Biphasic anaphylaxis manifested as type I Kounis syndrome induced by ingestion of raw f ish gallbladder: A case report
Long Lin, Benjamin J.Sandefur, Ronna L.Campbell, Zhi Liu, Xiao-wei Liu
1 Department of Emergency Medicine, the First Affi liated Hospital, China Medical University, Shenyang 110001, China
2 Department of Emergency Medicine, Mayo Clinic, Rochester 55905, USA
Dear editor,
Anaphylaxis and acute coronary syndromes(ACS) are discrete clinical presentations that usually present independently and are commonly treated in the emergency departments (EDs).[1]Kounis syndrome (KS)is a rare condition characterized by the coexistence of allergic reactions and ACS.KS was firstly described in detail by Kounis and Zavras in 1991 as an allergic angina syndrome.[2]The primary pathophysiological mechanism of KS is believed to be coronary artery vasospasm secondary to increased levels of inf lammatory mediators such as histamine, tryptase, platelet-activating factor,and various cytokines.[3]These inflammatory mediators are released through mast cell activation in response to a range of stimuli during episodes of allergic or hypersensitivity reactions.Researchers have described three variants of KS: ACS with or without troponin release resulting from co ronary vasospasm (type I);ACS among patients with pre-existing coronary artery disease (CAD) ca used by atheromatous plaque erosion or rupture (type II); and ACS secondary to coronary artery thrombosis, including coronary artery stent thrombosis(type III).[4,5]Type III KS is subdivided to type IIIa that includes stent thrombosis and type IIIb that includes stent restenosis.[6]KS can be caused by all kinds of seafood,such as finned fish, molluscan shellfish, cephalopods,and crustacean shellf ish.[7]We reported a case of biphasic anaphylaxis triggered by the ingestion of raw fish gallbladder that resulted in type I KS.
CASE
A 58-year-old woman was admitted to our ED by emergency medical services (EMS) for a potential allergic reaction.Past medical history included CAD,which was well-controlled by medications.Th ere was no history of an allergic reaction.She had intentionally ingested raw fish gallbladder of grass carp (unknown species and genus) on an empty stomach 55 minutes prior to the ED arrival.As described by the patient, the length of the fish gallbladder was >2 cm, with bile volume of approximately 10 mL.Thirty minutes after ingestion, she developed abrupt swelling of her lips and facial f lushing.She also reported generalized pruritic rash, diaphoresis,a sensation of throat tightness, nausea, vomiting, and watery diarrhea, followed by dizziness.E MS personnel found the patient to be hypotensive (systolic blood pressure 80 mmHg [1 mmHg=0.133 kPa]).EMS providers administered 0.5 mg intramuscular (IM)epinephrine and rapid intravenous (IV) f luid infusion of 1,000 mL normal saline.Before arrival in the ED, the rapid improvement in her symptoms was noted after the epinephrine administration.Upon ED arrival, the patient had stable vital signs with heart rate of 82 beats/minute,blood pressure of 110/60 mmHg, respiratory rate of 18 breaths/minute, and oxygen saturation of 94% on room air.Physical examination revealed bilateral expiratory wheezes and rash scattered all over the body.Twelvelead electrocardiogram (ECG) demonstrated sinus rhythm with 1-mm down-sloping ST-segment depression and low, flat, biphasic, or inverted T waves in leads I,aVL, V5, and V6 (Figure 1A).In the ED, she received 10 mg loratadine orally, 10 mg IV dexamethasone, and 20 mg IV famotidine.She was transferred to the ED observation unit.Approximately 6.5 hours after receiving epinephrine and 6 hours after symptom resolution,the patient developed lip swelling, facial flushing,generalized urticaria, and new-onset chest pain.The chest pain persisted for about 20 minutes, like pressurelike pain in the center of her chest, with radiation to the left shoulder and arm, and was rated 8/10 in severity.The pain was not improved with the administration of sublingual nitroglycerin.A repeat ECG was obtained and demonstrated ST-segment elevation in the inferior leads(II, III, and aVF) and reciprocal changes of ST-segment depression in the lateral wall leads (I and aVL) (Figure 1B).Oral aspirin, clopidogrel, and an infusion of IV nitroglycerin were administered.An emergent coronary angiography was performed and revealed mild coronary atherosclerosis with vasospasm of superdominant right coronary artery with almost complete segmental occlusion.The occluded segment returned to its normal caliber after intracoronary nitroglycerin administration.Her initial and six-hour myocardial enzyme levels(creatine kinase-MB and troponin T) remained within normal ranges.She was admitted to the cardiovascular ward and discharged in stable condition two days later.
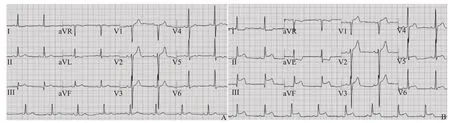
Figure 1.Results of twelve-lead electrocardiogram (ECG).A: upon arrival to the emergency department, ECG showed sinus rhythm with 1-mm down-sloping ST-segment depression and low, f lat, diphasic, or inverted T waves in leads I and aVL; B: repeat ECG demonstrated changes in the ST-segment and T waves at six hours after ED arrival.
DISCUSSION
KS has been increasingly recognized since it was firstly described in 1991,[8]and new triggers are implicated every year.Fish gallbladder, a traditional Chinese medicine, has been associated with multiple organ failure and primarily kidney failure.[9]Despite this,many people in China swallow raw f ish gallbladder every year as a traditional folk remedy for disease prevention and treatment.To our knowledge, this is the first case report of KS induced by raw f ish gallbladder.
The diagnosis of biphasic anaphylaxis was based on the food allergy and anaphylaxis network criteria for the diagnosis of anaphylaxis in EDs.[10]After the resolution of initial symptoms, the patient experienced an approximately six-hour asymptomatic period before the recurrence of anaphylaxis symptoms, without reexposure to the causative trigger.The diagnosis of type I KS as a manifestation of biphasic anaphylaxis was based on clinical symptoms of recurrent anaphylaxis in association with ischemic chest pain, ECG findings,coronary angiography findings, and normal serial troponin levels.
The rapid recognition, accurate diagnosis, and prompt treatment are important for optimal outcomes in KS.[11]KS should be considered when evaluating patients with evidence of anaphylaxis as well as symptoms of acute ischemic chest pain, with and without cardiovascular risk factors or known CAD.In such patients, prompt ECG and cardiac biomarkers should be obtained to detect potential myocardial ischemia or injury.
The treatment of KS can be challenging, requiring special consideration to concurrently address both the cardiac and anaphylactic manifestations of illness.[12,13]The management selected for one aspect of KS should be evaluated in consideration of the potential risk of aggravating the other.Epinephrine, which is first-line therapy and may relieve the life-threatening symptoms of anaphylaxis,[14]should be used in KS with cautionary monitoring, as it has the potential to worsen coronary vasospasm and coronary ischemia, especially if administrated intravenously.Emergency providers should consider KS in patients with both chest pain of ischemic nature and anaphylaxis, to allow for early identification and prompt initiation treatment.
Funding:None.
Ethical approval:Written informed consent was obtained from the patient for the publication of this case report and accompanying images.
Conflicts of interests: Authors have no conflicts of interest to declare.
Contributors:LL and XWL wrote the first draft.All authors contributed to the study and to further drafts.
 World journal of emergency medicine2021年3期
World journal of emergency medicine2021年3期
- World journal of emergency medicine的其它文章
- Chemical pneumonitis caused by intravenous injection of insecticide spray
- Myocardial infarction detected by a smartwatch after transcatheter aortic valve replacement during the COVID-19 pandemic
- Mediastinum metastasis in a post-surgical pancreatic cancer patient successfully conf irmed with endoscopic ultrasonography
- Tension hydropneumothorax in a Boerhaave syndrome patient: A case report
- Performance of extracorporeal membrane oxygenation in patients with fatal paraquat poisoning:grasp for straws?
- Intravenous haloperidol for the treatment of intractable vomiting, cyclical vomiting, and gastroparesis
