Deep Penetrating Nevus
Hang Zhang,I-Ting Lee,Jian-Min Chang?
Department of Dermatology,Beijing Hospital,National Center of Gerontology,Beijing 100730,China.
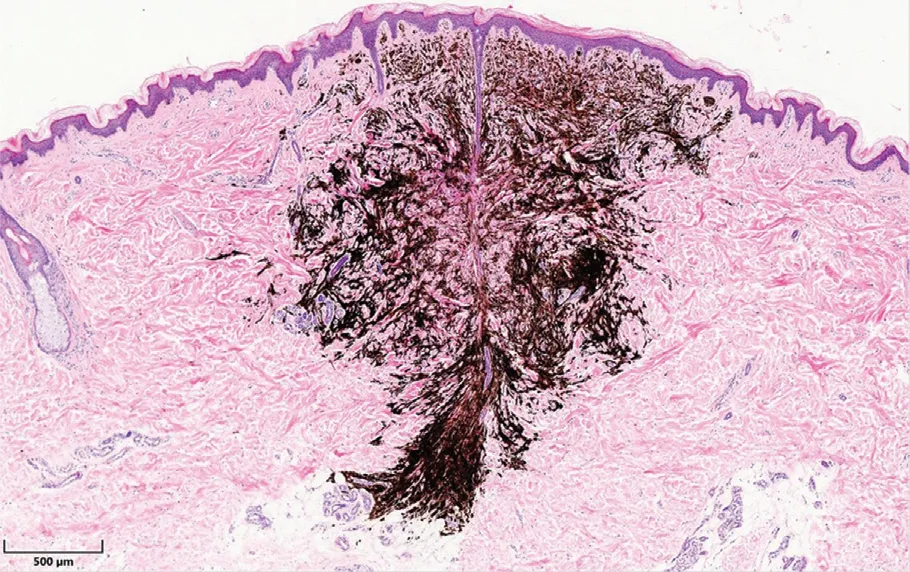
Figure 1.The tumor shows a wedge-shaped growth pattern:the broad base parallel to the epidermis and the apex penetrate into the deep reticular dermis and fat.The border is relatively clear(×40).
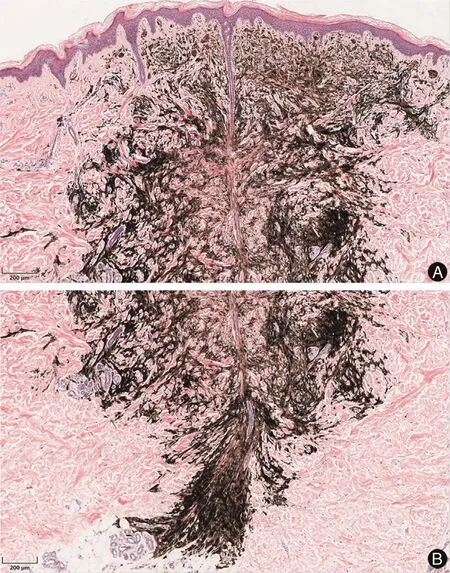
Figure 2.The tumor cells are melanocytes that mainly locate in the dermis,dermal papilla is not affected.The tumor consists of pigmentous spindle cells and epithelioid cells.There are a large number of pigment granules in cells.The tumor cells have no obvious heteromorphism.Collagen fiber proliferation are around the tumor mass.And there are no obvious inflammatory cell infiltration(A and B:×100).
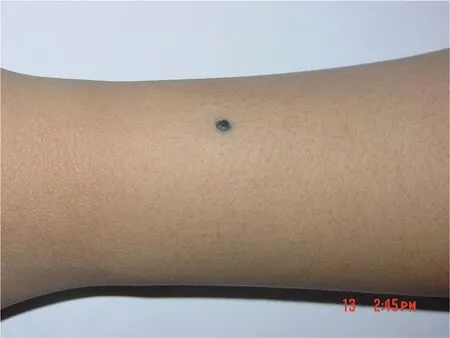
Figure 3.A single deeply blue-black maculopapule rash is on the left forearm,with a diameter about 3mm.And the boundary is clear.
Histopathology
The deep penetrating nevus(DPN)is mostly intradermal nevus, and a few are compound nevus. Under low magnification,the DPN shows a wedge-shaped growth pattern:The broad base parallel to the epidermis and the apex penetrate into the deep reticular dermis andfat(Fig.1).At higher magnification, tumor cells are identified as melanocytes that mainly locate in the dermis,generally without involvement of the dermal papilla not affected(Fig.2A).The tumor consists of pigmentous spindle cells and epithelioid cells.In the deep,cellular components gradually decrease(Fig.2B).The tumor can spread from the upper to the dermis along the sweat glands,hair follicles,and pilar muscles.1Immunohistochemistry shows that the nevus cells were positive for S-100 protein and HMB-45 staining.2
Histopathologically,the disease needs to be differentiated from common blue nevus and cellular blue nevus from the following aspects:
1.Melanocytes in common blue nevus are characteristically spindle-shaped and dendritic and located in the upper middle part of the dermis.It can be accompanied by collagen fiber proliferation;
2.Melanocytes in cellular blue nevus are mostly round or cuboid,pigments are less than common blue nevus and deep penetrating nevus.The distribution has no special form.2
Clinical Features
DPN is a rare,benign melanocytic tumor first described by Seab et al.in 1989.3Although the age at presentation is from 3 to 64 years.DPN generally presents between the second and third decades of life.It shows a slight female predominance.4Less than 5%of DPNs develop after the age of 50 years.
The most frequent clinical presentation is that of a deeply pigmented(brown to black)papule,<1cm in diameter(Fig.3).The most frequent site of DPN is face,neck,upper part of trunk,and proximal extremities.There is also a report that it occurred in the plantar surface.4A unique case of linear distribution of multiple DPNs in the preauricular skin has been reported.5
The disease is often misdiagnosed as blue nevus,because it is difficult to distinct from each other clinically.It also needs to be differentiated from malignant melanoma and congenital nevus.6Therefore,histopathological evaluation is essential for the correct diagnosis.
The disease cannot be treated by oral or topical medicine.Surgical removal is needed if necessary.
- 國際皮膚性病學(xué)雜志的其它文章
- Instructions for Authors
- Apocrine Sweat Gland Adenocarcinoma in the Left Retroauricular Area:A Rare Case Report
- Actinic Granuloma:A Case Report
- Cutaneous Metastasis of Uterine Cervical Carcinoma with a Cellulitis-Like Presentation
- Squamous Cell Carcinoma Secondary to Mutilating Palmoplantar Keratoderma
- Toxic Shock Syndrome Due to Streptococcus pyogenes Presenting with Purpura Fulminans in an Older Adult

