Research on the Impact of Venture Risk Tolerance on R&D Investments:Based on Entrepreneur Ability
Weng Yaqin
Sichuan Academy of Social Sciences
Han Wucheng*
University of Electronic Science and Technology
Abstract: How do start-ups enhance risk tolerance and core competition through product, technology, and service development? What is the relationship between the core competitiveness of start-ups and R&D investments?Based on the perspective of entrepreneurial ability, 222 questionnaires were used to study the factors affecting the risk tolerance of start-ups and analyze the effect of risk tolerance on R&D investments.The research shows that the interactions of entrepreneur ability and start-up funds have a positive effect on the risk tolerance of start-ups, and the risk tolerance can positively promote R&D investment willingness and intensity for new products, technologies, and services.Also, R&D investment willingness plays a partial intermediary role between the risk tolerance of start-ups and the intensity of R&D investments.
Keywords: start-ups, entrepreneurial ability, start-up funds, risk tolerance, R&D investments
Risk management affects enterprises; thus, healthy risk tolerance will be beneficial to obtaining a high return on investment.The enterprise’s ability to endure risks is a key factor that the enterprise must take into consideration when developing new technologies, products, services,and other important activities, especially those providing essential information for management decision-making.However, the impact of the current risk tolerance of start-ups on R&D investments is not obvious.Can start-ups launch new products, technologies, and services to enhance their risk tolerance? How can start-ups survive an epidemic, a cold economy, a shortage of funds, and other unexpected events, and how can the ability of entrepreneurs affect the risk tolerance of start-ups?Faced with many macro and micro risks, can entrepreneurs take risks involved with developing new enterprises, new products, technologies, services, research, and development to enhance the core competitiveness of enterprises? Scholars have conducted little research on the impact of R&D investments in new products, new technologies, and new services for start-ups, so this paper provides a reference for entrepreneurs to improve their entrepreneurial ability and enhance the risk tolerance of their start-ups from the perspective of entrepreneurs, aimed at (a) exploring the impact of entrepreneurial ability and entrepreneurial capital on the investment decisions regarding new products, technologies, and services of start-ups, and (b) investigating the effects of risk tolerance of start-ups on the R&D decisions regarding new products, technologies and services.
Summary of the Literature
Mainstream studies define entrepreneurial ability as entrepreneur competencies that reflect the individual characteristics of the entrepreneur.Entrepreneurial competencies are first a generalization of entrepreneurial characteristics, mainly referring to entrepreneurial behavior and internal psychological motivation, and then extended to aspects such as the entrepreneur environment.David C.McClelland(1973) first proposed the definition of competence as the knowledge, skills, competencies, and traits of high-performing employees in an organization who are capable of performing the job.Gaylen N.Chandler and Steven H.Hanks (1994) introduced the concept of competence into the field of entrepreneurial research for the first time, and defined entrepreneur competence as the ability of individuals to identify, anticipate and seize opportunities.David H.Holt (1997) pointed out that due to the differences between Chinese and Western societies, cultures, values, and educational concepts,the content preferences of Chinese and Western entrepreneurial competencies are different.Thomas W.Y Man et al.(2002) invented a six-dimensional entrepreneurial competencies model, believing that entrepreneurial competencies include opportunity competence, relationship competence, conceptual competence, organizational competence, strategic competence, and commitment competence.Soon thereafter, Chandler, Hanks, Thomas, and others, discussed their definitions of entrepreneurial competence, and Chinese scholars, after being exposed to the concept of entrepreneurial competence,also supplemented and explored the concept in accordance with China’s special national conditions,and built national characteristic entrepreneurial competency models.The Chinese scholar WangChongming and Chen Minke (2002).proposed eight dimensions of entrepreneurial competence:opportunity, relationship, concept, organization, strategy, commitment, emotion, and learning.From the perspective of enterprise resource reorganization, Ted Baker and Reed E.Nelson (2005) proposed that the ability of entrepreneurs to reuse resources is the process of transforming their personal capabilities into performance.Ghulam Nabi, Rick Holden, Andreas Walmsley (2010) explored the connotation and structure of entrepreneurial competencies, based on actual situations, and restored entrepreneurial activities to the entrepreneurial environment.They believed that entrepreneurial competencies should include cross-cultural competence, innovation ability, and learning ability.Maria Minniti and Moren Lévesque (2010) proposed that entrepreneurial qualities should cover both personal characteristics and social-economic factors.Ristophe Loué and Jacques Baronet (2010) believe that entrepreneurial competencies are the set of knowledge, skills, and abilities that entrepreneurs need to implement entrepreneurial activities, including self-efficacy, opportunity recognition, human capital, and social capital.Amina Omrane and Alain Fayolle (2011) divided entrepreneurial competencies according to the stages of entrepreneurship: before, during, and after entrepreneurship.H.Kaur and A.Bains(2013) understood entrepreneurial competencies as strategy, commitment, conceptual, opportunity,relationship, learning, and personal.Lawal, Worlu, and Ayoade (2016) found that perceptual factors,management skills, personality, attitude, management skills, and motivation are the key skills required for entrepreneurial sustainability.Zhou (2019) focused on the traits of entrepreneurs with a professional background in financial management; beyond the financial management knowledge base,preparatory entrepreneurs must also have strong professional judgment as well as the ability to solve practical problems.S.Jegadeeswari, Sudarvel Jayaraj and Velmurugan Ramaswamy (2020) argued that innovation capability is most important for micro, small, and medium entrepreneurs who not only introduce new products but also adopt new methods to reduce production costs.Siti Nurlaela and Sujono Sujono (2021) argue that having good entrepreneurial skills is essential to improving business success, such as the ability to take the initiative, risk-taking, creativity, and innovation.
The ten most prominent characteristics of foreign research are innovation ability, social ability,education level, perseverance, identification of business opportunities, organizational management ability, sense of responsibility, decision-making ability, independence, and adventure.Entrepreneur competencies should not only consider entrepreneurial psychological characteristics, but also include the aspects of entrepreneurial quality and entrepreneurial ability.Entrepreneurship and entrepreneurial competencies are very closely tied concepts.Entrepreneurship is the set of knowledge,skills, and attitudes required to create a business and successfully pass through the early stages of operation.It includes opportunities, financing, commitment, imagination, and operation.It is a multidisciplinary concept.The entrepreneurial ability training paradigm with vocational education characteristics should draw the essence from entrepreneurial practice.Entrepreneurs can improve their entrepreneurial ability through action learning.That is, the entrepreneurial ability should be cultivated and improved in entrepreneurial practice.The process from entrepreneurial learning to entrepreneurial ability to entrepreneurial success is a continuous relationship integration model.Based on the perspective of resource and ability theory, entrepreneurial resources and entrepreneurial abilities have a special effect on individual choice of part-time entrepreneurial behavior.Specifically,scholars have not made specific and clear distinctions between entrepreneurial competencies and entrepreneur abilities.These two words belong to the same vocabulary expansion.Therefore, through the comprehensive summary of various studies and the collection of expert opinions, our study indicates that entrepreneur ability includes the dimensions of opportunity recognition, operation management, learning, resources, and innovation.
Risk tolerance originated in the field of finance and referred to the ability of an individual or organization to withstand the risks, including the ability integrated into the overall process of identifying cognitive risks, regulating psychological interventions, and responding to behaviors.(Rosner, 2003).Corporate risk tolerance will affect the company’s earning management capabilities,and the company’s risk tolerance should be moderate.Excessive evasion or carrying of risk will damage the corporate value.John E.Grable and S.Joo (2004) and Grable, John E.and Roszkowski,Michael J.(2008) define this concept separately.The research on risk tolerance is mainly focused on the influencing factors of investors’ individual risk tolerance and the changes in the factors and the risk resistance of the investment portfolio and corresponding adjustments.Empirical research is the research method mainly adopted by many scholars during the past three years, using panel data as the main source.Research on corporate risk tolerance involves a wide variety of fields, including agriculture, construction, real estate, banking, foreign trade, and strategic emerging industries.With the widespread use of multivariate methods, many interdisciplinary research methods have been introduced into corporate risk tolerance, such as the 0-1 knapsack strategy method, the semi-variance risk measurement model, the black comprehensive evaluation method, the entropy method, the efficacy system method, and the fuzzy comprehensive evaluation method.In addition to researching the risk tolerance of individual investors, scholars have focused their research on the risk tolerance of certain groups, such as adolescents in China’s Hong Kong (Zhu, 2019), or whether the personal characteristics of the baby boomers who are retiring are at risk.Affordability has an impact (Rabbani,Yao, & Wang, 2019), using a research theme directly focused on the enterprise.For the research of enterprise risk tolerance, scholars mainly focus on the exploration of influencing factors of enterprise risk tolerance, the research of enterprise risk tolerance in different industries and how to evaluate the risk tolerance.Factors affecting corporate risk tolerance include many aspects, such as the educational background of company executives, corporate internal control, and technical factors.When the disclosure standards for accounting become higher, the investor protection environment is better, and the company’s risk tolerance is correspondingly enhanced.According to different evaluation methods,scholars have established different risk tolerance systems.For example, Liu and Jiang (2017) explored and established risk models for technical innovation of cooperative enterprises from three dimensions:internal factors, technical factors, and external environmental factors.The current research findings on corporate risk tolerance are mainly from a macro perspective, exploring the influencing factors and assessment systems of the risk tolerance of companies in a certain type of industry, andindividually studying the risk tolerance of start-ups and comparing the results to R&D investments.Therefore, after combining a complete entrepreneurial evaluation system with the characteristics of entrepreneurial enterprises and discussions with experts, our study indicates that the risk tolerance of start-ups includes the ability to withstand changes in policies and economic environments, the ability to withstand market fluctuations, the ability to acquire and strengthen political connections, the ability to obtain business and information resources, the ability to make profits, the ability to operate the business, the ability to pay debts, the ability to develop the company, the company’s cash flow situation, and the ability to withstand entrepreneurial losses.
R&D investment in this study refers to the investment in new technology, new products, and new services of the company or enterprise.The willingness to invest in R&D refers to the willingness of the start-up enterprise to invest in R&D new products, new technologies, and new services, and the R&D investment intensity (RDI), measured by “enterprise R&D investment / operating income,” which is the variable most scholars use to explain the factors affecting R&D investment.Hall (2002) pointed out that R&D investment differs from general investment mainly in the following aspects: R&D investment output has high uncertainty.Song, Zhou, and Jia (2019) studied the impact of economic openness and R&D investment on green economic growth.The effect of R&D scale on green economic growth is positive in the long run and negative in the current period for the eastern and western regions.Alam,et al.(2020) conclude that managers may want to enhance investor protection to promote high R&D investments to improve firm performance.Khan, et al.(2020) modeled an investigation on how uncertainty [firm-specific uncertainty (FSU), market-based uncertainty (MU), and economic policy uncertainty (EPU)] affect research and development (R&D) investment.Research on the internal factors affecting corporate R&D investment is very complicated and involves various financing constraints.Financing constraints were first proposed by Fazzari, Hubbard, and Petersen (1987), and refer to the phenomenon that information asymmetry and principal-agent problems cause external financing costs to be higher than internal financing costs.At present, there is much controversy in the measurement of financing constraints.When scholars at home and abroad carry out research on financing constraints, they look for suitable proxy variables to measure these constraints, and divide the proxy variables used to measure the constraints into internal variable indicators and external variable indicators.At present, the prevailing view is that the financing constraints faced by R&D investment are more severe than general investments, and because external financing costs are often higher than internal financing costs, companies tend to perform internal financing first (Himmelberg & Petersen,1991).Research by Brown, Martinsson, and Petersen (2012) found that for small-scale and short-term high-tech enterprises, endogenous financing is more important.According to the existing research results, scholars believe that the personal characteristics of the CEO (manager), the characteristics of the management team, and the internal control management of the enterprise are the main factors affecting the internal financing of the enterprise (Shams, 2009; Hsiang, 2014).Khan, Shah, and Rizwan (2021), using firm survey data from 21 countries published by the World Bank, concluded that financing constraints have a greater impact on incremental innovation than on radical innovation,and thus bank financing plays a key role in promoting all types of innovation in developing countries.There is a significant positive correlation between the personal characteristics of the CEO (manager)and R&D investment, manifested in the CEO’s work background, political connections, shareholding ratio, bargaining power, etc., especially in small-scale, low-profitability, and high-managementshareholding companies.With the expansion of the term, the effect of enhanced CEO management and control and CEO shareholding can promote corporate R&D investment.However, Wang and Sun(2018) found that the stronger the manager’s ability to increase prices, the lower the innovation input.For small companies in the industry, market competition does not have the effect of stimulating R&D investment.In addition, factors such as intermediary financial factors, corporate governance, corporate characteristics, and management team heterogeneity in organizational risk appetite will also affect R&D investment behaviors of enterprises to varying degrees.Bottazzi et al.(2001) and Nunes et al.(2012) believed that the company’s better financial flexibility (maintaining a lower debt ratio and higher cash holdings) would help promote the company’s growth and long-term development.Billett and Garfinkel (2004) argued that the amount of financial flexibility of a company should be kept within a reasonable range.If it is overloaded, it may increase the opportunity cost and capital cost of the company, and even hinder the growth and development of the company.Serrasqueiro, MacasNunes,and Leitao (2011) found that cash flow and short-term debt, regardless of their level, will have a positive impact on the R&D intensity of SMEs.Long-term debt and government subsidies are only important at higher levels of long-term debt and government subsidies.The research on the internal financing constraints of R&D investment has been mainly aimed at already mature companies or industries,with a lack of data from new ventures.Lin, He, and Yang (2020) find that targeted easing (TE) policy,an unconventional monetary policy aimed at reducing the reserve requirement ratio (RRR) of specific financial institutions, was implemented to significantly reduce the financing constraint of small firms as measured by cash flow sensitivity.Khan, Shah, and Rizwan (2021) using data from a survey of firms in 21 countries published by the World Bank, determined that financing constraints have a greater impact on incremental innovation than on radical innovation, and thus bank financing plays a key role in promoting all types of innovation in developing countries.
Research Assumptions
The Impact of Entrepreneur Ability and Start-up Funds on Venture Risk Tolerance
Entrepreneur ability includes opportunity identification ability, operation management ability, learning ability, resource ability, and innovation ability.Identifying opportunities means identifying, grasping,and seizing opportunities, which requires both an eye to identifying opportunities and a firm embrace of the market.Operation management refers to the ability to manage the personnel of the enterprise and properly master the business, the more skilled the entrepreneur, the greater the possibility of positive cash flow maintenance, self-responsibility, as well as continuous operation and development.Learning abilitymeans the ability to acquire knowledge, persist in learning, and transform the knowledge into reality.Resource ability includes the ability to acquire human resources, capital resources, information resources,and technical resources for the team, and to deal with the acquired resources in a coordinated manner.Innovation is the most profound characteristic of entrepreneurs.An important element of a successful enterprise is the enhancement of innovation abilities that can make the enterprise more competitive, more tolerant of the fluctuations in the markets, internal and external policy changes, and more able to obtain business and information resources that can enhance the ability of the enterprise to resist risks and sustain development.
Based on the above analysis, the following assumptions are proposed:
Hypothesis 1: Entrepreneur ability has a positive impact on risk tolerance.
Hypothesis 1a: The ability to identify opportunities has a positive impact on risk tolerance.
Hypothesis 1b: Operational management ability has a positive impact on risk tolerance.
Hypothesis 1c: Learning ability has a positive impact on risk tolerance.
Hypothesis 1d: Resource management ability has a positive impact on risk tolerance.
Hypothesis 1e: Innovation has a positive impact on risk tolerance.
Start-up funds refer to the funds required for an enterprise to first run, or rerun, and are the first capital necessary for the entrepreneur team to carry out entrepreneurial activities.When a start-up team raises more start-up funds (more start-up funds, a large stock of liquidity, rapid fund scheduling,etc.), in addition to the necessary expenditure items, the remaining part of the start-up funds can be retained as working capital in case of unexpected events such as fund gaps, higher risk expectations of the team, thus increasing the ability of the new enterprise to be successful.Accordingly, the following assumptions are made:
Hypothesis 2: Start-up funds contribute to risk tolerance.
From a rational person’s point of view, the stronger the ability of entrepreneurs, the more likely they are to participate in risk, and vice versa, the more likely they are to stay away from risks and adopt a conservative attitude.The stronger the entrepreneur’s ability is, the more flexible s/he is to deal with in an emergency.If the enterprise has sufficient capital and sufficient trial and error reserves, the enterprise’s risk-bearing ability will be strong.On the contrary, if the entrepreneur’s personal ability is weak, the ability to deal with an emergency will be slow and the outcome will be poor.If the enterprise has a lack of start-up funds, the enterprise is very fragile and does not allow trial and error at all.Thus the enterprise’s risk-bearing ability will be small.
Hypothesis 3: The interaction of entrepreneur ability with start-up funds has a positive impact on risk tolerance
Impact of Risk Tolerance on R&D Investments
The R&D investment index of this study includes two dimensions of investment willingness and investment intensity.Investment willingness refers to whether investors are willing to invest funds or capital into the enterprise.Investment intensity is also called “investment density,” which refers to theproportion of funds or capital that investors are willing to invest in the turnover.The greater the risk tolerance of start-ups, the more likely they are to survive and grow in changing markets and environments,the more willing investors are to invest in R&D for a bigger expected return, the more willing they are to invest.Conversely, the smaller the risk tolerance of start-ups, the less willing they are to invest in R&D.The greater the risk tolerance of start-ups, the higher the likelihood of becoming a “star enterprise” and the higher the proportion of investors’ investment in R&D.On the contrary, the smaller the risk tolerance of start-ups, the lower the proportion of entrepreneurs’ investment in R&D.The higher the willingness of investors to invest in R&D, the greater the willingness to increase the proportion of investment in R&D,and the greater the intensity of investment in R&D.Whereas the less the willingness of investors to invest in R&D, the lower the proportion of additional investment in R&D.
As above, risk tolerance has a catalytic effect on R&D investment willingness, and risk tolerance has a catalytic effect on R&D investment intensity, while investment willingness has a positive effect on investment intensity.The following assumptions are proposed:
Hypothesis 3: Risk tolerance has a positive impact on R&D investment.
Hypothesis 3a: Risk tolerance has a positive impact on R&D investment willingness.
Hypothesis 3b: Risk tolerance has a positive impact on R&D investment intensity.
Hypothesis 3c: R&D investment willingness mediates between risk tolerance and R&D investment intensity.
In summary, the theoretical model of this paper is shown in Figure 1.
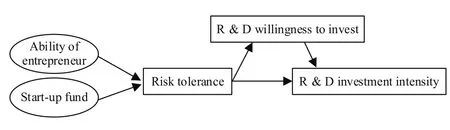
Figure 1.Theoretical Model
Research Methods
Questionnaire Design and Data Collection
By referring to previous scholars’ research work, we designed a questionnaire by drawing on research dimensions of the entrepreneurial capabilities defined by Noble (1999), Chandler (1994),etc., referring to the measurement dimensions of the enterprise’s risk tolerance proposed by Pan et al.(2013), Lu (2014), and research on R&D investment by Chen (2010) et al., using the Delphi method of multiple rounds of consulting experts to screen and supplement the core elements of entrepreneurship.As shown in Table 1, the questionnaire is divided into two parts.The first part contains the basic information of the entrepreneur, including gender, age, education, entrepreneur city, entrepreneur duration, industry field, enterprise size, type of enterprise, number and source of start-up funds.The second part measures the entrepreneur’s ability, risk tolerance, R&D investment willingness,and R&D investment intensity by evaluating the entrepreneur’s opportunity identification ability,operational management ability, learning ability, resource ability, and innovation ability.The willingness and intensity of R&D investments are measured in terms of policy tolerance, the ability to withstand changes in the economic environment, the ability to withstand market fluctuations, the ability to access and strengthen political connections, the ability to access business and information resources, the profitability of the enterprise, the ability of the enterprise to operate, the ability of the enterprise to pay its debts, the ability of the enterprise to develop, the cash flow of the enterprise and the ability to withstand the losses of the enterprise.
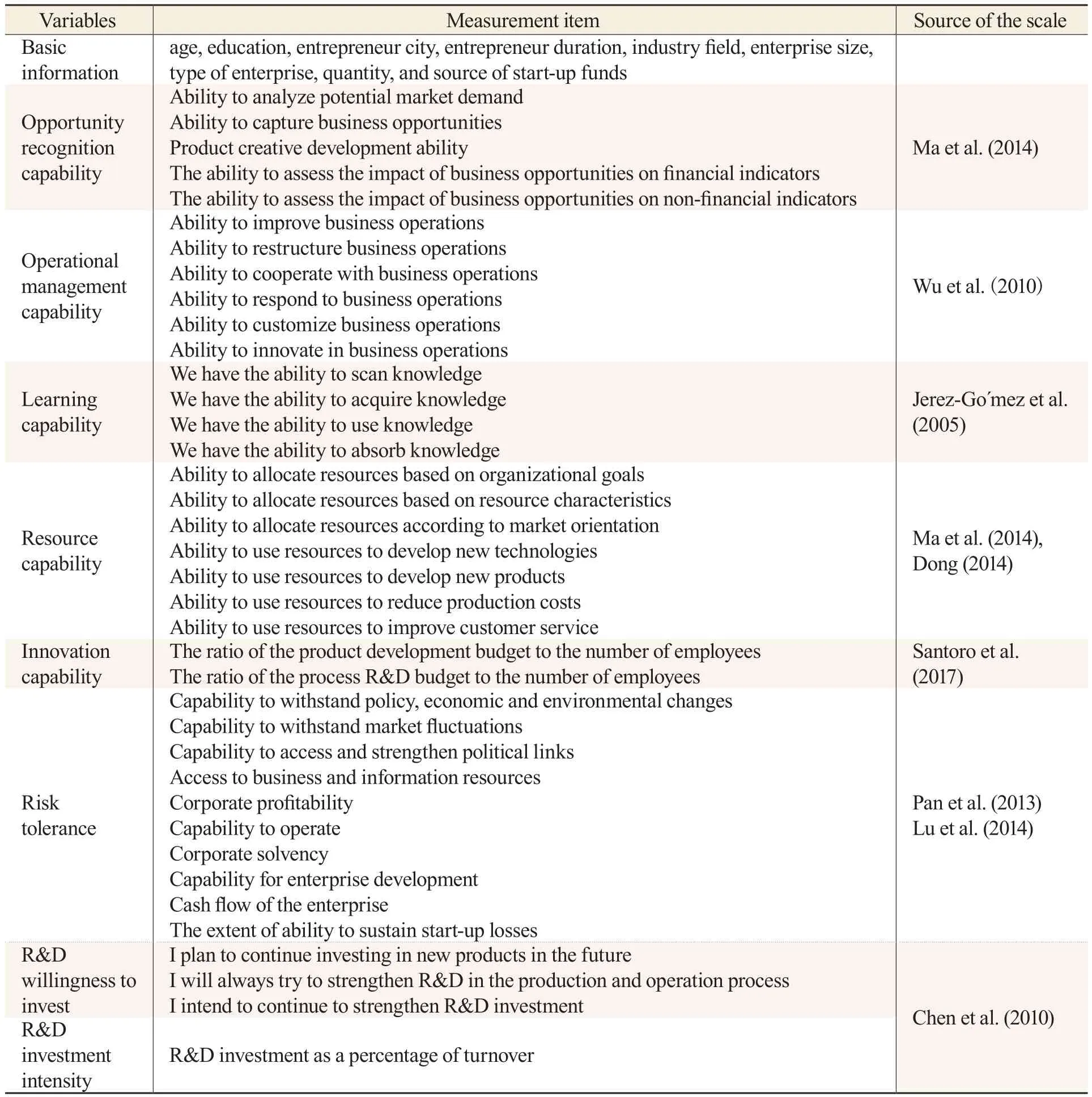
Table 1 Structure of Questionnaire
A total of 228 questionnaires were collected, including 222 valid questionnaires with blank itemsand more than 95 percent of the same options, and 97.4 percent of them were valid.The details are shown in Table 2.
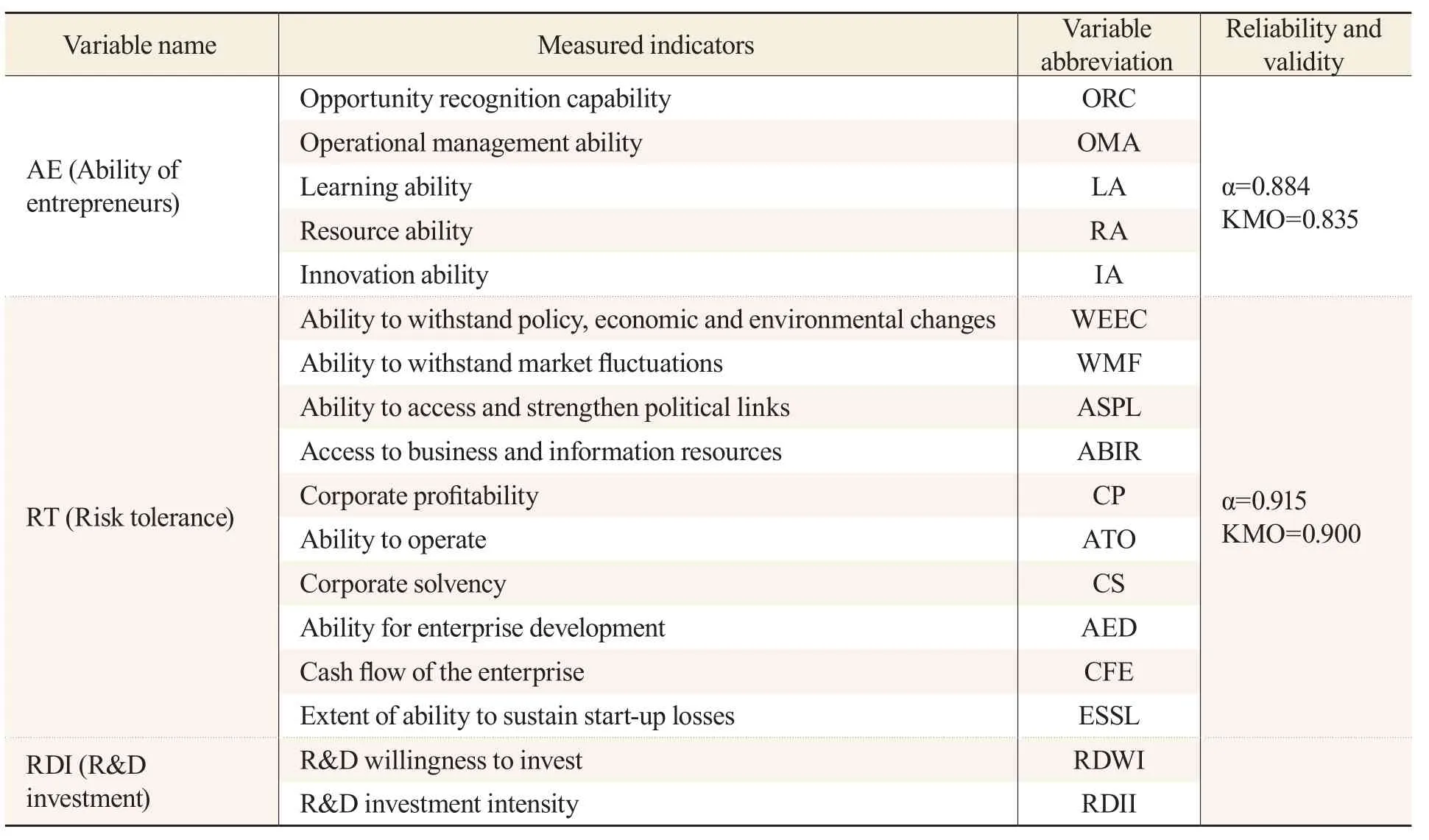
Table 2 Reliability and Validity Analysis of Variables
Reliability and Validity Analysis
The measuring dimensions of entrepreneur ability, risk tolerance and R&D investment of the entrepreneurs were extracted under the guidance of experts.In this part, there are 20 necessary items,the overall reliability is high (α=0.931, KMO =0.896), the factor load of each item of entrepreneur ability and risk tolerance is above 0.65, α value is above 0.85, KMO value is higher than 0.8.The overall reliability validity of the questionnaire is good.
Proven Studies
Descriptive Statistics
To investigate the entrepreneurs themselves and the basic conditions of the start-ups, we focused on the sex, age, education, length of the start-up and its size, type, and start-up funds.The entrepreneurs surveyed were mainly in Sichuan province (163), Beijing (28), and Shanghai (26), and the start-ups involved were doing business in the Internet, fast consumer goods, wholesale and retail, furniture and clothing, education and training, manufacturing, catering, real estate, consulting and others.
The details are shown in Table 3.
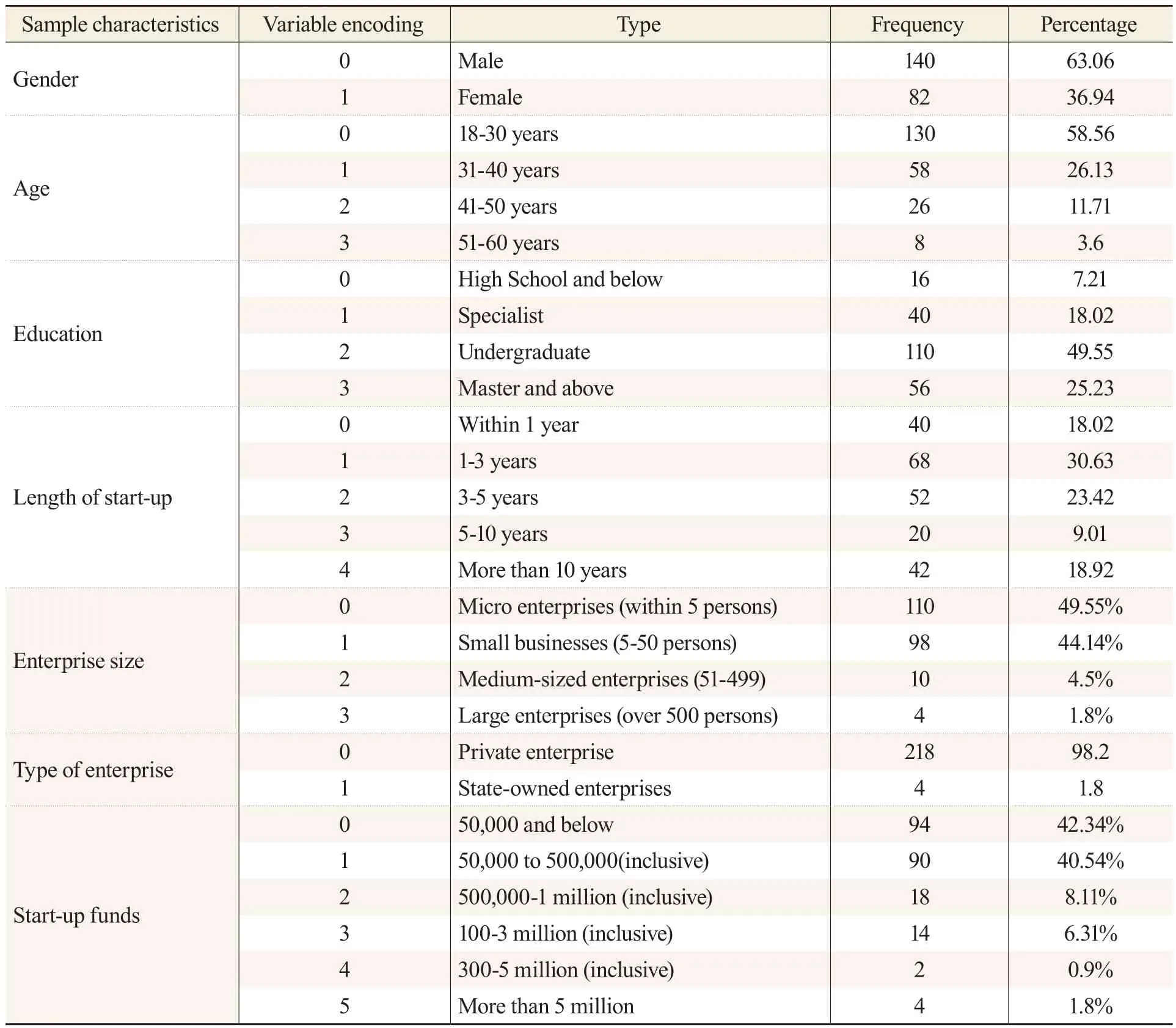
Table 3 Descriptive Statistics of Sample Characteristics
The statistics of entrepreneurs with different sample characteristics are classified, and the results show that: in terms of gender, the proportion of male entrepreneurs who have been in business for more than five years is higher than that of female, and the proportion of female operated enterprises that are small and micro enterprises is higher than male.The start-up funds of female entrepreneurs are mainly concentrated in less than 1 million, with a higher proportion of personal assets and a lower debt ratio, but female entrepreneurs believe that obtaining adequate financial support is more important for improved corporate risk tolerance.Male entrepreneurs have greater differences in startup capital, and the debt ratio is relatively high.Male entrepreneurs’ management leadership, ability to seize opportunities, communication and coordination, and ability to deal with social relations are slightly stronger than female entrepreneurs.Companies founded by male entrepreneurs are able towithstand changes in policies and economic environments.The ability of enterprises to make profits and the ability to pay off debts are significantly higher than those created by female entrepreneurs,and male entrepreneurs can tolerate higher business losses.As the age of the entrepreneurs increase,basic professional knowledge, communication, coordination and handling of social relations, and the ability to acquire resources gradually increased, and the degree of bearing entrepreneurial losses.With increased education, the amount of start-up funds for entrepreneurs gradually increased, and the channels for obtaining start-up funds became more diverse, and entrepreneurs’ capabilities gradually improve (We cannot predict the future.).Entrepreneurs with a college degree are generally less willing to invest, but when they do, research and development investments in new technologies and services have the highest intensity.From 1 to 10 years of entrepreneurship, the comprehensive capabilities of entrepreneurs improve, but the evaluation of their entrepreneurial capabilities decreases after more than 10 years.Similarly, within 10 years of entrepreneurship, the degree of business losses that can be sustained increases, but after ten years, the ability to bear losses declines to some extent.Entrepreneurs who have been in business for 1 to 3 years are more willing to invest in the research and development of new products, technologies, and services, and have greater R&D intensity.With the expansion in the size of their enterprises, the ability of entrepreneurs increased gradually, the degree of bearing corporate losses also soared, and the willingness to invest in new products, new technologies, and new services gradually increased as well.The most significant increase in R&D investment willingness and intensity is among the medium and large enterprises.
Correlation Analysis
Using SPSS 24.0 software to describe and analyze the independent variables, dependent variables,and adjusting variables, the correlation coefficients of start-up funds, opportunity identification ability,operation management ability, learning ability, resource ability, innovation ability, and risk-bearing ability is greater than 0.28, and significant value is less than 0.01, indicating that there is a correlation between start-up funds, entrepreneur ability, and risk-bearing ability.The correlation coefficient between R&D investment willingness and R&D investment intensity is 0.482, and significant value is less than 0.01, indicating that there is a correlation between R&D investment willingness and R&D investment intensity.The details are shown in Table 4.
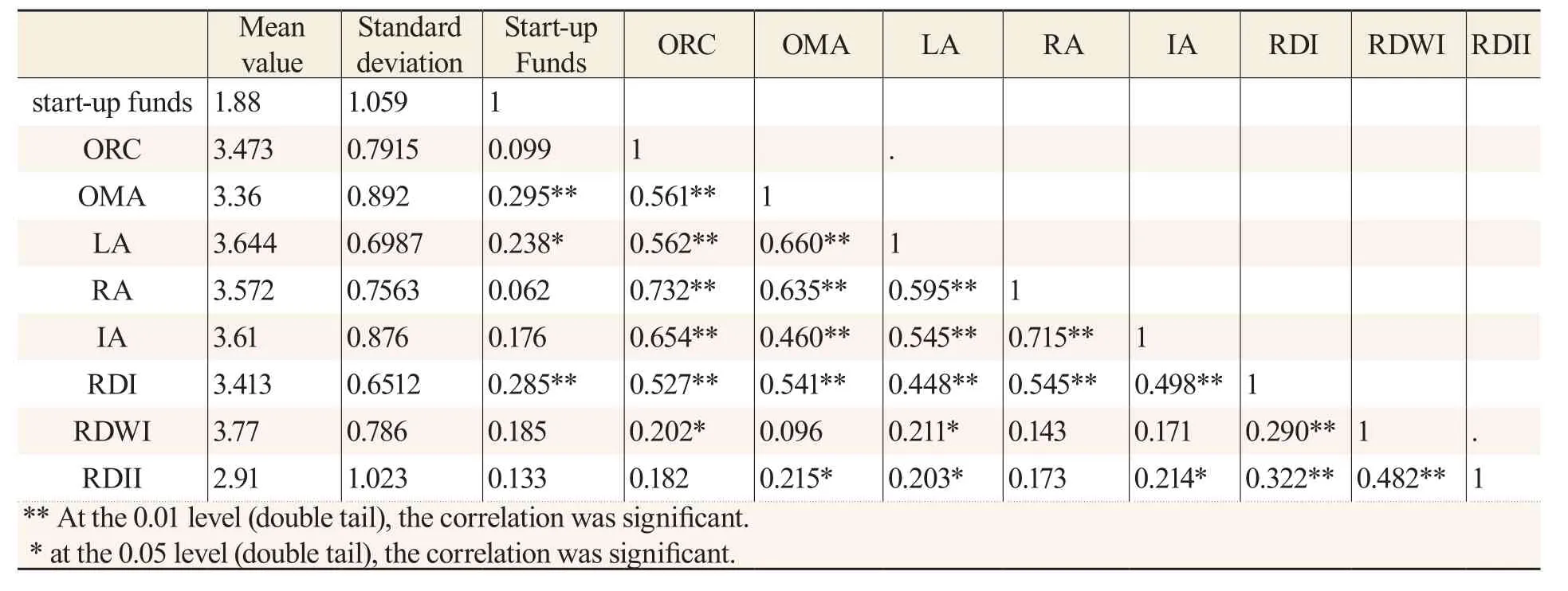
Table 4 Descriptive Statistics and Correlation Analysis of Main Effect
Hypothetical Test
We verified the impact of entrepreneur ability and risk tolerance on R&D investment by using SPSS 24.0 linear regression for hypothesis checking.Model 1 and Model 2 verified the impact of entrepreneur ability on risk tolerance.Using risk tolerance as a dependent variable, the regression coefficient of entrepreneur ability was 0.619, which was significant at 0.001, indicating that entrepreneur ability has a positive effect on risk tolerance, assuming H1%.Also, identification ability,operation management ability, learning ability, resource ability, and innovation ability were linearly regressed, returning regression coefficients of 0.527, 0.541, 0.448, 0.545, and 0.498, respectively.All were significant at less than 0.001, indicating that opportunity identification ability, operation management ability, learning ability, resource ability, and innovation ability had a promoting effect on risk tolerance, providing evidence that hypotheses 1a, 1b, 1c, 1d, and 1e were valid.
We also verified the promotion effect of start-up funds on risk tolerance.The stratified regression results showed that the regression coefficient was 0.285, and the significance coefficients were all less than 0.01, indicating that start-up funds had a positive effect on risk tolerance, providing evidence that Hypotheses 2 is valid.
To analyze the effect of the interaction between entrepreneur ability and the start-up funds on risk tolerance, we standardized the start-up funds and constructed the interaction item to carry on the stratified regression, and the results show that the interaction between the entrepreneur ability and the start-up funds has a promoting effect on risk tolerance, supporting H12%.It is convenient to clearly analyze the interaction mechanism between entrepreneur ability and the start-up funds and draw the conclusion that high start-up funds enhance the ability of the entrepreneur to bear risks, while low start-up funds weaken the ability of the entrepreneur to bear risks.The details are shown in Figure 2.
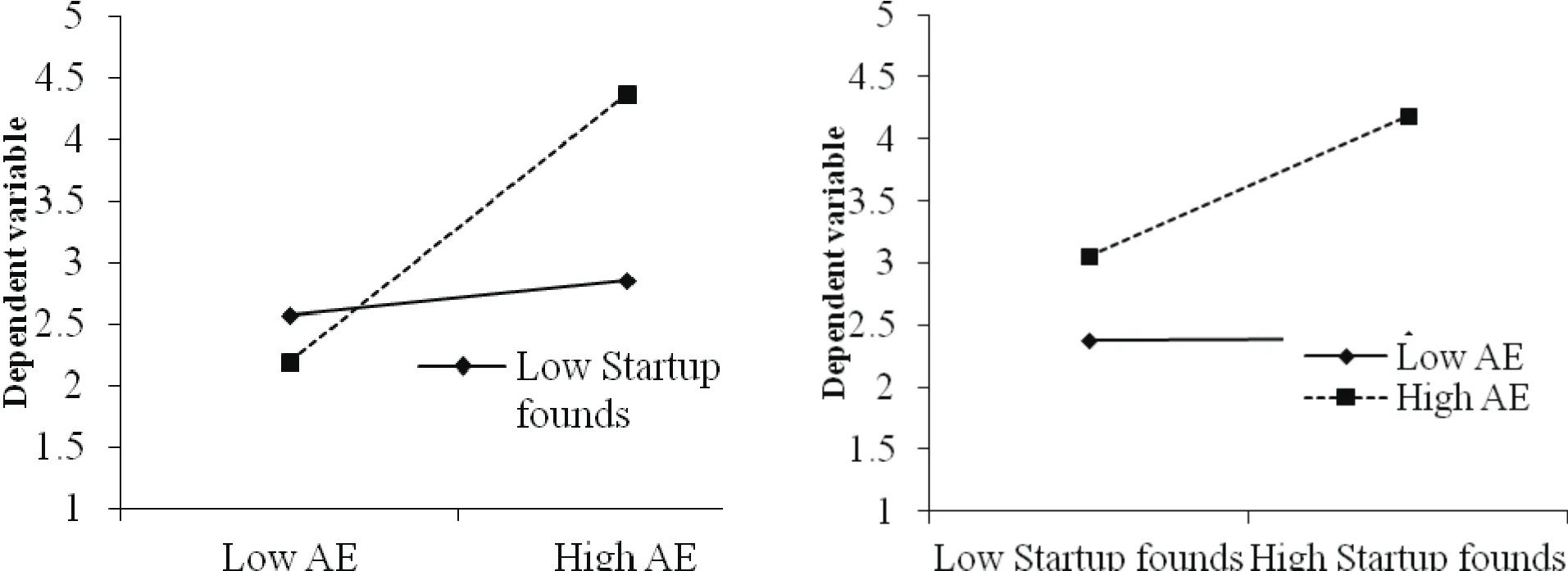
Figure 2.Interactive Effect Diagram
To verify the impact of risk tolerance on R&D investment, Model 3 and Model 4 verified the impact of risk tolerance on R&D investment willingness.The results show that risk tolerance has a catalytic effect on R&D investment willingness, meaning that the stronger the risk tolerance, the stronger the willingness of entrepreneurs to invest in R&D, supporting H3A.Model 5 and Model 6 verified the influence of risk tolerance and R&D investment willingness on R&D investment intensity.The regression coefficients of R&D investment willingness and risk tolerance were 0.322 and 0.482, respectively, and the significant coefficients were all less than 0.001, indicating that the regression effect was significant.Risk tolerance and R&D investment willingness promoted R&D investment intensity.Thus, risk tolerance positively affects R&D investment, and R&D investment willingness plays a partial intermediary role between risk tolerance and R&D investment intensity,supporting H3, H3a, H3b, and H3c.
The details are shown in Table 5.
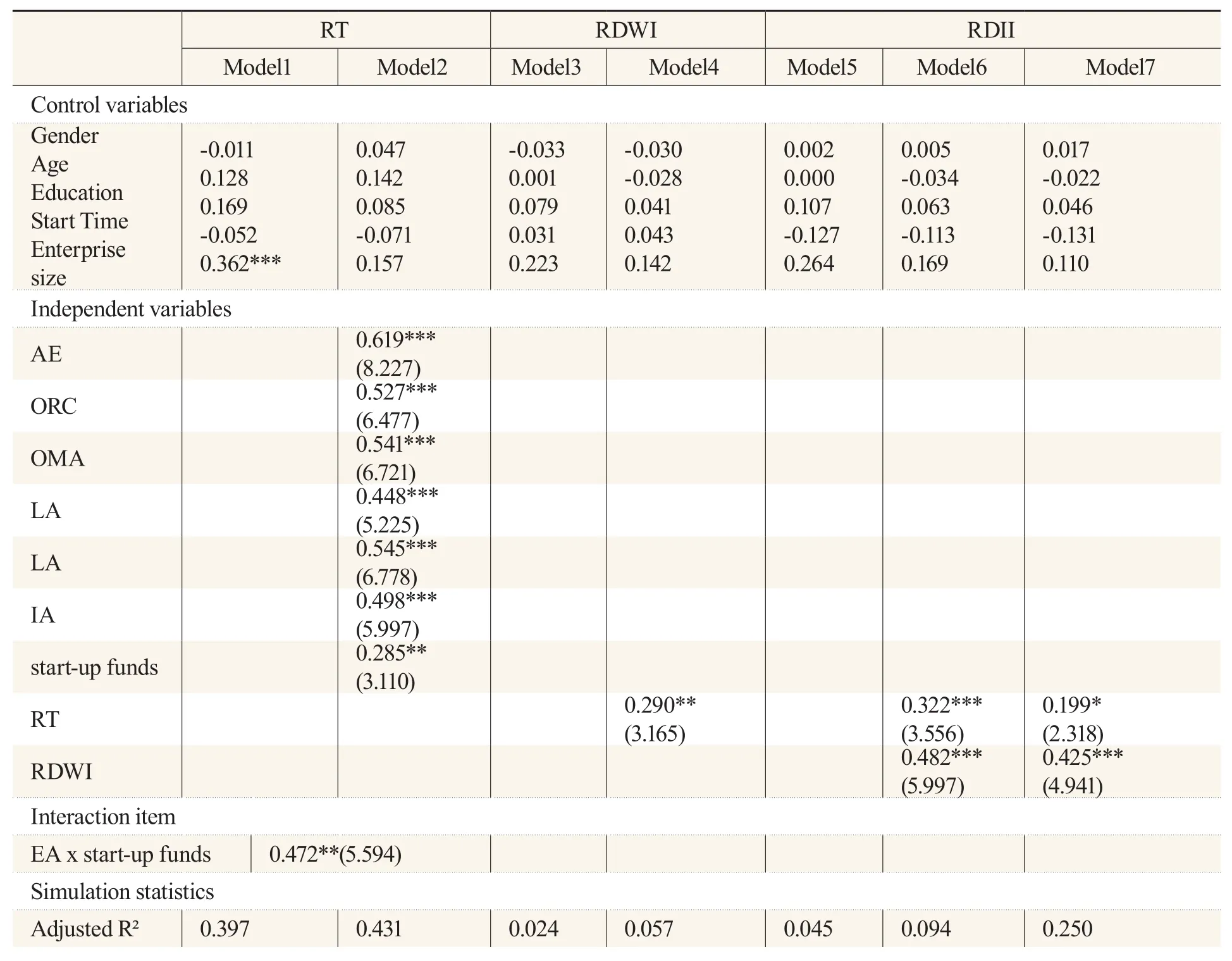
Table 5 Layered Regression Results
** Significant at level 0.001 (double tail)** Significant at level 0.01 (double tail)*Significant at 0.05 level (double tail)
Accordingly, the results of this validation are consistent with the assumptions presented, as shown in Table 6:
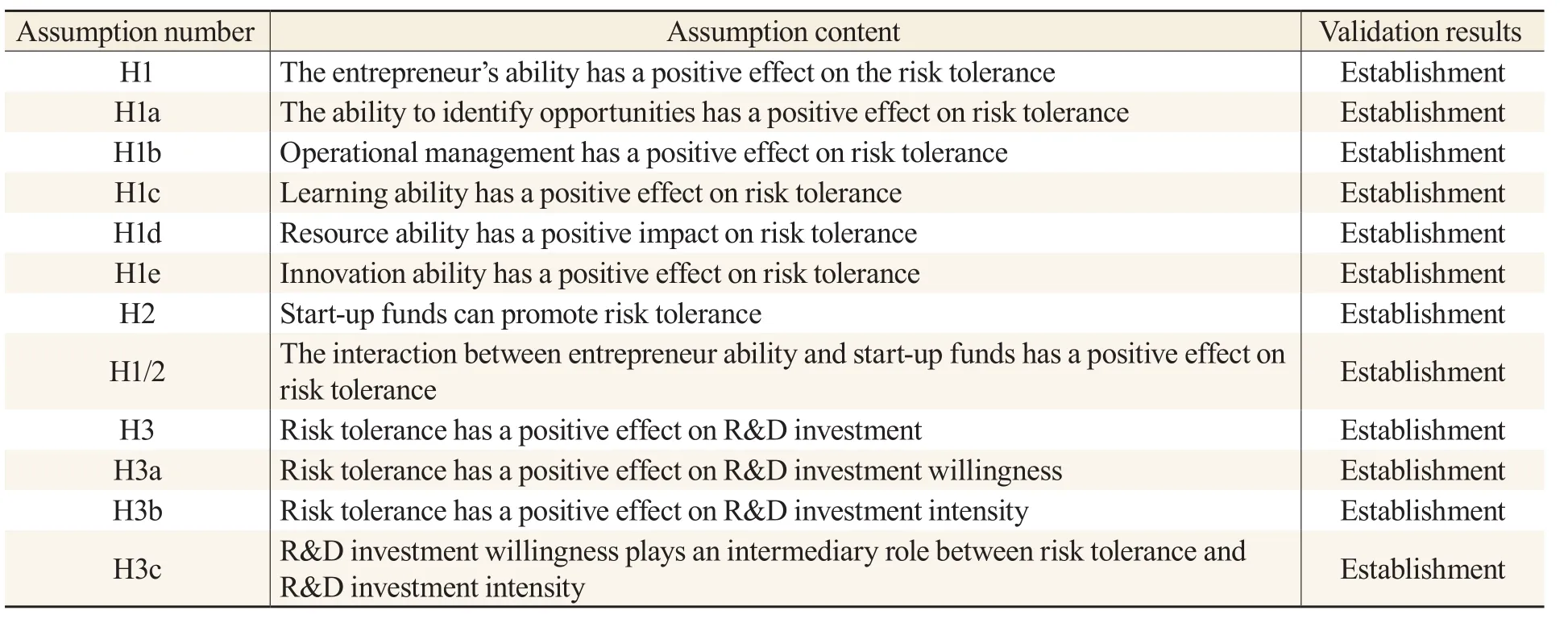
Table 6 Hypothesis Test Results
Research Conclusions and Prospects
Research Conclusions and Theoretical Contributions
Through the questionnaire survey of 222 entrepreneurs, the influence factors of risk tolerance were analyzed from the perspective of entrepreneur ability, and the relationship between risk tolerance and R&D investment was empirically studied.The conclusions of this study mainly focus on the following three aspects:
First, the ability of entrepreneurs and good start-up funding have a positive impact on the risk tolerance of start-ups.The stronger the ability of the entrepreneur, the more the knowledge and skills of the enterprise will be expanded, the more sensitive it will be to identifying venture risks and the more flexible the application and allocation of the entrepreneur’s resources will be.Start-up funds can enhance the solvency of enterprises and the ability to obtain business information resources, establish a better cash flow, and thus enhance the risk tolerance of enterprises.
Second, the interaction between entrepreneur ability and start-up funding has a positive effect onthe risk tolerance of start-ups.The stronger the ability of entrepreneurs, the higher the start-up funds,the stronger the risk tolerance, and vice versa.When entrepreneurs have strong ability and sufficient start-up capital, enterprises can resist policy or market interference, which can reduce losses through resource integration and effective operation.On the contrary, if entrepreneurs have poor ability and less start-up capital, enterprises will not be able to meet the challenge of survival and face the danger of bankruptcy.The interactive effect of the entrepreneur’s ability and the start-up funding shows that high start-up funds enhance the ability of the entrepreneur to promote the ability to bear risks.
Third, the enterprise’s risk tolerance is affecting its R&D investment in developing new products,technologies, and services.Enterprise risk tolerance can promote R&D investment willingness and R&D investment intensity, respectively.The stronger the risk-bearing ability of the enterprise, the stronger the ability of the enterprise to bear the changes in policies and economic environments, the better the solvency and capital flow of the enterprise, the more the enterprise managers can operate according to their existing standards, and have the time and energy to analyze the industry situation,grasp the future development trends, formulate the strategies for the enterprise’s future development,and produce the willingness to carry out the research and development of new products, new technologies, and new services.
Theoretical Contributions and Prospects
This study explored the relationship between risk tolerance and R&D investment based on the perspective of entrepreneur ability.It can provide a reference for improving entrepreneur ability and enhancing the risk tolerance of start-ups from the perspective of entrepreneurs.There are limitations as follow.First, it uses only the entrepreneur’s ability and the start-up funds to carry on the risk tolerance ability analysis, and only analyzes the enterprise’s internal characteristics to risk tolerance ability influence, without considering policy safeguards, industry markets, and other external influences and pressures of the macroscopic environment.Second, because the harvested data involves various fields and scattered industries, the sample size of individual industries is relatively small; thus the conclusions may not be universal in some fields or industries.Therefore, in our future research, we will continue to increase the strength of our questionnaire distribution, industry classification analysis, and strive to develop more universal and constructive theories and suggestions.
We propose optimized countermeasures from three subjects: governments, enterprises, and entrepreneurs.First, governments should strengthen policy guidance and risk control for SMEs,improve the institutional mechanisms for enterprise fundraising and financing, and organize entrepreneurial capacity enhancement training.Second, enterprises should enhance their risk tolerance capacity in two aspects, risk control and risk resolution, formulate strict rules and regulations, improve corporate governance and risk control mechanisms, assess the risks of major decisions, and regularly evaluate and control all aspects of enterprise risks to ensure normal and effective production and operation, financial management, and transaction activities, and avoid serious risks arising from mistakes in key processes or links.Third, entrepreneurs should strengthen their learning and developsufficient entrepreneurial knowledge in advance, and strengthen their own ability to correctly analyze market demands.At the same time, in the early stage of entrepreneurship, they should choose a good entrepreneurial project, form a good entrepreneurial team, obtain sufficient financial support, build a good business relationship network, and predict possible obstacles, setbacks, and precautions.
 Contemporary Social Sciences2022年2期
Contemporary Social Sciences2022年2期
- Contemporary Social Sciences的其它文章
- The Belt and Road Initiative: Multilingual Opportunities and Linguistic Challenges for Guangxi, China
- The Historical Fiction Based on True Stories: An Analysis of the Menghui Gushu by Huang Jianhua with the Aid of Historical Records and Archaeological Objects of Art
- Research on Big Data Platform Design in the Context of Digital Agriculture: Case Study of the Peony Industry in Heze City, China
- A Preliminary Study of Embedded Supervision Thoughts: Based on a Distributed Financial System
- Financial Knowledge, Capability to Guard Against Risks, and Rural Households’ Selection of Financial Assets: An Empirical Study Based on Rural Households in China
- A Brief Introduction to the English Periodical of Contemporary Social Sciences
