Establishment and evaluation of the primary cultured tibial osteoblast model of broiler chicks
CAO Su-mei ,Ll Ting-ting ,SHAO Yu-xin ,ZHAO Yu-zhen ,ZHANG Li-yangLU LinZHANG Ri-jun,HOU Shui-shengLlAO Xiu-dongLUO Xu-gangWANG Run-lian
1 Poultry Mineral Nutrition Laboratory,College of Animal Science and Technology,Yangzhou University,Yangzhou 225000,P.R.China
2 Mineral Nutrition Research Division,State Key Laboratory of Animal Nutrition,Institute of Animal Sciences,Chinese Academy of Agricultural Sciences,Beijing 100193,P.R.China
3 Laboratory of Feed Biotechnology,State Key Laboratory of Animal Nutrition,College of Animal Science and Technology,China Agricultural University,Beijing 100193,P.R.China
4 Department of Animal Science,Guangdong Ocean University,Zhanjiang 524088,P.R.China
Abstract Osteoblasts are considered as a major factor contributing to bone development and mineralization,however,few studies have been done to establish and evaluate the primary cultured tibial osteoblast model of broiler chicks.Therefore,in the present study,two experiments were conducted to establish and evaluate the primary cultured tibial osteoblast model of broiler chicks.In experiment 1,osteoblasts were isolated from the tibia of one-day-old Arbor Acre male broiler chicks using the explant method and identified through the cell morphology,alkaline phosphatase (ALP) and alizarin red staining.Experiment 2 was carried out to evaluate the vitality and mineralization of primary cultured tibial osteoblasts of broilers on days 4,8,12,16,20,24,28 and 32 after incubation,respectively.The results from experiment 1 demonstrated that primary cultured tibial osteoblasts of broilers showed a spindle-shaped,triangular or polygonal morphology.More than 95% of the cells were stained blue-black after ALP staining,and mineralized nodules were formed after 4 days of continuous incubation.In experiment 2,lactate dehydrogenase (LDH) activity stayed at a relatively stabilized level although incubation time affected (P=0.0012) it during the whole culture period.Additionally,incubation time affected(P≤0.0001) the number and proportion of the area of mineralized nodules.They increased linearly and quadratically(P<0.04) with the increase of incubation time,and remained at a stabilized level from 24 to 32 days of incubation.The estimates of the optimal incubation time were 17 and 26 days based on the best fitted broken-line or quadratic models(P<0.0001) of the number and proportion of the area of mineralized nodules,respectively.These results indicate that the primary cultured tibial osteoblast model of broilers has been established successfully by the explant method,and it showed typical osteoblast morphology and characteristics of ALP activity and mineralization,and could maintain a relatively stabilized vitality from 4 to 32 days of incubation;and the optimal incubation time of primary tibial osteoblasts was 17 to 26 days.Therefore,it could be used to further study the underlying mechanisms of bone development and mineralization of broiler chicks.
Keywords: broiler,tibial osteoblast,primary culture,vitality,mineralization
1.lntroduction
Over the past decades,constant improvements in genetic selection and nutrition have led to a fast growth rate in broiler chickens,but early fast growth rate is generally accompanied by a high incidence of leg problems as bone development can not keep pace with such a fast rate of increase in body weight (Thorp 1994;Williamset al.2000;Sanchez-Rodriguezet al.2019).Bone is a living tissue and the homeostasis in the skeletal system is maintained by coupling between bone-forming osteoblasts and boneresorbing osteoclasts,and the osteoblasts are considered as a major factor contributing to bone development and mineralization (Sanchez-Rodriguezet al.2019;Shaoet al.2019;Liet al.2020).Many studies have indicated that the primary cultured osteoblasts from newborn animals could retain more somatic cell functional characteristics and simulate biological changes compared with cell lines (Zhouet al.2013;Liet al.2015).Therefore,many researchers have established biological models for the study of bone development and metabolismin vitrousing the primary cultured osteoblasts (Guoet al.2011;Zhanget al.2015;Songet al.2017).The osteoblasts could be isolated from the calvarias,iliac cancellous bone,cervical bone and femurs of humans,rats,mice and rabbits using a sequential enzymatic digestion method,explant method or the combined method of the above two methods (Caoet al.2006;Liet al.2015;Chenet al.2017;Zhaoet al.2020),and also derived from mesenchymal stem cells in mice (Harada and Rodan 2003;Tanget al.2018).In addition,several studies also showed that the primary cultured osteoblasts of broilers could be obtained from chicken embryonic calvariae and cortical bone using enzyme digestion method (Guoet al.2011;Zhanget al.2015) or obtained from chicken mesenchymal stem cells (Adhikariet al.2018).Generally,the osteoblasts could be identified through alkaline phosphatase (ALP)activity and mineralized nodule formation (Kirschet al.1997;Liet al.2015).The ALP is one of the most frequently used biochemical markers of osteoblast activity(Magnussonet al.1999;Guoet al.2011),and it can hydrolyze phosphate ester to provide the phosphorus for promoting the hydroxyapatite formation (Janckilaet al.2001).Osteoblast mineralization is an important osteoplastic link and specific biological process of the bone in which calcium and phosphorus deposition occurs(Kirschet al.1997;Songet al.2017).Additionally,lactate dehydrogenase (LDH) activity is an indicator of osteoblast integrity and function (Sahaet al.2019;Krugeret al.2021).A previous study demonstrated that the LDH assay could be used to measure the cell vitality of human osteoblasts for 3 days (Krugeret al.2021);it was reported in other studies that the vitality of rat osteoblasts could be maintained for up to 7,14,21 or 28 days,and the mineralization could increase with the increase of incubation time (Zhanget al.2014;Songet al.2017).However,the vitality and mineralization of primary cultured tibial osteoblasts of broiler chicks at the different incubation times remain unclear.Therefore,this study aimed to establish the primary cultured tibial osteoblast model of broiler chicks and evaluate its osteoblast vitality and mineralization at the different incubation times.
2.Materials and methods
2.1.Reagents
Dulbecco’s modified eagle’s medium (DMEM) and 0.25% trypsin were purchased from Zhongke Maichen Technology Co.,Ltd.(Beijing,China).Dulbeccos phosphate-buffer saline (D-PBS),5 000 U mL-1penicillin,5 000 μg mL-1streptomycin,fetal bovine serum (FBS)and L-glutamine were purchased from Thermo Fisher Scientific Co.,Ltd.(Waltham,MA,USA).The NBT/BCIP ALP Color Development Kit was purchased from Beyotime Biotechnology (Shanghai,China).The 4%Paraformaldehyde and Alizarin Red Staining Kit were purchased from Beijing Solarbio Technology Co.,Ltd.(Beijing,China).The LDH Assay Kit was purchased from Nanjing Jiancheng Bioengineering Institute (Nanjing,China).
2.2.Animals,experimental design and treatments
One-day-old Arbor Acres male broiler chicks (Huadu Broiler Breeding Corporation,Luanping,China) were used to isolate tibial osteoblasts.Experiment 1 was carried out to establish the primary cultured tibial osteoblast model of broiler chicks.Experiment 2 was carried out in a completely randomized design to evaluate the vitality and mineralization of primary cultured tibial osteoblasts of broilers on days 4,8,12,16,20,24,28,and 32 after incubation,respectively.These time points were determined by the initial and maximum formed times of mineralized nodules according to some previous studies (Songet al.2017;Yuet al.2017).
2.3.lsolation and culture of primary tibial osteoblasts of broilers
Tibial osteoblasts from one-day-old Arbor Acre male broiler chicks were isolated according to a modified procedure (Guoet al.2011;Adhikariet al.2018).Briefly,the birds were killed by cervical dislocation,and then soaked in alcohol for 2 min as described by Adhikariet al.(2018).Legs were removed from hip joint and metacarpal,and then muscles and connective tissues around the tibia were removed immediately using a scalpel and micro-dissecting scissors and kept in DMEM in a bio-safety cabinet.The cleaned tibia was placed in washing buffer containing D-PBS with 1% 5 000 U mL-1penicillin and 5 000 μg mL-1streptomycin.The bones were cracked with a scalpel and washed three times with the aforementioned washing buffer,and the tibia bone specimens were minced into small pieces about 1-3 mm3in size.The tibia bone fragments were seeded evenly on 60-mm cell culture dishes (Corning Incorporated,Corning,NY,USA) with 5 mL medium composed of 83% DMEM,15% FBS,1% L-glutamine,and 1% 5 000 U mL-1penicillin and 5 000 μg mL-1streptomycin at 37°C with 5% CO2and 95% air.Once most of the bone fragments were covered with cells,the cells were washed twice with 5 mL D-PBS,dissociated with 0.25% trypsin for 1-3 min and subcultured at a ratio of 5×105cells mL-1in 6-well cell culture plates (Corning Incorporated).The fresh media were replaced every other day.
2.4.Morphology observation and identification of primary tibial osteoblasts of broilers (experiment 1)
When bone fragments were seeded and cultured for 3 and 6 days,cell morphology was determined and photographed to understand their morphology and growth characteristics.The cells from bone fragments were washed twice with 5 mL D-PBS,dissociated with 0.25% trypsin for 1-3 min and subcultured at a ratio of 5×105cells mL-1in 6-well cell culture plates (Corning Incorporated) at 6 days of culture,and once the subcultured cells were incubated for 2 days and reached 80-90% confluency,these cells were washed with D-PBS and fixed in 4% paraformaldehyde for 10 min in a 6-well plate.Then they were washed with D-PBS again,and finally stained and identified using NBT/BCIP ALP Color Development Kit.Alizarin Red Staining Kit was used to stain and observe the mineralized nodules at 3 and 4 days of incubation.All of the above stained cells were visualized using the Phase Contrast Microscope (Olympus CKX41,Tokyo,Japan).
2.5.Evaluation of primary tibial osteoblasts of broilers (experiment 2)
Once the cells reached 80-90% confluency,the cells were continually incubated for 4,8,12,16,20,24,28 and 32 days.There were three replicates for each incubation time point and two cell culture wells per replicate.The LDH activity in the culture medium was measured to evaluate the viability of primary cultured tibial osteoblasts.The culture media of the osteoblasts were collected at each time point,and stored at -20°C for further analysis.The LDH activity was measured using a commercial assay kit in accordance with the manufacturer’s instruction.The mineralized nodules of the osteoblasts in each well for each time point were stained by the alizarin red solution,and then were analyzed for their numbers by visual counting under the Phase Contrast Microscope(Olympus CKX41,Tokyo,Japan) and the proportions of the areas by Imaging Software (Liet al.2015).
2.6.Statistical analyses
Data were analyzed by one-way ANOVA with the general linear model (GLM) procedure of SAS (version 9.4;SAS Institute Inc.,Cary,NC),and differences among means were tested by the least significant difference(LSD) method.Orthogonal polynomials were applied for linear and quadratic effects of dependent variables to independent variables.Regression analyses of brokenline,quadratic and asymptotic models were performed,and the best fitted models between responsive criteria and incubation time were used to determine the optimal incubation time (the break point from the broken-line model or the maximum response from the quadratic model) (Maet al.2016).Each replicate served as an experimental unit,and statistical significance was set atP≤0.05.
3.Results
3.1.Cell morphology (experiment 1)
The tibial fragments were cultured for 3 days,and the cells showed a spindle-shaped,triangular or polygonal morphology (Fig.1-A).Then they continued to be incubated for 6 days,and most of the tibial fragments were surrounded by cells and formed growth halo(Fig.1-B).
3.2.ldentification of primary tibial osteoblasts(experiment 1)
The tibial osteoblasts from broiler chicks were identified through cytochemical staining (Fig.1-C).More than 95% of the cells were stained blue-black after ALP staining.The tibial osteoblasts exhibited the synthesis and secretion of ALP,and only the differentiated mature osteoblasts expressed ALP.The cells could form mineralized nodules at 4 days of continuous incubation(Fig.1-D).The staining results showed that the osteoblast differentiation was homogeneous and more than 95%cells were positive.

Fig.1 Isolation and identification of primary cultured tibial osteoblasts of broilers (experiment 1).A,the cells were cultured for 3 days (×40).B,the cells were cultured for 6 days (×40).C,alkaline phosphatase (ALP) staining when the cells were cultured for 2 days and reached 80-90% confluency (×40).D,alizarin red staining when the cells were cultured for 4 days and reached 80-90% confluency (×40).
3.3.LDH activity assay (experiment 2)
The LDH activity in the culture medium of the primary tibial osteoblasts was shown in Fig.2-A.Incubation time affected (P=0.0012) the LDH activity in the culture medium,but it did not change linearly and quadratically(P>0.51) with the increase of incubation time,while it stayed at a relatively stabilized level during the whole culture period.
3.4.Mineralized nodule formation of primary tibial osteoblasts and estimation of the optimal incubation time (experiment 2)
The number and the proportion of the area of mineralized nodules of primary cultured tibial osteoblasts were shown in Fig.2-B and C.Incubation time affected(P≤0.0001) the number and the proportion of the area of mineralized nodules,and they both increased linearly and quadratically (P<0.04) with the increase of incubation time.They increased from 4 to 20 days and then remained at a stabilized level during 24 to 32 days of incubation.Results of the optimal incubation time as estimated by the non-linear regression analyses are shown in Fig.3.The results indicate that the number and the proportion of the area of mineralized nodules of primary cultured tibial osteoblasts were suitable criteria for evaluating the optimal incubation time.Based on the best fitted broken-line or quadratic models of the above criteria,the optimal incubation time was estimated to be 17 and 26 days,respectively.
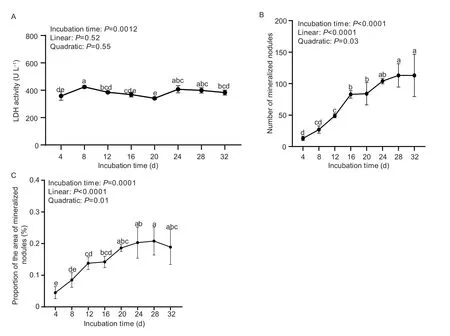
Fig.2 Effect of incubation time on the vitality and mineralization of primary cultured tibial osteoblasts of broilers (experiment 2).A,lactate dehydrogenase (LDH) activity.B,the number of mineralized nodules.C,the proportion of the area of mineralized nodules.All values were expressed as mean±SD (n=3).Lacking the same letters (a,b,c,d,or e) differs (P<0.05).
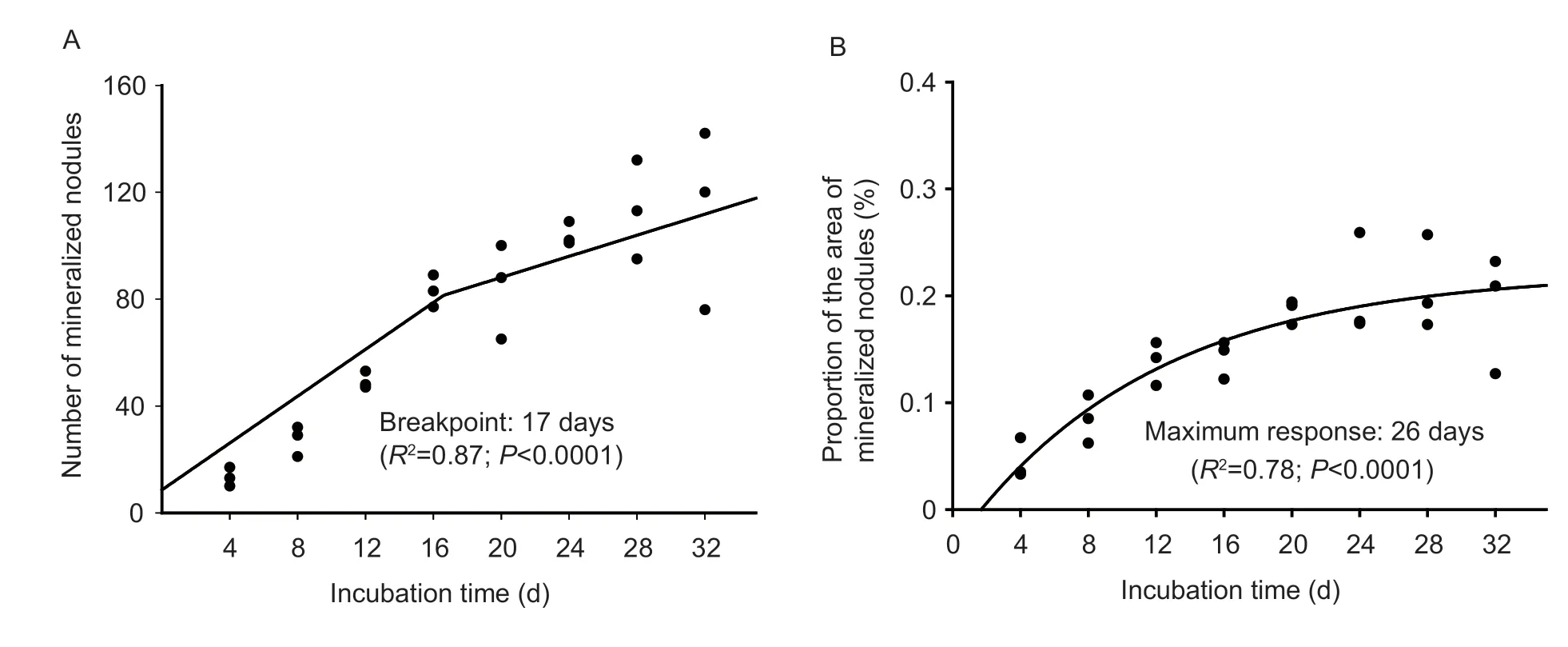
Fig.3 Estimation of the optimal incubation time based on the best fitted broken-line or quadratic models (experiment 2).A,the relation between incubation time and the number of mineralized nodules.B,the relation between incubation time and the proportion of the area of mineralized nodules.
4.Discussion
The major function of osteoblasts is to produce the organic constituents of the bone extracellular matrix that facilitate its mineralization by inorganic compounds(Shapiro and Heaney 2003;Heaney 2004).Our previousin vivostudies have indicated that the bone development and mineralization might be regulated by related hormone,local-derived regulators as well as bone morphogenetic protein (BMP) and mitogen-activated protein kinase (MAPK) signing pathways in the tibia of broiler chicks (Shaoet al.2019;Caoet al.2021;Liaoet al.2022).Furthermore,in the current study,we have successfully established thein vitroprimary cultured tibial osteoblast model of broilers and evaluated the optimal incubation time for the vitality and mineralization of tibial osteoblasts,which provided a good model for further studying the underlying mechanisms of bone development and mineralization in primary cultured tibial osteoblasts of broilers.
Several methods for the isolation of primary osteoblasts have been established,including enzymatic digestion method,explant method or the combined method of these above two methods (Caoet al.2006;Guoet al.2011;Czekanskaet al.2012).It was reported that the primary osteoblasts obtained through enzymatic isolation could proliferate faster than the cells obtained from other methods,but it is also easy to get contaminated by this method (Voegeleet al.2000).The combined method could eliminate some fibroblast cells and loose the bone tissue to enable osteoblasts to creep out easily.The explant method is simple to operate and make less damage to the cells,but it might take a long time to obtain the osteoblasts (Caoet al.2006).Therefore,we selected the explant method for the isolation of tibial osteoblasts of broilers.Additionally,ALP and alizarin red staining assays were performed to identify the tibial osteoblasts of broilers.The ALP is one of the most frequently used biochemical markers of the osteoblast activity and differentiation (Magnussonet al.1999),and mineralization function is a necessary condition of osteoblasts to form bone calcification eventuallyin vitro(Birminghamet al.2012).Our previousin vivostudy indicated that tibia ALP had a positive correlation with BMP and MAPK signaling pathways (Liaoet al.2022).The present study showed that the isolated cells had typical osteoblast morphology as well as characteristics of ALP activity and mineralization,which was in agreement with several previous studies in chickens (Guoet al.2011;Minet al.2019),indicating that primary cultured tibial osteoblast model of broiler chicks has been established successfully by the explant method.Additionally,the cell morphology was similar between chick osteoblasts and other animal osteoblasts with the spindle-shaped,triangular or polygonal morphology (Caoet al.2006;Minet al.2019).However,there are some differences in culture characteristics between chick osteoblasts and other animal osteoblasts,such as different bone tissues,different digestion methods and cultured time (Songet al.2017;Yuet al.2017).
The LDH activity is an indicator of cellular integrity and function,and is usually used to evaluate the damage of the osteoblasts and other cells (Krugeret al.2021;Leiet al.2021).Increased enzymatic activity is a consequence of disruption in cell membrane function and permeability (Xiaet al.2010;Qinet al.2017).In the present study,LDH assay was performed to evaluate the effect of incubation time on the viability of osteoblasts from 4 to 32 days.It was found that the LDH activity stayed at a relatively stabilized level although incubation time affected it during the whole culture period,indicating that the osteoblasts showed a stabilized activity up to 32 days of incubation.Bone mineralization is a complex process modulated by organic macromolecules under cellular control (Czekanskaet al.2012).It is reported that the osteoblasts isolated from rat tibia formed mineralized nodules after 41 days (Stringaet al.1995).Other studies also demonstrated that the osteoblasts from rat calvarial bones were cultured for 7,14,21 and 28 days,and the extent of mineralization increased continuously (Nefussiet al.1985;Zhanget al.2014;Song et al.2017;Yuet al.2017),which is similar to our present study.The results from the present study indicated that the number and the proportion of the area of mineralized nodules increased linearly and quadratically with the increase of incubation time,and tended to stabilize from 24 to 32 days of incubation,and the optimal incubation time of primary tibial osteoblasts of broiler chicks was estimated to be 17 to 26 days.These results have been not reported in poultry before.The present study provides a new primary cultured tibial osteoblast model for further studying the underlying mechanisms of bone development and mineralization of broilers.
5.Conclusion
The results from the present study indicate that the primary cultured tibial osteoblast model of broilers has been established successfully by the explant method,and it showed typical osteoblast morphology and characteristics of ALP activity and mineralization,and could maintain a relatively stabilized vitality from 4 to 32 days of incubation;and the optimal incubation time of primary tibial osteoblasts was 17 to 26 days.Therefore,it could be used to further study the underlying mechanisms of bone development and mineralization of broilers.
Acknowledgements
The present study was supported by the Key Program of the National Natural Science Foundation of China(31630073),the Initiation Funds of Yangzhou University for Distinguished Scientists,China,and the Agricultural Science and Technology Innovation Program of the Chinese Academy of Agricultural Sciences (ASTIP-IAS09).
Declaration of competing interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Ethical approval
All experimental procedures were approved by the Animal Management Committee (in charge of animal welfare) of the Institute of Animal Sciences,Chinese Academy of Agricultural Sciences (IAS-CAAS,Beijing,China) and performed in accordance with the guidelines.Ethical approval on animal survival was given by the animal ethics committee of IAS-CAAS.We have followed the ARRIVE guidelines for reporting animal research (Kilkennyet al.2010).
 Journal of Integrative Agriculture2023年2期
Journal of Integrative Agriculture2023年2期
- Journal of Integrative Agriculture的其它文章
- A 314-bp SlNE insertion in the ZNF2 promoter region may act as a repressor related to regulation of fat deposition in pigs
- An optimized protocol using Steedman’s wax for high-sensitivity RNA in situ hybridization in shoot apical meristems and flower buds of cucumber
- Characterization of subunits encoded by SnRK1 and dissection of combinations among these subunits in sorghum (Sorghum bicolor L.)
- The role of time preferences in contract breach: Evidence from Chinese poultry farmers participating in contract farming
- Optimal design of culling compensation policy under the African swine fever — Based on simulations of typical pig farms in China
- Drip fertigation and plant hedgerows significantly reduce nitrogen and phosphorus losses and maintain high fruit yields in intensive orchards
