Integrating Coarse Granularity Part-Level Features with Supervised Global-Level Features for Person Re-Identification
CAO Jiahao,MAO Xiaofei,LI Dongfang,ZHENG Qingfang,JIA Xia
(1.State Key Laboratory of Mobile Network and Mobile Multimedia Technology,Shenzhen 518057,China;2.ZTE Corporation,Shenzhen 518057,China)
Abstract:Person re-identification (Re-ID) has achieved great progress in recent years.However,person Re-ID methods are still suffering from body part missing and occlusion problems,which makes the learned representations less reliable.In this paper,we pro?pose a robust coarse granularity part-level network (CGPN) for person Re-ID,which ex?tracts robust regional features and integrates supervised global features for pedestrian im?ages.CGPN gains two-fold benefit toward higher accuracy for person Re-ID.On one hand,CGPN learns to extract effective regional features for pedestrian images.On the other hand,compared with extracting global features directly by backbone network,CGPN learns to extract more accurate global features with a supervision strategy.The single mod?el trained on three Re-ID datasets achieves state-of-the-art performances.Especially on CUHK03,the most challenging Re-ID dataset,we obtain a top result of Rank-1/mean av?erage precision(mAP)=87.1%/83.6%without re-ranking.
Keywords:person Re-ID;supervision;coarse granularity
1 Introduction
Person re-identification (Re-ID) aims to re?trieve a given person among all the gallery pe?destrian images captured by different camer?as.It is a challenging task to learn robust pe?destrian feature representations as realistic scenari?os are highly complicated with regards to the illumi?nation,the background,and occlusion problems.In recent years,person Re-ID has achieved great prog?ress[1–7].However,person Re-ID methods are still suffering from occluded or body part missing pedes?trian images,where they fail to extract discrimina?tive deep features for person Re-ID.Intuitively,the complexity of realistic scenarios increases the diffi?culty in making correct retrieval for person Re-ID[8–10].Therefore,existing person Re-ID methods usually decline a lot in performance when dealing with realistic person Re-ID dataset like CUHK03,which contains a lot of occluded or body part miss?ing pedestrian images,as illustrated in Fig.1.
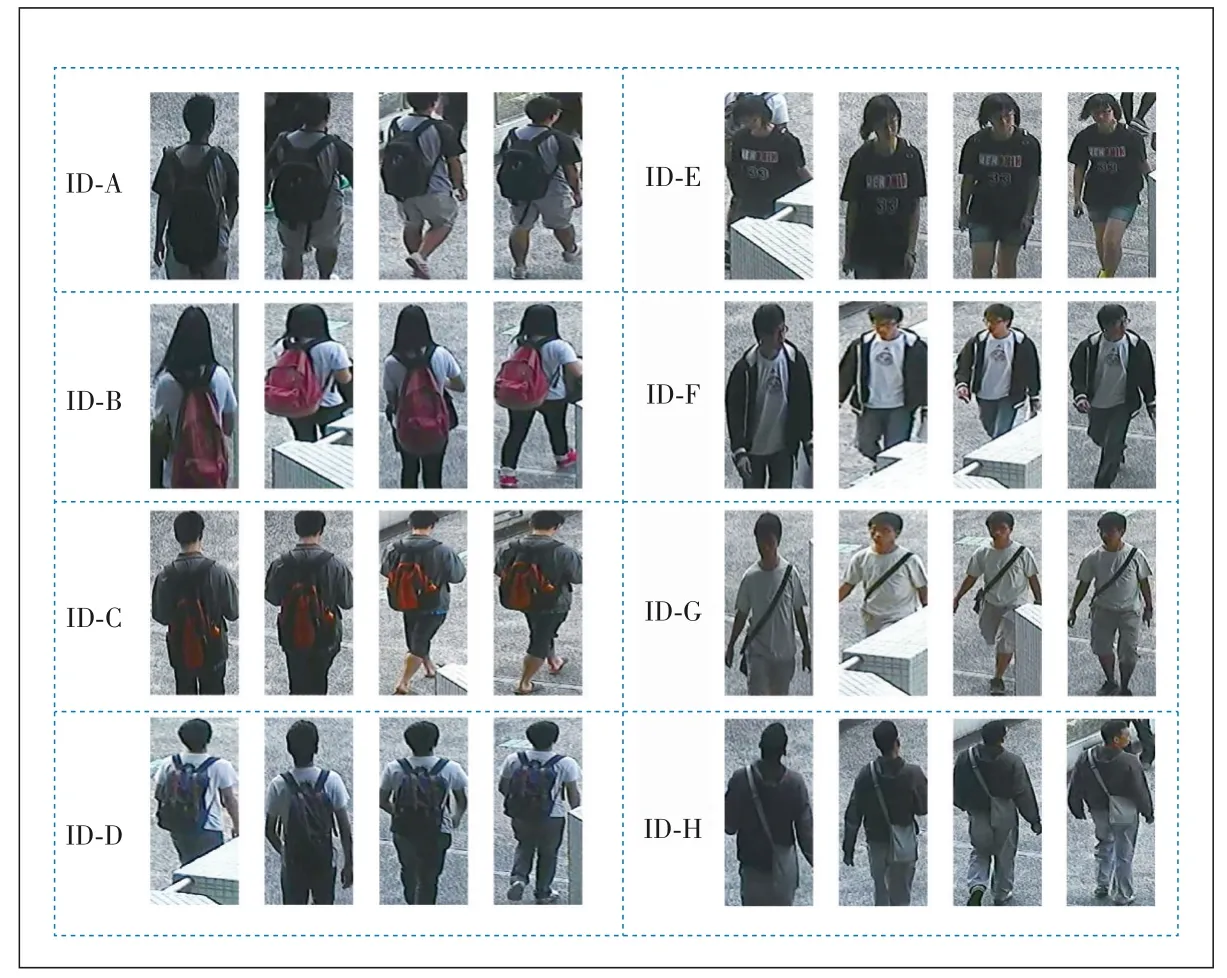

▲Figure 1.Pedestrian images in CUHK03-labeled dataset
As it is well known,part-based methods[5–7]like multiple granularity network (MGN)[5]are widely used in person Re-ID and have achieved promising performance.Generally,part-based methods learn to combine global features and dis?criminative regional features for person Re-ID.The global features in part-based methods are usually extracted direct?ly from the whole person image by the backbone network,while the regional features are generated by directly parti?tioning feature maps of the whole body into a fixed number of parts.Nevertheless,the overall performance of such partbased methods seriously depends on that all person images are well-bounded holistic person images with few occlusion or body part missing.As real-world scenarios are complicat?ed,the bounding boxes detected by the detection algorithm may not be accurate enough,which usually leads to occlud?ed or body part missing pedestrian images as Fig.1 shows.In Fig.1,ID-A means the ID of the pedestrian is A.We can see that for the same person in the realistic scenario,occluded and body-part missing pedestrian images are both captured as people are moving around the cameras.When dealing with such occluded or body part missing pedestrian images,the global features extracted from the whole image directly by the backbone network become less accurate;moreover,the regional features generated by directly partitioning fea?ture maps of the whole body may focus on occluded parts and become ineffective,which impair the person Re-ID ac?curacy evidently.
To address the above problems,in this paper,we propose the coarse granularity part-level network (CGPN) for person Re-ID model that learns discriminative and diverse feature representations without using any third models.Our CGPN model can be trained end-to-end and performs well on three person Re-ID datasets.Especially on CUHK03,which con?tains a lot of occluded or body part missing pedestrian images,our method achieves state-of-the-art performances and outper?forms the current best method by a large margin.CGPN has three branches,and each branch consists of a global part and a local part.The global part is supervised to learn more accu?rate global features by part-level body regions.With the super?vision strategy,the global part can learn more proper global features for occluded or body part missing pedestrian images.For the local part,as pedestrian images detected in realistic scenarios are often occluded or body-part missing,too many fine grained local features generated by partitioning the whole body feature maps may decrease model performance.There?fore we propose a coarse grained part-level feature strategy that can extract effective regional features and perform better on the three person Re-ID datasets.
CGPN gains two-fold benefit toward higher accuracy for per?son Re-ID.Firstly,compared with extracting global features directly by backbone network,CGPN learns to extract more accurate global features with the supervision strategy.Second?ly,with the coarse grained part-level feature strategy,CGPN is capable of extracting effective body part features as regional features for person Re-ID.Besides,our method is completely an end-to-end learning process,which is easy for learning and implementation.Experimental results confirm that our method achieves state-of-the-art performances on several mainstream Re-ID datasets,especially on CUHK03,the most challenging dataset for person Re-ID,in single query mode,and we obtain a top result of Rank-1/mean average precision (mAP)=87.1%/83.6%without re-ranking.
The main contributions of our work are summarized as follows:
? We propose a novel framework named CGPN,which ef?fectively integrates coarse grained part-level features and su?pervised global-level features and is more robust for person Re-ID.
? We develop the coarse grained part-level feature strategy for person Re-ID.
? We prove that the integration model of coarse grained part-level features and supervised global-level features achieves state-of-the-art results on three Re-ID datasets,espe?cially on the CUHK03 dataset,in which our model outper?forms the current best method by a large margin.
2 Related Works
2.1 Part-Based Re-ID Model
As deep learning is widely used in person Re-ID nowadays,most existing methods[11–12]choose to extract feature maps by directly applying a deep convolution network such as ResNet[13].However,the single global feature extracted from the whole person image by a deep convolution network does not perform as well as expected.The reason is that person im?ages captured by cameras usually contain random background information and are often occluded or body part missing,which impairs the performance a lot.Then part-based methods are proposed to get additional useful local information from person images for person Re-ID.As an effective way to extract local features,part-based methods[5–7,14]usually benefit from person structure and together with global features,push the performance of person Re-ID to a new level.The common solu?tion of part-based methods is to split the feature maps horizon?tally into several parts according to human body structure and concatenate the feature maps of each part.However,when dealing with occluded or body part missing pedestrian images,we find that part-based methods like MGN[5],which has re?ceived state-of-the-art results on person Re-ID datasets,face the problem of performance decrease.Obviously,part-based methods are common solutions to holistic pedestrian images as they can get correct body parts by uniform partitioning,however,these methods are less effective to occluded or body part missing pedestrian images.
2.2 Attention-Based Re-ID Model
Recently,some attention-based methods try to address the occlusion or body-part missing problems with the help of atten?tion mechanisms.Attention module is developed to help ex?tract more accurate features by locating the significant body parts and learning the discriminative features from these infor?mative regions.LI et al.[15]propose a part-aligning convolution?al neural network (CNN) network for locating latent regions(hard attention)and then extract these regional features for Re-ID.ZHAO et al.[16]employ the spatial transformer network[17]as the hard attention model to find discriminative image parts.LI et al.[18]use multiple spatial attention modules (by softmax function) to extract features at different spatial locations.XU et al.[19]propose to mask the convolutional maps via a poseguided attention module.LI et al.[14]jointly learn multi-granu?larity attention selection and feature representation for opti?mizing person Re-ID in deep learning.However,most of the attention-based methods are often more prone to higher fea?ture correlations,as these methods tend to have features focus?ing on a more compact subspace,which makes the extracted features attentive but less diverse,and therefore leads to sub?optimal matching performance.
2.3 Pose-Driven Re-ID Model
Some pose-driven methods utilize pose information to tack?le the occlusion or body-part missing problems.In these meth?ods,pose landmarks are introduced to help to align body parts as pose landmarks indicate the body position of persons.ZHENG et al.[10]propose to use a CNN-based external pose es?timator to normalize person images based on their pose,and the original and normalized images are then used to train a sin?gle deep Re-ID embedding.SARFRAZ et al.[20]directly con?catenate fourteen landmarks confidence maps with the image as network input,letting the model automatically learn align?ment way.HUANG et al.[21]propose a part aligned pooling(PAP) that utilizes seventeen human landmarks to enhance alignment.MIAO et al.[22]learn to exploit pose landmarks to disentangle the useful information from the occlusion noise.However,the landmarks of persons are obtained usually by a third pose estimation model trained on an extra dataset,which increases the complicity of the whole Re-ID network.What’s more,standard pose estimation datasets may not cover the drastic viewpoint variations in surveillance scenarios,and be?sides,surveillance images may not have sufficient resolution for stable landmarks prediction.
3 Proposed Method
3.1 Structure of CGPN
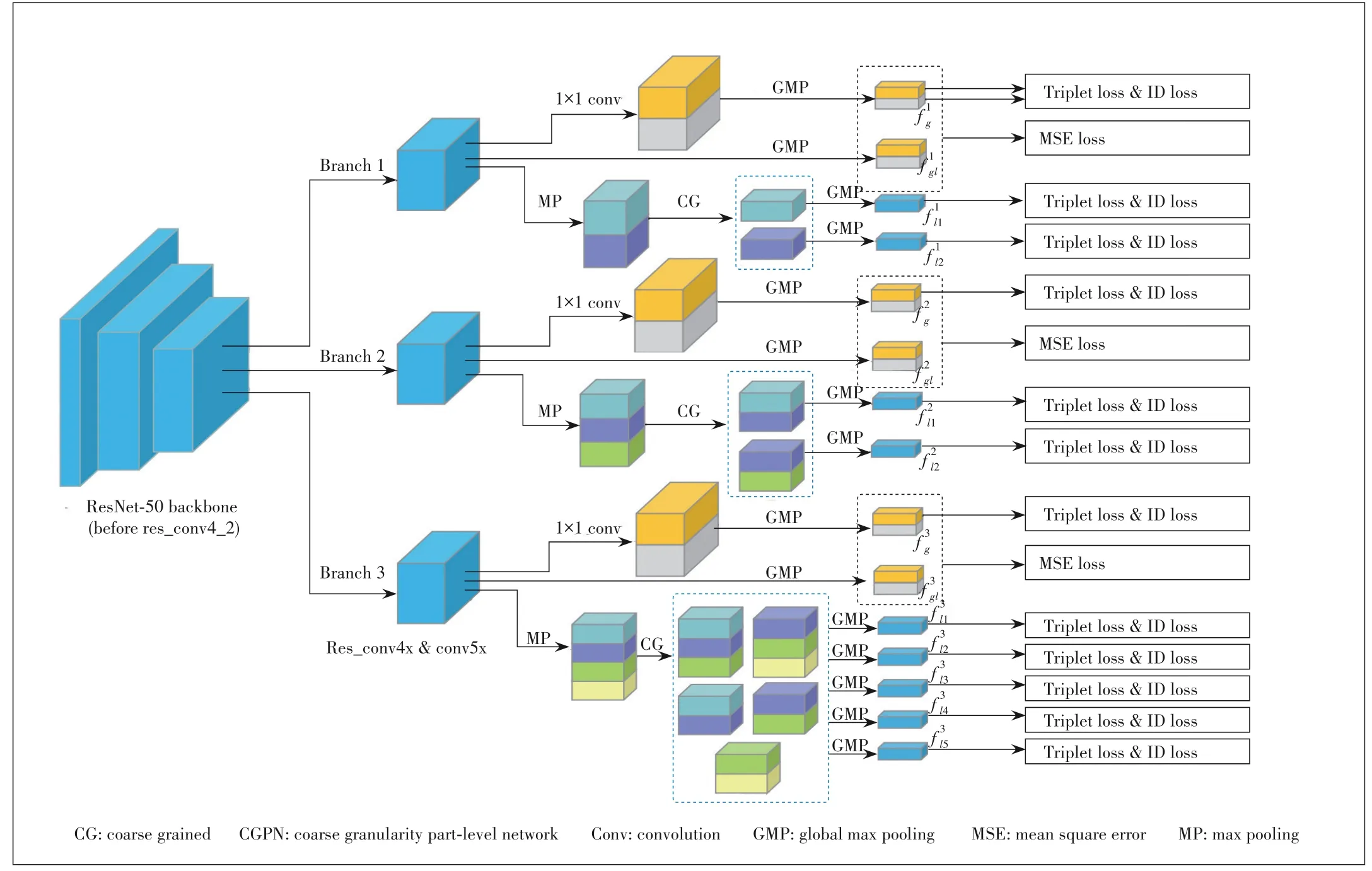
▲Figure 2.Structure of CGPN
In this part,we present our CGPN structure in Fig.2,in which the ResNet-50 backbone is split into three branches af?ter res_conv4_1 block.Each branch consists of a global part and a local part.In the global part,we apply two 1×1 convolu?tional layers and global max pooling (GMP) to generate global features.While in the local part,we apply a max pooling (MP)with different kernel sizes,split the feature maps into different spatial horizontal stripes,and then apply a coarse grained(CG) strategy and GMP to generate local features.The back?bone of our network is a CNN structure,such as ResNet[13],which achieves competitive results in many deep learning tasks.Like MGN[5],we divide the output of res_conv4_1 into three different branches.Through the backbone network,CG?PN transfers the input image into a 3D tensorTwith size ofc×h×w(cis the channel number,his the height,andwis the width).Each of the three branches contains a global part and a local part.The global part in three branches shares the same structure,while in every local part the output feature maps are uniformly partitioned into different stripes.
In the global part,two 1×1 convolution layers are applied to the output feature maps to extract regional features.Each of the 1×1 convolution layers will outputc-channel features and be supervised by the corresponding part features.In futher de?tail,fori-th branch’s global part,to supervise the global fea?tures,the output feature maps are uniformly divided into two parts in the vertical direction,and a global pooling is applied to each of them to extract two part featuresThe two part featuresare utilized in the training stage to su?pervise global featuresgenerated by the two 1×1 con?volution layers.After the training stage finishes,the two part features are no longer needed.The firstc-channel global fea?turesshould be closer to the upper part features,and in the same way,the secondc-channel global featuresshould be closer to the bottom part features.In the infer?ence stage,the firstc-channel global featuresand the sec?ondc-channel global featuresare concatenated to form 2cchannel features as final global featuresAs the global parts of the three branches all share the same structure,we can get three global featuresin total.With the supervision of the part features,in the final 2c-channel global features,the firstc-channel global features are forced to focus on the upper part of the human body,while the secondc-channel global features focus on the bottom part of the human body,which makes final global features more robust to person image occlusion or body-part missing.
For the local part in three branches,the output feature maps are divided intoNstripes in the verti?cal direction with each stripe having the size ofc×(h/N)×w,from which we prepare to extract local fea?tures.However,for person images that are occluded or body part missing,it might be harmful and de?crease the performance of person Re-ID,if the gran?ularity of local features is too fine.To alleviate the drawbacks of fine-grained local features,we choose to extract local features in a bigger receptive field that con?tains enough body structure information to well represent the corresponding body region.In this paper,we propose a coarsegrained part-level feature strategy in which the combined part stripes must be adjacent and the minimum height proportion of combined local features should be no less than half of the output feature maps.The detail of the coarse grained strategy is illustrated in Fig.3.In the local part of the first branch,the output feature maps are divided into two stripes in vertical di?rection as shown in Fig.3a,and then pooling operations are performed to get local feature representationscorre?sponding to the size ofc× (h/2) ×w.In the local part of the second branch,the output feature maps are divided into three stripes but we combine two adjacent stripes to get two 2/3 pro?portion local featurescorresponding to the size ofc×(2h/3)×w.For the local part of the third branch,the output feature maps are divided into four stripes,and then we com?bine two and three adjacent stripes to get three 1/2 propor?tion and two 2/3 proportion local features respectively,withcorresponding to the size ofc× (3h/4)×w,c× (3h/4) ×w,c× (3h/4) ×w,c× (h/2)×w,c× (h/2)×wre?spectively.
During the test,all featuresgenerated by the global part and the local part in each branch are reduced to 256-dimension and are concate?nated together as the final features,as different branches in CGPN actually learn representing information with different granularities which can cooperatively supplement discriminat?ing information after the concatenation operation.
3.2 Loss Functions
Like various deep Re-ID methods,we employ softmax loss for classification,and triplet loss[23]for metric learning.For the supervision of the global part in each branch,we use mean square error(MSE)loss in the training stage.
To be precise,in each branch,the local part is trained with the combination of softmax loss and triplet loss while the glob?al part is trained with MSE loss,softmax loss and triplet loss as illustrated in Fig.2.
Fori-th learned featuresfi,Wkis a weight vector for classkwith the total class numberC.Nis the number of training ex?amples in a mini-batch,and the softmax loss is formulated as:
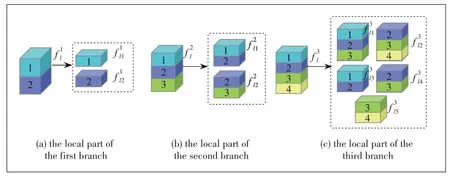
▲Figure 3.Coarse-grained part-level feature strategy
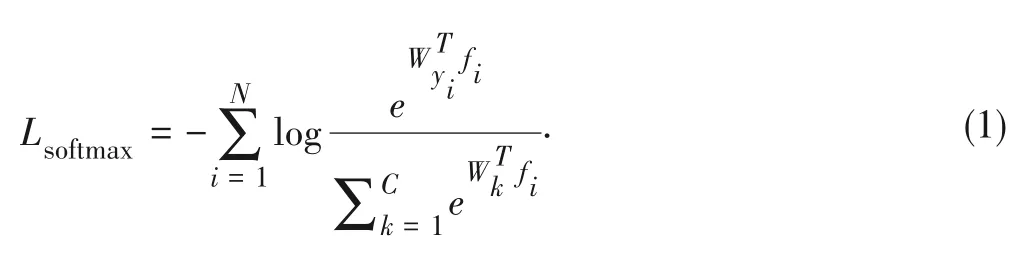
We employ the softmax loss to all global featuresandallcoarsegrainedlocalfeatures
Besides,all the global featuresare also trained with triplet loss.In the training stage,an improved batch hard triplet loss is applied with formula as follows:

In the above formula,Pis the number of selected identities andKis the number of images from each identity in a minibatch.is the anchor sample,is the positive sample,is the negative sample andαis the margin parameter to control the differences of intra-and inter-distances,which is set to 1.2 in our implementation.
To supervise the global features,we employ the MSE loss to all global featuresand the supervision local fea?tureswith the formula as follows:

The overall training loss is the sum of above three losses,which is formulated by:

4 Experiment
4.1 Datasets and Protocols
We train and test our model respectively on 4 mainstream Re-IDdatasets:Market-1501[24],DukeMTMC-reID[25],CUHK03[26]and Occluded-DukeMTMC[22].Especially the CUHK03 dataset,which is the most challenging realistic sce?nario Re-ID dataset as it consists of a lot of occluded or body part missing pedestrian images as illustrated in Fig.1.
Market-1501 is captured by six cameras in front of a cam?pus supermarket,which contains 1 501 person identities,12 936 training images from 751 identities and 19 732 test?ing images from 750 identities.All provided pedestrian bound?ing boxes are detected by deformable part models(DPM)[27].
DukeMTMC-reID contains 1 812 person identities captured by 8 high-resolution cameras.There are 1 404 identities in more than two cameras and the other 408 identities are regard?ed as distractors.The training set consists of 16 552 images from 702 identities and the testing set contains 17 661 images from the rest 702 identities.
CUHK03 contains 1 467 person identities captured by six cameras on campus of The Chinese University of Hong Kong(CUHK).Both manually labeled pedestrian bounding boxes and automatically detected bounding boxes are provided.In this paper,we use the manually labeled version and follow the new training/testing protocol proposed in Ref.[28],with 7 368 images from 767 identities for training and 5 328 images from 700 identities for testing.
Occluded-DukeMTMC is re-segmented from the original DukeMTMC-reID dataset.The training set contains 15 618 images,and the gallery set and query set contain 17 661 and 2 210 images,respectively,in which all query images and some gallery images are occluded images,and these occlud?ed images retain their occluded regions without being manu?ally cropped.
In our experiment,we report the average cumulative match characteristic (CMC) at Rank-1,Rank-5,Rank-10 and mean average precision(mAP)on all the candidate datasets to evalu?ate our method.
4.2 Implementation Details
All images are re-sized into 384×128 px and the backbone network is ResNet-50[13],pre-trained on ImageNet with the original fully connected layer discarded.In the training stage,the mini-batch size is set to 64,in which we randomly select 8 identities and 8 images for each identity (P=8,K=8).Besides,we deploy a randomly horizontal flipping strategy to images for data augmentation.Different branches in the network are all initialized with the same pre-trained weights of corresponding layers after res_conv4_1 block.Our model is implemented on Pytorch platform.We use stochastic gradient descent (SGD)as the optimizer with the default hyper-parameters (momentum=0.9,weight decay factor=0.0005) to minimize the network loss.The initial learning rate is set to 1e-2 and we decay it at epoch 60 and 80 to 1e-3 and 1e-4 respectively.The total train?ing takes 240 epochs.During the evaluation,we use the aver?age of original image features and horizontally flipped image features as the final features.All of our experiments on differ?ent datasets follow the settings above.
4.3 Comparison with State-of-the-Art Methods
In this section,we compare our proposed approach with cur?rent state-of-the-art methods on the three main-stream Re-ID datasets.
The statistical comparison between our PGCN network and the state-of-the-art methods on Market-1501,DukeMTMCreID and CUHK03 datasets is shown in Table 1.
On Market-1501 dataset,semantics aligning network(SAN) achieves the best published result without re-ranking,but our CGPN achieves 89.9% on the metric mAP,exceed?ing SAN by +1.9%.On the metric Rank-1,our CGPN achieves 96.1%,on a par with SAN,while our model is trained in an easier and end-to-end way.Compared with mul?tiple granularity network (MGN) which is also a multiple branches method,our model surpasses MGN by +0.4% on the metric Rank-1 and by+3.0%on the metric mAP.
Among the performance comparisons on DukeMTMC-reID dataset,Pyramid achieved the best published result on met?rics Rank-1 and mAP respectively.Our CGPN achieves the state-of-the-art result of Rank-1/mAP=90.4%/80.9%,outper?forming Pyramid by +1.4% on the metric Rank-1 and +1.9%on the metric mAP.
From Table 1,our CGPN model achieves Rank-1/mAP=87.1%/83.6% on the most challenging CUHK03 labeled da?taset under the new protocol.On the metric Rank-1,our CG?PN outperforms the best published result of SAN by +7.0%and outperforms the best published result of Pyramid by +6.7%on mAP.
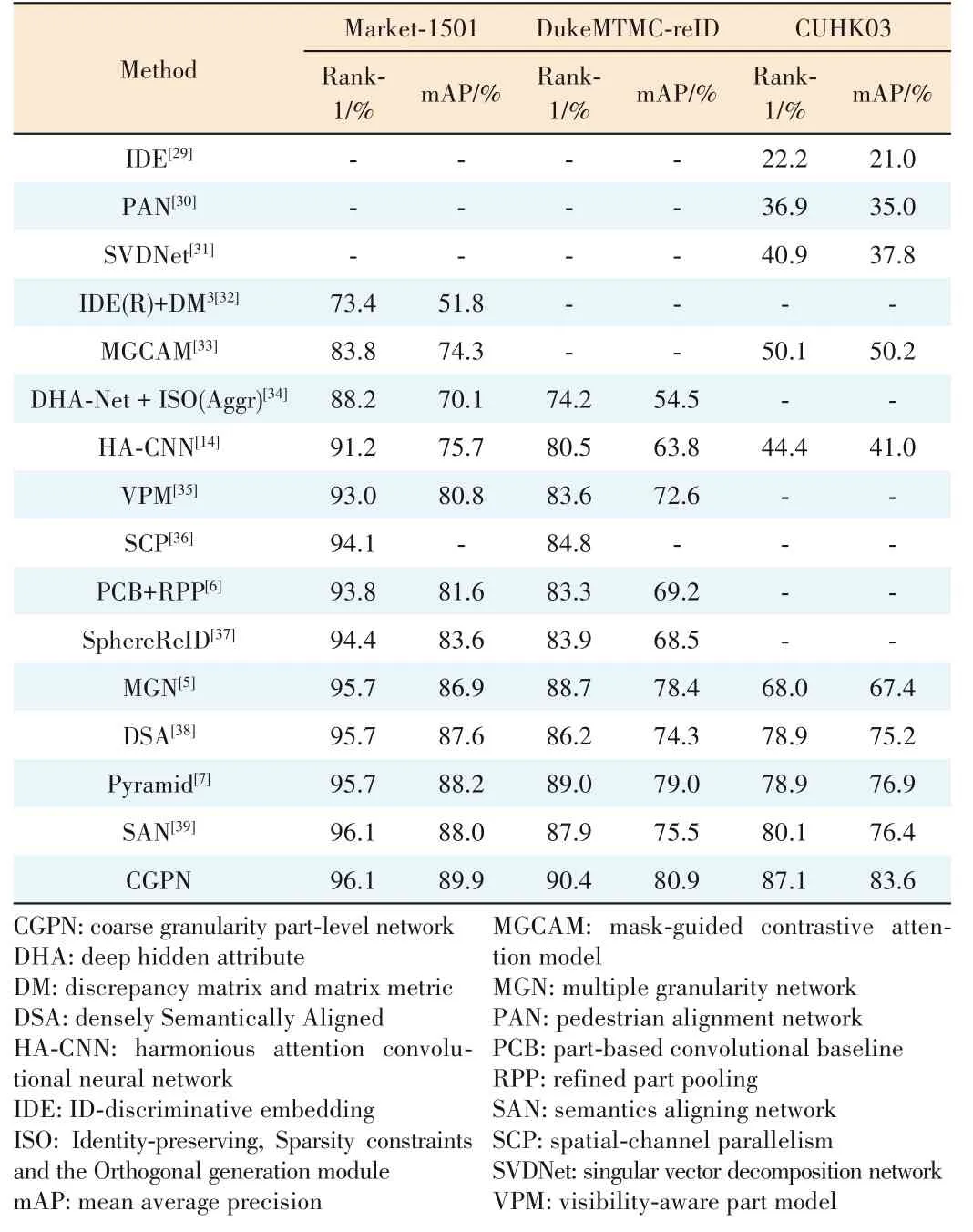
▼Table 1.Performance comparisons with the state-of-the-art results on Market-1501,DukeMTMC-reID and CUHK03 datasets in single query mode without re-ranking
In summary,our proposed CGPN can always outperform all other existing methods and shows strong robustness over different Re-ID datasets.According to the comparative exper?iments on the three datasets,especially on CUHK03 dataset,our approach can consistently outperform all other models by a large margin.Therefore,we can conclude that our method can effectively extract robust deep features from occluded or body part missing pedestrian images in person Re-ID.
We also conduct an experiment and compare the perfor?mances with the existing methods on Occluded-DukeMTMC.The results are listed in Table 2.As can be seen that,CGPN gets the top performance among the compared approaches,and obtains 58.5%/50.9% in rank-1/mAP.CGPN surpasses pose-guided feature alignment (PGFA)by +7.1% rank-1 accu?racy and +13.6% mAP,which is a large margin.Therefore,we can conclude that our proposed CGPN integrated with super?vised global-level features can effectively address the occlu?sion problem in person Re-ID.
4.4 Importance of Coarse-Grained Part-Level Features
To verify the effectiveness of coarse-grained part-level fea?ture strategy in the CGPN model,we train two mal-functioned CGPN for comparison:
? CGPN-1 abandons the local parts in three branches and keeps only global parts.
? CGPN-2 replaces coarse-grained part-level features with fine-grained part-level features.It abandons coarse-grained strategy in local parts of three branches,compared with the normal CGPN model.Its local parts in three branches directly divide the output feature maps into two,three and four parts as shown in Fig.4.
From the comparison of CGPN-1 with CGPN,we can seea significant performance decrease on Rank-1/mAP by-1.2%/-2.0%,-1.1%/-2.5% and -4.7%/-3.7% on Market-1501,DukeMTMC-reID and CUHK03 datasets respectively.Espe?cially on CUHK03,we can observe a sharp decrease by -4.7%/-3.7%on the metric Rank-1/mAP.As CGPN-1 is trained in ex?actly the same procedure with the CGPN model and the CUHK03 dataset typically consists of many occluded or body part missing person images,we can infer that the coarsegrained local part is critical for CGPN model,especially on the dataset which contains a lot of occluded or body part missing person images.
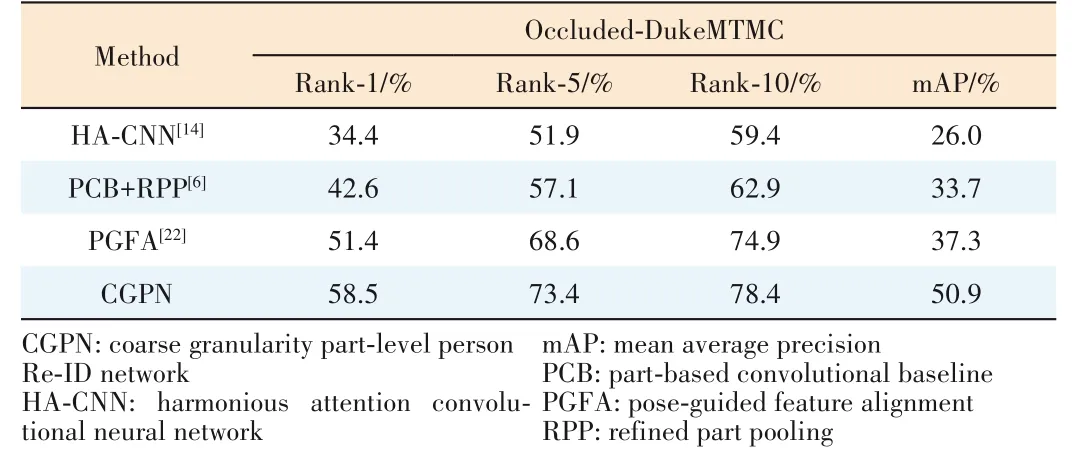
▼Table 2.Performance comparisons with the state-of-the-art results on Occluded-DukeMTMC dataset in single query mode without re-ranking.
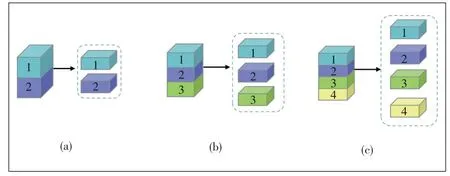
▲Figure 4.Fine grained local part structure in CGPN-2
Comparing CGPN-2 with CGPN,we can still observe a per?formance decrease by-0.8%/-0.5%,-0.1%/-0.7%and-1.8%/-1.1% on the metric Rank-1/mAP on Market-1501,DukeMT?MC-reID and CUHK03 datasets respectively.Compared with fine-grained part-level features,coarse-grained part-level fea?tures contain enough body structure information to better repre?sent the corresponding body regions,which makes CGPN learn more robust local features.Besides,on CUHK03,we can also see a sharper performance decrease compared with the other two datasets.The reason is that Market-1501 and DukeMTMCreID consist of mainly holistic person images with little occlu?sions or body part missing,and these images keep complete body structure and make fine-grained part-level features achieve comparable performance with coarse-grained part-level features.While on CUHK03,as it consists of a lot of occluded or body part missing person images,coarse-grained part-level features outperform fine-grained part-level features evidently.Our experiments clearly prove that our coarse-grained part-lev?el feature strategy can improve model performance significantly and is critical for model robustness,especially for occluded or body part missing person images.
4.5 Importance of Supervised Global Part
To further verify the effectiveness of the supervised global part in CGPN model,we train another two mal-functioned CG?PN for comparison:
? CGPN-3 abandons global parts in all three branches and keeps only local parts that are trained with triplet loss and soft?max loss.
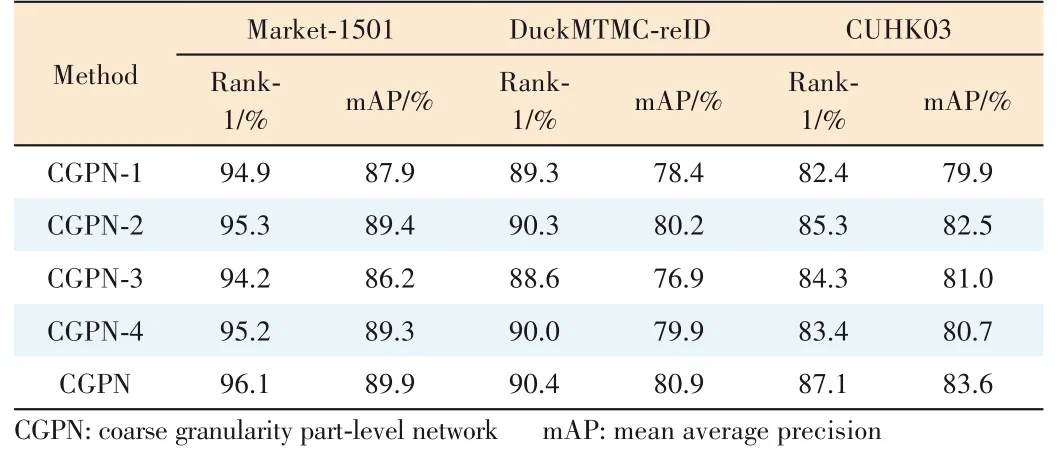
▼Table 3.Ablation study of CGPN coarse grained part-level feature strategy and supervised global part,with comparison results on Market-1501,DukeMTMC-reID and CUHK03-labeled at evaluation metrics of Rank-1 and mAP in single query mode without re-ranking
? CGPN-4 keeps the global parts but abandons the supervi?sion learning of all global parts in three branches,and these global parts are trained only with triplet loss and softmax loss.
Comparing CGPN-3 with CGPN,we observe a dramatic per?formance decrease on all three datasets.The performance on the metric Rank-1/mAP decreases by -1.9%/-3.7%,-1.8%/-4.0% and -2.8%/-2.6% on Market-1501,DukeMTMC-reID and CUHK03 respectively.As the three models are trained in exactly the same procedure,we conclude that the global part is critical to CGPN.
Comparing CGPN-4 with CGPN,after abandoning global su?pervision,we observe a performance decrease on Rank-1/mAP of-0.9%/-0.6%and-0.4%/-1.0%on Market-1501 and DukeMTMC-reID.While on CUHK03 we observe a dramatic performance decrease by -3.7%/-2.9%.The reason of such a different performance decrease is that Market-1501 and Duke?MTMC-reID mainly consist of holistic person images from which the global part can get enough good global features di?rectly even without supervision,while CUHK03 contains a lot of occluded or body part missing person images and the super?vised global part is much more important for extracting accu?rate global features.
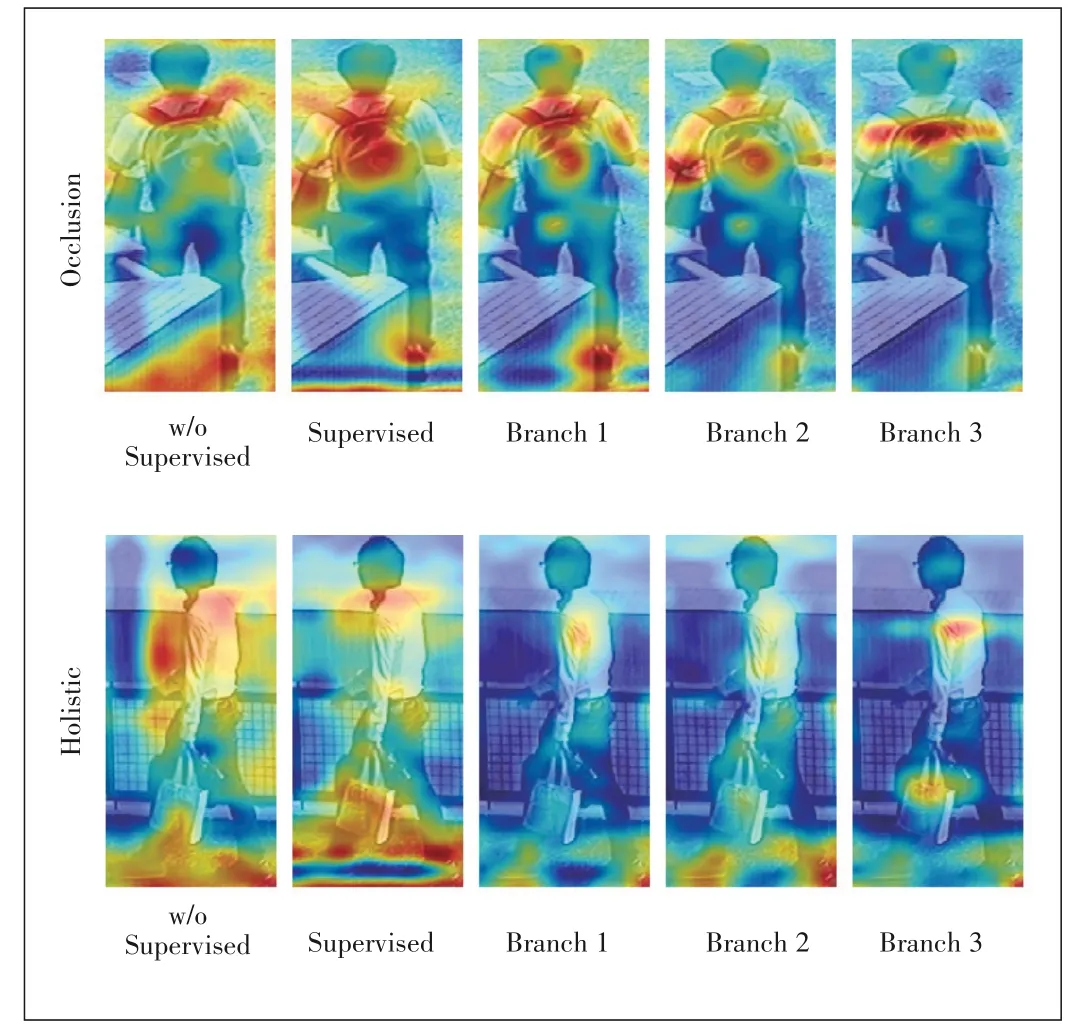
▲Figure 5.Feature visualization of different branches in the two cases of occluded pedestrian images and holistic pedestrian images
Comparing CGPN-4 with CGPN-3,after adding unsuper?vised global parts,we see a large performance improvement on Rank-1/mAP of+1.0%/+3.1% and +1.4%/+3.0% on Mar?ket-1501,DukeMTMC-reID.But on CUHK03 we observe a significant performance decrease by -0.9%/-0.3% unex?pectedly.As analyzed above,the image type is quite differ?ent in the three datasets,especially CUHK03 which con?tains a lot of occluded or body part missing person images.The unexpected performance decrease on CUHK03 further proves that unsupervised global features can be harmful and certainly impair model performance.We conclude that the supervision of global features is critical for high perfor?mance of person Re-ID and that unsupervised global fea?tures will result in inaccurate global features which impair model performance evidently.As shown in Fig.5,we can find that the unsupervised global features may receive inter?ference from the background or occlusion.But,our proposed supervised global features are more robust to person image occlusion or body-part missing.
4.6 Branch Settings Ablation Study
In this section,we conduct a large number of comparative experiments on CUHK03 dataset to verify the effectiveness of the numbers of 1×1 convolution layers in the global part and multi-branch architecture settings.
In the global part,the number of 1×1 convolution layers is a hyper-parameter and influences the receptive field of its corre?sponding supervision part features.To evaluate the effect of var?ious numbers of 1×1 convolution layers in the global part,as three branches’global part all share the same structure,we on?ly keep branch 1 of CGPN and abandon the other two branches of CGPN.We also aban?don the local part of branch 1 and only keep the global part of branch 1 denoted as Branch1-Global.
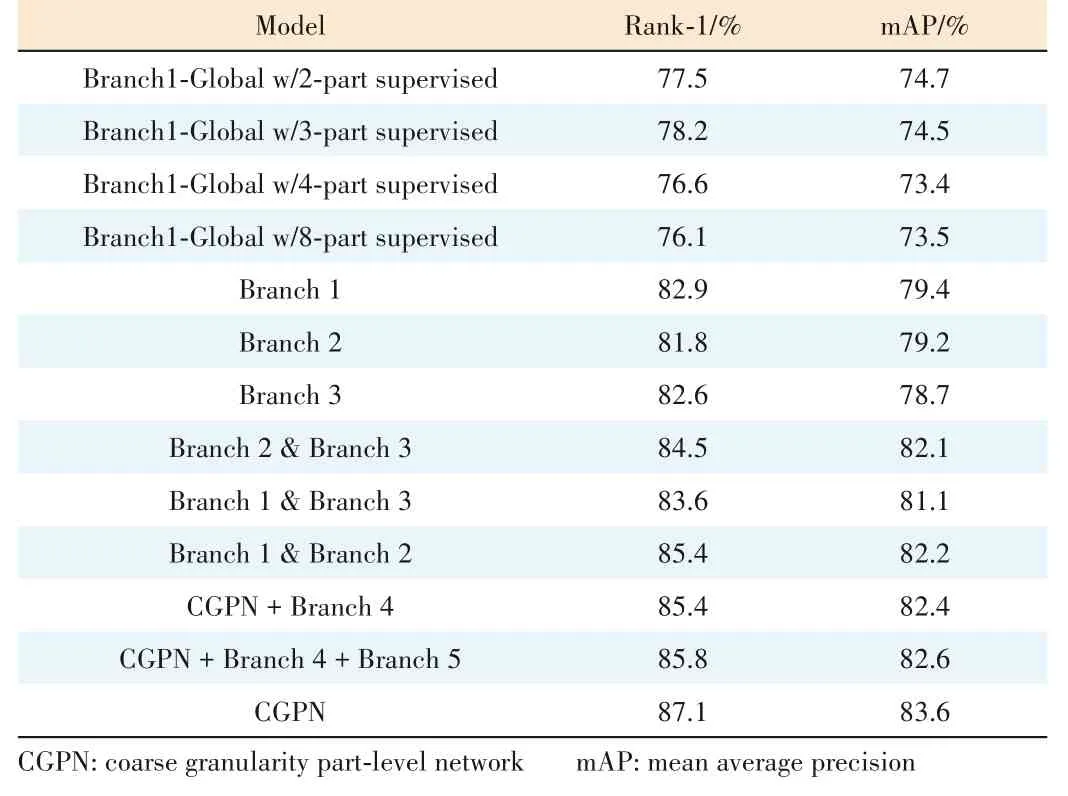
Table 4 shows the results of Branch1-Glob?al with different numbers of 1×1 convolution layers,i.e.2,3,4,8.From these results,we can find that Branch1-Global reaches the best performance with two 1×1 convolution layers,which achieves Rank-1/mAP=77.5%/74.7%on the CUHK03 dataset.The experiment re?sults further illustrate that coarse grained fea?tures can make full use of local information and preserve more semantic information,and thus help to extract more accurate global fea?tures.Therefore,We finally adopt two 1×1 convolution layers in our CGPN architecture.
We further perform experiments to verify the importance of various branch settings in CGPN.Here,Branchxmeans we only keep CGPN’s backbone and branchxafter res_conv4_1.For example,Branch 1 means just preserving CGPN’s backbone and branch 1 of CGPN and removing branches 2 and branch 3.With the increasing number of branches,Rank-1/mAP is significantly im?proved from 82.9%/79.4% to 85.4%/82.2%even to 87.1%/83.6%,as illustrated in Table 4.But,when we try more branches,such as CGPN+Branch 4 and CGPN+Branch 4 +Branch 5,we observe a significant performance decrease on Rank-1/mAP of-1.7%/-1.2%and-1.3%/-1.0%unexpected?ly.Therefore,we can conclude that the carefully-designed net?work architecture is also the main contributor to performance improvement,and three branches can effectively and efficient?ly capture enough complement information.
▼Table 4.Comparison results of different number of 1×1 convolution layers in the global part and multi-branch settings on CUHK03 dataset at evaluation metrics of Rank-1 and mAP in single query mode without re-ranking

▲Figure 6.Top-4 ranking list for some query images on CUHK03-labeled dataset by CGPN and MGN
Besides,from Fig.5,we can find that the three branches of CGPN focus on different parts of the pedestrian,and the extract?ed features are complementary to each other.
4.7 Visualization of Re-ID Results
We visualize the retrieval results by CGPN and MGN for some given query pedestrian images of CUHK03-labeled data?set in Fig.6,in which the retrieved images are all from the gallery set,but not from the same camera shot.The images with green borders belong to the same identity as the given query,and those with red borders do not.These retrieval re?sults show the great robustness of our CGPN model,regardless of the occlusions or body part missing of detected pedestrian images.CGPN can robustly extract discriminative features for different identities.
5 Conclusions
In this paper,we propose a coarse-grained part-level fea?tures learning network integrated with supervised global-lev?el features for person Re-ID.With the coarse-grained partlevel strategy,the local parts in three branches learn more discriminative local features.With the supervision learning of global parts in three branches,the global parts learn to ex?tract more accurate and suitable global features for pedestri?an images.Experiments have confirmed that our model not only achieves state-of-the-art results on all three mainstream person Re-ID datasets,but pushes the performance to an exceptional level.
- ZTE Communications的其它文章
- Editorial:Special Topic on Energy Consumption Challenges and Prospects on B5G Communication Systems
- Adaptability Analysis of Fluctuating Traffic for IP Switching and Optical Switching
- Next Generation Semantic and Spatial Joint Perception
——Neural Metric-Semantic Understanding - Kinetic Energy Harvesting Toward Battery-Free IoT:Fundamentals,Co-Design Necessity and Prospects
- Green Air-Ground Integrated Heterogeneous Network in 6G Era
- Cluster Head Selection Algorithm for UAV Assisted Clustered IoT Network Utilizing Blockchain

