Breeding System and Pollination Biology of Lespedeza davurica
TONG Li-rong, SONG Yu, WANG Peng, WANG Juan, CHE Di
(1.College of Grassland Science, Shanxi Agricultural University, Taigu, Shanxi Province 030801, China; 2. China National Institute of standardization, Beijing 100089, China)
Abstract:To reveal the pollination biological characteristics of L.davurica,wild L.davurica in eight regions of Shanxi province was used as test materials,and its breeding system and pollination medium were studied. Results showed that the maximum pollen number of single flowers in the Heshun population was 8 750 ± 1 946 grain·flower-1,while the lowest was 5 370±879 grain·flower-1 in the Zhongyang population. According to the pollen to ovule ratio (P/O),the breeding system type of L.davurica was obligate xenogamy. The outcrossing index of L.davurica was 4,and its breeding type was self-crossing and outcrossing,which needed pollination medium to spread pollen. The first peak in insect foraging behavior occurs between 10:00 and 11:00 a.m.,and a second peak between 3:00 and 4:00 p.m.,the first peak is smaller than the second. Pollination by hymenopterans,such as bees,is the most effective. There are few studies on flowering characteristics of L.davurica in China and abroad,and the breeding system and pollination biology have not been reported. The results of this study not only provide a reference for the breeding characteristics of L.davurica,but also provide a theoretical and practical basis for the hybrid breeding and new variety cultivation of L.davurica.
Key words:Lespedeza davurica;Pollination biology;Breeding system;Outcrossing index;Pollinator
Lespedezadavuricais a perennial herbaceous semi-shrub of the genus Legume,widely distributed in northeast China,northern China,northwest China,southwest China,central China,south China,Inner Mongolia,and Taiwan. It has strong resistance and environmental adaptability and can be used for soil improvement,wind prevention,and sand fixation. The stems and leaves are rich in protein,fat,and amino acids,which is of high feeding value. Some herbivores like to eat them very much. Abundant aboveground biomass inflorescence can be used as silage. Flavonoids in stems and leaves ofL.davuricahave significant antioxidant activity,which can promote the production performance of broilers and improve the antioxidant capacity of broilers[1]. Some compounds such as kaempferol,rutin,and vanillic acid contained in the aboveground parts have high medicinal value[2]. As a local grass species in China,growth adaptability ofL.davuricais strong and easy to be planted and managed. It can be planted in a large area in some areas. It has strong economic benefits and high application value.
The abundant wild resources ofL.davuricaprovide favorable conditions for the study ofL.davuricain Shanxi province of China. However,in China,studies onL.davuricamainly focus on stress resistance,nutritional components and medicinal value,while its pollination characteristics and pollination mechanism ofL.davuricahave not been reported. In recent years,studies on pollination biology have mainly focused on the following points:the relationship between floral characteristic structure and pollination medium[3-4].The competitive relationship of floral reproductive organs[5]. Effects of pollination biology on genetic diversity[6-7]. Transmission pathway and pollination efficiency of pollen flow[8]. Chemical constituents of pollination system[9]. In this paper,wildL.davuricafrom different regions of Shanxi Province was used as the experimental material to study its pollination mechanism,aiming to clarify the pollination biological characteristics ofL.davurica,and to explore the influence of the pollination mechanism ofL.davuricaon its reproductive development,so as to provide a reference for the development of sexual hybridization,the formulation of effective breeding programs and the promotion and application of excellent varieties.
1 Materials and Methods
1.1 Research materials and locations
L.davuricabear racemes on each branch,with 6 to 19 florets growing on each inflorescence. The florets have a flower stalk,a cup-shaped calyx with a white tomentose surface,and a typical papilionaceous corolla. The stems are single or several clustered,ternate pinnate leaf,with lanceolate-oblong leaflets,and flowering in July-August.
The experiment was conducted at the Herbology County,Shanxi Province. The research objects for the determination of pollen quantity of different populations ofL.davuricawere wildL.davuricafrom eight regions of Shanxi Province (Table1),and the other experimental materials wereL.davuricafrom the Taigu population.
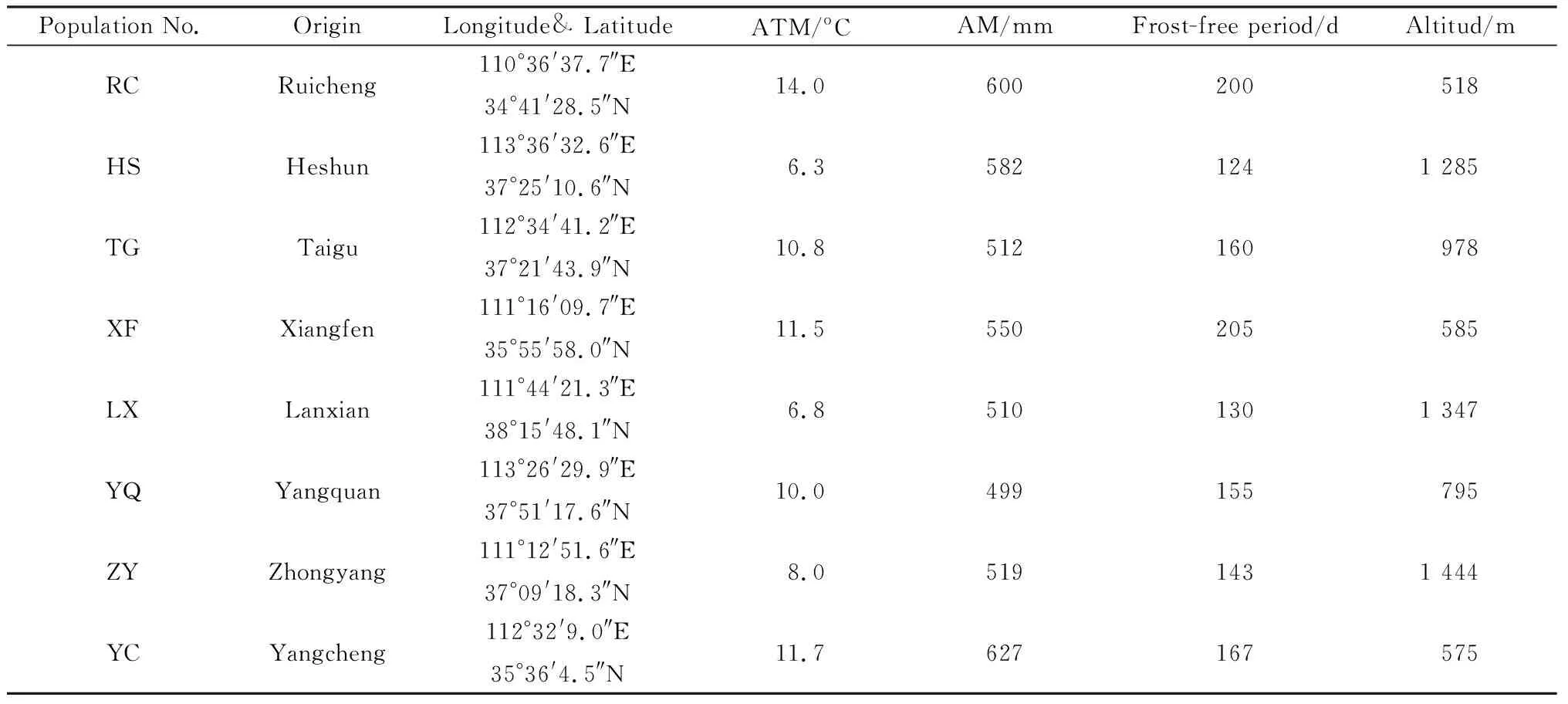
Table 1 The collection information of Lespedeza davurica from eight places
1.2 research method
1.2.1Estimation of the OCI(Outcrossing index) According to Dafni[10],the flower diameter,the time interval between stamen maturity and receptivity of stigma,and the spatial position between anther and stigma were observed and determined.
1.2.2Determination of pollen counts in single flowers,ovule number,and P/O(pollen-to-ovule ratio) According to Cruden[11],randomly select 20 flowers whose anthers were about to split,and then randomly select 2 anthers from each floret,place the individual anthers on a slide,add a drop of acetic acid magenta,cover the glass slide,gently squeeze the anthers to rupture them,observe and photograph them under an Olympus microscope,calculate the average number of pollen grains in the individual anthers,multiply the number of anthers as the amount of pollen in a single flower. Randomly select 10 florets,cut the ovary with a dissecting needle under a dissecting microscope,observe and count the average number of ovules.
P/O = average number of pollen in anthers/average number of ovules in the ovary
1.2.3Bagging,emasculation,and manual pollination According to Dafni (1992):(1) control,free pollination,no treatment of buds;(2) emasculation,bagged,no pollination;(3) emasculation,not bagged,allowed to pollinate naturally;(4) artificially self-pollinated,staminate with pollen from other inflorescences of the same plant;(5) artificially cross-pollinated,staminate with pollen from inflorescences of other plants;(6) emasculation,cover the net bag;(7) do not emasculation,cover the paper bag. All the above treatments were bagged before the flowers opened,emasculated before the anthers dehiscent,counting the number of pods,and calculating the seed setting rate after the pod fully developed and mature:
Seed-setting rate=number of fruits/ number of flowers × 100%
1.2.4Observation of pollinators Inflorescences with good branch growth and flowering conditions were selected,five branches were marked at a time,and all visiting insects were counted in 1-h units for species,the number of times,flower-visiting behavior,and flower-visiting time between 7:00 and 18:00,and observed continuously for 3 d. Flower visiting insects were captured for species identification. The role played by insects between pollen and stigma and the changes of flowers after insect visits were observed.
1.3 Data processing
Data were processed using Excel 2013. ANOVA and multiple comparisons of data were performed using SPSS 24.0 software. In this paper,Origin 2016 is used to complete the drawing.
2 Results
2.1 OCI (Outcrossing index),pollen counts,ovule number and P/O(Pollen-to-ovule ratio)
The single flower diameter ofL.davuricais 4.4~5.5 mm. Stigma receptivity is at stage IV of the flower morphology,and the anther dehiscence is at stage III,the anther dehiscence is earlier than stigma receptivity and belongs to the stamen prematurity. The spatial distance between the anther and the stigma was 0.76 mm. Therefore,the outcrossing index was 4. According to the standard reported Dafni[10],the breeding type is partially self-compatible with outcrossing,which requires insects to pollinate. (Tables 2 and 3)
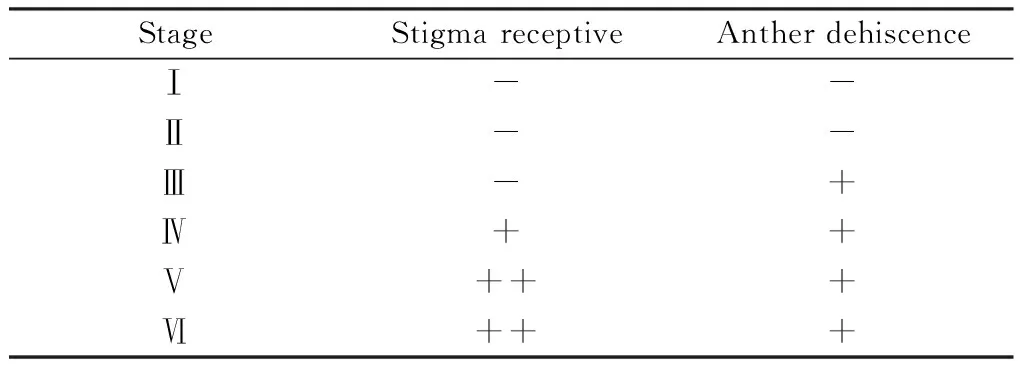
Table 2 The interval time between anther dehiscence and stigma receptivity
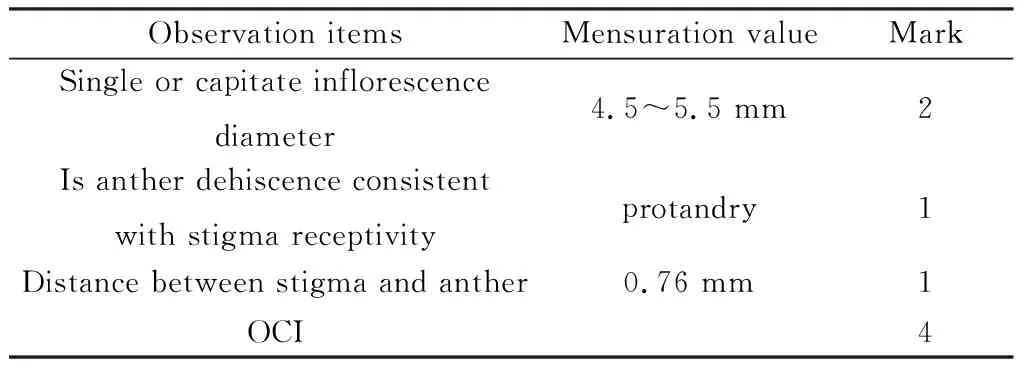
Table 3 The estimation of outcrossing index
The single-flowered pollen counts ofL.davuricavaries greatly among different populations. Among the eight populations,the pollen volume of single flowers in the Taigu population was the highest at 8 750±1 946 grains·flower-1,while the pollen volume in the Zhongyang population was the lowest at 5 370±879 grains·flower-1,and only the pollen volume in Xianfen population was more in one year of growth than in two years of growth. It was observed that the ovary ofL.davuricabranch contained one ovule. The highest P/O value was 8 750±2 643 for the Taigu population and the lowest P/O value was 5 370±879 for the Zhongyang population,and the breeding system was exclusively heterozygous according to the criteria of Cruden[11]. (Fig.1)
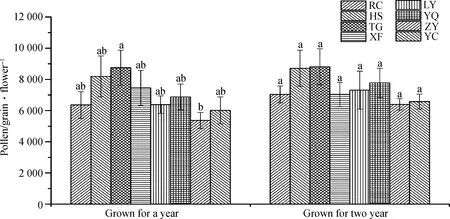
Fig.1 Pollen number of different populations of Lespedeza davuricaNote:different lowercase letters indicate pollen amount among different populations significant difference(P<0.05)
2.2 Bagging,emasculation,and manual pollination
Seed setting rate of free pollination ofL.davuricawas 58 %. After emasculation and bagging,the seed setting rate was 0 %,indicating that there was no fusion-free reproductive mode. The seed setting rate was 4 % after free pollination,and there was a natural cross phenomenon. The seed setting rates after artificial self-pollination and artificial cross-pollination were 15.00 % and 11.67%,respectively,indicating that the same plant with different flowers could be fertilized and seeded,and there was hybridization affinity to some extent. The seed setting rate of the net bag and paper bag treatments was 46 % and 39 % lower than those of the control group,respectively,which might be due to the effect of their treatments on the seed setting of flowers. (Fig.2)
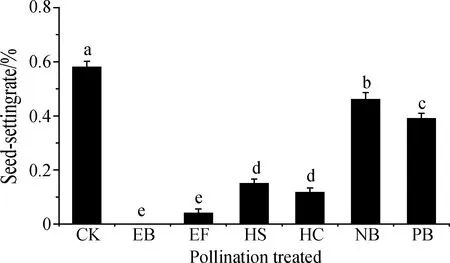
Fig.2 The seed-setting rate under different pollination methodsNote:CK:Control;EB:Emasculated and bagged;EF:Emasculated,free pollination;HS:Hand selfing;HC:Hand crossing;NB:Net bag;PB:Paper bag Different lowercase letters indicate seed setting rate under different pollination methods significant difference(P<0.05)
2.3 Insect pollinator
The color and smell ofL.davuricaflowers can attract the attention of some insects. Common visiting insects are Hymenoptera,Lepidoptera,Diptera,and Coleoptera. Bees (Hymenoptera) stay longer between flowers,pollination is more effective. Lepidopteran insects have a high frequency of visiting flowers,but the pollination effect is weak. Diptera insects lack pollination media. Coleoptera insects had no obvious pollination effect. In sunny mornings,with the increase of temperature,the frequency of insect flowering gradually increased,and the first flowering peak appeared from 10∶00 to 11∶00 am. Then,with the continuous increase of temperature,the frequency of insect activity decreased. When insect flower-visiting activity reached the minimum,the temperature was the highest and the atmospheric humidity was the lowest. Then,with the gradual decrease of temperature and the increase of atmospheric humidity,the frequency of insect flower visits also continued to rise. There was another peak of flower visits from 3∶00 to 4∶00 pm.,and the first peak was lower than the second. (Fig.3)
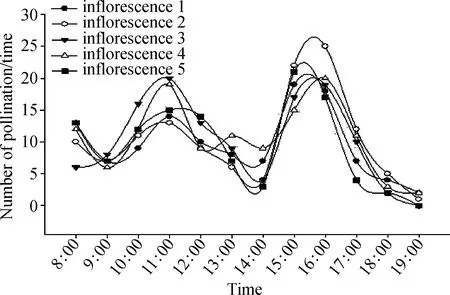
Fig.3 The diurnal variation of the number of flower-visiting insects
3 Discussion
3.1 Research results of population flowering
Studies have shown that inflorescence structure affects the pollination effect,and raceme helps to reduce self-pollination. On the other hand,raceme can output more pollen[5].L.davuricabelongs to the racemes,so it can still produce large amounts of pollen to promote crossbreeding when fewer insects visit. Flowers ofL.davuricabelong to male precocity. Flowers on the same branch are basically opened from the base to the top,and the flowering period of each flower can last about 3 days,which is basically consistent with the movement route of pollinators from bottom to top. In this way,when the current flower has passed through the male stage and is in the female stage,the exotic pollen carried by the visiting insects when visiting the flower completes pollination. In addition,a large number of pollen can be exported by insects moving from bottom to top in inflorescence.
3.2 Relationship between floral characteristics and pollinators
L.davuricabelongs to the Leguminosae butterflies subfamily,similar to most butterflies,is a typical flag petal,symmetrical on both sides. Flowers are open in the daytime. When they are open,flag petals are expanded first,which will release light aroma and have a certain attraction to flowers visiting insects. The keel petals play a role in protecting anthers and stigmas. At the same time,the keel petals and wing petals can provide landing points for insects and improve the number of flowers visiting insects. When insects visit the flowers and take honey,the flowers will infect the insects through a fluffing mechanism. Overall,through its own floral structure,L.davuricacan successfully transmit pollen to the stigma of other small flowers through insects,complete pollination and improve the probability of crossing.
3.3 Breeding types of L.davurica
The importance of breeding in the whole growth history of plants is self-evident,and the understanding of the breeding system is also a prerequisite for related research[12]. Biologists have always maintained a strong interest in the diversity of plant reproductive systems. The core of breeding system research is mating system. In the study of mating system,it is found that there are few absolute selfings or alien plants in nature,and in most cases,these two mating methods exist at the same time[13]. The bagging experiment showed a certain degree of self-cross and out-cross,and the hybridization also had a certain affinity,and there was no apomixis. Some scholars believe that the mating system of plants is gradually evolved with the change of environment,when the proportion of selfing offspring is more than that of hybrid offspring,the mating mode will gradually evolve to selfing. When the degree of adaptation of outcrossing offspring to the environment is greater than that of selfing offspring,the mating mode gradually evolves to hybridization. Although most angiosperms choose selfing in evolution,some plants still choose the mating mode of mixed pollination[14-15]. In the investigation of plant breeding systems and pollination characteristics,the proportion of selfing and crossing has always been the focus of the investigation.
Generally,the pistils and stamens of angiosperms grow on the same body,and the number of pollen and ovule produced by angiosperms is far more than that of seed or fruit produced[16-19]. When the pollen number was measured,it was found that the pollen amount was much more than the ovule number,and the pollen ovule ratio was high,indicating that there was enough pollen to invest in its reproduction. At the same time,the increase of pollen ovule ratio is accompanied by the increase of inbreeding ratio,and the decrease of pollen ovule ratio means the decrease of inbreeding ratio[10].
Hybridization index and P/O value are used by many researchers in the study of flowering plant breeding systems because they are relatively simple,convenient and fast[20]. However,in this experiment,the results of its hybridization index and pollen-ovule showed that there were certain differences in its breeding system. The results of artificial pollination ofL.davuricashowed that there was a certain degree of selfing and cross,hybridization also had a certain degree of affinity,there was no apomixis phenomenon. According to the P/O value,the type ofL.davuricabranch breeding system was exclusive. Although the determination of P/O value is relatively simple,there may be some errors,and the breeding type obtained from the hybridization index is basically consistent with the results obtained from artificial pollination. Therefore,this experiment also proved that the hybridization index was more accurate and reliable than the pollen-o vule ratio (P/O) in reflecting plant breeding types.
4 Conclusion
The maximum number of pollen grain per flower was 8 750±1 946 grains·flower-1inL.davuricaof the Heshun population,while the minimum number was 5 370±879 grains·flower-1in the Zhongyang population. Comparing different populations,it was found that the pollen amount of two years was generally more than that of one year. The results of artificial pollination ofL.davuricashowed that there was a certain degree of self-cross and cross,and the hybridization also had a certain affinity,and there was no apomixis. According to the P/O value,the type ofL.davuricabreeding system was exclusive. The hybrid index ofL.davuricawas 4,and its breeding type was self-crossing and outcrossing,which needed a pollination medium to spread pollen. The first peak of insect flower-visiting occurred between 10:00 and 11:00,and the second peak occurred between 15:00 and 16:00,and the first peak was less than the second peak. The pollination effect of Hymenoptera insects such as bees is the most obvious.

