Research on the Realization Mechanism of and Approach to Ecological Product Valuations
Li Mingxing
Chengdu Institution of New Economic Development
Zhang Kejun*
Sichuan Academy of Social Sciences
Abstract: Ecological product is an innovative practice for ecological valuations in China. Due to the influence of historical conditions and development stages in China, research on the realization of ecological valuations has lagged. In the new era, the construction of an ecological civilization guided by the “Two Mountains” theory has been promoted to the national strategic level and is supporting the growth of theoretical research and practical exploration based on the understanding of ecological product values. We want to innovate and improve the system used to realize the value of ecological products by applying the existing research,which focuses on the concept definition of ecological products and their correlation theories. Through systematic expansion and upgrades in this system, the evaluation accuracy of ecological products can be improved,providing valuable references for further practical exploration and promoting an ecological culture in China.
Keywords: value of ecological products, implementation mechanism, ecological civilization construction, value reference
Introduction
Over time, the interactions between the ecological environment and the development of human societies have become increasingly complex and the international community is paying more attention to the ecological environment and ecological products than ever before. As the development of China has entered a new era, the global situation and domestic reality force us to choose the path of green and sustainable development, which requires us to comply with the development concept of “Lucid waters and lush mountains are invaluable assets” and accelerate the construction of an ecological civilization. As President Xi Jinping pointed out that the ecological civilization system of China has been initially established and contains the main framework of“multiple pillars.” However, there are still three parts of the implementation of the system that need to be improved. These are property rights, market-oriented mechanisms, and management systems.Innovations and improvements in these mechanisms are critical to the successful construction of an ecological civilization.
The Definition of Ecological Products
Due to the lack of intuitive expression, a strict definition of the concept of ecological products has not been generally accepted although there has been a great deal of conceptual guidance.According to relevant theories, the concept of ecological products is based on the concept of ecosystem service value (Jiang & Ji, 2006). Relevant research conducted in the 1950s and 1960s includes the introduction of Holdren and Ehrlich’s concept of ecosystem service (Ehrlich,1974), which was the core of related research overseas. At the beginning of the 21st century, the international cooperation project of the International Millennium Ecosystem Assessment (MA)systematically divided the earth’s ecosystem services into such contents as supplying materials,regulating natural elements, providing spiritual and recreational services, and maintaining the earth’s living conditions, which formed the basis of ecosystem service.
The earlier research, which can be studied in China, started with the research and design of the vegetation system in the Loess Plateau (Hong & Yang, 1985). Later, Ren Yaowu et al.(1992) studied and defined the concept and connotation of ecological products and proposed that ecological products refer to safe, reliable, pollution-free and high-grade products produced by the ecological industry (agriculture) without ecological stagnation. Ren believed that ecological products had five characteristics: Naturalness, limitation, pertinence, localization and timeliness.On this basis, the academic community continued research on low-consumption, low-pollution industrial and agricultural products (Cai, 1996), and tended to define ecological products as specific material products that met certain environmental protection or ecological standards.Research also included studies on the theories and methods of product design around this concept(Li & Gao, 1998; Yang, 1999; Wang & Hu, 2000). Thus, the concepts of pollution-free products and green products were derived. After entering the 21st century, the concept of ecological products has been further defined by the domestic theoretical circles, which have expanded the boundaries from material products to service supplies and expanded the connotations of ecological protections and the realization of social public economic values. In 2010, the State Council of the People’s Republic of China issued a national plan for developing functional zones which pointed out that human beings have the demand for fresh air, clean water sources, a pleasant climate and other ecological products, and that ecological products, together with agricultural products,industrial products and service products, are necessary and consumable products for human life.Since then, the concept of ecological products has been summarized as, “Maintaining ecological security, ensuring ecological regulation functions, providing a good living environment including fresh air, clean water sources, growing forests, a suitable climate and other natural products not directly related to human labor, and organic food, green agricultural products, ecological industrial products and other material products produced through cleaner production, recycling,and consumption and emissions reduction to reduce the consumption of ecological resources”(Wang, Wang & Wang, 2002; Zeng, Yu & Xie, 2014).
On the basis of this concept, we hold that the traditional definition of ecological products as natural elements and material products is not adequate to meet the needs of the diversified development of modern society, especially with the continuous refinement of social service systems and the rapid development of interdisciplinary studies, and that ecological products in the modern sense should include the carrier of material products derivative-related services, such as technology transformation and application guidance. This definition can cover the traditional ecological products to the greatest extent, and better fit the system divisions of industrial types and industry categories in modern society (Fig. 1).
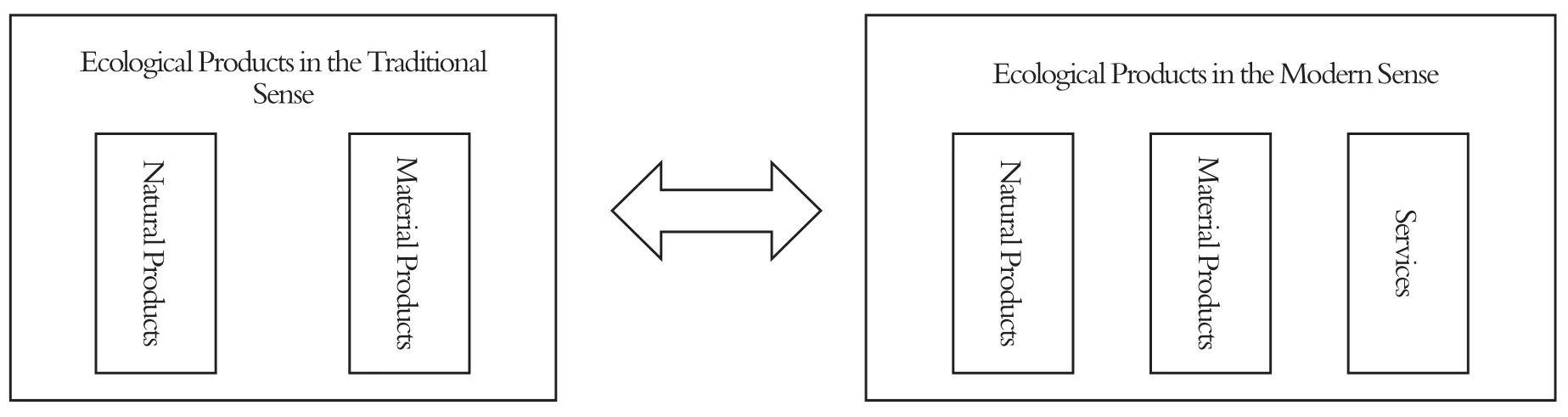
Figure 1 Classification of Ecological Products
The Theoretical Basis for the Value Realization of Ecological Products
Robyn Loomes, Kelli O’Neill, and others have done systematic research on different types of ecosystem service functions and their value evaluation by applying the principles of economics (Ma, 2012; Loomes & O’Neill, 1997), which played an important role in guiding the academic community in building a theoretical system with ecosystem service value as the core.Among these systems, the most representative are the brief history of total economic value by Krutila (1967), the division of tangible and material ecological environment economic value by Fisher (Kelso & Maurice, 1976), and the Total Enterprise Value (TEV) of ecosystem services classification framework proposed by Boland and Freeman (1981). In addition, there are also relevant theoretical and practical studies conducted by Matthew A. Wilson and others, who carried out value assessments of freshwater and forest ecosystems (Wilson & Carpenter, 1999). And during the 1980s, the UK, the US, France, and other countries put forward ecological environment protections and restorations (Qiu & Jin, 2019). In the early 1990s, Dutch public institutions and the United Nations first formally put forward the theory of multi-disciplinary integration, directed at “ecological design” which included the economy, environment, management and ecology, and then established the international organization for standardization and ISO14000, a new standard for environmental management systems.
There has also been an upsurge in research on the evaluation methodology of ecosystem service values, including conditional value methods (Davis, 1963), income cost reduction methods (Cuperas,1986), and market mechanism evaluation methods (Guo & Li, 1998). Based on this, the authors gradually explored ways and mechanisms such as finance, taxation, and finance to promote the market-oriented transformation of ecosystem service values, such as the “Ecological Bank” (Zhao& Li, 2020) and “Carbon Exchange Trading.” During this period, research in related fields was also started. Typical examples are: The analysis of the value connotation of ecological products from the perspective of public and non-public welfare (Wu & Du, 2014); value realization mechanisms from the perspective of economics, such as ecological purchase and ecological compensation (Li Yuansheng, 2018; Li & Qing, 2005); ecological agricultural development (Wen & Ting, 2019);ecological poverty alleviation and development (Mao & Xu, 2017; Xiao & Jiang, 2019); and ecological environmental protection (Luo, 2019). The systematic theories and methods of ecological valuation (He & Xu, 2019) include the shadow price method, alternative engineering method, the profit and loss analysis method, and the value equivalent method, among others (Huang, 2015;Ouyang, Wang & Miao, 1999; Peng, Wang, Chen, Li & Jiang, 2005; Yue, Jian, Hui, et al., 2017; Xie,Zhang, Zhang, et al., 2015).
Generally, although there are similarities and differences in the understanding of the value realization of ecological products, due to the differences in the definition of ecological products at home and abroad, the theoretical basis is still largely similar, which mainly includes several aspects. The first is the value theory. According to the Marxist stand, viewpoint and method of labor theory of value, the value of a commodity can be objectively measured by the average number of labor hours required to produce that commodity. Therefore, the value basis of ecological products is the use-value, and the core of this value is human labor. However, to realize the unity of use-value and value, it is necessary to define the human labor in ecological products and quantify and sum them in the form of price. The second is the utility theory. According to the micro theories of Western economics, product utility is the core basis of product payment cost, or the price. With the increase of supply, marginal utility presents a decreasing law, and its payment cost naturally decreases. This basic principle should be followed to complete the connections between supply and demand for ecological products. The third is the public goods theory. The new political economy divides products into public goods (including quasi-public goods) and private goods with the characteristics of “competition” and “exclusiveness.” In fact, ecological products have these two kinds of goods attributes, which determine that the socialized distribution of products must consider both public interests and private interests. The fourth is the property rights theory. The core idea of Coase’s property rights theory is that a clear property right relationship can greatly reduce transaction costs. Therefore, if the ecological products can be transformed into private products or quasi-private products through the definition of property rights, and then be supplied through market mechanisms, it undoubtedly provides an effective way for us to solve the external problems in the process of ecological construction.
The Mechanism System for Value Realization of Ecological Products
Through the application of the above theories, we can form the value realization mechanisms for ecological products, establish values for ecological commercialization, realize the convergence of supply and demand issues, and thus reach agreements on transaction prices. This will solve a series of problems, such as the value formation of ecological products, the connections between supply and demand, market transactions, income distribution and risk management.
How Is the Value of Ecological Products Formed?
Ecological resources have natural attributes and are the materials and conditions which are formed naturally and shared by human beings. Ecological products are formed by labor transformations of ecological resources, although the labor transformations may be purposeful and can be directly reflected or be unintentionally attached and indirectly reflected. Therefore,not matter which form or type the ecological products belong to must be based on the premise of human labor, including the transaction of materialized labor (the ecological capital, represented by the word “C”), the variable capital investment (the labor capital, input in the process of producing ecological products, represented by the word “V”), and the surplus value (the excess of ecological products compared with the total production of ecological capital and human capital, represented by the word “m”). However, this value formation mechanism of ecological products is from the perspective of general products only. For ecological products with strong externality, such as fresh air, water, and land, the above elements are obviously not enough. The boundlessness of natural resources and the unintentionalness of labor transformations lead to complex and pluralistic characteristics in the value of ecological products, including multi-level use, complex sources,diversity of composition, quantitative dynamics and spatial differences (Li, Bo & Cui, 2020).Relevant scholars have conducted a more in-depth studies on this issue. Among them, the most referential one is the binary price system of ecological products proposed by Zhang Ying and others (Zhang, Cheng, Wang, Lu & He, 2016). These studies point out that the different economic behaviors of buying and selling ecological products correspond to two opposite development modes of ecological environment protection and development, and that there are positive and negative externalities in these two market behaviors. Therefore, from the perspective of a more complete value system, ecological products should be based on the labor transformations of ecological elements and combined with different labor attributes to fully consider the external influences on their existence (Fig. 2).
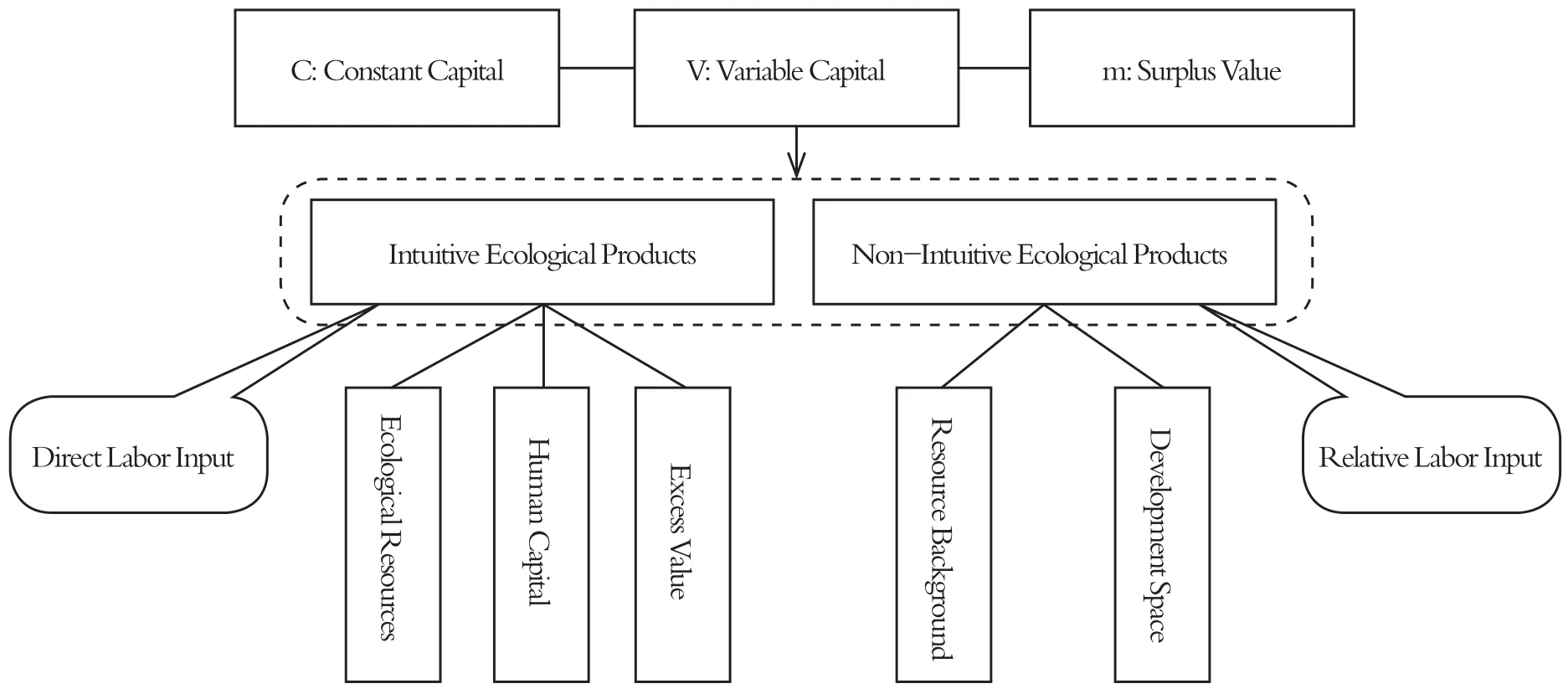
Figure 2 Value composition of ecological products
Ecological products are formed through labor transformations, for which their purpose can be directly reflected and referred to as intuitive ecological products. Examples are landscape design, water source protection, environmental restoration, and green agricultural products.Value formation for these is relatively simple. Like ordinary commercial products, they are mainly quantified by the positive reflection of human labor. Ecological products formed by labor transformations that are not directly attached or reflected can be referred to as nonintuitive ecological products, for example, air and water resources with relative quality differences which are caused by industrial environments, the space or environments created by the needs of urban development, and other differential resources and environmental conditions which are caused by the differences in human economic activities. The value formation for these is more complex and is not reflected by the simple positive results of human labor, but the relative value formed by the differential input of human labor. Human labor input with high quality will reduce the negative impact on ecology, and then produce a higher relative value for ecological products. However, it may also produce a lower relative value for the ecological products. Therefore, consideration of the value for non-intuitive ecological products should be based on two aspects. The first is the background of the resource, for example, the natural attribute basis of the ecological products such as the size of the spatial range, the balance of the water and soil ratio, and the amount of nutrient content. The second is the development space.This is the resources that can be achieved through the corresponding implementable technical means within a certain period of time, the degree of utility development, the degree of pollution that can be tolerated, the activity intensity that can be carried, and the consumption satisfaction that can be achieved.
The Supply and Demand Mechanism of the Ecological Products
The connection between supply and demand for the ecological products, the transactions of value and their form of transformation can determine the value of ecological products.According to utility theory, to realize the connection between supply and demand, what is essential is the balance between the marginal utility of ecological products and the transaction costs between supply and demand as subjects reach the Pareto Optimal state. Analysis reveals three meanings.
Reasonably defined property rights.
The basic condition of the establishment of the relationship between supply and demand of ecological products is the clear division of product ownership and power. From the perspective of the value formation mechanisms of ecological products, the value of intuitive ecological products or non-intuitive ecological products can be derived from public labor and private labor. Therefore, the definition of property rights of ecological products should also include public and private attributes, and we should carry out confirmation of rights at different levels comprehensively and systematically, and establish a corresponding legal protection system for property rights.
To scientifically determine property rights.
As discussed above, there are many forms of expression for ecological products, including natural products, material products, and service products, all of which are different from normal products. But this does not mean there are differences in the property rights between ecological products and normal products just because of the differences in the forms of expression. Thus, we should promote innovations for the value realization of ecological products with full consideration of different demands of stakeholders, actively improve the positive rights and rights of the owners,including the owner’s exercise of possession, use, disposal and income, and the owner’s negative right to exclude other people’s interference, to realize the return, exclusion, and prevention of interference claims.

Figure 3 The Supply and Demand Patterns of Ecological Products
The patterns of supply and demand for ecological products are naturally different and are based on the differences in the attributes of ecological products. Generally, the modes can be divided into two categories. One is passive while the other is active. The “Passive Supply”category refers to the pattern formed when the supply of ecological products is driven by the specific needs of the demand side and the purpose of the supply is to meet the private need of the demand. Examples are organic vegetables, energy-saving and environmental protectionoriented electronic products, and services helping to control air pollution. Under the conditions of passive supply, the demand side maintains the state by accepting the terms of the suppliers,especially the price. The “Active Supply” category refers to the pattern formed when the supply of ecological products is based on consideration for the public welfare. While the demand side does not clearly express demand intentions such as upgraded urban parks, national ecological protection of forests, and improved water treatment facilities, the demand side is guided by the state through its responsibility for the welfare of the people, especially considering their obligation of paying taxes.
The Essential Factor of Ecological Products Trading
In order to realize transactions of ecological products, it is necessary, according to the basic law of market transactions, to have a system, which is based on prices, platforms, procedures, and a few other elements. (Fig. 4)
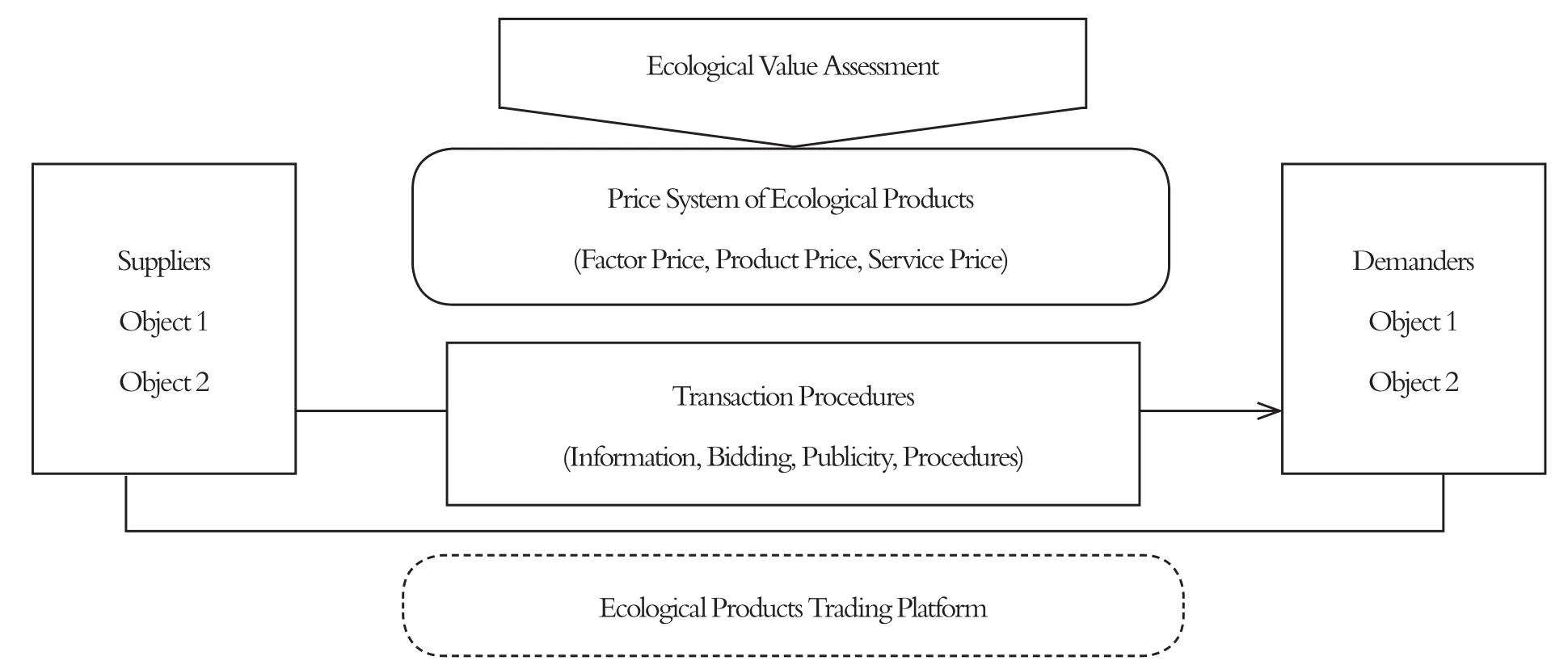
Figure 4 Ecological Products Trading Platform System
First, we should build a price system for ecological products based on the law of value. We have analyzed the value formation mechanisms and the calculation of the values of ecological products based on value formation, which is usually called the value evaluation, and the result of value evaluations is the price system of ecological products. Overall, the mature ecological value evaluation methods currently used can be roughly divided into three categories (Liu, Y., Du,X., & Zou, M., et al., 2017). The first is the direct market method. This mainly includes the cost expenditure method, the market value method, the opportunity cost method, the recovery and protection cost method, the shadow engineering method, the human capital method, and others.The second is the alternative market method. This mainly includes the travel expense and hedonic value method. The third is the simulated market method. This mainly includes the conditional value method. Generally, the direct market method is more suitable for intuitive ecological products, while the alternative market method and the simulated market method are more suitable for non-intuitive ecological products. Of course, in specific operation processes, there may be ecological products with the characteristics of both types of products, so it is necessary to use a variety of compatible evaluation methods.
Second, we should build an efficient and convenient trading platform for ecological products. In terms of function, it is the space-time carrier for the trading of ecological products.From the perspective of practice, the ecological bank, which emerged earlier in foreign countries, is the most typical. For example, the water bank, the wetland mitigation bank, and the forest bank have been gradually introduced to China. However, there are still many weak spots in the construction of ecological products trading platforms. Especially, their service systems have yet to be perfected and need continuous innovation. For example, it is necessary to increase capital investments, to gradually optimize the platforms to raise social capita, and then to gradually change the construction situation now dominated by government investment.We should continue to enrich the platforms, not only in regard to the existing modes, such as the ecological bank, but also to strengthen the two-way innovations and extensions of the platform service chains. In addition, we should focus on the application of advanced technologies and concepts, especially the in-depth integration of digital technology, the Internet, artificial intelligence, and block chains, to meet the diversified needs of the market.
Third, we should design standardized and orderly ecological products trading procedures.Considering the strong externality of many ecological products, the trading procedures for ecological products should strictly follow the closed-loop trading rules, that is, the ecological products should be traded on a particular platform with normal standards. Taking marketoriented transaction of land resources as an example, the transaction procedures can be roughly divided into four parts, which are the product information release, fair bidding, political result announcements, and procedure fulfillment. Among these, the information release is the basis of transaction docking between the supply and demand sides. Fair bidding is the core link in the transaction procedure, of course, and according to the different properties of the ecological products, we can choose collective bargaining or agreement pricing. The announcement is a kind of open system for the conclusion of the transaction, which aims to ensure that the transaction of the products conforms to the basic rules of the market and accurately conveys information to relevant parties. Procedure fulfillment mainly refers to perfecting the transaction restrictions and identifications after the transaction between the supply and demand sides is concluded, which can be conducted by the government or third-party entities based on the procedural specifications,such as the environmental protection record, the price record and the ownership change registration.
The Income Distribution of Ecological Products
The income distribution of general product transactions mainly includes three parts, namely,compensation for the resource consumption of the products, profits for the capital investments in the production of the products and the obligation to pay for the public expenses. As to the primary market, the primary transaction of the product property rights, the income distribution mainly includes compensation for resources consumed by the product, and the obligation to pay for the public expenses. Regarding the secondary market, the secondary transaction of the product property rights, the income distribution mainly includes the profit for the capital investments in the production, and the obligation to pay for the public expenses. For ecological products, the resources consumed come from public property or private property, and the capital investments in the production of ecological products can come from public capital or private capital. Therefore,the income distribution of ecological products is relatively complex. In general, there are several matters that should be made clear.
The first matter concerns who the beneficiary is. On the whole, the realization of the ecological product involves the work of the property rights subjects (mainly refers to the ownership of the products), the investment subjects and the management. According to the basic principle of the income distribution, which is guided by the property rights system:First, the subjects of the property rights are the primary subjects who have the right and the qualifications to enjoy the income. According to the basic principle that the one who owns the product resource will get the benefits that comes from it, and under the current ownership system current Chinese ownership system, we should clearly define two types of beneficiary objects, the collective organizations and the citizens, and clarify the benefit rules among the members within the subject; second, the investment subjects are the main bodies who have the qualifications to enjoy the income. Generally, the amount of the investment is used to measure the benefit from the income, which contains the monetary capital investment, the labor capital investment, the technology investment, etc., which are generally in the form of share quantifications; third, the management service subjects are also important subjects of the income enjoyment, which is mainly based on their reasonable service in the process of product value realization, and of course, there is another purpose, which is to keep a balance for the public welfare. The public benefits can be explored in the form of taxes, fees, funds, etc.
The second matter concerns how to develop a reasonable income standard. In essence, there are two meanings regarding the income division. One is how to allocate the overall income rationally, and the other is how to limit the amount of the partial income. Generally, we usually realize that the profit of the investors is achieved through the products transaction, and that therefore, the division of income is mainly applicable to the limit of the profit margin. But for the income standard division of the property rights subjects and the management, there need to be more necessary considerations. On the one hand, we should consider the basic rights and interests of the subjects of the property rights, and on the other hand, we should consider the external benefits. Therefore, the standard is generally dynamic. In principle, the division of income standards does not consider the overlapping relationships among the beneficiaries. For example,when the state invests in the construction of regional ecological projects, the government, as the executor of the public property rights of the resources and the investor of the ecological products,naturally enjoys double benefits. Of course, the government can transfer the revenue because of the necessary input for the public service.
The third matter concerns how to set the form of income scientifically. The realization forms of ecological product income are diverse. The most common form is the same material income as that of the common market products. For example, the most general monetary income includes direct monetary income, stock appreciation equivalent to monetary type, and material pricing.In addition, there are non-material benefits, which can also be called hidden benefits, such as the optimization and improvement of production and living environments, the improvement of the functional levels and service quality of supporting facilities, and the improvement of the happiness index of stakeholders. In fact, in view of China’s economic and social development,it should be more suitable to take the form of combination of material income and non-material income, or even the form of pure non-material income, which is more conducive to the sustainable development of an economic society.
Ecological Risk Management of Products
Ecological risks have attracted people’s attention through the economic and social development. Generally, ecological security can be defined as the degree of protections for human production, life and health, which are not affected by ecological damage and environmental pollution. This includes basic elements such as drinking water food safety, air quality and green environments (Xiao & Chen, 2002). In essence, the risk of ecological products comes from not only the ecological risks, but also from the technical and market risks related to ecological products. However, no matter what kind of risk it is, the main content of risk management mechanisms is consistent and includes three elements.
Risk identification and assessment.
The risk sources of ecological products are diverse and can be roughly divided into two areas.One is the uncontrollable factors that form naturally, such as geological disasters, meteorological disasters, sudden diseases, and other uncontrollable factors. The other is human factors such as unreasonable ecological development and utilization, technical errors in product development, and unqualified product delivery. Of course, there may be a combination of natural and human factors.Therefore, it is particularly important to establish a suitable risk identification and assessment system for ecological products. At present, the state has implemented the relevant system requirements and technology applications in some fields, such as product energy consumption identification, industrial “three wastes” (waste water, waste gases and residues) emission standard system, and the “san pin yi biao”①Pollution-free agricultural products, green food and organic agricultural products and geographical indications of agricultural products generally referred to as the “san pin yi biao”.agricultural product certification system. However, these systems are limited to specific products and industries and the comprehensive risk assessment of ecosystem services, such as the stability of the regional water and soil supply, is still in the early development stage, which causes great obstacles to the realization of the valuation of ecological products in the broader sense.
The risk disposal mechanism.
Generally, the risk disposal of ecological products includes active disposal and passive disposal. Active disposal generally includes the recovery and improvement of the products or services provided by the supplier, while passive disposal is generally terminated by the corresponding market or administrative supervision subjects punishment. According to the actual situations, passive disposal is often used, such as environmental law enforcement, and industrial and commercial fines for non-standard products. However, this form of risk disposal has an adverse effect with time-delays and faces a large social cost which is often difficult to make up for the existing losses, and it is easy to lead to “rent-seeking” of rights. Therefore, we should find a way to transfer a product’s risk to the supply costs and construct a complementary risk disposal mechanism of market.
Dispute arbitration for ecological product transactions.
Disputes about ecological environments have always existed. Because the ecological products and the ecological environment are closely related, they will inevitably encounter the same problems. Settlement mechanisms for environmental disputes, such as reconciliation, mediation,administrative treatment and litigation, all have great limitations. However, as a typical mode for civil disputes coordination of civil state power, arbitration is more effective than simple civil consultation and pure court judgments in solving ecological products disputes and other risk issues. However, due to the imperfection of the market system of ecological products and the construction of an ecological civilization system, the dispute arbitration mechanisms related to ecological products also face many problems. The existing arbitration mechanisms and relevant implementations, such as environmental dispute arbitration, are basically implemented by the dispute arbitration mechanism of general civil disputes. However, because of legislative restrictions, property rights definitions and public awareness (Liu & Tian, 2007), the dispute arbitration for ecological products or services with “publicity” or “quasi-publicity” are mostly non-existent. Therefore, it is particularly urgent to establish and improve ecological products dispute arbitration mechanisms which are compatible with the property rights system, laws and regulations and the market system of ecological products.
Innovative Ways to Realize the Value of Ecological Products
Combined with the existing research, in order to innovate the approaches to realizing the value of ecological products from the directions of market-oriented management and public compensation, we should focus on the common characteristics and individual differences of the ecological products, and stand on the basis of constantly improving the mechanism system, which is necessary for the value realization of the ecological products. In addition, we should also take overseas experience as a reference, combining this with national conditions.
The first is based on market operations. It is about through the platform, which is based on the legal definition of the property rights of the ecological products, and the corresponding development rights derived around the development and utilization of the products, such as water pollutant emission rights, carbon emission rights, and ecological and environmental protection products identification rights. According to the different transaction subjects and forms, this platform can be divided in three ways.
Direct transactions between the supply side and the demand side of ecological development rights. This is basically consistent with general commodity transactions. The specific steps include: First, product design, which refers to the establishment of ecological development rights for innovation and development of ecological resources; second, product bidding, which refers to the supply side and the demand side conducting fair bidding around the guiding price which is formed by the methods of evaluation for ecological resources values, and completing the transactions using the corresponding principles; third, product transaction, which refers to the fair transaction of ecological development rights under the conditions of market access and the completion of registration or filing of the property rights; fourth, product consumption, which refers to the transaction of the development rights, the utilization of the ecological resources or the ecological products based on the content of the property rights and the obtaining of income after the transaction. This approach is generally applicable to private ecological products with simple property rights and less external influence.
The government or public organizations should receive and reserve the ecological development rights, which is a second transaction with the third party and is similar to the transaction of public goods or quasi-public products. The specific steps include: First, property rights collection and storage which refers to the government or other public organizations with the power to collect and store the ecological resources or ecological products to be developed and utilized; second,planning and designing, which refers to the suppliers who carry out a product marketing plan according to the regional development; third, price hearings. In view of the particularity of public rights collection and storage, public hearings will be adopted in the process of product delivery;fourth, product trading, which refers to the fair transaction of ecological development rights under the condition of market access and the completion of registration or filing of the property rights; fifth, supervision after supplying, which refers to the government and other organizations with public power who supervise the consumption behavior of products based on the need to reasonably protect public rights and interests to reduce any negative external influences as far as possible.
Transfer and cooperation of ecological development rights. This belongs to the compound trading mode of multiple participation, which is more of a cooperative mechanism. The specific steps include: First, value quantification, which refers to the quantifying of the subject matter or non-material ecological products as the basic characterization of the transaction of the right to ecological development; second, stock cooperation, which refers to all sides reaching a share agreement to build a cooperation mechanism for the development and utilization of the product development right while taking the product value as a reference; third, transfer operation, which refers to the parties to joint-stock cooperation agreeing on the forms of using and management,according to the real situation regarding consumption and supervision; fourth, income distribution, which refers to all sides sharing the benefits from the products, which is based on the agreements on sharing income in joint stock cooperation.
The second is based on ecological public compensation. It is about restricting the realization of the benefits of market-oriented operations and development rights of different regions and entities through public power according to different objects, which are based on the legal definition of the property rights of ecological products. This method aims to achieve a particular goal, such as public security, through tax or ecological income compensation. The realization mode of the value of ecological products is usually called “ecological compensation” which can be divided into two specific ways, based on the different objects.
Compensation for the supply of ecological products, which means the ecological compensation is mainly for the body of the ecological products suppliers. The models include “returning farmland to forest” and “returning grazing land to grassland.” There are three main steps: First,formulating the compensation standard, that is, quantifying the degree of the income restriction of the transaction of the ecological development right and formulating the corresponding compensation standard system in combination with the relevant policy requirements; second,carrying out compensation accounting according to the actual rights and interest losses of the beneficiary to be compensated, and the compensation shall be checked and registered according to the appropriate compensation standard system; third, transferring payment implemented by the governments at all levels, or requiring public authorities to realize the compensation through special financial transfers.
Compensation for consumption of ecological products, which means that the ecological compensation is mainly for the consumers of the ecological products. Models include “energy saving subsidies,” “environmental protection subsidies” and “free tax deductions.” There are three main steps. First, formulating the compensation standard by calculating the space balance of the transaction of the right to ecological development in the development and utilization of ecological products, and formulating a reasonable compensation standard system in combination with the relevant policy requirements. Second, carrying out compensation accounting and combining the actual consumption savings or income loss of the intended beneficiary according to the corresponding compensation standard system. The compensation accounting, verification and registration procedures should be carried out. Third, transferring payment implemented by the governments at all levels or requiring the public authorities to realize the compensation through special financial transfers.
The ways of realizing the value of ecological products discussed above are not mutually exclusive. According to the differences between private benefits and public welfare attributes of ecological products, there might be overlapping use of different realization paths. In addition, as far as a single way is concerned, there may also be some supplements including green financial support, policy, and institutional incentives in specific links.
Conclusion
First, we should accelerate the construction of the ecological property rights system. According to the design concept of ecological products, the definition of property rights is the logical starting point for the realization of the value of ecological products. Whether it is public property rights or private property rights, the ownership relationship should be clearly defined, and relatively sound and complete powers and functions should be given to ensure the effectiveness of the market-oriented mechanism. China should speed up the construction of its property rights system in the field of ecological resources and ecological products, formulate corresponding laws and regulations, and implement corresponding policy guidance.
Second, we should focus on the cultivation of the main supply of ecological products. We should adhere to the idea of “government supply” and “market supply” in parallel, give full play to the market laws, create a good policy environment for the cultivation of business entities in the fields and markets of ecological products, stimulate the market potential of ecological products,and then promote the development of new industries in the ecological field, realize the qualitative change from ecological protection to ecological development and utilization, and create a national ecological growth pole of economic development.
Third, we should improve the value service system of ecological products. Guided by the connotation of the mechanism for realizing the value of ecological products, we should constantly improve the platform construction and functional service construction including research for an ecological property rights system, the innovation of ecological products, the evaluation of ecological values, and the construction of functional services.
Fourth, we should establish a national ecological economic accounting system while developing a catalogue of ecological products and a value system for ecological products.This ecological economic accounting system should be connected to the current national economic classification accounting system to accelerate the establishment and improvement of a management system for ecological assets including the production and consumption of ecological products in the national economic and social development plan.
Fifth, we should strengthen the supply guarantees of fiscal and financial policies. We should formulate policies and measures including finance and insurance to support the development of ecological products industry, increase financial input, improve policy mechanisms, deepen policy connotations, and develop policy tools to form a complementary and closely policy guarantee system for the realization of ecological product value.
Finally, we should guide the establishment of ecological product consumption concepts.Through in-depth publicity, sample demonstrations, reward and punishment mechanisms and other means we should continuously strengthen positive ecological concepts in economic and social life, guide the formation of a good awareness of ecological product consumption, and gradually improve the overall layout of an ecological society.
 Contemporary Social Sciences2021年2期
Contemporary Social Sciences2021年2期
- Contemporary Social Sciences的其它文章
- The Information Efficiency of QFII’s Investment in China’s Capital Market
- Research on the Cultivation of the Innovative Subcenters in Sichuan Based on the Chengdu-Chongqing Economic Circle Strategic Background
- Analysis of the Focal Issues of the Implementation of the Block System Reform in China—From the Perspective of the Protection of Civil Rights
- A Comparative Study on the Buddhist and Brahmanic Conceptions of the Relationship between the Secular World and the Emancipation Realm
- The International Profile of Chinese Visiting Scholars in the UK:Improvement Needed in Linguistic,Cultural, and Academic Confidence
- Fractal Analyses Reveal the Origin of Aesthetics in Chinese Calligraphy
