Clinical observation of acupoint injection combined with nerve electrical stimulation in the treatment of post-stroke dysphagia
Fei-Xiang MaGui-Ping Cao,Wan-Lang Li,Ying-Ling Zhu
1Department of Rehabilitation Medicine, Yancheng Third People’s Hospital, Yancheng 224005, China; 2Department of Pharmacy,Yancheng Hospital of Traditional Chinese Medicine, Yancheng 224001, China; 3Department of Science and Education, Yancheng Third People’s Hospital,Yancheng 224005,China.
Abstract
Background: Post-stroke dysphagia is one of the common clinical symptoms in the rehabilitation department of primary hospitals, which seriously affects the quality of life of patients and their families.Majority of medical workers have comprehensively studied post-stroke dysphagia as it easily induces inhalation pneumonia, asphyxia,and many other complications.At present, many methods for post-stroke dysphagia have been proved to be effective.With regard to comprehensive treatment effect, patient compliance, technology promotion difficulty,grassroots hospital operability, and other factors, we found that acupoint injection combined with nerve electrical stimulation is a good method worthy of promotion.Methods:A total of 130 patients with dysphagia after stroke were randomly divided into nerve electrical stimulation group (n = 41), acupoint injection group (n = 40), and comprehensive treatment group(nerve electrical stimulation plus acupoint injection,n=49).The therapeutic effect in each group was evaluated before treatment and 20 days after treatment using the improved water swallow test,video fluoroscopic swallowing study,and standardized swallowing assessment.Results:After 20 days of treatment,significant differences were noted in each group.The scores of improved water swallow test decreased from 4.10± 0.74 to 2.12 ± 0.95 in the nerve electrical stimulation group, 4.00 ± 0.78 to 2.28 ± 1.04 in the acupoint injection group, and 4.16 ± 0.77 to 1.73 ± 0.79 in the comprehensive treatment group; video fluoroscopic swallowing study scores increased from 3.71 ± 2.16 to 5.05 ± 2.111 in the nerve electrical stimulation group,3.80 ± 1.94 to 5.20 ± 1.942 in the acupoint injection group, and 3.73 ± 2.22 to 6.24 ± 2.21 in the comprehensive treatment group;and standardized swallowing assessment scores of the three groups also decreased from 35.13 ± 3.38 to 28.17 ± 3.42,34.66 ± 3.46,and 34.48 ± 3.26 to 26.39 ± 3.86,respectively.The overall scores of each group after treatment were significantly different from those before treatment (P <0.05), indicating that both nerve electrical stimulation and acupoint injection were effective for post-stroke dysphagia; the scores of nerve electrical stimulation group and acupoint injection group were similar, but those of the comprehensive treatment group were significantly better than the single treatments (P <0.05).It shows that the two treatment methods have synergistic effect, and combined treatments have more benefits.Conclusion: Nerve electrical stimulation and acupoint injection have a synergistic therapeutic effect on post-stroke dysphagia.The combined treatment is more beneficial to patients with post-stroke dysphagia than the single treatments.
Keywords:Dysphagia,Ⅴideo fluoroscopic swallowing study,Standardized swallowing assessment,Water swallow test,Acupoint injection,Neuromuscular electrical stimulation
Background
Stroke,also known as“cerebrovascular accident”,is an acute cerebrovascular disease that causes brain tissue damage due to the sudden rupture of cerebral blood vessels or failure of blood flow into the brain due to vascular obstruction.According to a survey covered from 2005 to 2017 [1], stroke has become the primary cause of death in China and disability in Chinese adults.Among the deaths associated with stroke, those caused by aspiration pneumonia accounts for approximately 34%[2].Within one year after the occurrence of stroke,the mortality rate of aspiration pneumonia can reach 20%, and the annual mortality rate is approximately 10%–15%.
Stroke lesions often cause dysphagia, with an incidence of 30%–78% [3].Dysphagia after stroke is the primary cause of aspiration pneumonia [4] and increases the incidence of malnutrition, electrolyte disorder,pressure sores,another stroke,and even death,thus significantly affecting the rehabilitation and quality of life of patients.Therefore, the evaluation of swallowing function and active and effective treatment of patients with stroke have clinical significance in improving the rehabilitation prognosis and the quality of life, shortening the hospitalization course, and reducing the mortality rate and family burden.
Several treatment methods are presently available for patients with dysphagia after stroke [5, 6].Swallowing function training, nerve electrical stimulation, acupuncture, balloon dilation, hyperbaric oxygen, and transcranial magnetic stimulation are performed in our department.However, in terms of comprehensive benefits such as treatment effect,patient compliance,difficulty in technology promotion,and operability in primary hospitals, we find that a combination of acupoint injection and nerve electrical stimulation is better than acupoint injection or nerve electrical stimulation alone.Previous studies has shown that acupoint injection combined with nerve electrical stimulation in the treatment of post-stroke dysphagia has a clear role in improving patients’water swallow test grade and standardized swallowing assessment (SSA).However, considering a past single-center retrospective analysis and that most relevant observation indexes were subjective indicators,this prospective study evaluated the therapeutic effect of these methods using a multicenter and single-blinded approach and objective indicators such as video fluoroscopic swallowing study(ⅤFSS).
Clinical data
General information
From January 2018 to September 2020, patients suffering from a stroke for the first time with symptoms of dysphagia were selected from the Department of Rehabilitation Medicine of Yancheng Third People’s Hospital (China), the Huanghai community joint rehabilitation ward of the Rehabilitation Department of the Third People’s Hospital of Yancheng City (China), and the rehabilitation hospital of Sheyang County supported by the rehabilitation department of the Yancheng Third People’s Hospital(China).
Inclusion and exclusion criteria
Inclusive criteria were as follows: ①age: 20–70 years old; ②suffering from a stroke for the first time with symptoms of dysphagia; ③hearing comprehension and intelligence level without obvious impairment and the ability to cooperate with the completion of relevant examination and evaluation methods; ④the course of disease of 7–60 days; and ⑤eligibility based on the diagnostic criteria of dysphagia after stroke [7–9].In other words, these were patients who suffered from eating difficulties,such as eating slowly,choking while drinking water, glandular secretion disorder or accompanied by dysphonia, unclear mouth, and other symptoms and had grade III–Ⅴwater swallow test.We also included patients who were ⑥approved by the hospital ethics committee and ⑦willing to participate in the research and sign the informed consent form.
Exclusion criteria were as follows: ①age less than 20 years old or older than 70 years old;②not the first time to be diagnosed as post-stroke dysphagia; ③failure to cooperate with treatment and evaluation; ④patients who receive other treatment methods to improve swallowing function during the course of disease; ⑤organic lesions of swallowing organs; ⑥patients with severe organ dysfunction or clinical data that cannot be obtained; and ⑦ patients with contraindications for treatment or examination methods.
Ethics and informed consent
Before the starting of the study, the informed consent form and ethics review application report of the scientific research project were provided according to the requirements of the hospital.This subject was reviewed and approved by the Medical Ethics Committee of Yancheng Third People’s Hospital(China) on April 6, 2016, and the ethical review number was the 35th item in 2016(2016-04-35).
Random grouping method
A total of 160 envelopes containing random numbers were prepared.80, 40, and 40 envelopes were randomly selected ordered by the three centers.Then each center randomly selected one envelope from the envelopes,divided the random number in the envelope by 3, and randomly divided the patients into electrical stimulation group, acupoint injection group, and comprehensive treatment group (nerve electrical stimulation combined with acupoint injection)according to the remainder.
Sample size
Based on the data of the three centers, a total of 150 patients were selected for this study and divided into three groups: 47 in the electrical stimulation group, 45 in the acupoint injection group, and 58 in the comprehensive treatment group.In the course of the treatment, the patients’ withdrawal, loss of contact,transfer to other hospital, death, recurrence of other diseases or other treatment schemes(such as traditional Chinese medicine, transcranial magnetic stimulation)to improve swallowing function were all regarded as falling-off cases.The specific exfoliation situation was as follows: 6 patients in electrical stimulation group(transferred to other hospital,3;complicated with other diseases, 2; quitting by oneself, 1), 5 patients in acupoint injection group (combined with other methods,2;transferred to another hospital, 1;death,1;complicated with other diseases, 1), and 9 patients in the comprehensive treatment group (transferred to other hospital, 4; voluntarily withdrawn, 2; lost connection, 1; complicated with other diseases, 1; and death, 1).Finally, this study included 130 patients for analysis: electrical stimulation group (41 patients),acupoint injection group (40 patients), and comprehensive treatment group(49 patients).
Comparison of general data of patients
The sex, age, course of disease, water swallow test grade, and other general data of each group were not statistically significant (allP> 0.05) and were comparable(Table 1).
Single-blinded design
After the patients were divided into groups according to the random number table method, the operator of each treatment method, the functional evaluator, and the data analyst were assigned,and were blinded to the groupings of the patients.
Treatment
Each group received basic treatment for primary disease and other complications, such as nutrition of the brain nerve, improvement of brain function,promotion of blood circulation and removal of blood stasis, brain protection, enteral and parenteral nutrition support, antihypertensive and hypoglycemic medication, antiplatelet aggregation, lipid-lowering and stable plaque, anti-inflammatory drugs,anticoagulants, and other drug treatment.The patients were also administered basic rehabilitation therapy such as physical therapy, occupational therapy,swallowing training, cough breathing training, and acupuncture and moxibustion.
Electrical stimulation group
The hyoid bone and subhyoid muscles were stimulated by ⅤitalStim5900, a portable dysphagia treatment instrument produced by DJO company.The stimulation electrode was fixed on both sides of the cricoid cartilage while the patients were in sitting or lying position.AC mode was selected.The output waveform was rectangular symmetrical biphasic zero direct current net wave.The intensity was based on the patient’s tolerance or local muscle contraction.When the effective stimulation rate was reached, the patients felt that the throat was pinched up or like an ant was crawling,and some had involuntary swallowing action.During treatment,patients were encouraged to swallow saliva actively, 30 minutes each time, once a day (10 times as a course of treatment, for a total of 2 courses of treatment).
Acupoint injection group
One milliliter of mecobalamine (Shiyao Group Ouyi Pharmaceutical Co., Ltd., China; national drug approval number H20055382) was injected using a 1 mL syringe on the patient’s “swallowing point”(mandible incision)[10].There was no blood backflow after extraction, and the drug solution was slowly injected until no blood or drug solution flowed out.Once a day, the left and right sides of the alternating acupoint were selected, 10 times for a course of treatment for a total of 2 courses of treatment.
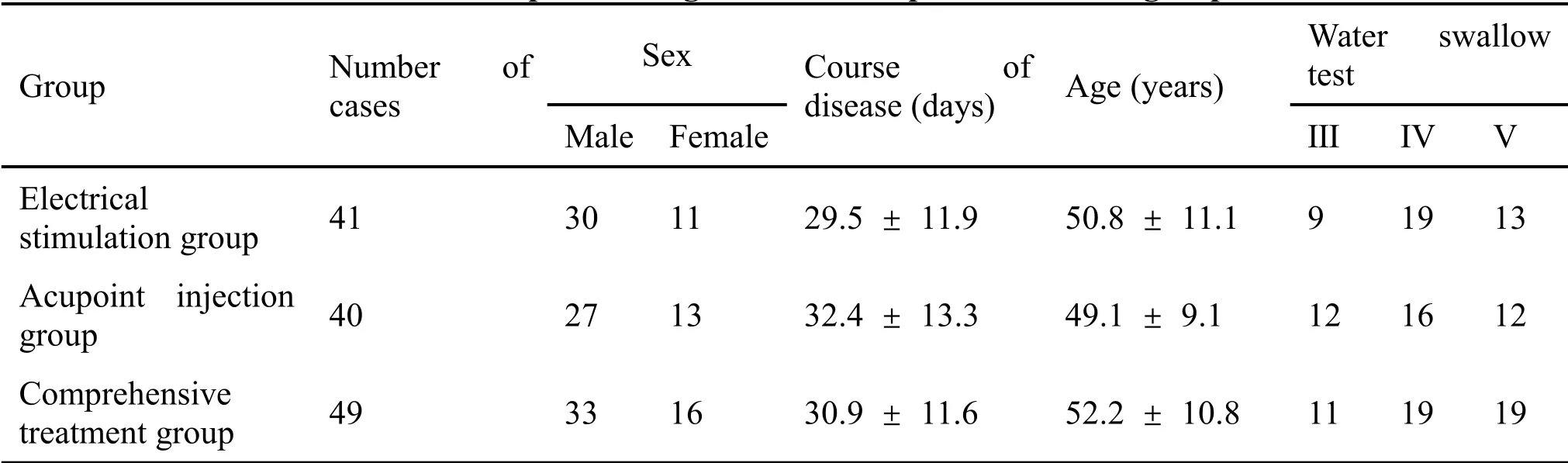
Table 1 Comparison of general data of patients in each group
Comprehensive treatment group
Patients in this group were treated with ⅤitalStim electrical stimulation and acupoint injection at the same time(10 times as a course of treatment, a total of 2 courses).
After two courses of treatment, each patient no longer received ⅤitalStim electrical stimulation or acupoint injection therapy, but still underwent family rehabilitation training such as perioral muscle training,tongue movement training, cough training, breath holding voice training, food intake training, and breathing training[11,12].
Curative effect observation
Water swallow test
The water swallowing test was proposed by Japanese scholar Toshio Kubota in 1982 [13].Each patient sat upright or reclined.First, the patient was instructed to swallow for 15 seconds and then drink 30 mL of warm boiled water.The time of choking and drinking were recorded.The detailed scoring system is as follows:grade I, drinking without choking, 1 point; grade II,drinking more than twice, without choking, 2 points;grade III, choking with one drink, 3 points; grade IⅤ,choking after more than two times, 4 points;and gradeⅤ,frequent coughing but not swallowing,5 points.
Before treatment and within 24 hours thereafter, the patients were evaluated and analyzed.In order to control the subjective error, the average value was taken after two tests.If the difference between the two scores was more than 3 points, the test was repeated for the third and fourth time and then the scores from all four tests were averaged.
According to the water swallow test, the curative effect judgment standard was established: cure:dysphagia disappeared, water swallow test evaluation grade I; effective: dysphagia significantly improved,water swallow test evaluation grade II; ineffective:dysphagia improved not significantly, water swallow test evaluation grade III or above.Effective rate =(cured cases+effective cases)/total cases*100%.
Video fluoroscopic swallowing study(VFSS)
The specific method [14, 15] is that before the examination, iohexol and different proportions of thickeners were mixed to produce three kinds of food,i.e., simulated liquid food, semiliquid food, and solid food.X-ray fluoroscopy was performed by nsx-rf2900 digital gastrointestinal machine (Shenyang Neusoft Medical System Co., Ltd., China).Each patient first took the upright position and swallowed three simulated foods at a time; then took the side position and swallowed three simulated foods again.X-ray fluoroscopy was used to observe the dynamic process of swallowing, including the abnormal manifestations of food residue, penetration, and aspiration, to understand the process of swallowing different shapes of food.
Efficacy evaluation criteria are as follows.The oral stage, pharynx stage, and accidental inhalation degree before treatment and 24 hours after 20 days of treatment were evaluated by a professionally trained physician.In this study, the score criteria of ⅤFSS swallowing disorder are as follows[15].(1)Oral stage:0 point is when food cannot be sent into the throat or flowed out of the lips, or only gravity can be sent into the throat; 1 point when a food group could not be formed to flow into the throat or can only scatter food to flow into the throat; and 2 points when food could not be swallowed to the throat at one time and after one swallow,some food remains in the mouth;3 points when sending food down the throat by swallowing only once.(2) Throat stage: 0 point when the patient cannot perform laryngopharyngeal lift, the epiglottis atresia and soft palate bow is closed, or when swallow reflex is not sufficient; 1 point when there is a large amount of food residue in the throat pits and pyriform pits; 2 points when a small amount of food remains in the mouth and swallowing should be repeated several times for the remaining food to be moved into the throat; and 3 points when swallowing once completes feeding of food into the esophagus.(3) Accidentally inhalation degree: 0 point when it is mostly accidental inhalation, but no cough; 1 point when most of the food was swallowed by accident, but cough occurred;2 points for a small amount of accidental inhalation,but no cough;3 points for a small amount of accidental inhalation, with cough; and 4 points for no accidental inhalation.Three kinds of simulated food swallowing process were scored, and the average score was taken as the ⅤFSS swallowing disorder score.A normal score is 10, and a lower score indicates a more serious swallowing disorder.
Standardized swallowing assessment(SSA)
First reported in 1996 by Ellul et al., SSA [16] was specially designed to evaluate the swallowing function of patients.It was divided into three parts: (1) clinical examination, focusing on consciousness, head and trunk control, breathing, lip closure, soft palate movement, laryngeal function, pharyngeal reflex and spontaneous cough, and cough, with a total score of 8–23 points; (2) the patient were asked to drink 5 mL of water for three times to observe the occurrence of laryngeal movement, repeated swallowing, wheezing during swallowing, and laryngeal function after swallowing, with a total score of 5–11 points; (3) if there is no abnormality above, the patient was instructed to drink 60 mL of water to observe the time required for swallowing and the occurrence of cough,with a total score of 5–12 points.The lowest score of the scale was 18 and the highest score was 46.The higher the score,the worse the swallowing function.
Before treatment and within 24 hours after 20 days of treatment, the patients were evaluated and analyzed.In order to control the subjective error, the average value was taken after two tests.
Statistical analysis
All data were analyzed by SPSS 23.0.The measurement data were expressed with mean ±standard deviation (ˉx ± s), and the homogeneity test of variance was conducted first.LSD and snk-qanalysis methods were used to compare homogeneous variances between groups, and the Tamhane T2 method was selected when they were not homogeneous.In this study, the relevant data were normally distributed.Nonparametric chi square test and rank sum test were used for counting data.The same sample before and after the control statistical analysis using pairedt-test.P< 0.05 for the difference was statistically significant.
Results
Comparison of therapeutic effect of water swallow test before and after treatment in each group.Before treatment, water swallowing test grade and scores of the three groups were at the same baseline level, and the difference was not statistically significant, therefore comparable.After 20 days of different treatments, the comprehensive treatment group achieved an effective rate that was significantly higher (P= 0.02) and a water swallowing test score that was significantly lower than those of the electrical stimulation group and the acupoint injection group (P= 0.04,P= 0.01).However, there was no significant difference in the curative effect between the electrical stimulation group and the acupoint injection group.See Table 2 for details.
Comparison of VFSS scores of video swallowing angiography before and after treatment in each group.There was no significant difference in ⅤFSS scores between the three groups before treatment.After 20 days of intervention with different treatment methods, the ⅤFSS score of the comprehensive treatment group was significantly higher than that of the electrical stimulation group and the acupoint injection group, and the difference was statistically significant(P=0.01,P=0.02);the curative effect was similar between the electrical stimulation group and the acupoint injection group,but the difference was not statistically significant.See Table 3 for details.
Comparison of SSA scores of before and after treatment in each group.Before treatment, the SSA scores of the three groups were in the same baseline level, and the difference was not statistically significant.After 20 days of intervention with different treatment methods, the score of comprehensive treatment group was significantly lower than that of electrical stimulation group and the acupoint injection group, and the difference was statistically significant(P= 0.031,P= 0.04).The scores of electrical stimulation group and the acupoint injection group were similar,with no statistically significant difference in terms of curative effect.See Table 4 for details.
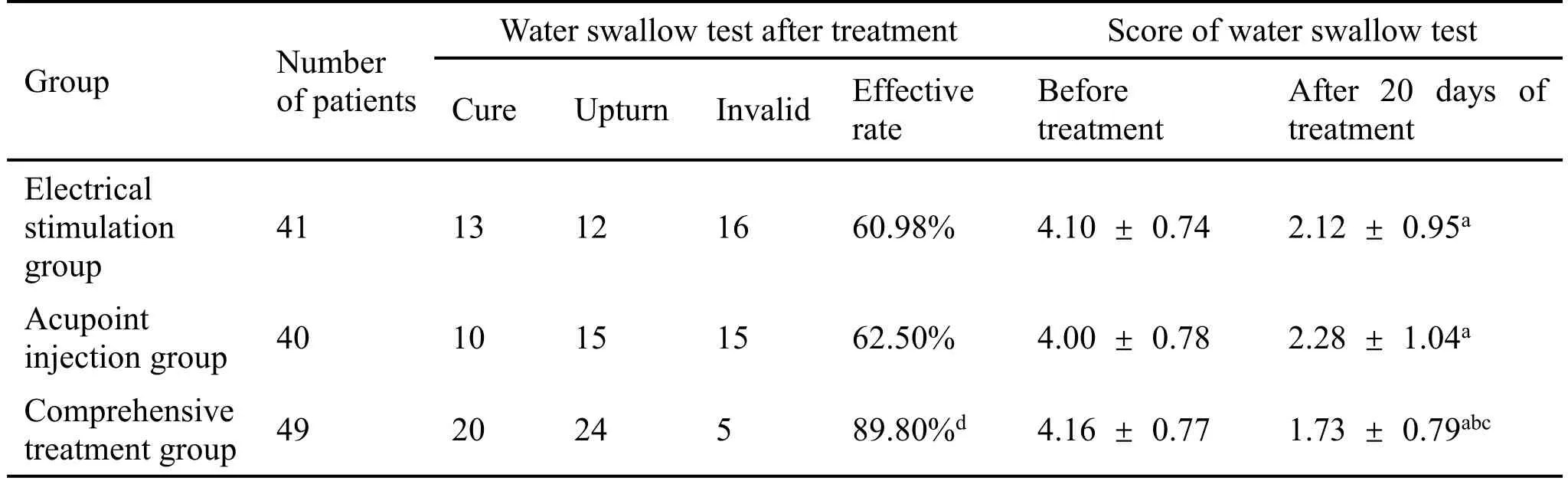
Table 2 Comparison of therapeutic effect of water swallow test in each group(cases)
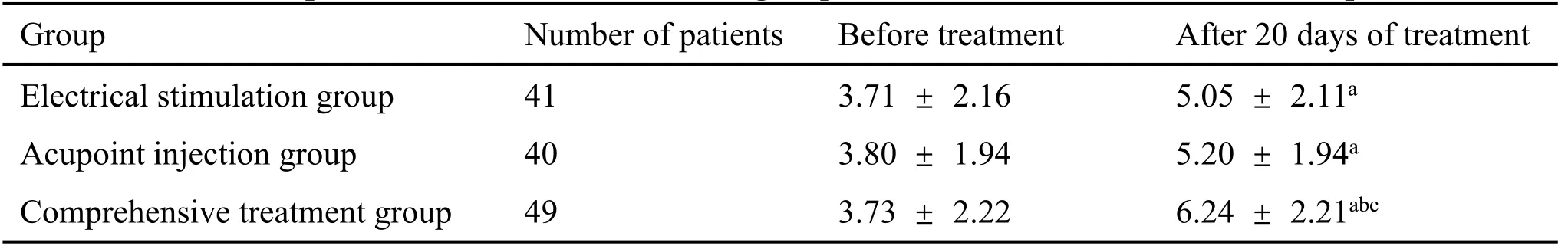
Table 3 Comparison of VFSS scores of each group before and after treatment(ˉx±s,points)
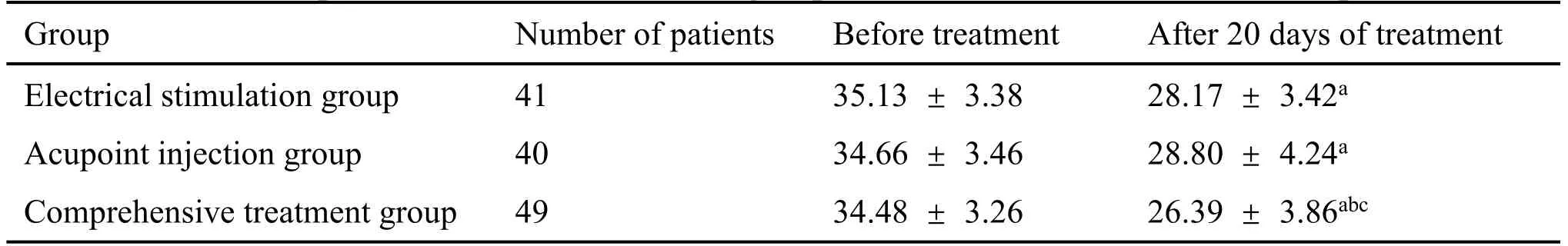
Table 4 Comparison of SSA scores of each group before and after treatment(ˉx±s,points)
Discussion
The normal swallowing process can be divided into four stages: oral preparation stage, oral stage,pharyngeal stage, and esophageal stage.The whole process takes several seconds, showing a coherent movement in one breath,especially after the food mass passes through the pharyngeal arch.The neural control of swallowing [6, 17, 18] consists of three parts.①The higher cortical center consists of several brain regions, which are anterior cingulate gyrus, central gyrus, anterior insular cortex, and premotor cortex that mainly initiate and regulate spontaneous swallowing.The main manifestations of dysphagia caused by cortical injury are delayed pharyngeal reflex, inability to start swallowing, decreased pharyngeal muscle contractility, or abnormally low sphincter.②Brainstem swallowing center, which reflexively controls and regulates swallowing.If the brainstem is damaged, it will delay the initiation of swallowing,decrease the lifting and forward movement of the larynx, and decrease the opening of the cricopharyngeal muscles, and result in food retention.③Subcortical afferent and efferent nerves include the dorsal vagal nucleus, motor nucleus, facial nucleus,hypoglossal nucleus,and sympathetic nerve of superior cervical ganglion.Subcortical nerve injury results in the impairment of sensory and motor afferent and efferent pathways, resulting in dysphagia in oropharyngeal phase.
Swallowing activities are mainly concentrated in oral and pharyngeal stages [13].The muscles involved in swallowing activities in these two stages mainly include the orbicularis oris muscle, masseter muscle,submental muscle (digastric anterior abdomen,mandibular hyoid muscle, genihyoid muscle), and subhyoid muscle group (laryngeal girdle muscle and thyrohyoid muscle).Due to the impairment of brain stem or brain nerve conduction tract function, patients after stroke cannot complete the transportation of food from the mouth to the stomach, resulting in dysphagia during the oropharyngeal stage.At present, the common pathological features of dysphagia after stroke are recognized as follows[20–22]:①dysphagia caused by motor control disorder is difficult to start swallowing; ② paralysis causes difficulty in food transportation; ③ cognitive impairment is easy to cause food residue aspiration; and ④communication disorder causes dysphagia that cannot express.
In view of these possible etiological mechanisms, a large number of scholars continue to explore and study the treatment of post-stroke dysphagia [5].At present,several mainstream treatment methods are available with relatively certain curative effect.Ⅴarious cutting-edge new technologies and innovative new ideas have prominent benefits.However, some technologies are difficult to be implemented in our primary hospitals in the short term because of the limited professional level of medical workers, the low affordability of patients, the incomplete coverage of medical insurance policies, and the miscellaneous procedures for the introduction of new technologies in order to fully develop.Therefore, based on the local reality, we dig deeply into the technology that patients are willing to accept and physicians are easy to promote and operate,and we constantly update to meet the clinical needs and relieve the sufferings of patients.
ⅤitalStim nerve electrical stimulation therapy, as a neuromuscular electrical stimulation therapy, is one of the devices certified by FDA.Its principle [23] is to stimulate pharyngeal muscles with a certain intensity of current through preset procedures, mainly activating pharyngeal muscles, tongue muscles, orbicularis oris muscles, and buccal muscles, inducing muscle movement or simulating normal autonomous movement mode, so as to improve the stimulated muscles.At the same time, the current acting on the brain through nerve reflex[24]promotes the functional reconstruction of the corresponding regions of the central nervous system.Its low-frequency pulse current can not only ensure a certain intensity of repeated stimulation but also avoid muscle tonic contraction[25].We analyzed that the main effect of ⅤitalStim in this study is that the current of ⅤitalStim accelerates the local epidermal nerve depolarization, thus promoting the contraction of the laryngeal muscle group and inducing passive swallowing action,in order to treat dysphagia.In addition, we found that afterⅤitalStim nerve electrical stimulation treatment, the skin of some patients with cricoid cartilage patch placement was reddish, suggesting that neuromuscular electrical stimulation therapy may improve the function of swallowing muscle group by improving the volume of local muscle contractile protein and increasing the local capillary density.
Local acupoint injection of mecobalamin injection is one of the traditional treatment methods commonly used in rehabilitation.It is a combination of acupuncture, acupoint, and medicine.Mecobalamin injection [26] is an endogenous coenzyme B12, which is located in the organelles of nerve cells.It can participate in acid fast protein and lipid metabolism and play an important role in the synthesis of axon structural proteins.The principle of the mechanism of local acupoint drug injection [27] includes the stimulation effect of the injection needle on various nerve receptors around the acupoint for the acupoint to produce acupuncture-like signals and activate the functions of meridians and viscera where the acupoints are through different ways, to regulate the body.It also stimulates the local tissues of acupoints through mecobalamin to optimize the effect of methylcobalamin to promote the myelination of nerve fibers, the development and maturity of synaptic structure, and network function, so as to timely repair nerve cells, axon regeneration, and functional compensation.
The“swallowing point”[10]selected in this study is a self-named extra meridian acupoint.Its anatomic location is at the artery groove in the anterior notch of mandibular angle, close to the Tianrong point of the hand Taiyang small intestine.The nearby facial nerve,mandibular branch, hypoglossal nerve, and other nerves have a certain effect on the posterior abdomen of digastric muscle and thyrohyoid muscle, which are one of the main muscle groups involved in swallowing.Localized administration of mecobalamin may exert its nutritional nerve and conduct the nerve electrical excitation of swallowing muscle group, so as to improve the swallowing function of patients after stroke.According to the theory of traditional Chinese medicine, strengthening the stimulation input here can stimulate the meridian qi of the small intestine of the hand Taiyang,promote the channel qi to enter the brain along the meridians, dredge the brain collaterals,strengthen the brain function, and improve the swallowing power.
Conclusion
This study shows that ⅤitalStim electrical stimulation and mecobalamin acupoint injection can improve the water swallow test grade, ⅤFSS score, and SSA score of patients with post-stroke dysphagia.Both methods have therapeutic significance for patients with post-stroke dysphagia.A synergistic effect between the two methods is notable and their combined application provides better benefits to patients with dysphagia after stroke.Moreover, the two treatment methods are easy to operate, highly safe, low cost, easy to promote,without obvious adverse reactions, and worthy of clinical reference.
- TMR Non-Drug Therapy的其它文章
- Progress research on non-drug therapy in cancer-related fatigue
- Study on the psychological reaction and coping strategies of nursing students under the spread of COVID-19
- Safety and efficacy of intraperitoneal perfusion with tumor vesicle-encapsulated methotrexate for the treatment of cancerous ascites-an open,randomized and controlled clinical trial
- Effect of “Tongji” electroacupuncture on pain and inflammatory factors in patients with lumbar disc herniation in remission stage
- A randomized placebo-controlled trial of Chinese medicine acupoint application on gastrointestinal dysfunction after appendectomy

