Quantitation of tadala fil in human plasma using a sensitive and rapid LC-MS/MS method for a bioequivalence study
Ahysingh Bhdoriy,Bhvesh Dsndi,Dhrmesh Prmr,Priynk A.Shh,Prnv S.Shrivstv,*
aBioanalytical Department,Synchron Research Services Pvt.Ltd.,5th Floor,the Chambers,Sarkhej-Gandhinagar Highway,Bodakdev,Ahmedabad 380054,India
bDepartment of Chemistry,School of Sciences,Gujarat University,Ahmedabad 380009,India
Keywords:Tadala fil Tadala fil-d3 LC-MS/MS Sensitive Bioequivalence study Human plasma
ABSTRACT A highly sensitive liquid chromatography-tandem mass spectrometry(LC-MS/MS)method was developed for the determination of tadala fil(TAD)in human plasma.TAD and its deuterated internal standard(IS),tadala fil-d3,were extracted from 200 μL plasma using Phenomenex Strata-X-C 33 μ extraction cartridges.Chromatographic analysis was carried out on Synergi? Hydro-RP C18(100 mm × 4.6 mm,4 μm)column with a mobile phase consisting of methanol and 10 mM ammonium formate,pH 4.0(90:10,v/v),delivered at a flow rate of 0.9 mL/min.Quantitation of the protonated analyte was done on a triple quadrupole mass spectrometer using multiple reaction monitoring via electrospray ionization.The precursor to product ions transitions monitored for TAD and TAD-d3 were m/z 390.3→268.2 and m/z 393.1→ 271.2,respectively.The calibration curve was linear over the concentration range of 0.50–500ng/mL with correlation coefficient,r2≥ 0.9994.Acceptable intra-batch and inter-batch precision(≤3.7%)and accuracy(97.8%to 104.1%)were obtained at five concentration levels.The recovery of TAD from spiked plasma was highly precise and quantitative(98.95%to 100.61%).Further,the effect of endogenous matrix components was minimal.TAD was found to be stable under different storage conditions in human plasma and also in whole blood samples.The validated method was successfully used to determine TAD plasma concentration in a bioequivalence study with 20 mg TAD tablets in 24 healthy volunteers.Method performance was evaluated by reanalyzing 115 study samples.
1.Introduction
Oral synthetic phosphodiesterase type-5(PDE-5)inhibitor drugs have become first-line treatment option for erectile dysfunction(ED)in males and are also used for pulmonary arterial hypertension(PAH),a debilitating chronic disease of the small pulmonary arteries[1–3].These inhibitors bind with PDE-5 isozymes,which helps in increasing the concentrations of cyclic guanosine monophosphate(cGMP)in smooth muscle of arteries in the penis,producing smooth muscle relaxation and increasing blood flow to the corpus cavernosum for better erectile response.Currently four PDE-5 inhibitors,namely sildena fil,tadala fil(TAD),vardena fil and avana fil,are approved by the US Food and Drug Administration[4].Sildena fil and TAD are two of the most widely used PDE-5 inhibitors worldwide.However,due to their different molecular structures they have markedly different pharmacodynamics and pharmacokinetic behavior.The key pharmacodynamic difference between sildena fil and TAD is towards selectivity for PDE isozymes.TAD is 1000 times more selective for PDE-5 than for PDE-1–4 and PDE-7–10,while sildena fil is only 41 times more selective for PDE-5 than other PDE isozymes[5].One of the major pharmacokinetic differences is the long plasma half-life(t1/2,17.5h)of TAD,which facilitates once-daily dosing as compared to the required three times daily dosing of sildena fil.The prolonged half-life of tadala fil is mainly due to the low volume of distribution,slow hepatic clearance,and approximately 80%bioavailability.This feature of TAD is beneficial in terms of patient convenience and adherence[2].
TAD has the longest duration of action in its class and a maximum duration of 72 h.After oral administration,the peak plasma concentration is reached in 2 h.TAD is primarily metabolized by CYP450 3A4 to its inactive catechol metabolite,which is further metabolized to its circulatory metabolite,methylcatechol glucuronide.TAD is eliminated primarily through feces,while one third of the metabolized drug is excreted in the urine.Unlike other members of its class,the absorption of TAD is unaffected by food.It is 94%plasma bound and shows linear pharmacokinetics over the dose range of 2.5–20 mg[2,6,7].
Several bioanalytical methods are available in the literature for the determination of TAD as a single analyte[8–14],and with other PDE-5 inhibitors[15–23]in different biological samples like rat plasma[9,14],rat serum and brain tissue[17],mouse plasma[11],human and rat hair[20],human whole blood[12,18],seminal plasma [13],human urine [15,22] and human plasma[8,10,13,16,19,21,23].Varieties of analytical techniques have been employed for its estimation including spectro fluorometry[21],gas chromatography-mass spectrometry(GC-MS)[12,15],high performance liquid chromatography-ultraviolet(HPLC-UV)[9,10],HPLC- fluorescence[11],liquid chromatography-tandem mass spectrometry(LC-MS/MS)[8,13,14,16,17,19,20,22,23]and ultra performance liquid chromatography-tandem mass spectrometry(UPLC-MS/MS)[18].A comparative summary of chromatographic methods developed for TAD in different biological samples is shown in Table S1.Majority of these methods have either low sensitivity(≥ 5.0 ng/mL)[8–11,15,16,18],long analysis time(>5.0 min)[9–12,15–18,20,22,23]or require large sample volume for processing(≥ 500 μL)[10,12,15,16,18,22].Thus,it is essential to develop a highly sensitive,selective and rapid bioanalytical assay especially to meet the requirement of pharmacokinetic studies.The developed method presents high sensitivity(0.50 ng/mL),and a short turnaround time(2.5 min)using 200 μL plasma samples.The method was successfully applied for a bioequivalence study in healthy Indian subjects with required accuracy and precision.
2.Experimental
2.1.Chemicals and materials
Reference standards of tadala fil(TAD,99.59%)and tadala fil-d3(TAD-d3,99.99%),used as an internal standard(IS),were obtained from Vivan Life Sciences(P)Ltd.(Mumbai,India).HPLC grade methanol was procured from J T Baker,S.A.de C.V.(Estado de Mexico,Mexico),while ammonium formate and formic acid were obtained from S.D.Fine Chemicals Ltd.(Mumbai,India).Strata-X-C 33μ reversed phase extraction cartridges(30mg,1 mL)were obtained from Phenomenex India(Hyderabad,India).Water used in the entire analysis was prepared using Milli-Q water purification system from Millipore(Bangalore,India).Blank human plasma in K3EDTA was obtained from Supratech Micropath(Ahmedabad,India)and was stored at–70°C until use.
2.2.Instruments and conditions
A Shimadzu Nexera X2 UHPLC equipped with Shimadzu LCMS-8040 triple quadrupole mass spectrometer(MS)detector(Shimadzu Corporation,Kyoto,Japan)was used.Chromatographic analysis was performed on Phenomenex Synergi?Hydro-RP C18(100 mm × 4.6 mm,4 μm)column using methanol and 10 mM ammonium formate,pH 4.0 adjusted with formic acid(90:10,v/v)as the mobile phase.The flow rate was kept at 0.9 mL/min.The column oven temperature and autosampler temperature was maintained at 40 °C and 5 °C,respectively.Electrospray ionization(ESI)source operating in the positive ionization mode was used for multiple reaction monitoring(MRM)LC-MS/MS analysis.The optimized MS/MS conditions for quantification of TAD and TAD-d3 are shown in Table S2.Data processing was done using Shimadzu LabSolution software.
2.3.Preparation of stock solutions,calibration standards(CSs)and quality control(QC)samples
The stock solution of TAD(500 μg/mL)was prepared by dissolving requisite amount in methanol.Working solutions were prepared by diluting the stock solution with methanol.The stock and working solutions were stored at 2–8 °C.CSs and samples were prepared by spiking blank plasma with working solutions.The concentration of CSs was in the range of 0.50–500 ng/mL.QC samples were prepared at five concentration levels(0.50,1.50,30.0,200 and 400 ng/mL).All the samples prepared in plasma werekeptat-70°Cuntiluse.StocksolutionofTAD-d3(100 μg/mL)was prepared by dissolving 1.0 mg in 10.0 mL of methanol.Its working solution(1000 ng/mL)was prepared by appropriate dilution of the stock solution in methanol.
2.4.Sample extraction procedure
To an aliquot of 200 μL of spiked plasma/subject samples,25 μL of TAD-d3 working solution was added and vortexed for 10 s.Further,500 μL of Milli-Q water was added and vortexed again to mix.Samples were then loaded on Strata-X-C 33μ extraction cartridges which were conditioned with 1.0 mL methanol,followed by 1.0 mL water.Washing of samples was done with 2×1.0 mL water,followed by drying of cartridges for 2.0 min by applying nitrogen(1.72×105Pa)at 2.4 L/min flow rate.Elution of TAD and TAD-d3 was carried out using 500μL of mobile phase solution into pre-labeled vials,and 10μL was used for injection in the chromatographic system.
2.5.Validation procedures
The method validation was performed as per the USFDA guidelines[24]and was similar to our previous work[25,26].The detailed procedures and their acceptance criteria are summarized in Supplementary material.
2.6.Bioequivalence study and method reliability
The developed method was applied to measure plasma concentration of TAD for a bioequivalence study after oral administration of single dose of a test(20 mg TAD tablet from an Indian Company)and a reference(20 mg CIALIS(tadala fil)tablets from Lilly,LLC Indianapolis,IN 46,285,USA)formulation to 24 healthy Indian subjects under fasting.The study was performed as per International Conference on Harmonization,E6 Good Clinical Practice Guidelines[27].The experimental details of the study are described in Supplementary material.The pharmacokinetic parameters of TAD were estimated by non-compartmental analysis using WinNonlin?software version 5.3(Certara,Princeton,NJ 08540,USA).Method reliability was ascertained by reanalysis of 115 incurred samples.These samples had concentration near the Cmaxand the elimination phase in the pharmacokinetic profile of the drug.According to the acceptance criterion,at least two-thirds of the original and repeat results should be within 20%of each other[28].
3.Results and discussion
3.1.LC-MS/MS method development
Though currently there are several methods to determine TAD in different biological matrices,the aim of the present work was to develop a highly sensitive and rapid method to meet the requirement of pharmacokinetic studies in healthy humans.All existing chromatographic methods have a limit of quantitation(LOQ),≥2.0 ng/mL except one report in rat serum which reports LOQ of 1.0 ng/mL[17].Further,only two methods[8,14]have a chromatographic analysis time of less than 5.0 min.In light of this,we developed a highly sensitive,selective and rapid method to determine TAD using UHPLC-MS/MS instrumentation and solid phase extraction(SPE)employing a deuterated IS,which helped in controlling any variability during extraction and analyte ionization.
Mass spectrometer parameters were optimized by infusing 500 ng/mL solution of TAD and TAD-d3 in the positive ESI mode as reported previously[8,13,17].The infusion was performed directly in the ionization source at a flow of 10mL/min.The Q1 MS spectra of the analyte and IS showed abundant protonated molecular ions[M+H]+at m/z 390.3 and m/z 393.1 for TAD and TAD-d3,respectively.MS/MS spectra gave highly stable and intense product ions at m/z 268.2 and m/z 271.2 corresponding to the loss of benzodioxole moiety from the precursor ions of TAD and TAD-d3,respectively(Fig.S1).Other product ion observed at m/z 240.1 can be attributed to the loss of CO molecule from m/z 268.2 and m/z 271.2,respectively.Q1 and Q3 potential and collision energy were suitably optimized to achieve the desired specificity and sensitivity of the method.
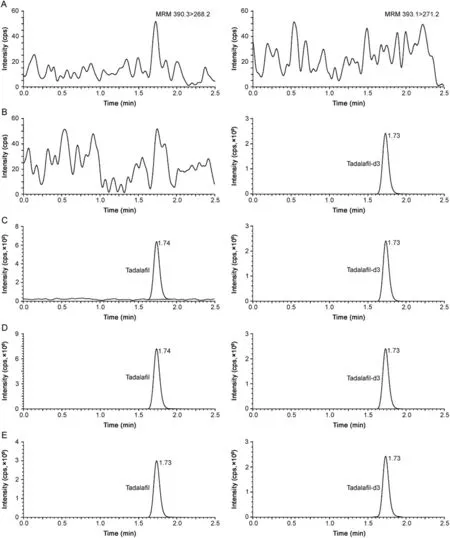
Fig.1.Representative chromatograms of(A)double blank plasma(without tadala fil and tadala fil-d3),(B)blank plasma spiked with tadala fil-d3(100 ng/mL),(C)tadala fil(0.50 ng/mL)and tadala fil-d3(100 ng/mL),(D)tadala fil(500 ng/mL)and tadala fil-d3(100 ng/mL),and(E)real subject sample at Cmaxafter oral administration of 20 mg dose of tadala fil.
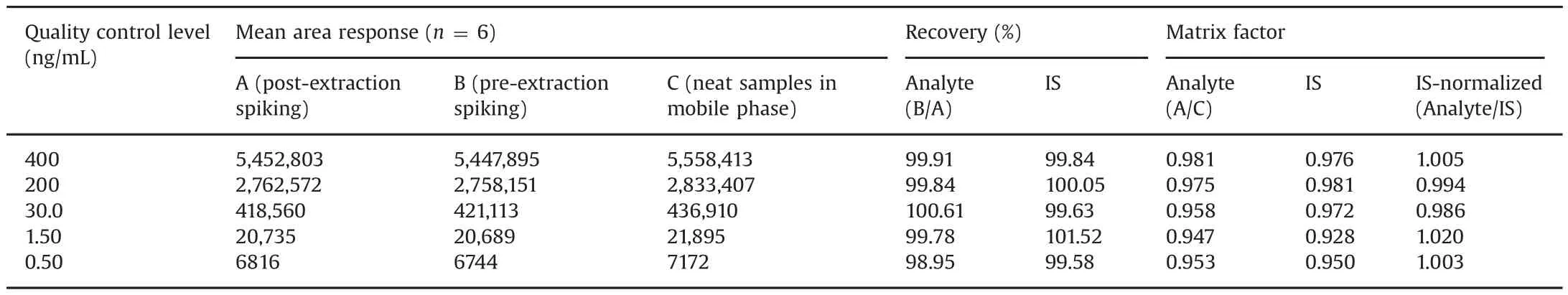
Table 1 Extraction recovery and matrix factor for tadala fil from human plasma.
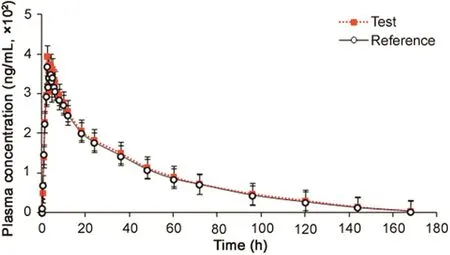
Fig.2.Mean plasma concentration-time profile of tadala fil after oral administration of 20 mg test and reference tablet formulations to 24 healthy Indian subjects.
Several methods developed in human plasma have used liquidliquid extraction(LLE)as the sample clean-up step with varying degree of success[8,10,16].Recovery ranging from~63%to 87%was obtained using diethyl ether-dichloromethane or diethyl ether-ethyl acetate solvent mixture in these methods.Thus,initial attempts for sample preparation of TAD were done by LLE using these solvents together with methyltert-butylether-dichloromethane solvent combination.Although the recovery was quantitative(75%–82%)for higher QC samples(30.0,200 and 400 ng/mL),it was largelyinconsistent atlower(0.50 and 1.5 ng/mL)concentrations.This prompted us to employ SPE for sample clean-up,which was initiated on two different cartridges,namely Strata-X-C and Oasis HLB.Both the cartridges provided adequate recovery(>80%),but Strata-X-C cartridge,which is mainly used for weakly basic compounds,gave about 10%–12%higher recoveries for TAD and TAD-d3 and was therefore employed in the current method.
Several C18reversed-phase columns like Xterra MS[8],Hypersil[13,14],Nucleodur EC[16]and Cadenza CD[19]have been used for separation of PDE-5 inhibitors.Thus,to optimize the best chromatographic conditions for adequate retention,peak shape,analytical response and analysis time,four different C18columns having different dimensions and particle size were investigated.These included Kromasil(150 mm × 4.6 mm,3.5 μm),Hypurity(100 mm × 4.6 mm,5 μm),Zorbax Eclipse XDB(150 × 4.6 mm,5μm)and Synergi Hydro-RP(100mm × 4.6 mm,4 μm).Different combinations of acetonitrile/methanol and acidic buffers(ammonium formate and ammonium acetate)were tested on these columns.Although adequate response and retention was attained on all four columns,slight peak tailing was observed on all the columns except Synergi Hydro-RP.Based on this criterion,the mobile phase comprising of methanol and 10mM ammonium formate(pH 4.0 adjusted with formic acid)(90:10,v/v)was finalized.The role of pH was also studied by changing the pH from 3.0 to 6.0.Higher pH(≥5)resulted in some peak asymmetry and decrease in capacity factor of TAD.Under the finalized conditions,the retention time of TAD and TAD-d3 was 1.74 and 1.73,respectively in a single run of 2.5 min(Fig.1).Use of deuterated IS ensured acceptable method performance based on similar extraction recovery,chromatographic retention and ionization efficiency.
Further,the developed method is more sensitive than all existing methods in the literature.Higher sensitivity is required to have a better assessment of pharmacokinetics of TAD especially during the elimination phase.Moreover,the developed method can also be used for clinical studies with lower dose strength of TAD.The analysis time of 2.5 min is much shorter than other methods except one report[8],which is beneficial when large numbers of samples are to be analyzed in a clinical setting.Also,the sample volume used for processing(200μL)is much less than several established methods.A detailed comparison of chromatographic methods developed for TAD in different biological matrices is shown in Table S1.

Table 2 Mean pharmacokinetic(±SD)parameters,comparison of treatment ratios and 90%CIs of natural log(Ln)-transformed parameters following oral administration of 20 mg tadala fil tablet formulation in 24 healthy Indian subjects under fasting.
3.2.Assay validation results
The results for system suitability,ruggedness,dilution integrity and auto-sampler carryover showed satisfactory method performance as evident from the data presented in Table S3.The selectivity of the method can be seen from the chromatograms of double blank plasma,plasma spiked with TAD-d3,TAD at different concentration levels and in subject sample at Cmaxin Fig.1.There was no interference due to endogenous components at the retention time of TAD and TAD-d3.Furthermore,none of the commonly used medications by human volunteers interfered at their retentio n times.The calibration curves showed good linearity over the established concentration range of 0.50–500ng/mL(r2≥ 0.9994).Linearity was determined using the least-square linear regression with a weighting factor of 1/x2.The mean linear equation established for TAD was y=(0.0050±0.0004)x+(0.0010±0.0001).The precision(%CV)and accuracy values for calibrator concentrations were in the range of 0.10%–3.23%and 96.4%–102.0%,respectively.The limit of detection(LOD)and limit of quantitation(LOQ)for TAD were 0.17ng/mL and 0.50ng/mL at a signal-to-noise ratio of 5 and 14,respectively.The intra-batch precision(%CV)ranged from 1.0%to 3.7%and the accuracy was within 97.9%–102.0%for TAD.Similarly for interbatch experiments,the precision varied from 0.9%to 3.2%and the accuracy was within 97.8%–104.1%(Table S4).
The extraction recovery and matrix effect(expressed as IS-normalized matrix factors,MF)for TAD are presented in Table 1.Highly precise and quantitative recovery in the range of 98.95%–100.61%were obtained across QC levels.The mean recovery of TAD-d3 was 100.12%.The IS-normalized MFs ranged from 0.986 to 1.020.Matrix effect was also checked in lipemic and haemolysed plasma samples.This was determined by examining the precision(%CV)values of the slopes of the calibrations curves prepared from eight different plasma lots,which included six K3EDTA,one lipemic and one haemolysed plasma samples.The%CV of the slopes of calibration lines for relative matrix effect in eight different plasma lots was in the range of 1.2%–1.9%,which is within the acceptance criteria of 3%–4%.
Stock solutions of TAD and TAD-d3 kept for short-term stability remained stable up to 7 h,while the long-term stability of these solutions was determined up to 10 days with no significant change.The stabilities of TAD in human plasma and also in whole blood were estimated under a variety of storage and process conditions.TAD was found stable in controlled blank plasma at room temperature up to 12h and for six freeze-thaw cycles.The analyte in extracted plasma samples was stable for 98 h under refrigerated conditions(5°C)and for 12h at room temperature.The concentration of spiked plasma samples of TAD stored at-20 °C and-70 °C for long-term stability showed no apparent change up to 74 days.Whole blood stability evaluated up to 2h showed no evidence of degradation.The detailed results for stability experiments are presented in Table S5.
3.3.Application to a bioequivalence study
The validated method was successfully applied in a clinical study for the determination of TAD after oral administration of a single dose of 20 mg tablet in 24 healthy Indian volunteers under fasting.The mean plasma concentration–time profiles of TAD obtained for test and reference formulations are shown in Fig.2 and pharmacokinetic parameters estimated using non-compartmental method are shown in Table 2.It was found that TAD was absorbed into the systemic circulation with its peak concentration(396.45 ng/mL)in about 2.37h.The half life(t1/2)for elimination of TAD was 18.6±2.47 h after oral administration.The method demonstrated adequate sensitivity to measure plasma concentration of TAD up to 168h.Comparison of the results with previous reports[8,13]showed no significant changes in any pharmacokinetic parameter.The ratios of mean log-transformed parameters,Cmax,AUC0–168hand AUC0-infand their 90%confidence intervals ranged from 99.2%to 110.9%for TAD,which is within the acceptance criterion of 80%–125%.These results confirm the bioequivalence of the test formulation with the reference product in terms of rate and extent of absorption.Furthermore,the assay reliability test performed with 115 incurred samples showed%change within±15%of the initial results.
4.Conclusions
In summary,a sensitive,accurate and reliable LC-MS/MS method was developed and validated for the quantitation of TAD in human plasma using SPE as the sample clean-up step following current regulatory guidelines.The method is more sensitive than all the existing methods in any biological matrix and has a short turnaround time of 2.5 min.Further,the method provided highly reproducible recovery of TAD with minimal matrix interference.It was successfully applied to a bioequivalence study in healthy subjects with good accuracy and precision.
Conflicts of interest
The authors declare that there are no conflicts of interest.
Acknowledgments
The authors wish to thank the management of Synchron Research Services Pvt.Ltd,Ahmedabad for carrying out this research.
Appendix A.Supplementary material
Supplementary data associated with this article can be found in the online version at doi:10.1016/j.jpha.2018.01.003.
 Journal of Pharmaceutical Analysis2018年4期
Journal of Pharmaceutical Analysis2018年4期
- Journal of Pharmaceutical Analysis的其它文章
- Duplex microRNAs assay based on target-triggered universal reporter hybridization
- Extracellular synthesis of silver nanoparticles by Pseudomonas sp.THG-LS1.4 and their antimicrobial application
- Simultaneous determination of steroid drugs in the ointment via magnetic solid phase extraction followed by HPLC-UV
- Screening potential mitochondria-targeting compounds from traditional Chinese medicines using a mitochondria-based centrifugal ultra filtration/liquid chromatography/mass spectrometry method
- Unusual retention behavior of omeprazole and its chiral impurities B and E on the amylose tris(3-chloro-5-methylphenylcarbamate)chiral stationary phase in polar organic mode
- Recent advances in screening of enzymes inhibitors based on capillary electrophoresis
