Study on the psychological reaction and coping strategies of nursing students under the spread of COVID-19
Li-Mei Zhao,Wei Wang,Yuan Zhao,Yan Wang*
1The First Affiliated Hospital of Xiamen University, Xiamen 361000, China.2Graduate School of Tianjin University of Traditional Chinese Medicine,Tianjin 300000,China.
Abstract
Background:To understand the psychological reaction and coping strategies of infectious diseases among nursing students.Methods:A convenience sampling method was used to select 455 nursing students in the school, and a questionnaire survey was conducted on the general data table and the psychological reaction and coping strategy scale of infectious diseases of college students and coronavirus disease 2019 (COⅤID-19)was used as an example of the infectious diseases.Results:the psychological reaction of nursing students was related to gender(P=0.006),age(P=0.001),education level(P=0.019),professional category of senior high school(P=0.014),whether they were student cadres(P <0.001)and whether there were immediate relatives engaged in medical and health related work (P =0.022).Different education level (P= 0.017), different age (P =0.041), different residence(P= 0.003),high school professional category (P = 0.008) and whether there are immediate relatives engaged in medical and health related work (P = 0.021) are related to their coping strategies.Conclusion: Nursing students with different demographic data have different psychological reactions and coping strategies.In the future research on the infectious diseases related to nursing students,it is suggested to focus on the female,the younger,the less educated,the liberal arts students and the nursing students who have no immediate family members engaged in medical and health related work,so as to promote the physical and mental health development of the nursing students in school.
Keywords:Infection disease,COⅤID-19,Psychological reaction,Coping strategies,Nursing students
Background
Infectious disease is a type of infectious disease caused by various pathogens [1], and its incidence accounts for 87.5%of public health incidents[2].In recent years,infectious diseases such as H1N1 flu and Ebola outbreaks have occurred frequently.The widespread worldwide spread of coronavirus disease 2019(COⅤID-19)in 2019[3]and the severe outbreak of the“information epidemic” not only brought great threats to the physical health of the people, but also caused psychological problems [4–5], especially for the unworldly student group.This group lacks serious crisis awareness and cannot correctly assess the risk information of the epidemic.Infectious diseases as a strong stressor and some of the information will aggravate their psychological stress responses such as panic and anxiety.Surveys during the COⅤID-19 show that the incidence of negative emotions such as anxiety and depression among college students is higher than that those during the non-epidemic period[6].
Nurses, as the backbone of rescue, have been researched on it [7–9], while nursing students, as the reserve army of clinical nurses in the future and the weak link in their development, are currently less relevant [10–11].With the global breakthrough of COⅤID-19, the research on nursing students is imminent.The purpose of this study was to understand the influencing factors of the psychological reaction and coping strategies of nursing students under the influence of OⅤID-19 epidemic, so as to provide the correct guidance method for the group to correctly deal with the psychological problems caused by infectious diseases, and provide theoretical reference for future related research.
Objects and methods
Research object
Convenience sampling method was used to select college students, undergraduate and postgraduate nursing students in Tianjin medical colleges as research objects from January to February 2020.Inclusion criteria: ①age ≥18 years old; ②informed consent and volunteers to participate in this research.Exclusion criteria: ① those recruited during the investigation; ② those who took leave; ③questionnaires with obvious regular responses; ④questionnaires where the number of answers did not exceed 95%of the total.
Survey tools
General Information Questionnaire.The general data questionnaire was compiled by researchers on the basis of consulting relevant literature [12], including 8 items such as age, gender, education level, residence,whether it is an only child, professional category of senior high school, whether it is a student cadre,whether there are direct relatives engaged in medical related work,etc.
College students’ psychological reaction of COVID-19 and coping strategies scale.The scale was designed by Ran Lijuan [12] to measure college students’ psychological impact on infectious diseases and coping strategies, including two dimensions of psychological impact (16 items) and coping strategies(19 items), a total of 35 items.Using Likert’s 5-level scoring method, 0 point means very inconsistent, 4 points means very consistent.The score of the psychological impact subscale ranges from 0 to 64 points.The lower the score, the more positive the psychological feeling, and Cronbach’s α is 0.856.The score of the coping strategy scale ranges from 0 to 76 points, the higher the score of coping strategy scale is,the more positive the coping is, and Cronbach’s α is 0.954[12].
Statistical methods
The collected questionnaires are entered into Excel data and checked by two people.SPSS17.0 was used for data analysis.The measurement data is described by the mean ± standard deviation or the distance between the median and the quartile, and the count data is described by the frequency (percentage); the difference test of the general data is by t test and analysis of variance.P< 0.05 indicates statistical difference.
Results
Data collection
The sample size is calculated as 10 times the number of entries, and consider the 20% invalid questionnaire,that is 39 × 10 + 390 × 20% = 468.Finally, 470 questionnaires were issued, and 460 were actually recovered.A total of 455 valid questionnaires were recovered,with an effective recovery rate of 96.80%.
Single factor analysis of psychological reaction of different characteristics of nursing students on infectious diseases
There were statistically significant differences in the psychological impact scores of nursing students in six items, such as gender, age, education level,professional category of senior high school, whether they were student cadres and whether they had direct relatives engaged in medical and health related work(P<0.05).The score of men is lower than that of women (P= 0.006); the distribution of age and education scores shows a trend of lower scores with age (P= 0.019); the psychological impact score of science students in high school is lower than that of liberal arts students (P= 0.014); the score of nursing students who are student cadres is lower than that of students who are not student cadres (P<0.001); the psychological impact scores of nursing students who have immediate family members engaged in medical and health-related work are low (P= 0.022).The two psychological impact scores of the place of residence and whether it is an only child were not statistically significant(P>0.05).See Table 1.These data indicate that we should pay attention to the psychological impact of female, young, low educational background,liberal arts students, not student cadres, no immediate family members engaged in medical and health care work.
Coping strategies for infectious diseases among nursing students with different characteristics
The scores of coping strategies of different characteristics of nursing students to infectious diseases showed that the scores of coping strategies of nursing students with different education level,different age, different high school professional category, different residence and whether there are direct relatives engaged in medical and health related work were statistically different (P<0.05).Coping strategy scores show a trend with higher academic qualifications and age, and higher scores (P<0.05).Nursing students living in towns score higher than rural nursing students (P= 0.003).Science students and nursing students with immediate family members engaged in medical and health-related work scored higher(P<0.05).There was no statistically significant difference in the scores of coping strategies for nursing students such as gender, whether they were only children and whether they were student cadres (P>0.05)(Table 2.These data suggest that we should improve the coping strategies of nursing students from the aspects of low age, low education, liberal arts students, no direct relatives engaged in medical care and rural nursing students.
Discussion
The National Center for Disease Control has included pneumonia caused by COⅤID-19 infection in the category of national Class B infectious diseases and has taken measures to prevent and control Class A infectious diseases [13].With the development of the epidemic, the number of confirmed cases and suspected patients has reached hundreds of thousands.Mental health education plays an important role in our country’s response to emergency public health incidents[14–15].Effective psychological interventionwill help maintain the physical and mental health of college students.If it continues to be ignored, it may cause psychological barriers [4].It is difficult to predict the occurrence time, location, scale, shape and damage degree of public health emergencies due to the dense personnel and active action in colleges and universities [16].At this time, nursing students are in the stage of formation and steady development of their concepts and behaviors.Their self-awareness,self-assessment, self-response and attention to the prevention and control of the epidemic situation are also important for the overall prevention and control of the epidemic.Therefore,we investigate its mental state and response strategies to provide certain guidance for correct guidance and help.The theoretical basis for it to maintain a positive attitude towards pneumonia caused by COⅤID-19 infection and respond scientifically to improve its own resistance and ability to face COⅤID-19 pneumonia.
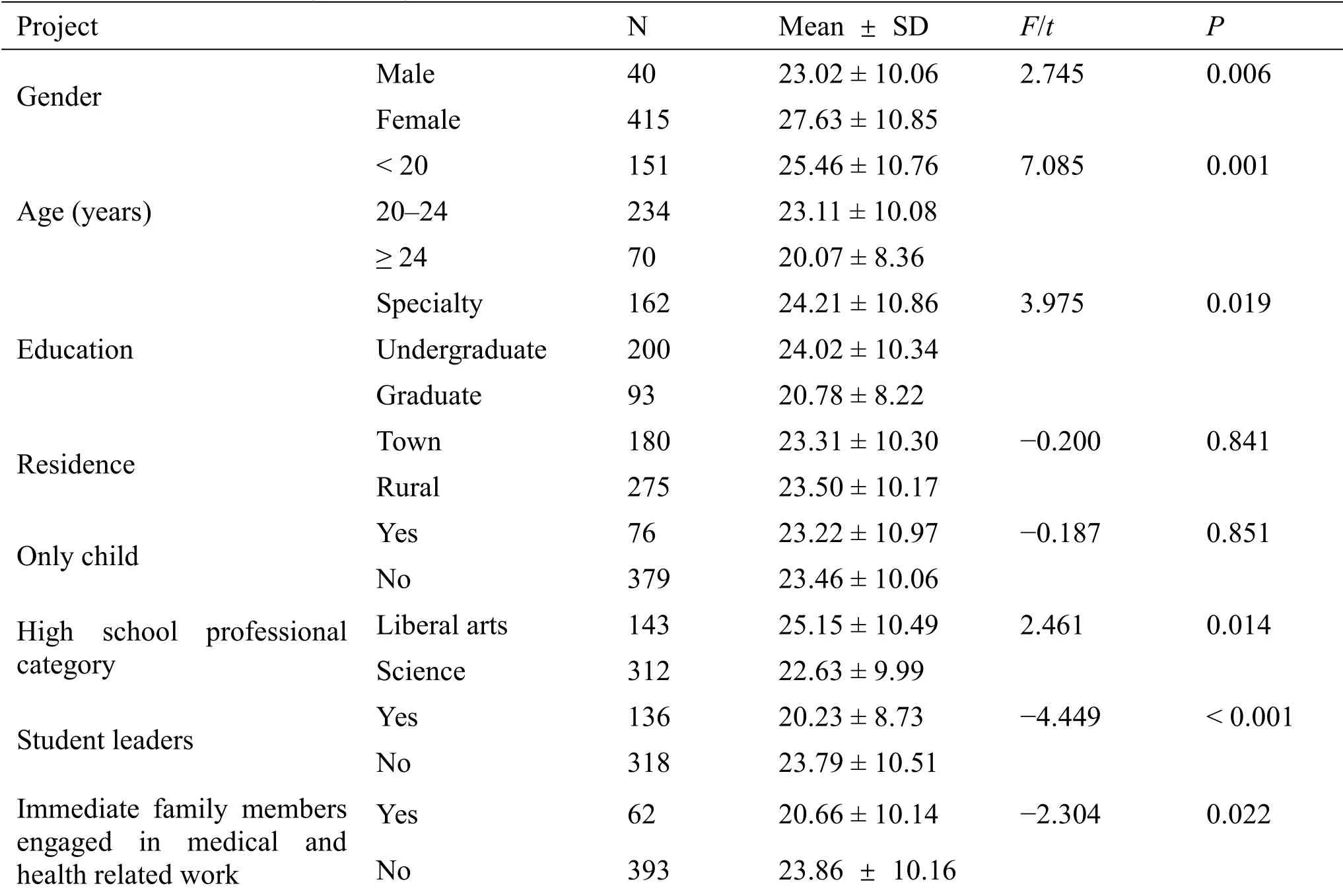
Table 1 Comparison of psychological impact scores of infectious diseases among school nursing students with different characteristics(n=455)
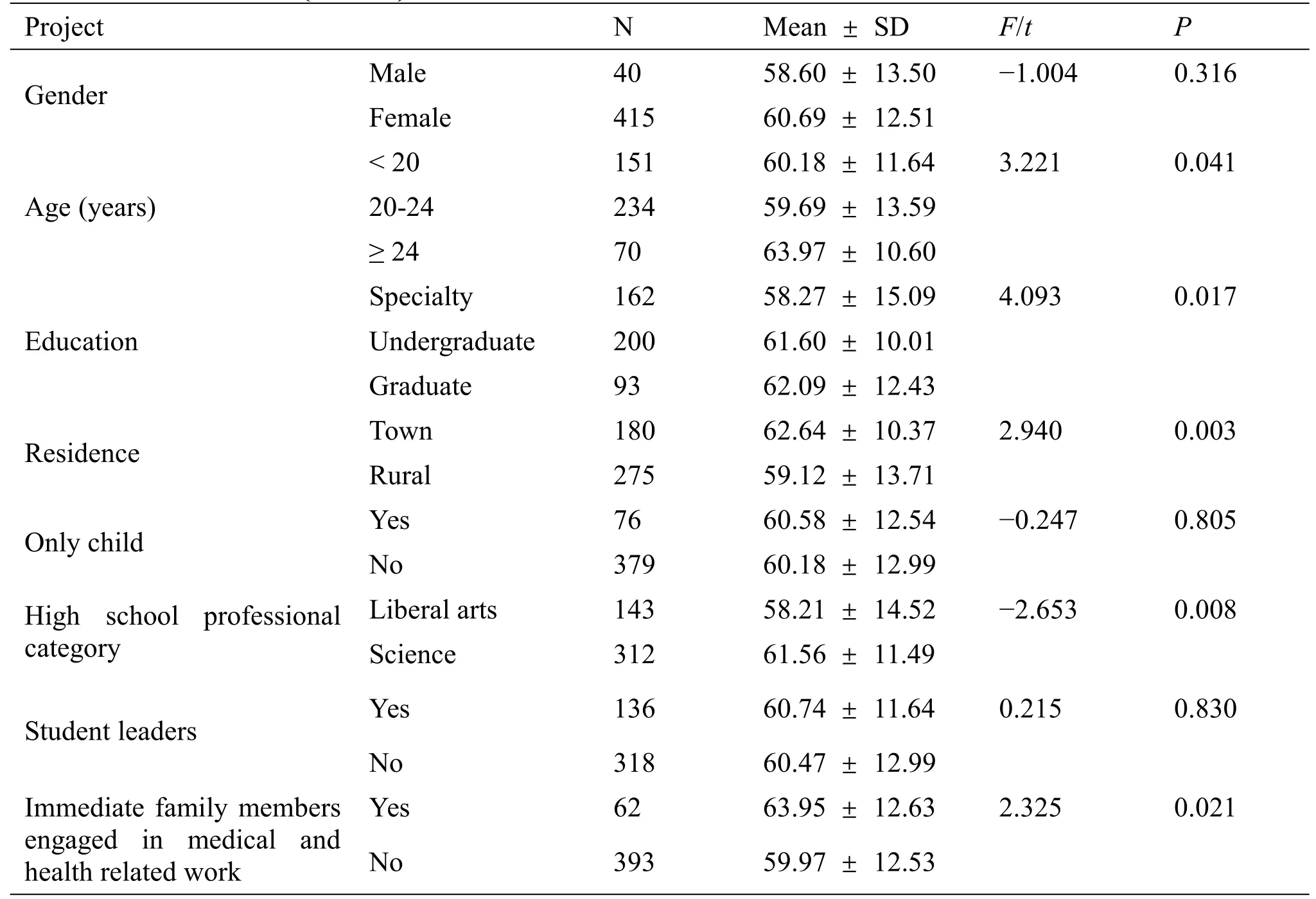
Table 2 Comparison of scores of coping strategies for infectious diseases among nursing students with different characteristics(n=455)
The psychological reaction score of male nursing students is lower than that of female nursing students,showing higher positive emotions, which is consistent with the results of Ran Lijuan’s[1]investigation on the mental state of infectious diseases of college students,and also consistent with Tian Tian’s[17]conclusion on the mental health of college students with hepatitis B.It may be related to boys’ unhealthy lifestyle and behavior habits such as smoking, Internet addiction,fighting,rebellious and obstinate.Compared with boys,girls generally pay more attention to their own health[18].In terms of coping strategies, there is no significant difference between male and female nursing students.This shows that when schools carry out mental health education of infectious diseases for nursing students, they should not only pay attention to the external performance of nursing students and the measures taken, but also pay attention to the psychological stress of nursing students, especially the psychological state of female nursing students.
With the increase of age and education level, the more active the psychological emotions and coping strategies of nursing students are,which may be related to the accumulation of medical knowledge, the continuous enrichment of experience in dealing with unknown situations [19] and the fact that most of junior college and undergraduate courses are taught by teachers [20], and the lower ability of self-learning than that of graduate students, which makes them have worse psychological tolerance and less active coping measures in the face of infectious disease emergencies correct.This shows that schools should pay attention to the younger and less educated nursing students.
There was no significant difference in psychological feeling between urban nursing students and rural nursing students, but there was statistical difference in coping strategies,which may be related to the complex social environment and rich medical resources in cities and towns, which makes them more active in dealing with the emergency situation of infectious diseases.The qualified rate of infectious disease prevention and control knowledge of urban college students is higher than that of rural students [18].Compared with urban areas, the construction of primary health institutions is relatively backward, medical resources are scarce, and the health foundation is weak.These differences may be the reason why the coping strategies of urban nursing students are more positive.
In this study, science students and nursing students with immediate family members who are engaged in health-related work have more biological and medical-related information, which may be the reason for their better psychological state and more active coping strategies.This is consistent with the research results of Luo Shengmei [21].This is contrary to the research results of Liu Jing [18], who believes that liberal arts students have a wider range of reading and knowledge, while science students are more focused on the professional knowledge of science, and their knowledge is relatively narrow.Therefore,in the future research, we should analyze the situation of arts and science students and take targeted measures.
Conclusion
Nursing students are in a critical period of physical development and personality formation.Attention should be paid to the psychological impact nursing students, especially to those who are female, younger,low education background, liberal arts students, not student cadres and those who have no immediate family members engaged in medical and health related work.In addition, in the future research, we can improve the coping strategies of nursing students from the aspects of low age, low education, liberal arts students, no direct relatives engaged in medical care and rural nursing students.
- TMR Non-Drug Therapy的其它文章
- Progress research on non-drug therapy in cancer-related fatigue
- Clinical observation of acupoint injection combined with nerve electrical stimulation in the treatment of post-stroke dysphagia
- Safety and efficacy of intraperitoneal perfusion with tumor vesicle-encapsulated methotrexate for the treatment of cancerous ascites-an open,randomized and controlled clinical trial
- Effect of “Tongji” electroacupuncture on pain and inflammatory factors in patients with lumbar disc herniation in remission stage
- A randomized placebo-controlled trial of Chinese medicine acupoint application on gastrointestinal dysfunction after appendectomy

