Dynamic interaction nursing intervention on functional rehabilitation and self-care ability of patients after aneurysm surgery
INTRODUCTION
Intracranial aneurysm is a cerebral hemangiomatous protrusion of the intracranial arterial wall caused by abnormal localized enlargement of intracranial arterial vessels, with a high disability rate, mortality rate, and relatively sudden onset[1,2]. The main pathological features of intracranial aneurysm are subarachnoid hemorrhage. Congenital cerebral artery wall defects and increased intracranial pressure lead to cerebral vascular cystic expansion and protrusions, which are important factors for the occurrence of subarachnoid hemorrhage of intracranial aneurysms and greatly increase the difficulty of disease management[3,4]. At the same time, with the progress of medical technology, the clinical treatment of intracranial aneurysms tends to be minimally invasive and can effectively seal the aneurysm wall. However, the postoperative condition changes are complex and rapid; therefore,effective nursing intervention is of great significance to ensure the safety of patients[5].
Current clinical routine nursing can only meet the basic needs of patients, involving only medication,health guidance, related matters needing attention,, failing to fully meet the pathophysiological needs of patients[6]. Interactive care for Florida in 1989 put forward a nursing management concept; the core idea is to shift the patient from always adapting to the modularity of medical services and instead to establish the patient as the central focus, in order to satisfy the demands of patients' medical rehabilitation nursing, with emphasis on the management mode, to provide patients with pertinent and systemic high-quality nursing service[7,8].
“Who should know better than I do?” said the animal, while his eyes sparkled. “I was born and brought up there, and used to run about the snow-covered plains.”
As I cared for my patients, George was right alongside. I watched him spread holiday cheer as he became a guest to the patients who had no visitors that day. When trays arrived he knew who needed assistance and who needed to be fed. He read letters and cards to those whose eyes could no longer see the letters on a printed page. George’s powerful body and tender hands were always ready to help hold, turn, pull-up or lift a patient. He was a “gopher” who made countless15 trips to the supply room for the “needs of the moment.”
Before the intervention, the activities of daily living (ADL), Simple Intelligent Mental State Scale(MMSE), Generic Quality of Life Inventory-74 (GQOL-74) scores of the study group were not significantly different from those of the control group. After the intervention, the scores of ADL, MMSE,and GQOL-74 of the study group were higher than those of the control group. After the intervention,the study group’s self-concept, self-care skills, self-care knowledge and self-care responsibility score higher than the control group. The incidence of complications in the study group was lower than that in the control group. The nursing satisfaction of the study group was higher than that of the control group.
MATERIALS AND METHODS
Baseline data
A total of 86 patients at our hospital, with intracranial aneurysms from April 2019 to April 2021, were selected. Inclusion criteria were as follows: (1) intracranial aneurysm diagnosed after total cerebral digital subtraction angiography (DSA); (2) all patients were treated with coil embolization; (3) age above 18 and below 70 years; (4) patients were aware of the study and had signed the available consent form;and (5) the vital signs were stable. The exclusion criteria were as follows: (1) female patients in lactation/pregnancy; (2) patients with psychological problems or mental diseases; (3) patients with mental retardation and cognitive impairment; (4) patients with audio-visual impairment; and (5)patients with the presence of other organic brain lesions. Patients were divided into the study group and the control group, with 43 patients assigned into each group. In the study group, there were 23 male and 20 female patients. The average age was 45.11 ± 13.12 years, ranging from 26 to 64 years. According to Hunt-Hess grading, the included cases were as follows: grade I (9 cases), grade II (10 cases), grade III (7 cases), grade IV (11 cases), and grade V (6 cases). The diameter of the aneurysms ranged from 2 mm to 11 mm, with an average of 6.49 ± 3.07 mm. In the control group, the average age was 44.60 ± 11.98 years,ranging from 23 to 66 years old. Hunt-Hess grading: I (7 cases), II (13 cases), III (8 cases), IV (10 cases),and V (5 cases). Aneurysms were 2 mm to 12 mm in diameter, with an average of 7.01 ± 2.99 mm. The clinical data regarding sex, age, Hunt-Hess grading, and aneurysm diameter were equally comparable between the two groups (> 0.05). This study was approved by the ethics Committee of our hospital.
Control group
Conventional nursing lacks targeted and systematic interventions, and nursing staff are mostly passive in implementing the relevant intervention; patients are difficult to benefit effectively, so it is gradually difficult to meet the clinical status[12]. Interactive nursing, is a nursing management mode based on the concept of seamless medical management. It mainly takes patients as the central focus of nursing and combines the specific conditions of the patients to provide effective, rapid, personalized,and diversified nursing services, rather than simply allowing intervention objects to adapt to modular medical care services[13,14]. Relevant studies show that the main problem of interactive nursing lies in information exchange, as well as nurse-patient and doctor-patient information asymmetry, resulting in patients having difficulty getting professional and reasonable information support. Effective information exchange can shorten the doctor-patient relationship and improve the patients’ self-care executive ability[15-17]. Other researchers believe that family members are important caregivers for patients during hospitalization and home rehabilitation, and the enthusiasm and understanding of family members for rehabilitation intervention can affect the speed and degree of patient recovery.Therefore, attention should be paid to the role of family members in disease rehabilitation treatment.Simultaneously, patients with similar symptoms or the same disease can form positive interaction effects, through mutual communication and dynamic interaction in the social, psychological, and physiological aspects, prompting resonance between patients with the same disease. This can encourage patients to partake in entertainment, communication, and learning from each other disease rehabilitation knowledge and corresponding treatment measures of adverse events, thus reducing the sense of inferiority, loneliness, and so on. Such an environment can inspire patients' confidence in rehabilitation treatment, which is also of great significance in improving rehabilitation compliance[18].
Study group
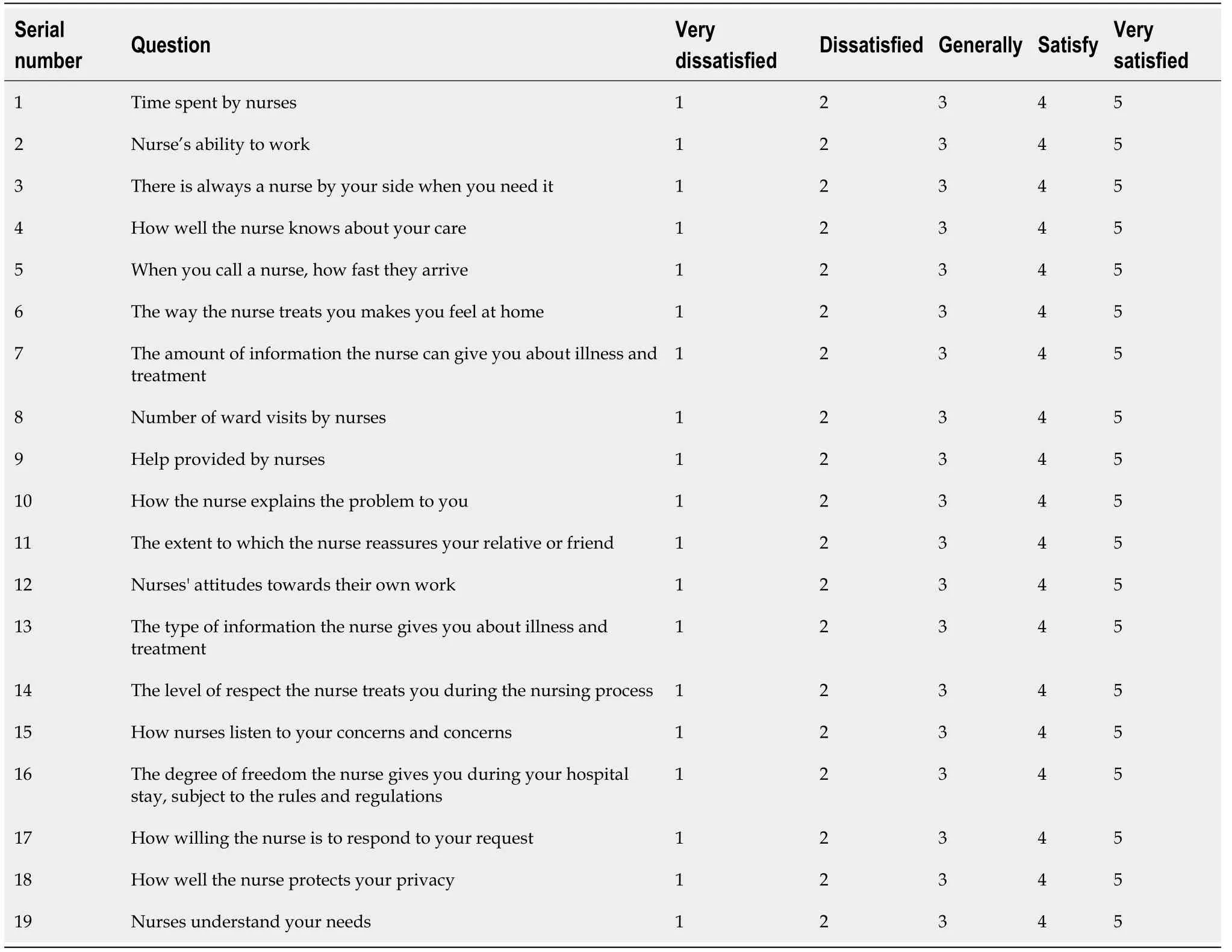
The NSNS, daily activities scale (ADL), MMSE scale, GQOL-74 scale and ESCA scale involved in the assessment are detailed in the appendix of the manuscript (Table 1, Table 2).
Observation indices
The daily living ability, cognitive function, and quality of life of the two groups before and after intervention were measured. Daily living ability was evaluated according to the Daily Activity Ability Scale (ADL), with a total of 100 points. The higher the score, the better the daily living ability. Cognitive function was assessed by the Simple Intelligent Mental State Scale (MMSE), with a total of 30 points. The higher the score, the better the cognitive function. Quality of life was evaluated based on the Comprehensive Assessment Questionnaire for Quality of Life (GQOL-74), with a total of 100 points. The higher the score, the better the quality of life. The self-care abilities of the two groups before and after intervention were evaluated according to the self-care ability scale (ESCA), including self-concept, selfcare skills, self-care knowledge, and self-care responsibility, with a total of 172 points. The lower the score, the worse the self-care ability. The incidence of complications in the two groups was determined.The satisfaction level of inpatients with the quality of nursing care was assessed using the Newcastle satisfaction with nursing scale (NSNS). The total score was 95, very satisfied: > 85, general satisfied:67–85, unsatisfied: < 67, nursing satisfaction = (general satisfied + very satisfied)/total number of cases× 100%.
A nursing intervention based on the dynamic interaction model was adopted based on the control group. (1) Dynamic interaction between nursing staff and patients was undertaken, with reference to personal information such as patients’ personality characteristics and education level. Patients were communicated with in an appropriate manner in order to establish a close and trusting relationship and to obtain the patient's understanding and cooperation. Through conversations with patients and family members, psychological scale evaluation, and other forms of communication, the patient's social relationship, life background, personal preferences,were gathered, so as to alleviate and eliminate their feelings of strangeness and fear of the hospital environment, to effectively master their treatment and rehabilitation needs, and to correct patients' misunderstanding of the disease and rehabilitation treatment. Through an example, such as presenting a case who had achieved good effects through rehabilitation treatment, or inviting that exemplar patient to the rehabilitation sessions of patients at the hospital, the patient’s desire and confidence to partake in the rehabilitation was stimulated. This helped them form a notion of "Bearing witness to good rehabilitation, means with effective treatment and training, I too can achieve restoration of bodily functions.", this notion can improve patients' rehabilitation training compliance; (2) there was dynamic interaction between nursing staff and family members. Rehabilitation training for patients with intracranial aneurysms usually requires the assistance of family members. By introducing the relevant knowledge of postoperative rehabilitation of intracranial aneurysms to the family members in detail, the patients were aware of the importance of active cooperation and assistance in functional rehabilitation training. The staff aimed to guide the patient's family to systematically learn the knowledge associated with postoperative rehabilitation nursing of intracranial aneurysm, in order to provide the patient with the best nursing services. In addition, WeChat accounts of family members were added by staff to keep close communication with family members of the patients and improve their out-of-hospital rehabilitation and self-care. Through WeChat, family members could communicate with nursing staff about the problems encountered during the patient’s out-of-hospital rehabilitation, and the nursing staff provided professional guidance;and (3) dynamic interaction was observed between the patients and the change room. Patients were guided to join staff-mediated QQ and WeChat groups by scanning QR codes, and they were encouraged to actively share their own rehabilitation experience and problems encountered, about nursing skills,such as emotional management and wound management, and to encourage each other to improve treatment and rehabilitation confidence.
Nursing intervention based on dynamic interaction model can improve postoperative cognitive function, daily living ability, self-care ability, and quality of life, while reducing the risk of complications and improving patient satisfaction. However, this study had a small sample size and did not follow up with the patients to observe their prognosis; therefore, it is still necessary to increase the sample size clinically and extend the follow-up duration to further explore and confirm the relevant contents of this intervention model.

Statistical analysis
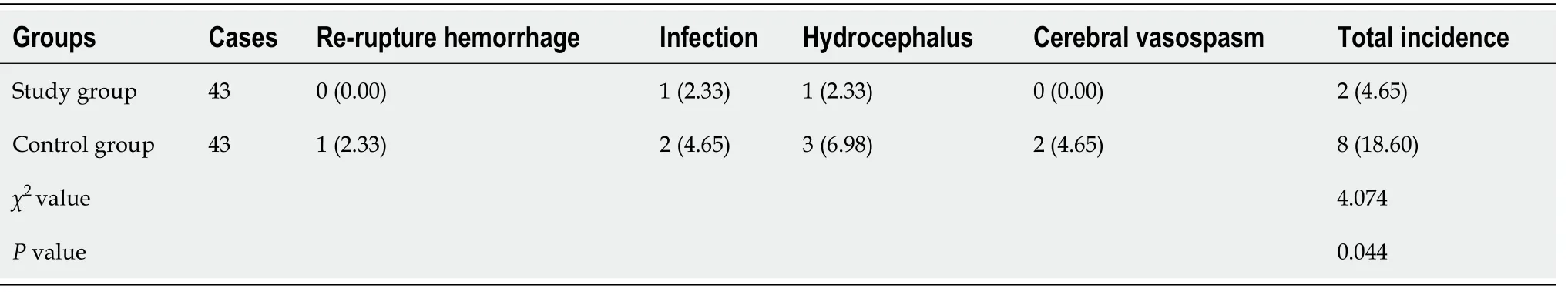
The incidences of complications in the study group (4.65%) were lower than that in the control group(18.60%) (< 0.05) (Table 5).
RESULTS
Comparison of ADL, MMSE, and GQOL-74 scores between the two groups before and after intervention
Before intervention, ADL (52.09 ± 6.44), MMSE (18.03 ± 4.11), and GQOL-74 (53.68 ± 4.34) scores in the study group were similar to those in the control group (ADL: 50.97 ± 7.32 points, MMSE: 17.59 ± 3.82 points, and GQOL-74: 55.06 ± 3.98 points) (> 0.05). After intervention, ADL (86.12 ± 5.07), MMSE(26.64 ± 2.66), and GQOL-74 (83.13 ± 5.67) scores in the study group were higher than those in the control group (ADL: 79.81 ± 6.35, MMSE: 24.51 ± 3.00, and GQOL-74: 77.96 ± 6.27 scores) (< 0.05)(Table 3).

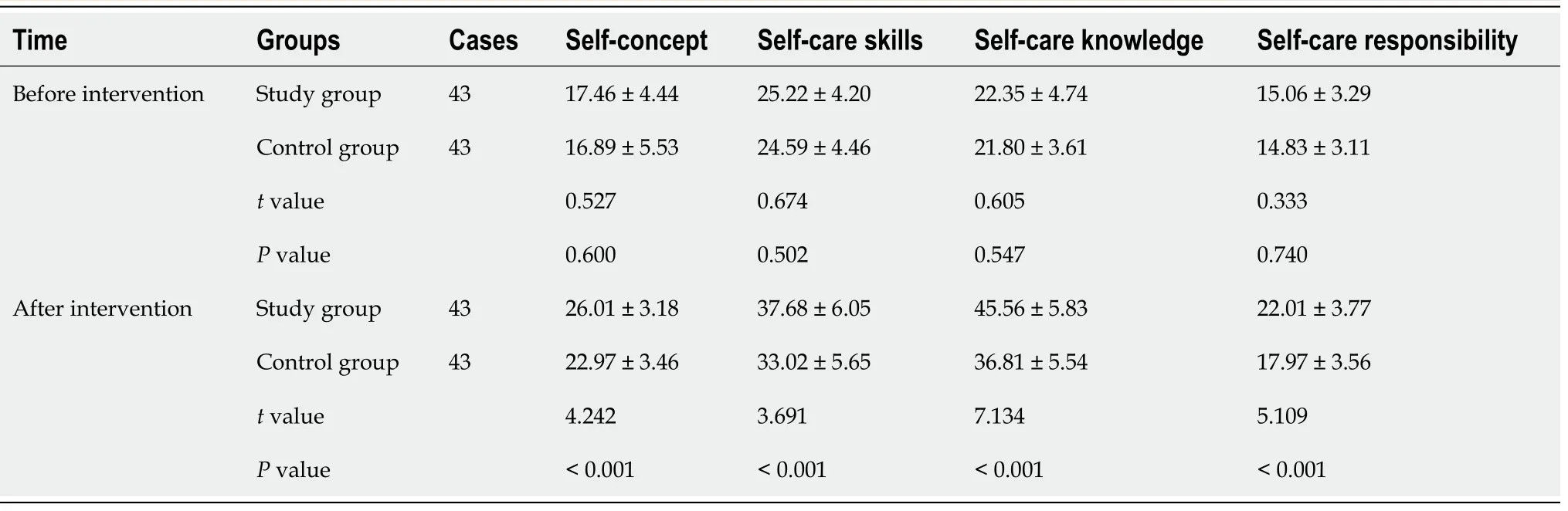
Comparison of ESCA scores between the two groups before and after intervention
Before intervention, self-concept (17.46 ± 4.44), self-care skills (25.22 ± 4.20), self-care knowledge (22.35 ±4.74), and self-care responsibility (15.06 ± 3.29) scores in the study group were similar to those in the control group (self-concept: 16.89 ± 5.53, self-care skills: 24.59 ± 4.46, self-care knowledge: 21.80 ± 3.61,and self-care responsibility: 14.83 ± 3.11 scores) (> 0.05). After intervention, self-concept (26.01 ± 3.18),self-care skills (37.68 ± 6.05), self-care knowledge (45.56 ± 5.83), and self-care responsibility (22.01 ± 3.77)scores in the study group were higher than those in the control group (self-concept: 22.97 ± 3.46, selfcare skills: 33.02 ± 5.65, self-care knowledge: 36.81 ± 5.54, and self-care responsibility: 17.97 ± 3.56 scores)(< 0.05) (Table 4).
Comparison of incidences of complications between the two groups
SPSS 22.0 (IBM SPSS Statistics for Windows, Version 22.0 Armonk, NY: IBM Corp.) was used for data analysis. Measurement data are expressed as mean ± SD, and differences were tested using the Student’stest. Enumeration data are expressed as(%), and the distribution was tested using thetest.< 0.05 indicated that the difference was statistically significant.
Coloured pictures gleamed from their golden background, and on the altar stood the figure of the Virgin with the child Jesus, surrounded by lights and flowers; priests in festive robes were chanting, and choir boys in dazzling attire swungsilver censers
Comparison of nursing satisfaction between the two groups
Nursing satisfaction in the study group (95.35%) was higher than that in the control group (81.40%) (<0.05) (Table 6).

DISCUSSION
As a common condition in neurosurgery, intracranial aneurysms usually have a small tumor diameter,but their harm and mortality rates are high. Moreover, the structural stability of the intracranial aneurysm wall is poor, making them prone to rupture and causing subarachnoid hemorrhage,threatening the cognitive function and quality of life of patients[9,10]. Endovascular intervention is animportant measure for the clinical treatment of intracranial aneurysms and has the advantages of little trauma and quick recovery. Effective and reasonable postoperative nursing interventions play a positive role in ensuring the rehabilitation effect of the disease[11].
Routine care for the patients was adopted as follows: (1) When the patients woke up, they were greeted at the bedside immediately with gentle language and asked about their subjective feelings. Attention was paid to the tone, expression, and other details during the conversation in order to master the patient's psychological dynamics, and to strengthen psychological intervention for those suffering from depression (assistance was sought from a psychologist when it was necessary); (2) the dressing at the puncture site for the subcutaneous hematoma was observed to see if it was bleeding, and the doctor was informed to immediately provide corresponding treatment if there was any abnormality; (3) for patients with lumbar cistern catheterization or lumbar puncture, the drainage tube was properly fixed to ensure smooth drainage; the color and characteristics of the cerebrospinal fluid was checked regularly; (4)patients were instructed to avoid excessive exertion during defecation, to avoid strenuous activity, and to maintain a stable mood, in order to avoid tumor rupture and bleeding caused by such factors.Patients were observed for signs and symptoms of nerve damage, such as meningeal irritation,disturbance of consciousness, vomiting, headache,; (5) patients’ limb skin color, temperature, blood pressure, and pulse were closely monitored, and if thromboembolism was suspected, DSA and computed tomography examinations were immediately carried out, according to the specific situation,for targeted intervention; (6) during the patient's stay in bed, the nursing staff assisted the patient with good limb placement and performed passive joint movement exercises. Limb function training began at the proximal joint and gradually increased the range of activity until complete flexion and extension,and then the distal joint was trained. According to the patient's physical condition, the patient was assisted with daily living exercises and ground walking exercises, and the transition from standing exercise to slow walking was 30 min/time, twice/day; and (7) discharge guidance: patients were routinely discharged. Before discharge, they were instructed to stabilize their mood, combine work and rest, have a healthy diet, quit smoking and alcohol consumption, measure blood pressure every day,and take medical drugs routinely.
Based on the above background, nursing intervention based on a dynamic interaction model was adopted in this study to intervene in patients after aneurysm surgery. The results showed that ADL,MMSE, and GQOL-74 scores in the study group were higher than those in the control group; the ESCA dimension scores were higher than those in the control group, and the complication rate (4.65%) was lower than that in the control group (18.60%). It has been confirmed that nursing interventions based on the dynamic interaction model have high application value in patients after aneurysm surgery, which is beneficial in restoring the daily living ability and cognitive function of patients, improving self-care ability, reducing the occurrence of complications, and having positive benefits for improving the quality of life of patients. The main reason is that nursing intervention based on the dynamic interaction model can realize information interaction and emotional interaction, increase the patients’ cooperation in nursing work, and facilitate the establishment of stable and harmonious medical relationships. At the same time, the nursing model based on the dynamic interaction model is patient-centered, focusing on interaction with the patient and family during the intervention, can effectively solve the problem of information asymmetry between nursing staff and patients, and between nursing staff and patients’families, so as to provide the hospital and the hospital rehabilitation treatment with effective professional information support. Increasing the interaction between patients can alleviate their feelings of inferiority. It can also stimulate the patients' confidence in rehabilitation and help them obtain rehabilitation inspiration and experience through the example of others[19,20]. In addition, family members are important participants in out-of-hospital rehabilitation of patients. Timely communication between nursing staff and family members of patients through WeChat can solve their confusions and problems during out-of-hospital rehabilitation in real time and provide systematic and professional medical care services for them continuously. The results of this study also found that the nursing satisfaction of the study group (95.35%) was higher than that of the control group (81.40%), indicating that the dynamic interaction model can also improve the nursing satisfaction of aneurysm patients. This may be because this nursing program can restore patients' functions and reduce complications, resulting in higher patient satisfaction.
When Charles went to Switzerland for a ski vacation, Diana missed him terribly. He called her after a day or two, and told Diana he had something important to ask her.
CONCLUSION
Romance is not something that can be taught or copied. One can only be romantic through another. Patricia, my wife of fourteen years, has instilled4 the romance in me. I am romantic because of her. Patricia has always brought out the best in me. The many aspects of our romance are too numerous to mention. However, there is one special romantic interlude that I began over fifteen years ago.
ARTICLE HIGHLIGHTS
Research background
Nursing practice based on dynamic interaction model has been proven to be superior to general nursing practice. However, the efficacy of this model on patients who have recovered from intracranial aneurysm surgery has not been well studied.
He walked many hours, whistling and calling for it, but it never came, and he went sadly home, resolved to be out with the dawn and never to rest till he had brought the wanderer back
Research motivation
Explore the impact of nursing based on dynamic interaction model on the functional rehabilitation of patients after aneurysm surgery.
I had returned to work after only six weeks leave and on the tail end of postpartum blahs. I felt fat and incompetent4. My husband felt guilty and alienated5. The few words in passing each morning and the brief hug and peck in the evening were, at best, meager6 tokens of the attention we desperately7 needed to give each other.
Research objectives
Explore the application of nursing based on dynamic interactive model in functional rehabilitation of patients after aneurysm surgery, and provide reference for clinical nursing work.
Research methods
A total of 86 cases in our hospital with intracranial aneurysm from April 2019 to April 2021 were selected and divided into the study group and the control group, with 43 patients in each group.
Research results
However, there are few systematic studies on the application value of the dynamic interaction model in patients after aneurysm surgery. Therefore, this study selected 86 patients with intracranial aneurysms in our hospital and divided them equally into a control group and a study group, in order to explore the application value of the dynamic interaction model.
Research conclusions
Nursing intervention based on a dynamic interaction model can improve postoperative cognitive function, daily living ability, self-care ability, quality of life, and patient satisfaction, while reducing the risk of complications.
Research perspectives
Nursing intervention based on dynamic interaction model has a wider application prospect in clinical nursing work.
FOOTNOTES
Xie YE and Huang WC design the study; Li YP drafted the work; Deng JH and Huang JT collected the data; Xie YE and Huang WC analyzed and interpreted data; Li YP and Deng JH wrote and revised the manuscript.
This study was approved by the Central People’s Hospital of Huizhou City Ethics Committee.
All study participants, or their legal guardian, provided informed written consent prior to study enrollment.
Then she sat down to her work once more and span on, and as she did so an old saying which, she had often heard her godmother repeat whilst at work, came into her head, and she began to sing: Spindle, spindle, go and see, If my love will come to me
The authors declared that there is no conflict of interest between them.
She answered, The good God has caused my natural hands to grow again; and the angel went into the inner room, and brought the silver hands, and showed them to him
No additional data are available.
The sculptor10 Rodin’s father said, “I have an idiot for a son.” Described as the worst pupil in the school, Rodin failed three times to secure admittance to the school of art. His uncle called him uneducable.
This article is an open-access article that was selected by an in-house editor and fully peer-reviewed by external reviewers. It is distributed in accordance with the Creative Commons Attribution NonCommercial (CC BYNC 4.0) license, which permits others to distribute, remix, adapt, build upon this work non-commercially, and license their derivative works on different terms, provided the original work is properly cited and the use is noncommercial. See: https://creativecommons.org/Licenses/by-nc/4.0/
China
Yan-E Xie 0000-0001-9507-3605; Wei-Cheng Huang 0000-0002-8253-7551; Yu-Ping Li 0000-0003-0679-5628; Jia-Huan Deng 0000-0003-2015-2442; Jian-Ting Huang 0000-0003-3794-8324.
Wang JL
A
Wang JL
 World Journal of Clinical Cases2022年15期
World Journal of Clinical Cases2022年15期
- World Journal of Clinical Cases的其它文章
- Diet and intestinal bacterial overgrowth: Is there evidence?
- Spontaneous liver rupture following SARS-CoV-2 infection in late pregnancy: A case report
- Metastasis of liver cancer to the thyroid after surgery: A case report
- Solitary primary pulmonary synovial sarcoma: A case report
- Knot impingement after arthroscopic rotator cuff repair mimicking infection: A case report
- Clear aligner treatment for a four-year-old patient with anterior crossbite and facial asymmetry: A case report
