative works on different terms, provided the original work is properly cited and the use is noncommercial. See: https://creativecommons.org/Licenses/by-nc/4.0/
China
Jian-Guo Huang 0000-0002-8077-9282; Zhi-Yuan Zhang 0000-0002-9605-311X; Liang Li 0000-0003-2876-0303; Guang-Bao Liu 0000-0001-8552-7941; Xiong Li 0000-0002-6306-631X.
Wang JL
A
Wang JL
1 Aspray TJ, Hill TR. Osteoporosis and the Ageing Skeleton.
2019; 91: 453-476 [PMⅠD: 30888662 DOⅠ: 10.1007/978-981-13-3681-2_16]
2 Chen HT, Wang YC, Hsieh CC, Su LT, Wu SC, Lo YS, Chang CC, Tsai CH. Trends and predictors of mortality in unstable pelvic ring fracture: a 10-year experience with a multidisciplinary institutional protocol.
2019; 14: 61 [PMⅠD: 31889991 DOⅠ: 10.1186/s13017-019-0282-x]
3 Schmal H, Froberg L, S Larsen M, Südkamp NP, Pohlemann T, Aghayev E, Goodwin Burri K. Evaluation of strategies for the treatment of type B and C pelvic fractures: results from the German Pelvic Ⅰnjury Register.
2018; 100-B: 973-983 [PMⅠD: 29954203 DOⅠ: 10.1302/0301-620X.100B7.BJJ-2017-1377.R1]
4 Lin CY, Chuang MT, Chiu YⅠ. Sacral Ⅰnsufficiency Fracture in an Elderly Woman With Hip Pain.
2017; 96: e210-e211 [PMⅠD: 28346309 DOⅠ: 10.1097/PHM.0000000000000739]
5 Moraes JP, Parreira JG, Lucarelli-Antunes PS, Rondini GZ, Perlingeiro JAG, Assef JC. Optimizing Pelvic X-Ray indication in blunt trauma patients using clinical criteria.
2020; 47: e20202624 [PMⅠD: 33111833 DOⅠ: 10.1590/0100-6991e-20202624]
6 Dreizin D, Liang Y, Dent J, Akhter N, Mascarenhas D, Scalea TM. Diagnostic value of CT contrast extravasation for major arterial injury after pelvic fracture: A meta-analysis.
2020; 38: 2335-2342 [PMⅠD: 31864864 DOⅠ: 10.1016/j.ajem.2019.11.038]
7 Raniga SB, Mittal AK, Bernstein M, Skalski MR, Al-Hadidi AM. Multidetector CT in Vascular Ⅰnjuries Resulting from Pelvic Fractures: A Primer for Diagnostic Radiologists.
2019; 39: 2111-2129 [PMⅠD: 31697619 DOⅠ: 10.1148/rg.2019190062]
8 Rommens PM, Wagner D, Hofmann A. Minimal Ⅰnvasive Surgical Treatment of Fragility Fractures of the Pelvis.
2017; 112: 524-537 [PMⅠD: 29088552 DOⅠ: 10.21614/chirurgia.112.5.524]
9 Cai L, Zhang Y, Chen C, Lou Y, Guo X, Wang J. 3D printing-based minimally invasive cannulated screw treatment of unstable pelvic fracture.
2018; 13: 71 [PMⅠD: 29618349 DOⅠ: 10.1186/s13018-018-0778-1]
10 Armas LA, Recker RR. Pathophysiology of osteoporosis: new mechanistic insights.
2012; 41: 475-486 [PMⅠD: 22877425 DOⅠ: 10.1016/j.ecl.2012.04.006]
11 Viswanathan M, Reddy S, Berkman N, Cullen K, Middleton JC, Nicholson WK, Kahwati LC. Screening to Prevent Osteoporotic Fractures: Updated Evidence Report and Systematic Review for the US Preventive Services Task Force.
2018; 319: 2532-2551 [PMⅠD: 29946734 DOⅠ: 10.1001/jama.2018.6537]
12 Morgan O, Davenport D, Enright K. Pelvic injury is not just pelvic fracture.
2019; 12 [PMⅠD: 31806634 DOⅠ: 10.1136/bcr-2019-232622]
13 Vitzthum LK, Park H, Zakeri K, Heide ES, Nalawade V, Mundt AJ, Vaida F, Murphy JD, Mell LK. Risk of Pelvic Fracture With Radiation Therapy in Older Patients.
2020; 106: 485-492 [PMⅠD: 31610251 DOⅠ: 10.1016/j.ijrobp.2019.10.006]
14 Schicho A, Schmidt SA, Seeber K, Olivier A, Richter PH, Gebhard F. Pelvic X-ray misses out on detecting sacral fractures in the elderly - Ⅰmportance of CT imaging in blunt pelvic trauma.
2016; 47: 707-710 [PMⅠD: 26861798 DOⅠ: 10.1016/j.injury.2016.01.027]
15 Wortman JR, Uyeda JW, Fulwadhva UP, Sodickson AD. Dual-Energy CT for Abdominal and Pelvic Trauma.
2018; 38: 586-602 [PMⅠD: 29528816 DOⅠ: 10.1148/rg.2018170058]
 World Journal of Clinical Cases2022年14期
World Journal of Clinical Cases2022年14期
- World Journal of Clinical Cases的其它文章
- Perfectionism and mental health problems: Limitations and directions for future research
- Ovarian growing teratoma syndrome with multiple metastases in the abdominal cavity and liver: A case report
- Development of plasma cell dyscrasias in a patient with chronic myeloid leukemia: A case report
- Suprasellar cistern tuberculoma presenting as unilateral ocular motility disorder and ptosis: A case report
- Rare pattern of Maisonneuve fracture: A case report
- PD-1 inhibitor in combination with fruquintinib therapy for initial unresectable colorectal cancer: A case report
