Dehydrocostus lactone exerts the antitumor effect in non-small cell lung cancer H1299 cells
Chao-Yue Su,Hui Wang,Yan-Rui Pan,Ling-Ling Zhang,Qiao-Ru Guo,Yan-Yan Yan,Jia-Jun Li,Jia-Li Fu,Xin-Yue Fan,Yu-Qing Wang*,Jian-Ye Zhang,4*
1Guangdong Provincial Key Laboratory of Molecular Target & Clinical Pharmacology,School of Pharmaceutical Sciences and the Fifth Affiliated Hospital,Guangzhou Medical University,Guangzhou 511436,China.2Guangzhou Institute of Pediatrics/Guangzhou Women and Children’s Medical Center,Guangzhou Medical University,Guangzhou 510623,China.3Institute of Respiratory and Occupational Diseases,Collaborative Innovation Center for Cancer,Medical College,Shanxi Datong University,Datong 037009,China.4Key Laboratory of Tropical Translational Medicine of Ministry of Education,Hainan Medical University,Haikou,571199,P.R.China.
Abstract
Background:Dehydrocostus lactone (DHC),a sesquiterpene lactone derived from Aucklandiae Radix,has been proved to possess various pharmacological activities.Recently,studies have reported that DHC has potential antitumor activity.However,few studies have reported the effect of DHC on non-small cell lung cancer(NSCLC).Here,we investigated the antitumor effect of DHC in NSCLC H1299 cells.Methods:MTT assay and colony formation assay was used to assess the anti-proliferation effects of DHC in H1299 cells.Wound healing and Transwell assays were utilized to determine the inhibitory effects of migration and invasion,respectively.Apoptosis was detected using the Annexin V/propidium iodide test.Real-time-quantitative PCR (RT-qPCR) was used to detect the mRNA expression level.Results:We demonstrated here that DHC inhibited the proliferation,migration and invasion of H1299 cells in a dose-or time-dependent manner.Additionally,after treating with DHC at the concentration of 32.0 μM,the apoptosis of H1299 cells was significantly induced.Moreover,DHC affected the mRNA expression of E-cadherin,N-cadherin,Snail,c-Myc,integrin α2,Survivin and matrix metalloproteinase 2.Conclusion:To summarize,our data support that DHC can inhibit proliferation,invasion,migration and induced apoptosis of NSCLC H1299 cells.DHC should be considered for its potential for adjuvant therapeutic development.
Keywords:Dehydrocostus lactone,Non-small cell lung cancer,Apoptosis,Migration,Invasion
Introduction
The GLOBOCAN 2018 cancer report released by the International Agency for Research on Cancer of the World Health Organization showed that there were approximately 2.09 million new cases of lung cancer worldwide and nearly 1.76 million deaths [1-3].Non-small cell lung cancer (NSCLC) is the most common type of lung cancer,constituting more than 80% of all lung malignancies [4].Currently,the main treatments for lung cancer are still chemotherapy,radiotherapy and surgery[5-8].Based on the toxic side effect of radiation and chemotherapy and some patients are not suitable for surgical treatment,it is necessary to develop new high-efficiency and low-toxicity antitumor drugs[9,10].
Natural medicinal plants provide a rich resource of bioactive structure for pharmaceutical drug development [11].The bioactive chemicals derived from plants have been perceived relatively safely.Dehydrocostus lactone (DHC) (Figure1A) is one of the active ingredients in theAucklandia lappa[12].A series of pharmacological activities of DHC have been reported,including anti-osteoporosis,anti-inflammation,anti-allergy and anti-cardiovascular diseases [13-15].It was initially reported that DHC has been investigated as potential antitumor agents[16],which showed inhibitory activity in colon cancer,breast cancer and prostate cancer [17,18].DHC acts on thiol-containing enzymes or proteins through its effective active group α,β-unsaturated carbonyl or α,β,γ-unsaturated carbonyl structure,which interferes with key biological processes in the body and exerts antitumor effects [16].However,little information has been done to consider the potential antitumor efficacy of DHC in NSCLC.
In this study,we aimed to investigate the potential antitumor effect and determine the possible mechanism of DHC in NSCLC.We found that DHC can inhibit H1299 cell proliferation,invasion and migration.Besides,our results revealed DHC could induce apoptosis and enhance the influence of mRNA expression sensitivity of E-cadherin,N-cadherin,Snail,integrin α2,matrix metalloproteinase 2 (MMP2),c-Myc and Survivin.Therefore,we determined this natural product might deserve further attention in the development of anti-NSCLC therapy.
Materials and methods
Cell culture and reagents
The human NSCLC cell line NCI-H1299 was purchased from iCell Bioscience Inc.,Shanghai,China,and authenticated via short-tandem repeat profiling.Cells were maintained in RPMI1640 medium supplemented with 1% penicillin-streptomycin and 10% fetal bovine serum,and incubated at 37 °C in a humidified 5% CO2.DHC (Figure1A) with a purity of > 98% purchased from the Spring & Autumn Biological Engineering Co.,Ltd.(Nanjing,China),and was dissolved in dimethyl sulfoxide and stored at-20°C as single-use aliquots.
Cell proliferation assay
We used MTT assay to measure cell viability as previously described [19].Briefly,3 × 103cells were seeded into 96-well plates.After 24 h,the cells were treated with DHC in different concentrations.After 68 h incubation with DHC,the MTT solution was added in an amount of 20 μL per well for an additional 4 h.The absorbance of each sample was determined at 540 nm by a microplate reader (BIO-RAD Model 550).The inhibitory effect of DHC on the proliferation of NSCLC cells was evaluated by experimentally measured IC50values.
Colony formation assay
H1299 cells were counted and plated into six-well plates at the density of 800 cells per well.Then,the cells were incubated with continuous concentrations(2.0,4.0,8.0 and 16.0 μM) of DHC.After 2 weeks of co-incubation,the medium was removed from the six-well plate and washed twice with PBS,then the cells were fixed and stained with 0.5% crystal violet.Finally,the dried plates were scanned and the number of cloned cells was counted[20].
Cell migration and invasion assays
The effect of DHC on the migratory ability of H1299 was determined by a wound-healing assay.After treatment with different concentrations of DHC,H1299 cells were scratched with 200 μL yellow tips.Then,images were taken at 0,24 and 48 h after wounding scratch.For the determination of cell invasion,we used Transwell 24-well plates (8 μM pores; Corning).Briefly,1 × 104cells/well of DHC-treated cells were seeded onto the upper chambers pre-coated with Matrigel (Matrigel: basal medium 1: 4),followed by placement in the Transwell plates with 600 μL of 10% fetal bovine serum complete medium.After incubation for 24 h,the upper chambers were fixed with methanol and stained with 0.5%crystal violet solution[21].
Apoptosis analysis
Apoptosis was detected by the FITC Annexin V Apoptosis Detection kit according to the manufacturer's protocol.After incubation with continuous concentrations (8.0,16.0 and 32.0 μM) of DHC for 48 h,H1299 cells were harvested and resuspended in 0.5 mL binding buffer containing Annexin-V/propidium iodide for 30 min at 37 °C in the dark.The stained samples were analyzed using a flow cytometer (Beckman Coulter,Inc.,USA) and CytExpert software.The rate of apoptosis (%) was determined by dividing the number of apoptotic cells by the number of total cells observed,and multiplying the product obtained with 100[22].
RT-qPCR
TRIzol (Thermo,MA,USA) was used to extract the total RNA of H1299 cells after DHC (16.0 μM)stimulation for 6 h and 12 h.The PrimeScript?RT Master Mix (TaKaRa,Japan) was used to transcribe mRNAs into cDNA.The forward and reverse primers(TaKaRa,Japan) were designed to detect the expression of E-cadherin,N-cadherin,Snail,integrin α2,MMP2,c-Myc and Survivin.SYBR?Premix Ex Taq?(Tli RNaseH Plus) (TaKaRa,Japan) was used for RT-qPCR and GAPDH was used to normalize mRNA expression.RT-qPCR was carried out using a QuantStudio 5 (Thermo Fisher Scientific,USA),and the condition was defined as follows: 95 °C 30 sec,1 cycle; 95 °C 5 sec,60 °C 34 sec,40 cycles; 95 °C 15 sec,60 °C 1 min,95 °C 15 sec,1 cycle.The primer sequences employed are listed in Table1[23].
Statistical analysis
All experiments were performed in triplicate unless otherwise stated.Statistical analysis was carried out using SPSS 16.0 software and the data were tested for significance using Student's test or one-way ANOVA.All quantitative data were expressed as mean ±standard deviation.Differences between groups were considered statistically significant ifP<0.05.
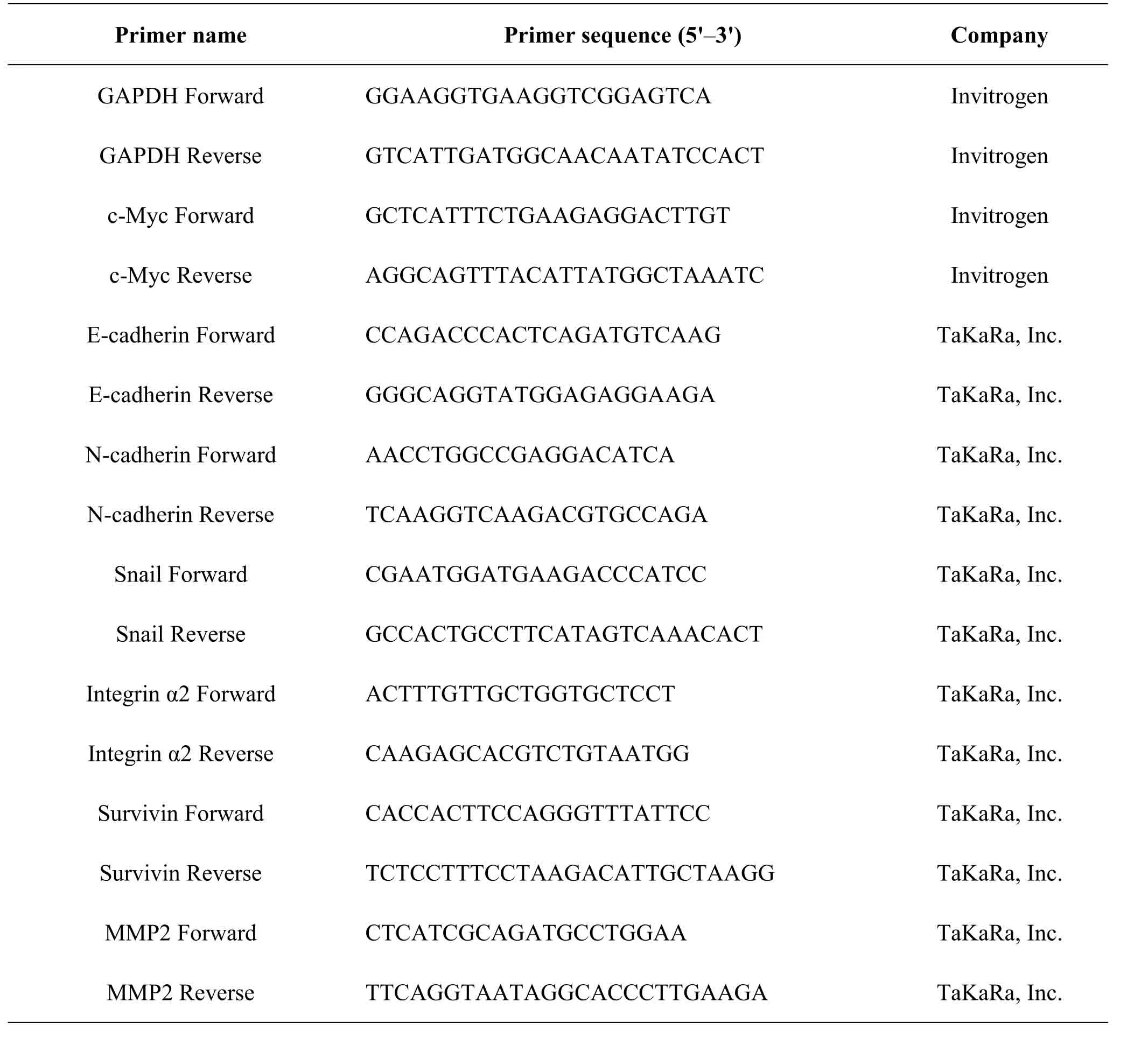
Table1 Sequence of primers for RT-qPCR
Results
DHC exerted an obvious inhibitory effect against H1299 cells
To investigate the effects of DHC (Figure1A) on the viability of NSCLC H1299 cells,MTT assay was used to examine the cell viability.H1299 cells were incubated with DHC in different concentrations.As shown in Figure1B,DHC significantly inhibited the proliferation of H1299 cells with an IC50value of 16.12±3.06μM.
DHC inhibited colony formation of H1299 cells
Furthermore,a plate colony formation assay was performed to examine the anti-proliferative effects of DHC on H1299 cells.DHC inhibited colony formation with a concentration of 2.0,4.0,8.0 and 16.0 μM distinctly compared to the control,and showed increasing inhibitory activity with the prolonging of time (Figure2A and Figure2B).Therefore,these results suggested that treatment with DHC presented a dose- and time-dependent inhibition of H1299 cell growth.
DHC inhibited the migration of H1299 cells
For metastasis greatly limited treatment options of NSCLC,wound healing assay was used to investigate the DHC on cell mobility in H1299 cells.Compared with the control group,DHC significantly inhibited the migrative ability of H1299 cells at the concentration of 8.0 and 16.0 μM (Figure3A).After treating with DHC for 24 h,the mobility ratios to control were 28.96 ±2.25%,20.46 ± 3.35%,13.24 ± 1.53%,respectively.When prolonging the action time of DHC to 48 h,the mobility ratios to control were 64.99± 0.52%,41.34±2.81%,23.48 ± 4.09%,respectively.Time course and concentration gradient analyses were shown in Figure3B,indicating that DHC could inhibit the migrative ability of H1299 cells.
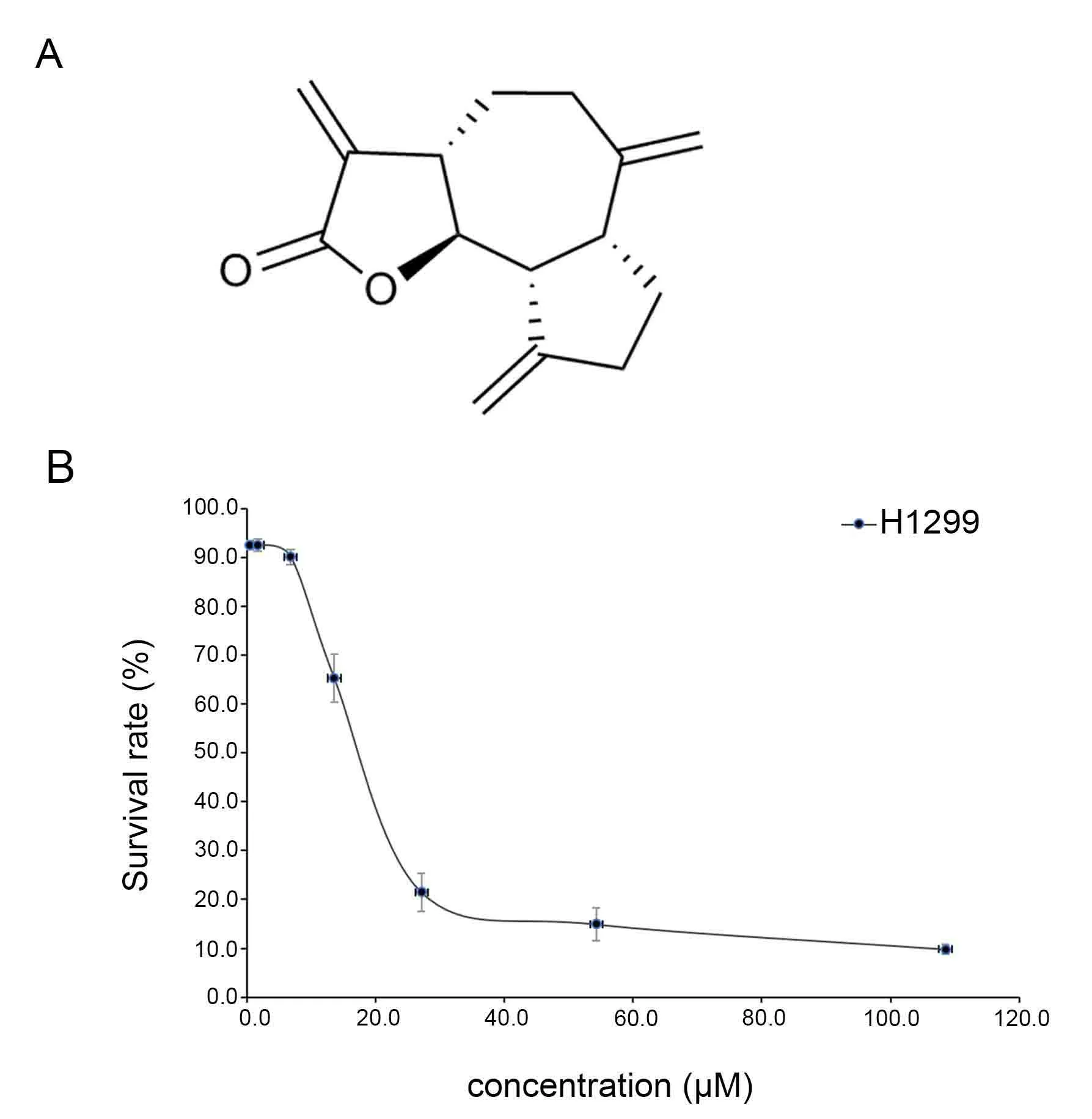
Figure1 Structure of DHC and its cytotoxicity to H1299 cells.(A)Chemical structure of DHC.(B)H1299 lung cancer cells were cultured with DHC at different concentrations for 68 h and the cells viability were assayed by MTT.
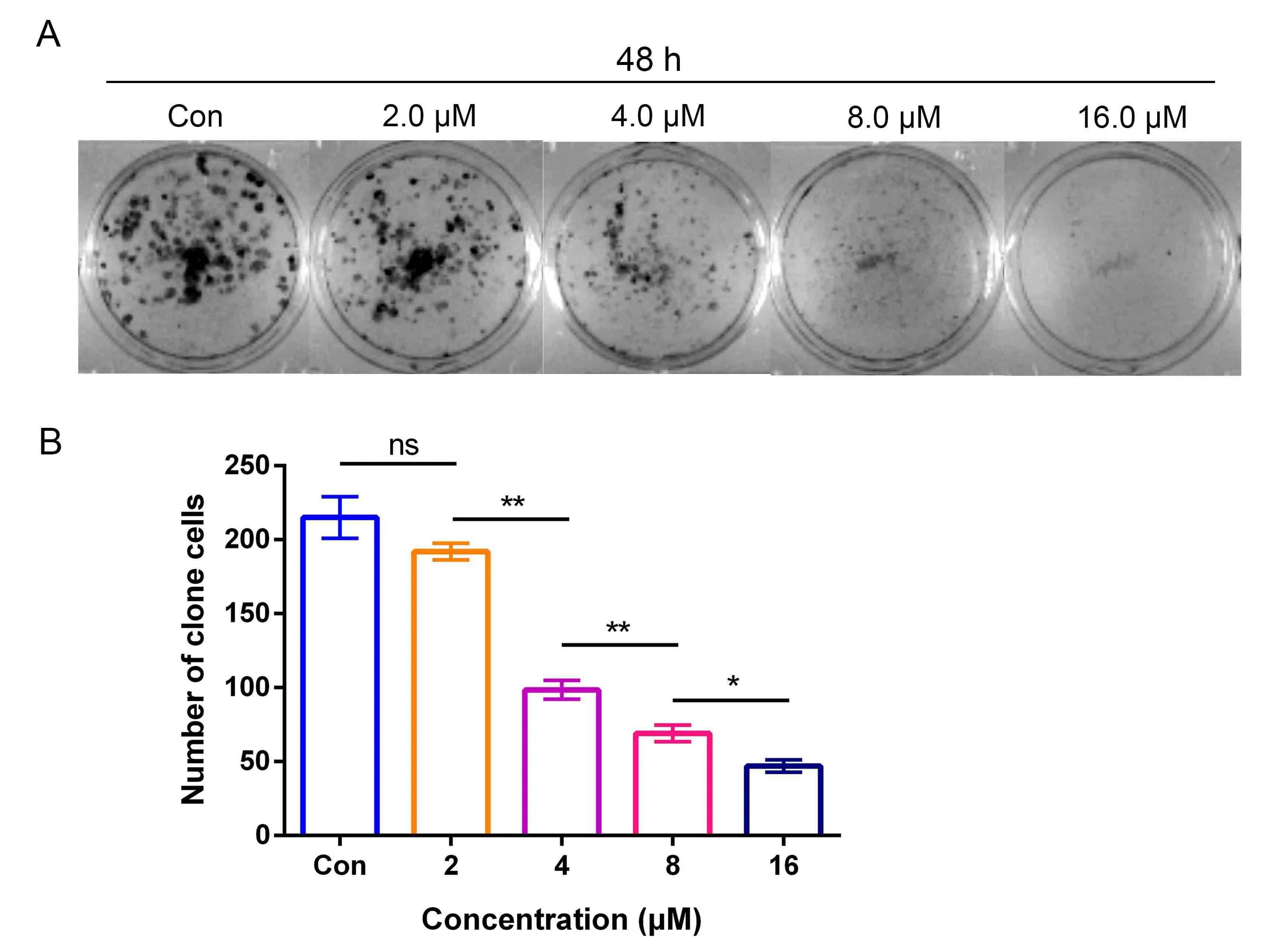
Figure2 DHC inhibited colony formation ability of H1299 cells.(A)Colony formation assay,after treating with different concentrations of DHC for 48 h.The colony formation assay was used to detect the proliferative ability of H1299 lung cancer cells,and the number of colonies was evaluated.(B)Data were quantified as mean±SD(n=3 independent experiments).*,P <0.05;**,P <0.01;ns,no significant;Con,control.
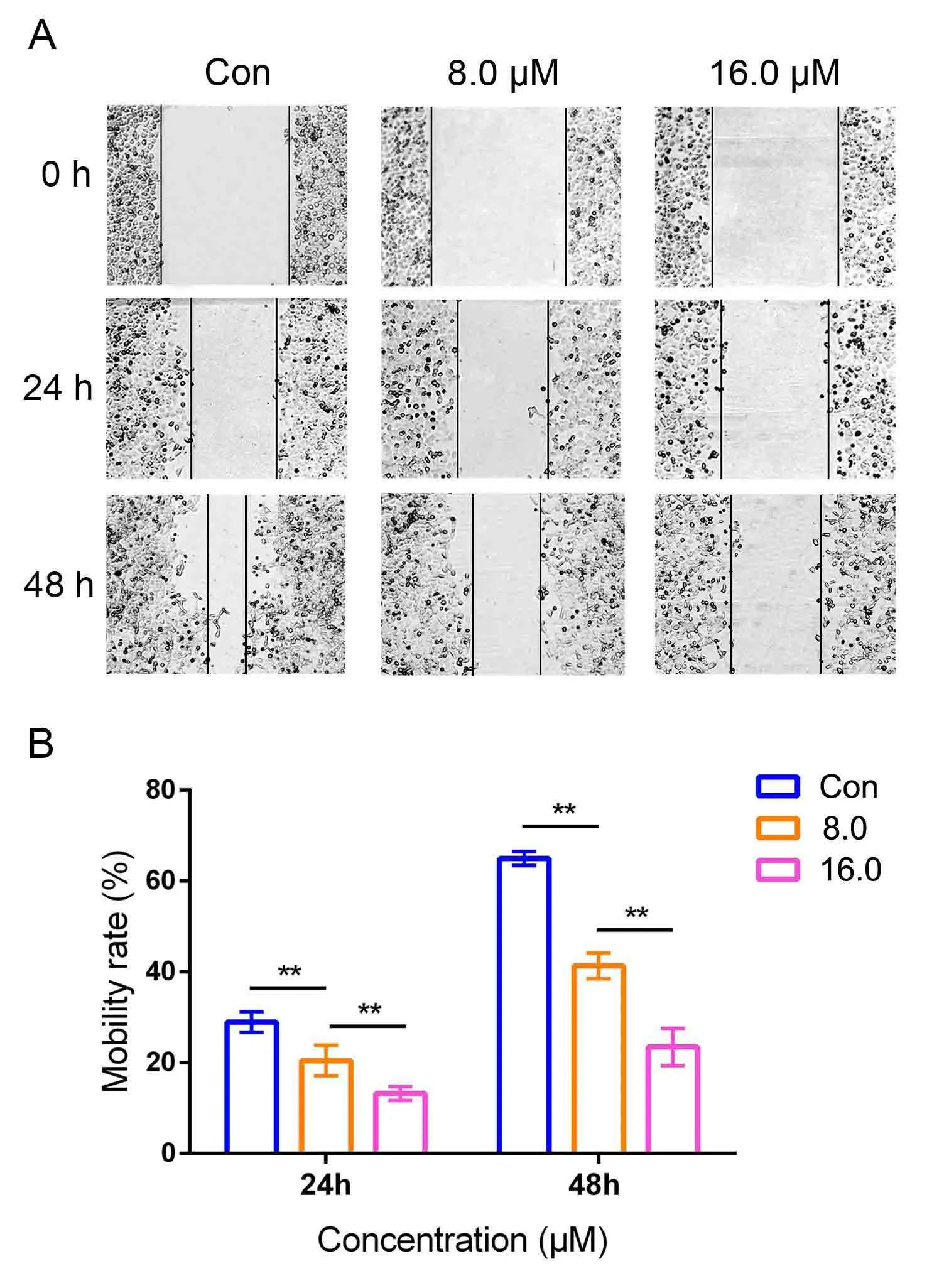
Figure3 DHC inhibited the migration of H1299 cells.(A) Wound-healing assay.The lung cancer H1299 cells was cultured with DHC at different concentrations and cell monolayers were scratched by 200 μL yellow tips.Images were taken at 0,24 and 48 h after wounding scratch.Representative images were displayed.(B)Data were quantified as mean ± SD (n = 3 independent experiments).Differences between concentrations were tested using one-way ANOVA.*,P <0.05;**,P <0.01;Con,control.
DHC inhibited the invasion of H1299 cells
Then,we further studied the ability of DHC to inhibit invasion in H1299 cells by Transwell assay.As shown in Figure4A and Figure4B,after exposing to 2.0,4.0,8.0,16.0 μM DHC for 48 h,the number of H1299 cells invaded decreased in a dose-dependent manner.Consistently,when treated with 16.0 μM DHC for 24 or 48 h,the invasive ability of H1299 cells was also significantly suppressed in a time-dependent manner.In conclusion,the above results showed that the invasive ability of H1299 cells was dose- and time-dependently reduced by DHC.
DHC induced apoptosis in H1299 cells
To investigate the apoptosis-inducing effects of DHC,annexin V-FITC/propidium iodide apoptosis detection kit was used to detect apoptosis by flow cytometry.H1299 cells were treated with DHC at different concentrations of 8.0,16.0 and 32.0 μM for 48h.As shown in Figure5A and Figure5B,DHC induced H1299 cells apoptosis at a concentration of 32.0 μM.The apoptosis cell percentage in H1299 cells was 5.01±0.28%,4.81±0.12%,4.85±0.15%,9.98±0.28%at control,8.0,16.0 and 32.0 μM DHC,respectively.
DHC regulated mRNA expression associated with metastasis and proliferation
For DHC showing excellent potential anti-proliferative,anti-migratory and anti-invasive activities,we investigated the antitumor mechanism by RT-qPCR assay.H1299 cells were incubated with DHC (16.0 μM) for 0,6 and 12 h and then the mRNA expression level of E-cadherin,N-cadherin,Snail,integrin α2,MMP2,c-Myc and Survivin were examined in turn.It is well known that a lack of E-cadherin leads to tumor metastatic transmission [24].As shown in Figure6A,DHC significantly increased the E-cadherin level in a time-dependent manner,which exhibited the anti-migrative activity of DHC.Additionally,the transcription level of N-cadherin and Snail which resulted in cell separation and enhanced mobility was far less than those from the control group (Figure6A).On the other hand,the mRNA levels of MMP2 and integrin α2 which are closely related to cancer metastasis were down-regulated after treating with DHC for 6 and 12 h (Figure6B).As shown in Figure6C,the oncogene c-Myc and Survivin (a member of the inhibitor of apoptosis gene family) were also significantly down-regulated by DHC.Therefore,we speculated that the apoptosis induced by DHC in NSCLC cells might be regulated by c-Myc and Survivin signaling pathways.
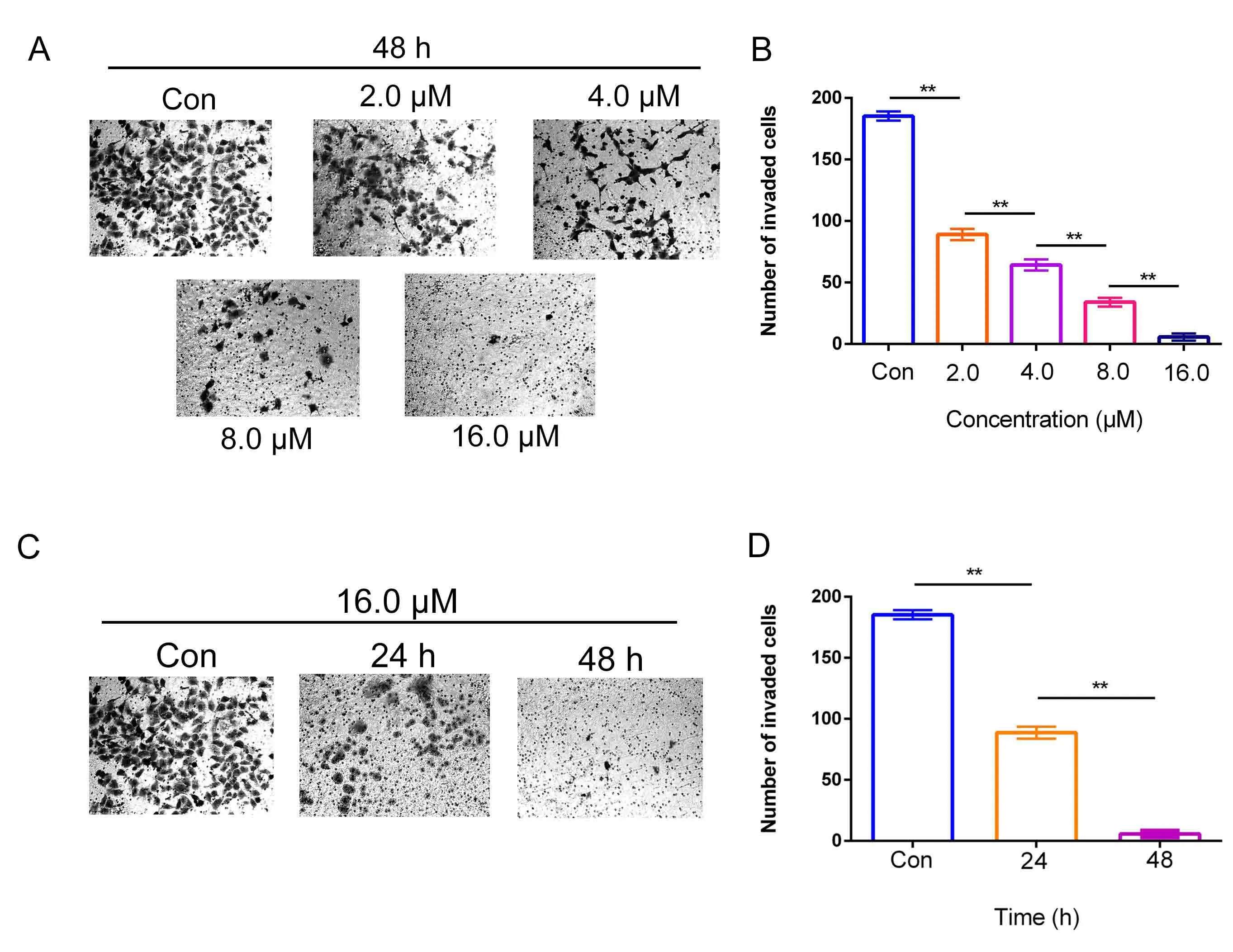
Figure4 DHC inhibited the invasion of H1299 cells.(A)Cell invasion assay using Matrigel-coated Transwell in H1299 treated with different concentrations of DHC for 48 h.Representative images were displayed.(B)Data were quantified as mean ± SD (n = 3 independent experiments).Differences between concentrations were tested using one-way ANOVA.*, P <0.05; **, P <0.01.(C) Cell invasion assay using Matrigel-coated Transwell in H1299 treated with 16.0μM DHC for 24 and 48 h.Representative images are displayed.(D)Data were quantified as mean±SD(n=3 independent experiments).Differences between concentrations were tested using one-way ANOVA.*,P <0.05;**,P <0.01;Con,control.
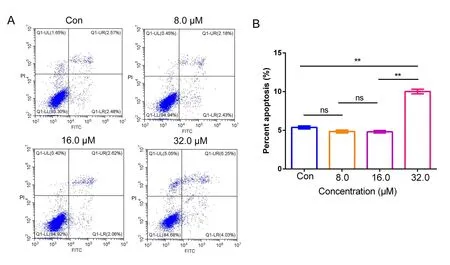
Figure5 DHC induced lung cancer H1299 cells apoptosis in vitro.(A) The lung cancer H1299 cells were treated with DHC for 48 h and apoptosis was detected by FACS.Representative images were displayed.(B) Data were quantified as mean ± SD (n = 3 independent experiments).Differences between concentrations were tested using one-way ANOVA.*,P <0.05;**,P <0.01;ns,no significant;Con,control.
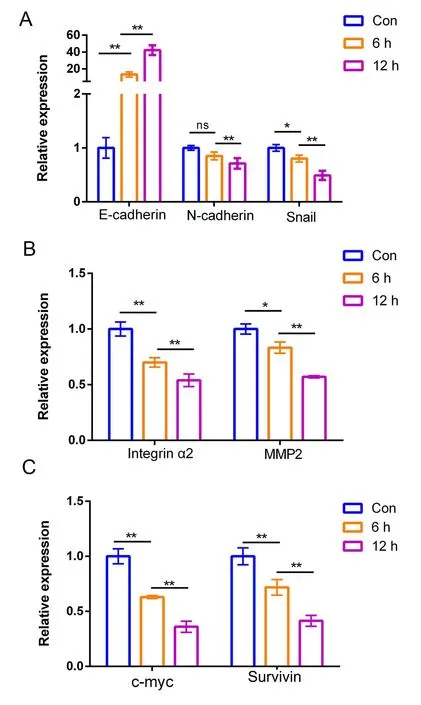
Figure6 DHC regulated metastasis- and proliferation-related mRNA levels of H1299 cells.(A)-(C) mRNA level of E-cadherin,N-cadherin,Snail,integrin α2,MMP2,c-Myc and Survivin gene in H1299 lung cancer cells.After treated with 16.0 μM DHC for 0,6,12 h,the mRNA expression levels of E-cadherin,N-cadherin,Snail,integrin α2,MMP2,c-Myc and Survivin were quantified using real-time PCR.Data were quantified as mean ± SD(n = 3 independent experiments).Differences between concentrations were tested using one-way ANOVA.*, P <0.05;**,P <0.01;ns,not significant.
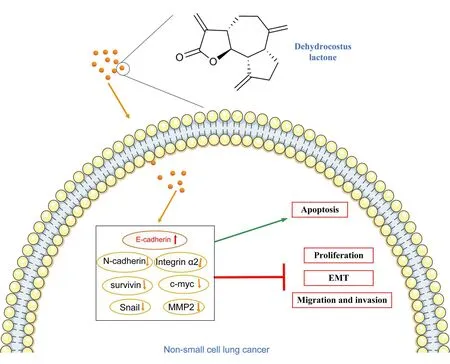
Figure7 A summary of mechanisms involved in DHC against NSCLC cells
Discussion
Clinically,despite the use of several therapeutics,the 5-year survival of NSCLC patients still remains low,for NSCLC shows strong invasion and metastasis phenotype [3,25,26].In view of the strong toxic and the gradually emerging drug resistance of traditional chemotherapy in the treatment of NSCLC,it is urgent to develop new antitumor drugs with mild toxicity[27].Natural plants are rich in bioactive molecules and are an important source of cancer treatment drugs.Many studies have shown that the plant active ingredient sesquiterpene lactone has a powerful antitumor effect[28].DHC,a natural sesquiterpene lactone,is one of the active compounds of the roots ofAucklandia lappa[29].Multiple studies have shown that DHC has antitumor activity in colorectal,gastric,and hematological tumors [16,17,30].In this study,we found that DHC could inhibit the proliferation,migration,invasion and induce apoptosis in H1299 lung cancer cells.
DHC has the ability to induce apoptosis and exert anti-proliferative effects in multiple cancer types.Sun et al.[17]found that DHC suppressed the proliferation of colorectal carcinoma through the downregulation of eIF4E expression.Moreover,in a study on chronic myelogenous leukemia,Het et al.[16] demonstrated that DHC could inhibit the proliferation of chronic myelogenous leukemia cells.Further research found that it was mainly through inhibiting the activation of Bcr/Abl-JAK/STAT signaling pathway.In our study,we evaluated the cell proliferation inhibitory activities of DHC via MTT assay and colony formation assay,the results showed that DHC exerted a significant inhibitory activity with an IC50value of 16.12 ± 3.06μM.Also,we found that proliferation-related genes c-Myc and Survivin were suppressed in H1299 lung cancer cells.Dong et al.[31] demonstrated that DHC induced the apoptosis of colon cancer cells SW-480 through inhibiting cyclin D1 and Survivin.Some previous studies reported that DHC induced apoptosis in gastrinoma cancer cells with 100 μM [30] and Hela cells with 40 μM [32].These suggested that DHC might possess the potential to induce apoptosis in lung cancer cells.We examined cell apoptosis in H1299,and found that DHC induced the percentages of early and late apoptosis cells at the concentration of 32.0μM.
Tumor cells undergoing the epithelial-mesenchymal transition (EMT) process have lost the integrity of epithelial cells and exhibited a mesenchymal cell phenotype,thus possessing strong invasive and migratory characteristics [33,34].Many studies have found that matrix metalloproteinases (such as MMP2 and MMP9) were overexpressed in metastatic cancer cells and were closely related to the metastasis of many cancers,including lung cancer [26,35].MMP2 is constitutively expressed in tissues and plays an important role in cancer metastasis [36].Previous studies have found that the combined use of DHC and doxorubicin cause a synergistic inhibitory effect of MMP2,showing enhanced anti-angiogenic properties in a mouse model [18].To explore the mechanism of the anti-migratory and anti-invasive activities of DHC,the mRNA expression level of MMP2 was tested.As shown in Figure6,the mRNA expression of MMP2 was significantly down-regulated after incubating with DHC.E-cadherin is low expressed in most cancers.Loss of epithelial adhesion molecule E-cadherin disrupts cell-to-cell contact,leading to metastatic transmission [24].During the EMT process,proteins with stronger connection flexibility (such as N-cadherin) replace the adhesion proteins that connect epithelial cells,leading to cell separation and enhanced mobility [37].From Figure6,we found that the transcription level of N-cadherin and Snail was down-regulated by DHC.Besides,integrins are the major cell adhesion receptors,which are involved in almost the entire process of cancer progression from primary tumor development to metastasis [38,39].More importantly,integrins determine the colonization of metastatic sites and promote the survival of circulating tumor cells independent of anchoring [38].ZiaeeHere et al.[40] found that pancreatic cancer mediated bone metastasis by enhancing the expression of integrin α2.Here,we detected that DHC inhibited the expression of integrin α2 in H1299 lung cancer cells.
Taken together,the results of the present study demonstrated that DHC has the ability to inhibit NSCLC cell proliferation,migration,invasion and induce apoptosis.Mechanically,DHC inhibited EMT-related signaling pathways via transcriptionally downregulating of N-cadherin and Snail,and transcriptionally upregulating of E-cadherin.Additionally,the downregulation of MMP2 and integrin α2 might further influence the invasion and metastasis progress in NSCLC.We also found that DHC induced apoptosis,which might be associated with the downregulation of c-Myc and Survivin signaling pathways.Overall,our study may provide a new therapeutic agent for disrupting the growth and metastasis of NSCLC(Figure7).
- Cancer Advances的其它文章
- On the regulation of PP2A and its role in controlling sister chromatid cohesion and microtubule-kinetochore attachment
- The practical value of serum TK1 concentration expression in clinical research of malignant tumors
- Clinical efficacy of Qingxin Fupi Jieyu formula in the treatment of 28 cases with digestive tract cancer-related cognitive impairment
- Tumor-associated macrophages,exosomes and tumor metastasis: a mini-review

