Determination of Content of Hyperin and Luteolin in Vernonia cinerea (L.) Less.
Zhiying WEI, Jiahui HE, Hailin LU
Guangxi University of Chinese Medicine, Nanning 530200, China
Abstract [Objectives] To determine the content of hyperin and luteolin in Vernonia cinerea (L.) Less., and to provide basic experimental data for experimental research and clinical application of V. cinerea (L.) Less. [Methods] The components to be determined were extracted by ultrasonic extraction, and the hyperin and luteolin in V. cinerea (L.) Less. were separated and determined by reversed-phase high performance liquid chromatography (chromatographic conditions: reverse C18 column, methanol-0.4% phosphoric acid as mobile phase for gradient elution, flow rate of 1.0 mL/min, detector wavelength of 360 nm). [Results] The precision and repeatability of the experimental method were good, and the solution of V. cinerea (L.) Less. was stable within 18 h. There was a good linear relationship between the injection volume of hyperin and luteolin and the chromatographic peak area within the prescribed range, and the recovery rate was qualified. The content of hyperin and luteolin in V. cinerea (L.) Less. was 0.066 5 mg/g (n=3) and 0.100 4 mg/g (n=3), respectively. [Conclusions] The experimental method is sensitive, specific, stable, accurate and reliable, and can be used for the determination of hyperin and luteolin in V. cinerea (L.) Less.
Key words Vernonia cinerea (L.) Less., Hyperin, Luteolin
1 Introduction
Vernoniacinerea(L.) Less., also known as Xiao Shanhu, or Herb of Ashycoloured Ironweed, is a herbaceous plant of the genusVernoniain the Compositae family, widely distributed in the tropics all over the world. It is distributed in Guangxi, Guangdong, Fujian, Yunnan, Sichuan and other hot areas, mostly in roadsides, fields, wasteland, hillsides and other places with sparse vegetation distribution. There is an early medicinal record inLingnanMedicineCollection: the whole grass or root ofV.cinerea(L.) Less. can be used as medicine, and it is harvested in summer or autumn, washed and used in fresh state or dried in the sun.V.cinerea(L.) Less. tastes bitter, pungent, and is cool in nature, with the effects of dispelling wind and heat, cooling blood to calm the mind, dehumidification and detoxification[1-4]. It can be taken orally for the treatment of snakebite, icteric hepatitis, cold and fever, dysentery, neurasthenia and so on. It can be used externally to treat carbuncle, toxic swelling, snakebite and other diseases.
V.cinerea(L.) Less. is a traditional Chinese medicine commonly used by the Zhuang nationality in Guangxi, which has a long history, and related experimental research has been gradually carried out in recent years. Experimental pharmacological studies have found thatV.cinerea(L.) Less. has bacteriostatic, anti-inflammatory and antioxidant effects, and can be used in the treatment of a variety of inflammations, such as acute tonsillitis, mumps, hepatitis, gastroenteritis, bronchitis, and urinary tract infection[5-7]. Scholars have studied the ingredients ofV.cinerea(L.) Less. and found thatV.cinerea(L.) Less. contain many kinds of chemical components, such as amino acids, mineral elements, vitamins, flavonoids, sesquiterpenes and triterpenes[5-10]. Zhu Huaxuetal. separated and identified luteolin, hyperin, apigenin, chrysoeriol, quercetin and other components with significant pharmacological activity inV.cinerea(L.) Less. by column chromatography, which may be the material basis for the remarkable curative effect ofV.cinerea(L.) Less. The correlation between the specific efficacy and the corresponding active basic substances and the synergism between the components need to be studied.
Taking the whole grass ofV.cinerea(L.) Less. as the research object, the hyperin and luteolin in GuangxiV.cinerea(L.) Less. were separated and determined by reverse high performance liquid chromatography[11-22]. The purpose of this study is to provide basic experimental data for experimental research and clinical application ofV.cinerea(L.) Less.
2 Materials
2.1 Major medicineThe medicinal material was collected from Longtou Village, Lingjing Town, Teng County, Wuzhou City, Guangxi in October 2018. It was identified asV.cinerea(L.) Less., a Compositae plant, by Lu Hailin, senior experimenter of Guangxi University of Chinese Medicine. The medicinal materials ofV.cinerea(L.) Less. were dried at 50 ℃ and crushed with a high-speed grinder. Medicinal samples and powders are stored in the Drug Analysis Laboratory of Guangxi University of Chinese Medicine. The reference substances of hyperin and luteolin were purchased from Shanghai Ronghe Pharmaceutical Technology Co., Ltd. (the content≥98%, the batch number of hyperin-180209, the product batch number of luteolin-171026).
2.2 Main instrumentsHigh speed crusher, Shandong Qingzhou Yikang Traditional Chinese Medicine Machinery Co., Ltd., YK-100A; electronic analytical balance, Sedorius Scientific Instruments (Beijing) Co., Ltd., SQP; ultrasonic cleaner, Kunshan Ultrasonic Instrument Co., Ltd., KQ-500E; high-speed centrifuge, Hunan Xiangyi Laboratory Instrument Development Co., Ltd., H1650-W; ultra-pure water purifier, Merck Millipore, France, Direct-Q5; high performance liquid chromatograph, Agilent Technology Co., Ltd., Agilent1260.
3 Methods and results
3.1 Preparation of reference solutionThe reference substances of hyperin and luteolin were precisely weighed with a balance (an accuracy of 0.000 1 g). Dissolved with 95% ethanol, the mixture solution was prepared with 0.027 0 mg/mL hyperin and 0.042 0 mg/mL luteolin, and sealed for later use.
3.2 Preparation of sample solution10.0 g ofV.cinerea(L.) Less. powder under Section2.1was weighed with a balance (an accuracy of 0.000 1 g), 100 mL of analytically pure 95%ethanol was added and it was soaked overnight. The solution was heated to boiling in a water bath and treated with ultrasonic for 45 min, then cooled to room temperature. After filtering and drying under reduced pressure, the extract was dissolved with 95% ethanol and the volume was fixed to 25.0 mL. After filtration, the continuous filtrate was centrifuged at 20 000 rpm/min, and the supernatant was taken as the sample solution.
3.3 Chromatographic conditionsThe chromatographic column is C18column (4.6 mm×250 mm, 5 μm) with a constant temperature of 30 ℃; gradient elution was carried out with methanol-0.4% phosphoric acid as mobile phase (the conditions of gradient elution are shown in Table 1 below), and the flow rate of mobile phase is 1.0 mL/min; the working wavelength of the detector is 360 nm.
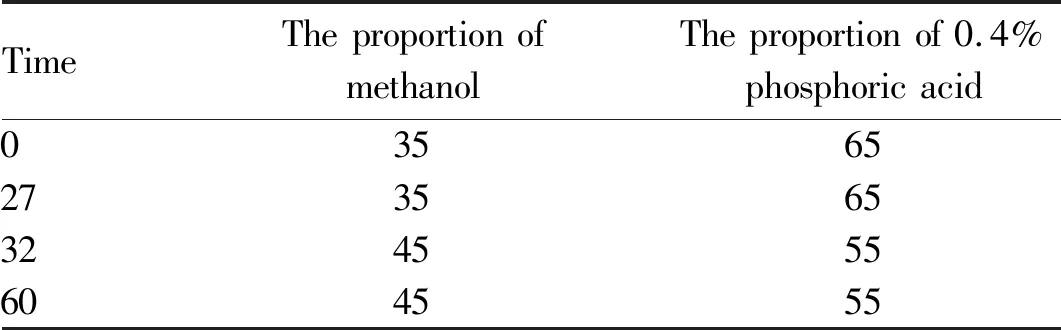
Table 1 Gradient variation of mobile phase
3.4 Methodological investigation
3.4.1Investigation of linear relationship. The mixed reference substance solutions of known concentrations in Section3.1were injected at 5 different volumes of 2, 6, 10, 14 and 18 μL, respectively, and the linear regression equations were made with the injection volume as ordinate) and the corresponding peak area value as abscissa, respectively. The results showed that there was a good linear relationship between the injection volume and the chromatographic peak area in the range of 0.054 0-0.486 μg for hyperin (linear equation:y=406.51x+374.54,r=0.999 5) and 0.084-0.756 μg for luteolin (linear equation:y=192.46x+204.08,r=0.999 8).
3.4.2Investigation of precision. The reference substance solution prepared under Section3.1was determined in parallel for 5 times under the chromatographic conditions in Section3.3.RSDwas calculated according to the peak area of the components to be tested:RSD=0.90% (n=5) for hyperin andRSD=0.18% (n=5) for luteolin. This showed that the precision of the determination method met the requirements.
3.4.3Investigation of repeatability. Five solution samples ofV.cinerea(L.)Less. were prepared in parallel according to the method in Section3.2and the chromatographic conditions under Section3.3were used to determine the content of the components to be tested, and the correspondingRSDvalues were calculated:RSD=2.70% (n=5) for hyperin,RSD=2.17% (n=5) for luteolin.
It showed that the repeatability of the method met the requirements.
3.4.4Stability test. One sample solution ofV.cinerea(L.) Less. was prepared by the same method in Section3.2and determined every 3 h for 7 times, and the chromatographic peak area of the two components to be tested was recorded. The calculation results are as follows:RSD=1.58% for hyperin,RSD=0.18% for luteolin.
3.4.5Sample recovery test. Five samples ofV.cinerea(L.) Less. powder (about 5 g each) were precisely weighed, and two kinds of reference substances with the same weight as the components to be tested in the medicinal material (the theoretical value of hyperin was 0.275 mg and the theoretical value of luteolin was 0.487 5 mg) were added respectively. Analytically pure 95% ethanol was added to 100 mL and the mixture was soaked overnight. It was then heated to boiling in a water bath and treated with ultrasound for 45 min, cooled to room temperature, and dried under reduced pressure. The extract was dissolved with 95% ethanol and the volume was fixed to 25.0 mL. After filtration, the continuous filtrate was centrifuged at 20 000 rpm/min at high speed, and the supernatant was taken as the mixed solution. The peak area of each component of the mixed solution was determined according to the chromatographic conditions under Section3.3. The content of each component in the mixed solution was calculated according to the regression equation. The recovery rate andRSDvalue of each component to be tested were calculated according to the experimental data. The results showed that the average recovery rate of hyperin and luteolin was 97.0% and 97.52%, respectively, and theRSDwas 1.39% and 1.23%, respectively. The results showed that the accuracy of the method met the requirements, and the data are shown in Table 2-3.
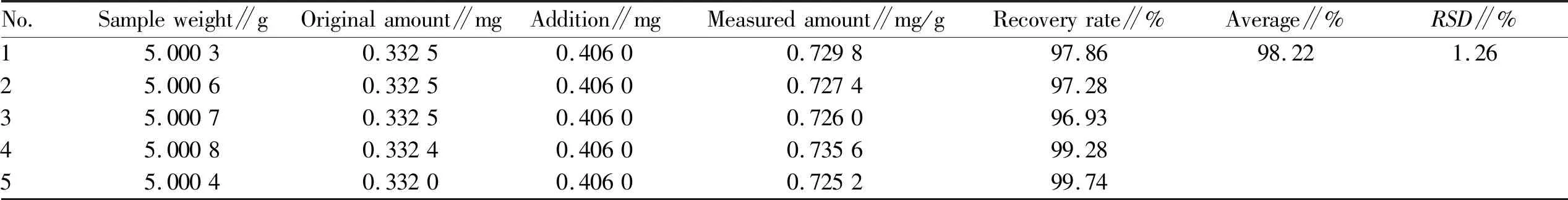
Table 2 The recovery rate of hyperin in Vernonia cinerea (L.) Less. (n=7)
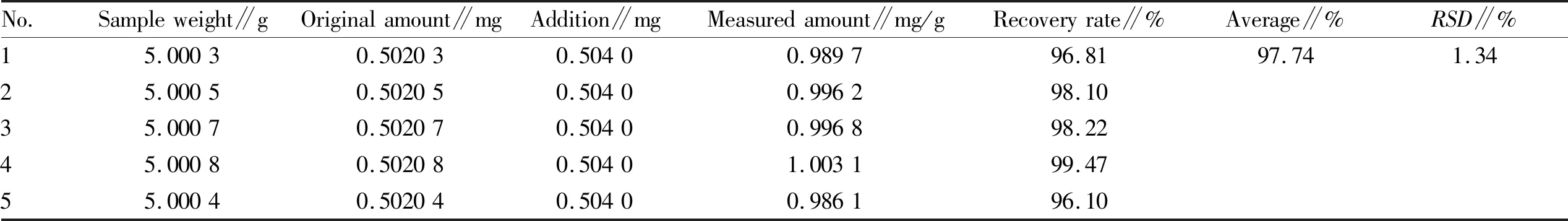
Table 3 The results of recovery of luteolin in Vernonia cinerea (L.) Less. (n=7)
3.5 Determination of content of hyperin and luteolin inV.cinerea(L.) Less.Three sample solutions ofV.cinerea(L.) Less. were prepared in parallel according to the same method in Section3.2. The content of hyperin and luteolin in the solution was determined according to the liquid chromatographic conditions under Section3.3(Fig.1-2). According to the experimental data, the average content of hyperin and luteolin inV.cinerea(L.) Less. was calculated, and the correspondingRSDwas calculated. The results are shown in Table 4 and Table 5 below.
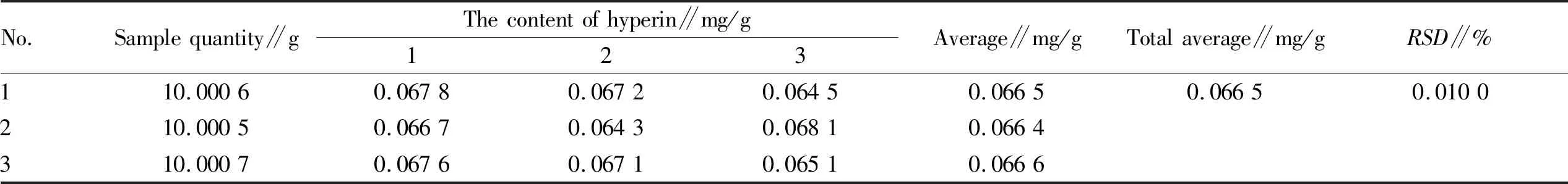
Table 4 Determination results of content of hyperin in Vernonia cinerea (L.) Less. (n=3)
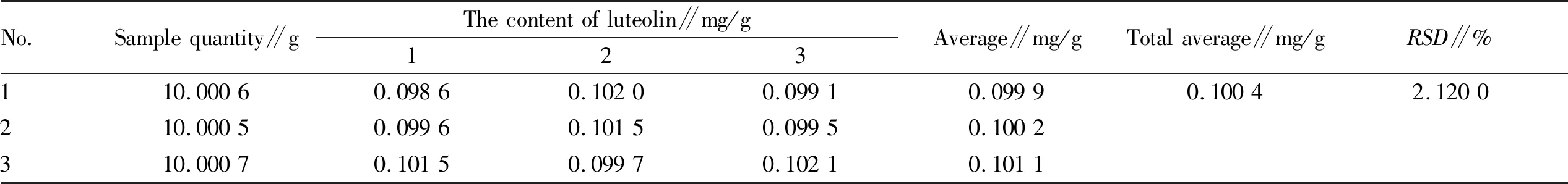
Table 5 Determination results of content of luteolin in Vernonia cinerea (L.) Less. (n=3)
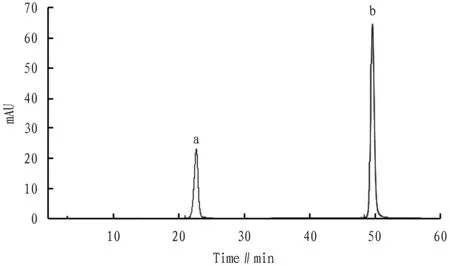
Fig. 1 Chromatogram of mixed reference substance (a. hyperin; b. luteolin)
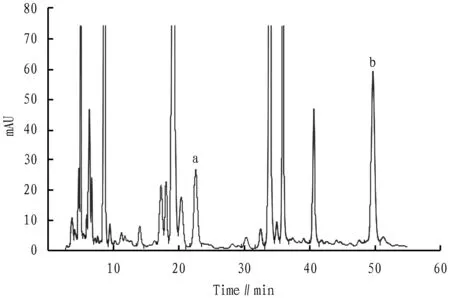
Fig. 2 Chromatogram of Vernonia cinerea (L.) Less. test solution (a. hyperin; b. luteolin)
4 Discussion
4.1 Optimization of sample extraction conditionsIn the course of the experiment, methanol, anhydrous ethanol, 95% ethanol and 75% ethanol were used as solvents to investigate and compare the dissolution rates of the two components inV.cinerea(L.) Less. The results showed that the dissolution rate of hyperin and luteolin inV.cinerea(L.) Less. was high when 95% ethanol was used as extraction solvent.
In the process of solution extraction, three extraction methods (ultrasonic extraction, water bath heating to boiling and 45 min ultrasonic treatment, water bath reflux extraction) were compared. The results showed that the dissolution rates of the two components extracted by water bath heating and ultrasonic extraction were higher.
4.2 Selection of chromatographic conditionsAfter repeated experiments, it was found that good separation and analysis results could be obtained by gradient elution with methanol-0.4% phosphoric acid as mobile phase; the column pressure and the peak shape and retention time of the detected components were good; the degree of separation was higher than 1.5, and there was no interference in coexisting components; the number of theoretical plates was more than 5 000.
V.cinerea(L.) Less. is convenient to collect and rich in resources, so it has high value of development and utilization. With the application of modern science and technology, a comprehensive and systematic study ofV.cinerea(L.) Less. and elucidating its effective chemical composition and pharmacological mechanism will become the focus of future research.
- Medicinal Plant的其它文章
- A Textual Research on Materia Medica of Origin of Orthonym and Synonym of Cuscutae Semen
- Research Progress on Chemical Constituents and Pharmacological Effect of Semen Cuscutae
- Advances in Research of Cichorium intybus L. in Preventing and Treating Hyperuricemia
- Research Progress of Mongolian Medicine Zadi-5 Pills in the Treatment of Depression
- Effects of Dachengqi Decoctions Made from Different Processed Products of Rhubarb on ABP Mice
- Effects of Diet with "Lianteng" Additive of Chinese Herbal Medicine on Blood Biochemical Indexes, Immune and Antioxidant Function of Guangxi Sanhuang Chickens

