Study on the Determination Conditions of Lipase Activity and the Effects of Commercial Detergent Products
Zhang Jian, Yang Yuan
College of Chemistry and Chemical Engineering, Shanxi University, China
Introduction
The proper substrate for enzymatic hydrolysis are usually natural oils, and the hydrolytic site in oil molecule is the ester bond between fatty acid and glycerol.[1]Lipase can hydrolyze hydrophobic triglyceride into hydrophilic diglyceride,monoglyceride, glycerol and fatty acids.[2~5]In view of the special mechanism and specificity of lipase for the degradation of grease dirt, more and more manufacturers began to apply lipase into their high end washing products.[6,7]
Different from other hydrolases, lipase catalytic action occurs in the heterogeneous system. Catalytic properties of lipase is that the water soluble lipase acts on the waterinsoluble oil substrate. The reaction is carried out on phase interface.[8]Reports about the determination of lipase activity at home and abroad are plenty. There are many kinds of methods, such as alkaline titration method,[9]copper soap method,[10]p-nitrophenol method,[11]and so on.The procedure of Copper soap method is that fatty acid produced in the experiment is extracted by benzene and centrifuged first; then, copper acetate as coloring reagent is added into organic phase and centrifuged again;finally, the absorbance of organic benzene solution containing fatty acid copper salt is measured at 710 nm by spectrophotometer to determine the enzyme activity.The process of this method is complicated for the determination of lipase activity, and toxic benzene is involved in the procedure.
P-nitrophenol method is based on p-nitrophenol palmitate as the substrate. The substrate is preheated and enzyme is added. After 10 min of reaction time,trichloroacetic acid is put in immediately and mixed evenly, place stand for 5 min to terminate the reaction.Then, neutralize the pH to the same value as that before reaction by adding NaOH solution. Absorbance at 405 nm is measured to determine the enzyme activity. It turned out that the reaction termination procedure[12]has certain trouble for P-nitrophenol method.
Alkaline titration is based on the neutralization process, in which NaOH solution is employed to neutralize the fatty acids produced during the experiment with phenolphthalein as indicator. The enzyme activity is associated with consumption of NaOH. This method not only is faster than the other two mentioned above, but excludes any other toxic and hazardous substances.
In this paper, we used the alkaline titration method in GB/T 23535-2009 to determine the enzyme activity of lipase. Various influencing factors, such as olive oil volume fraction, temperature and pH, were investigated;and effect of four anionic surfactants and four nonionic ones on lipase activity was studied further. In addition,the applicability of this analytical method for the determination of enzyme activity of lipase in commercial liquid detergents and detergent powders was investigated in detail.
Materials and methods
Reagents and Equipment
Absorbent cotton gauze, Caoxian Hua Lu Health Materials Co., Ltd.; Polyvinyl alcohol (PVA), the degree of polymerization of 1,750 ± 50, analytical grade, Tianjin Dingshengxin Chemical Co., Ltd.; olive oil, analytical grade, Chengdu Kelon Chemical Reagent Factory;ethanol, φ= 95%, analytical grade, Tianjin Yongda Chemical Reagent Co. Ltd.; sodium hydroxide, analytical grade, Beijing chemical plant; potassium hydrogen phthalate, potassium dihydrogen phosphate (KH2PO4),both of analytical grade, Tianjin Beichen Founder Reagent Factory; phenolphthalein, Tianjin Fuchen chemical reagents plant; disodium hydrogen phosphate (Na2HPO4),analytical grade, Tianjin Bodi Chemical Co., Ltd.; liquid detergent and washing powder sample were purchased in domestic market (3 brands). Electronic balance,AR224CN, Ohaus instrument (Shanghai) Co. Ltd.;magnetic stirrer, CJJ-931, Changzhou Guoyu Instrument Manufacturing Co., Ltd.; water bath with temperature control, DZKW-4, Beijing Zhongxingweiye Instrument Co., Ltd.; Kinematica, JJ-2, Jintan Chengxi towering experimental equipment factory.
Preparation of solution [13]
Substrate Preparation
1) 4 g of PVA and 80 mL of water were added into 250 mL beaker, then heated and stirred in boiling water bath until fully dissolved. Then transfer the solution into a 100 mL volumetric flask, and make up to Filtrate with double layer gauze, and keep the filtrate volume.
2) 60 mL of 4% PVA (mass fraction) solution and 20 mL of olive oil were added to JJ-2 tissue crusher. Then treat the mixture for 6 min (3 min stirring for two times, a 5 min interval, 3 min stirring again), until form stable milky white PVA emulsion. The solution should be used right after preparation. If stored in the refrigerator, the solution is valid for 3 ~ 7 days.
Preparation of enzyme to be tested
1) Weigh 1 g of enzyme (accurate to 0.0002 g) in a 100 mL beaker, dissolve the enzyme with a small amount of phosphate buffer solution (KH2PO4-Na2HPO4, pH = 7.5).Stir with a glass rod and pour the supernatant into 100 mL volumetric flask carefully. Add another small amount of phosphate buffer to dissolve the sediment and transfer into the flask again. Repeat this procedure 3 to 4 times.Make up to volume with phosphate buffer. Finally, transfer this solution to JJ-2 tissue crusher, and process for 3 min for the following measurement.
2) The concentration of enzyme must be carefully controlled in the determination to ensure the difference of the consumption of alkali between sample and control in the range of 1~2 mL.
Alkaline titration assay of lipase
Hydrolysis: take two 100 mL Erlenmeyer bottles, add 4.0 mL of the substrate solution and 5.0 mL of the phosphate buffer in the blank bottle (A) and the vial (B). Then, add 15 mL of 95% ethanol in the bottle A and heat it in the water bath (40 ± 0.2)℃ for 5 min. Add 1.0 mL of enzyme solution into bottle A and bottle B, mix immediately, heat in water bath (40 ± 0.2)℃ for 15 min accurately. Add 15.0 mL 95% of ethanol in bottle B only to stop the reaction.
Titration of hydrolyzed fatty acids: pipette 2 drops of phenolphthalein indicator each in the blank and the sample solution, titrate with 0.05 mol / L sodium hydroxide standard solution until the reddish is obtained and kept 30 s unfade as the end of the titration, recording the consumption volume of the sodium hydroxide standard solution. Enzyme activity is calculated as follows:
where,
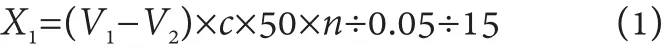
X1: the enzyme activity of the sample, U / g;
V1: the volume of sodium hydroxide standard solution consumed when titrating the sample, mL;
V2: the volume of sodium hydroxide standard solution consumed by blank titration, mL;
c: concentration of the sodium hydroxide standard solution , mol / L;
50: 0.05 mol / L sodium hydroxide solution 1.0 mL(equivalent to 50 μmol of fatty acids);
n: the dilution factor of the sample;
0.05: the sodium hydroxide standard solution concentration conversion factor;
15: reaction time, minute.
The results shall be rounded to integer.
Results and discussion
Determination of lipase activity
Effect of olive oil volume fraction on lipase activity
Lipase analysis method in GB/T 23535-2009 is based on olive oil emulsion as a substrate. The main component of olive oil is triglycerides, the mass fraction is about 98.5%. The saponification value of olive oil used in the experiment is from 190 to 195 mg / g (KOH, the same below). This saponification value can be inferred that the fatty acid chain length of olive oil is about C16. Usually iodine value reflects the unsaturated degree of oil. The iodine value of olive oil is in between 79 ~ 88 mg / g. The olive oil used in the experiment is non-drying oil (It refers to the oil which can not be oxidized in the air to form a solid dry film. Olive oil is yellow liquid, the iodine value below 100 mg / g , its main component is fatty acid triglyceride). The acid value of olive oil, less than 2 mg / g,reflects the freshness of grease, indicating that the olive oil used in the experiment contains little free fatty acids and oil is not oxidized to rancidity. The hydrolyzation formula of triglyceride by lipase is as follows:
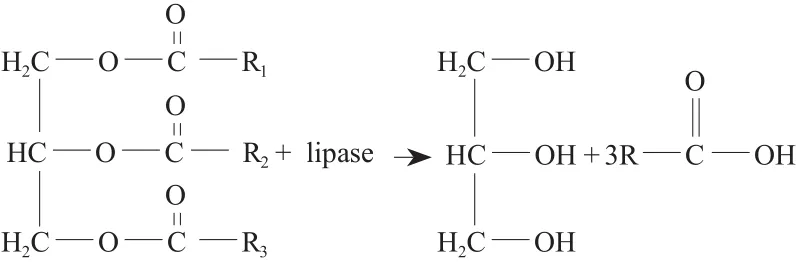
Lipase can hydrolyze triglycerides of olive oil into glycerol and fatty acids. The fatty acids produced during the experiment is titrated by NaOH solution. Lipase hydrolyzes olive oil emulsion per minute to produce 1 μmol fatty acids, by which the consumed amount of alkali determines the enzyme activity of lipase.

The olive oil emulsion used in the experiment was prepared by mixing olive oil and PVA in a volume ratio of 1 : 3. This is because the ratio of olive oil to PVA has some effects on the stability of the emulsion. The emulsions with the volume fraction of olive oil as low as possible were selected to prolong the storage time and simplify the repeated preparation, in the premise of ensuring the accuracy of the determination results. The emulsions containing 5%,10%, 20%, 25%, 30% and 35% olive oil were prepared for the determination of lipase activity. The effects of olive oil volume fraction on lipase activity were investigated at 40℃and pH=7.5. The results are shown in Table 1.
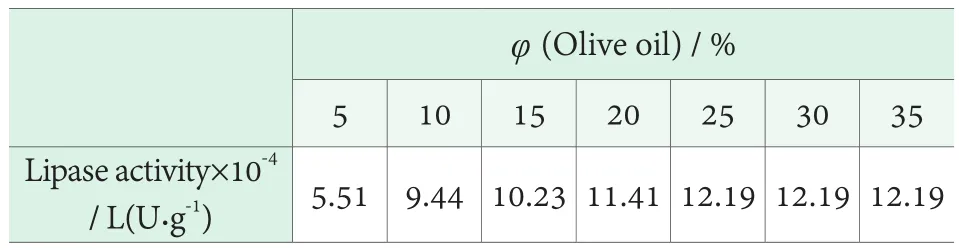
Table 1. Effect of volume fraction of olive oil on lipase activity
It can be seen from Table 1 that when the volume fraction of olive oil was 5%~25%, the activity of lipase increased with the increase of the volume fraction of olive oil. When the volume of olive oil was 25%, the activity of lipase reached the maximum. The lipase activity was no longer increased when the volume fraction of olive oil was increased further. This is because the lipase catalytic reaction exists enzyme saturation phenomenon. When the volume fraction of olive oil is less than 25%, the olive oil does not fully saturate lipase, so the enzyme activity increases with the increase of substrate concentration.However, when the olive oil volume is more than 25%,the substrate is overdosed and the lipase is completely saturated. At the same time, the enzyme catalytic reaction has nothing to do with the substrate concentration.Therefore, when the amount of emulsions is the same, the volume fraction of olive oil is determined to be 25% in the experiment.
Effect of temperature on lipase activity
The effect of temperature on the activity of lipase was investigated by changing the temperature of water bath in the condition that the volume fraction of olive oil was 25%and pH=7.5. The results are shown in Table 2. It can be seen from Table 2, when the lipase in low temperature, the enzyme activity increased with the increase of temperature.When the temperature reached 40℃, the enzyme activity was the maximum. The enzyme activity decreased gradually with increasing temperature. Therefore, the reaction temperature was determined to be 40℃.
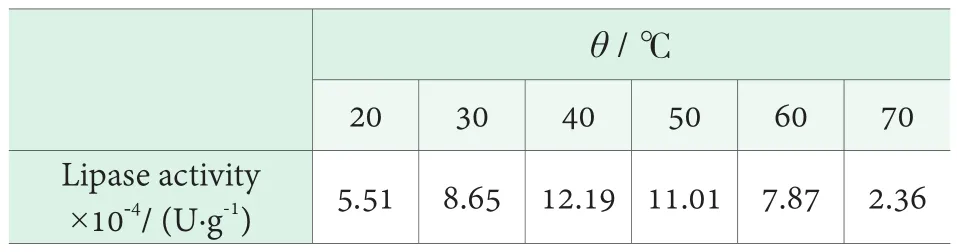
Table 2. Effect of temperature on the activity of lipase
Effect of pH on lipase activity
The effect of pH on the lipase activity was investigated by using buffer solution with different pH when the volume fraction of olive oil was 25% and the temperature at 40℃. The results are shown in Table 3. As can be seen from Table 3, the lipase activity was highest in pH=7.5.
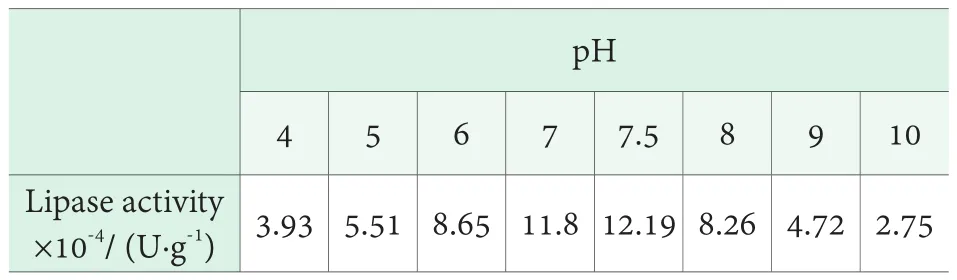
Table 3. Effect of pH on the activity of lipase
The effect of surfactant type on the determination of lipase activity
The main active ingredients in the detergent formulation are surfactants, which accounts for about 30% of total.Therefore, before the study of the applicability of this method for the detergent, it is important to investigate the effects under the background of surfactants.
The effect of anionic surfactants
The anionic surfactant was added during the preparation of the enzyme, and the Linear Alkylbenzene Sulfonates (LAS), Sodium laurylsulfonate (LS), Sodium Alcohol Ether Sulphate (AES) were taken as examples.The effects of four kinds of anionic surfactants on determination method of lipase were studied in the condition of the volume fraction of olive oil as 25% , the temperature at 40℃ and pH=7.5. The results are shown in Figure 1.
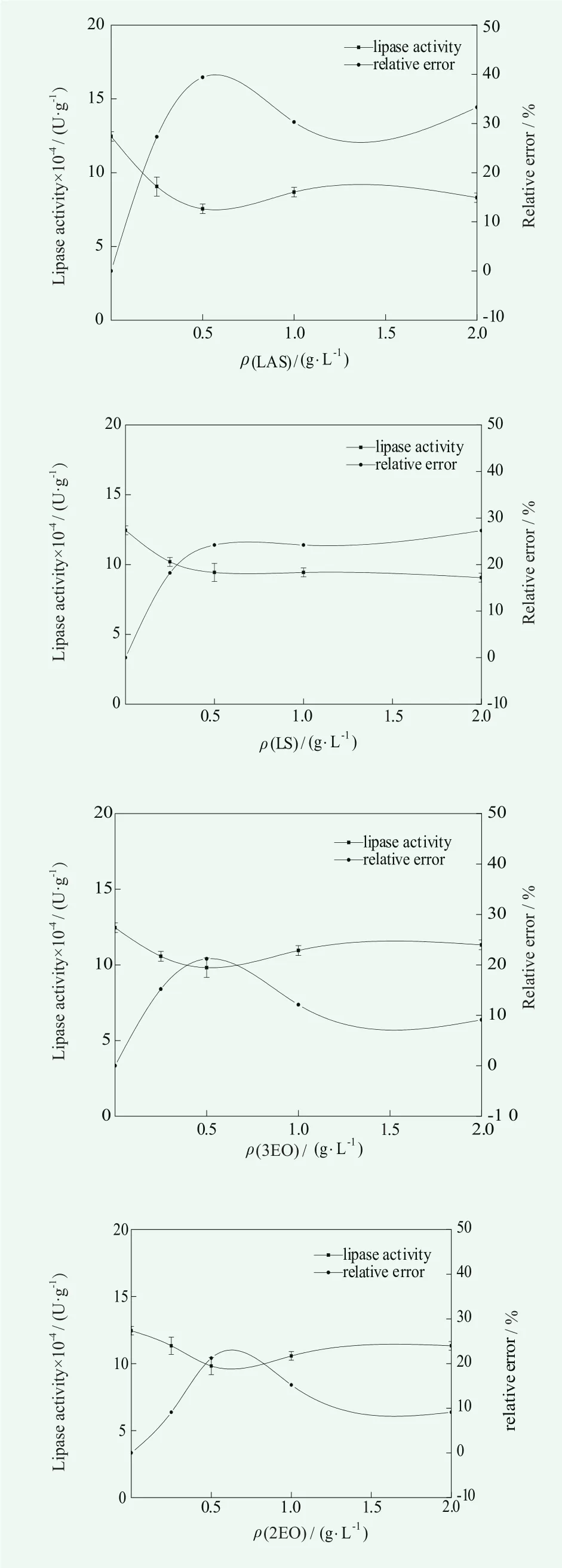
Figure1. Effect of anionic surfactants on the determination of lipase activity
In combination with the enzyme activity and relative error in Figure 1, it can be seen that the order of influence of anionic surfactant on the lipase activity is LAS>LS>AES (3EO) >AES (2EO). For LAS, its critical micelle concentration is 0.4 g/L. When the amount of LAS is lower than the critical micelle concentration, which was ρ(LAS)=0.25 g / L, the relative error of the enzyme activity compared with that of no surfactant was 27.3%.About LS, the relative error was only 18.2% in the same condition. The reason may be related to the structure of benzene ring of LAS. The sulfonation of aromatic nucleus will greatly enhance the amphipathy of LAS, which makes LAS exhibit better surface activity than other surfactants, resulting in a greater effect of LAS on lipase.Above the critical micelle concentration, the deviation of the LAS and LS did not show a gradual increase trend,but gradually became stabilized. In the AES series, the enzyme activity changed little with the change of mass concentration and the relative error was about 10%.
Four kinds of anionic surfactants have different effects on the determination of lipase, which may be due to the different electrostatic attraction between the four anionic surfactants and lipase.
The effect of nonionic surfactants
The nonionic surfactant was added during the preparation of enzyme, and the Primary Alcobol Ethoxylate(AEO Series) was taken as an example. The effects of four kinds of nonionic surfactants on determination method of lipase in the condition of the volume fraction of olive oil as 25% , the temperature at 40℃ and pH=7.5. The results are shown in Figure 2.
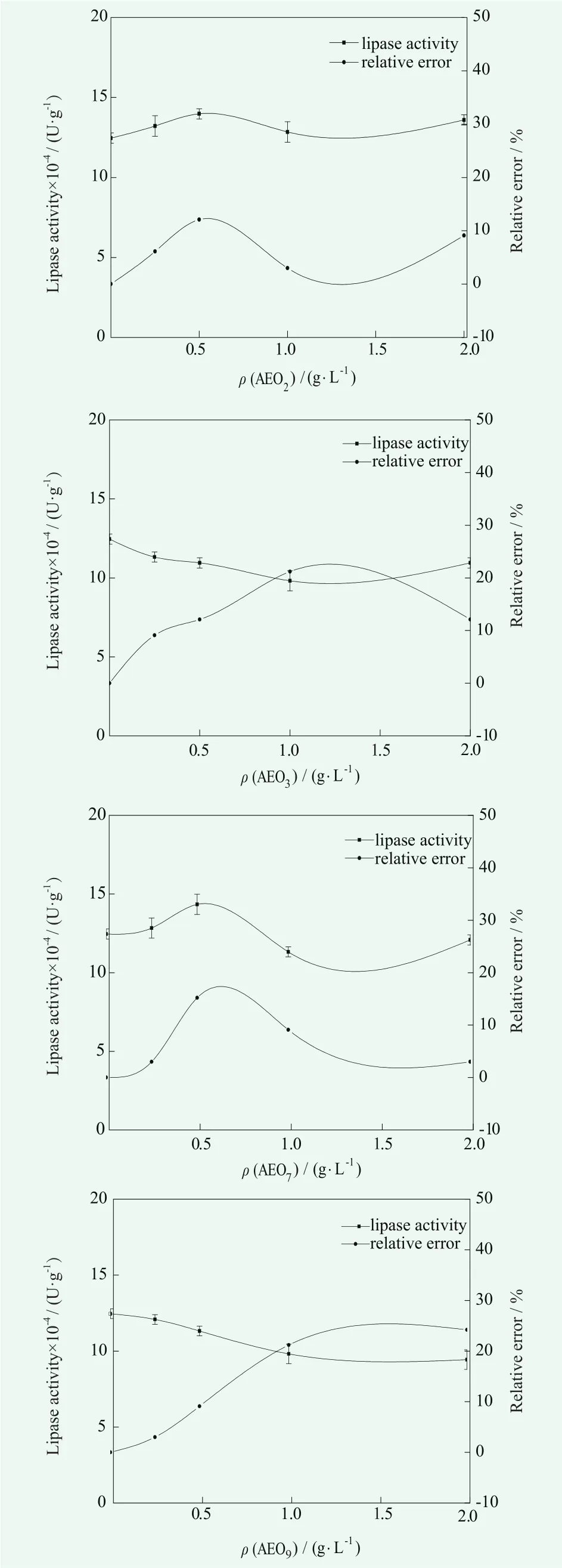
Figure 2. Effect of nonionic surfactants on the determination of lipase activity
According to the enzyme activity and relative error in Figure 2, we can see that the influence of nonionic surfactant on the lipase activity is AEO3>AEO9>AEO7>AEO2.Compared with anionic surfactant, the effect of nonionic surfactants on determination method of lipase activity is relatively small. Probably because the nonionic surfactant does not produce ions in aqueous solution. Its hydrophilic groups interact with lipases through hydrogen bonding.This effect does not have a strong effect on the spatial conformation of the lipase and its active site.
Determination of enzyme activity in washing products
Determination of enzyme activity in liquid detergent
Three kinds of commercially available liquid detergents without lipase were selected, then the lipase with the mass fraction of 1% was added to the liquid detergents. Under the condition that the volume fraction of olive oil was 25%, the temperature was 40℃ and pH = 7.5, the determination of lipase activity in liquid detergents were studied. The results are shown in Figure 3.
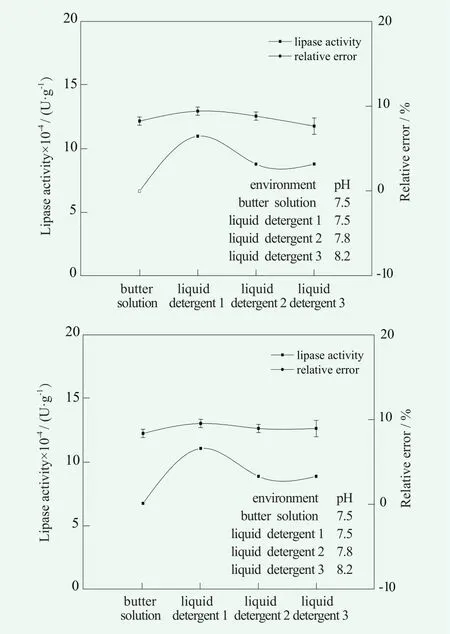
Figure 3. The accuracy and precision of lipase activity in liquid detergent
As can be seen from Figure 3, before adjusting the pH of the buffer, the enzyme activity of lipase in the liquid detergent solution of 1, 2 and 3 was slightly different from that in the buffer solution, the deviation was only 7,867, 3,934 and 3,933 U/g, respectively. At the same time, the relative error was less than 10% and the precision was good. After adjusting pH, the accuracy and precision did not change much. In the presence of liquid detergent, although the pH was similar, the lipase activity was different because of the interference of different components in liquid detergents with the determination of enzyme activity.
Determination of enzyme activity in washing powder
Three kinds of commercially available washing powders without lipase were selected, then the lipase with the mass fraction of 1% was added to the washing powders. Under the condition that the volume fraction of olive oil was 25%, the temperature was 40℃ and pH = 7.5,the determination of lipase activity in washing powder were studied. The results are shown in Figure 4.
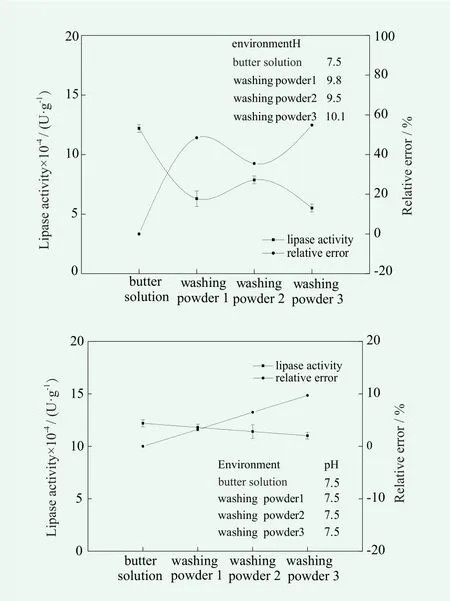
Figure 4. The accuracy and precision of the lipase activity in the washing powder
As can be seen from Figure 4, before adjusting the pH of the buffer, the enzyme activity of lipase in the washing powder solution of 1, 2 and 3 was widely different compared with that in the buffer solution, the deviation was 59,000, 43,266 and 66,866 U / g, respectively. The accuracy was low, the main reason is that pH has a great influence on the determination of enzyme activity. At the same time, the relative error is relatively large, the maximum was 54.8%, thus the precision was poor.Therefore, a further study on the determination of enzyme activity in laundry powder was carried out, namely adjusting the pH value of 3 kinds of washing powder commercially available stable at 7.5. It was found that the measured enzyme activity in commercially available washing powder 1, 2 and 3 was slightly different from that in the buffer solution, the variance was only 3,933, 7,866 and 11,800 U / g, respectively.The accuracy was better than before with a obvious rise,relative errors were controlled within 10%. After adjusting pH, the difference of lipase activity between the presence and the absence of detergent powder was analyzed, and was found the same as that of liquid detergent.
The results showed that the method can be used for the determination of lipase activity in liquid detergent and washing powder, but the temperature and pH of detergent or washing powder solution should be strictly controlled.
Conclusion
The activity of lipase were determined by the alkaline titration method (GB/T 23535-2009). Under the condition that the volume fraction of olive oil was 25%, temperature was 40℃ and pH = 7.5, the effects of anionic and nonionic surfactants on the determination of lipase activity were investigated. The experimental results showed that the influence of anionic surfactants on the determination of lipase activity is greater than that of nonionic surfactant. The method was applied to the determination of lipase activity in commercially available washing products. The results showed that the method could be used for the determination of lipase activity in liquid detergent and washing powder, but the temperature and pH of detergent or detergent solution should be strictly controlled.
Fund project
2016 annual Shanxi Province key research and development projects international cooperation projects(201603D421029)
[1] Wei Yutuo; Teng Kun. Advance in molecular structure and application of lipase. Guangxi Sciences 2014, 21 (2),93-98.
[2] Dong Rong. Study on application of penicillium lipase in washing and decontamination. China Surfactant Detergent and Cosmetics 1991, 21 (5), 1-5.
[3] Maria H.; Guo Jing. A new type of lipase with a washing effect:Lipex. China detergent industry 2004, (1), 44-46.
[4] Chen Guiyuan; Wei Yunlin. The research status and application prospect of cold-adapted lipases. Biotechnology Bulletin 2006,(2), 29-32.
[5] Yang D. J.; Qiu X. Q.; Chen H. Q. Studies on the application of lipase in detergency. Journal of South China University of Technology (Natural Science Edition) 2002, 30 (1), 75-78.
[6] Zheng Yi; Ye Haiyan; Wu Chaoyuan; et al. Progress in the determination of lipase activity. Industrial Microbiology 2005,35 (4), 36-40.
[7] Wu Manjun. Multi-enzyme in household detergents. China Detergent Industry 2001, (2), 18-25.
[8] Delorme V.; Dhouib R.; Canaan S.; et al. Effects of surfactants on lipase structure, activity, and inhibition. Pharmaceutical Research 2011, 28 (8), 1831-1842.
[9] Jiang Huifang;Wang Yaqin; Liu Chunguo. Comparison and improvement of three determination methods for lipase activity. Chemistry Bio-engineering 2007, 24 (8), 72-75.
[10] Hou Aijun; Xu Bingbin; Liang Liang; et al. Improvement of determination of lipase activity by copper soap spectrophotometry. Leather Science and Engineering 2011, 21 (1), 22-27.
[11] Lei Qiyi; Zou Kai; Zhou Jiangju; et al. Determination of lipase activity and its comparison. Journal of Carey College 2011, 29(6), 43-45.
[12] Teng Kun; Zhang Jifu; Niu Fuxing; et al. Comparative analysis of the methods for termination of lipase activity determination. Guangxi Science 2014, 21 (2), 115-118.
[13] China National Standardization Administration Committee.Lipase preparation: GB/T 23535-2009. State Administration of Quality Supervision, Inspection and Quarantine, 2009.
 China Detergent & Cosmetics2017年2期
China Detergent & Cosmetics2017年2期
- China Detergent & Cosmetics的其它文章
- Research Progress for Kitchen Cleaner
- Evaluation for Whitening Efficacy of Cosmetics Containning Extract from Tricholoma Matsutake Sing
- Formation of Stable Lamellar Gel Structure Containing Pseudoceramide and Its Evaluation of Barrier Recovery Function
- Trend of the Latest Regulation—Efficacy Claims of Cosmetics
- Interpretations on Safety and TSSC for Cosmetics
- China National Standard—Technical Specification for Safety of Soaps and Detergents(GB/T 26396-2011)
