The study on neuroprotective mechanism of water extract of Fomitopsis Pinicola on mesencephala dopaminergic neurons induced by MPP+
Shanshan Guo ,Wolf Dieter Rausch
1 Institute of Chinese Materia Medica, China Academy of Chinese Medical Sciences, Beijing, China. 2 Institute for Medical Biochemistry,University for Veterinary Medicine,Veterinaerplatz 1,A-1210 Vienna,Austria.
Background
Parkinson's disease is a neurodegenerative disease in human beings, which seriously affects the health of more than 6.5 million people worldwide.The prevalence of the elderly over 65 years old is about 1-2% [1, 2].Although the exact etiology and pathogenesis of Parkinson's disease remains unclear, oxidative stress has been proven to be a key factor in the selective degeneration of dopaminergic neurons in the nigrostriatal striatum [3, 4]. Studies have showed that excessive production of Reactive Oxygen Species (ROS) induceS mitochondrial dysfunction,including decreased the mitochondrial membrane potential (△Ψm) and the activity of respiratory chain complex enzymes Ⅰ, as well as abnormal mitochondria DNA[5, 6]. In addition, the sensitivity and selectivity of the nigrostriatal pathway to oxidative stress can also lead to DNA damage of dopaminergic neurons in patients with Parkinson's disease[7].
Fomitopsis Pinicola is a medicinal fungus which belongs to the Polyporaceae and Pseudomonas. It has a flat, slightly bitter taste and has pharmacological effects such as anti-oxidation, anti-bacterial, anti-tumor and immune enhancement [8, 9]. Our previous studies have confirmed that aqueous extracts of Fomitopsis Pinicola have a protective effect on MPP+-induced apoptosis of fetal midbrain dopaminergic cells,which can significantly increase the number of dopaminergic neurons and axonal length, and Increase the activity of mitochondrial respiratory chain complex enzyme I[10].
In this study, we will use the Ferric reducing antioxidant power method (FRAP) to observe the antioxidant capacity of aqueous extracts of Fomitopsis Pinicola, and observe the anti-inflammatory effect of lipopolysaccharide (LPS)-induced NO release in BV2 microglia.The effects of cultured midbrain dopaminergic neurons on nuclear morphology,mitochondrial membrane potential and ROS production were observed in vitro, so as to reveal the protective mechanism of endomycetes on dopaminergic neurons.
Material
Animal
The 14-day-pregnancy mice, OF1/SPF, from the Austrian Laboratory Animal and Veterinary Genetics Institute,experimented with experimental animals in accordance with European Commission Directive 86/609/EU.
Test sample
Fomitopsis Pinicola was produced in Austria and was identified by Professor Wolf Dieter Rausch as Footmitopsis Pinicola. After the pulverization of the Fomitopsis Pinicola, the water extract extract was obtained by hot water extraction, and the crude polysaccharide content was 8.95%.
cell line
Mouse microglioma cell line BV2, from the Department of Biochemistry,Vienna Veterinary University,in DMEM medium (sigma) containing 10% fetal bovine serum, 2%B27(Gibco),2%glutamine,37°C 5%CO2 culture.
cell culture medium
BM (basic medium) medium to which DMEM medium was supplemented with 10% fetal bovine serum, 30 mM glucose, 2 mM glutamine, 1% streptomycin and 0.5%amphotericin.
main reagents and instruments
MPP+ is sigma product, purity ≥ 98%; anti-tyrosine hydroxylase(TH) primary and secondary antibody are all products of American Vectastain. TPTZ (2,4,6-tripyridine triazine), FeCl3 ? 6H2O, FeSO4?7H2O are products of American sigma-Aldrich. DAPI dyeing solution, JC-1 dyeing solution and C-DCDHF-DA dyeing solution are all products of Invitrogen Molecular Probes.The original solution concentration was 1mg/ml, 1mg/ml and 1M,respectively. Fluorescence microscope, made by Nikon company in Japan, model TS-100-F. Spectrophotometer for Germany Pharmacia Biotech products, models for Novaspec Ⅱ.
method
Determination of antioxidant capacity of extracts by FRAP method
After the preparation of 30 ml of FRAP work fluid (300 mmol/L acetate buffer, 10 mmol/L TPTZ solution, 20 mmol/L FeCl3solution mixed uniformly at a volume ratio of 10:1:1), 450 mu L FRAP working liquid was added with different concentrations of 60 μl aqueous extracts of Fomitopsis Pinicola and 45 μl double evaporate water.Blending 37 °C avoid light reaction after 30 min, then determin its absorbance values at 593 nm. The total antioxidant capacity of each extract was quantified using Trolox as the standard. Three parallel assays were performed for each sample.The results were expressed as Trolox equivalent (TEAC) (mol TEAC/g) per gramme extract.
NO release assay was used to detect the anti-inflammatory effect of the extract
The logarithmic phase BV2 cells inoculated in 48-well plates at the concentration of 1 x 105cells/ ml. After inclubation for 37 °C and 5% CO2, the lipopolysaccharide (LPS) was added for stimulation, the final concentration was 1μg/ml. Then, different concentrations of the extract were added, and the cells were cultured at 37 °C under 5% CO2for 48 h, after which the concentration of NO2-was measured. Before the trial, Griess reagents A and B were taken out from refrigerator at 4 °C and allowed to equilibrate room temperature for 30 min. The nitrite standards were serially diluted (20, 10, 5, 2, 1, and 0.5μM) to produce standard curves. Add 50 μL of the diluted standard and the supernatant of the sample to be tested(4 replicates for each concentration),add to the 96-well plate,then add 50 μL of the A solution,incubate at room temperature for 10 min in the dark, and add 50 μL of the B solution. After incubation for 10 min at room temperature in the dark,the absorbance was measured at 550 nm with a microplate reader within 30 min,and the release of NO in the supernatant was calculated according to the standard curve [11]. At the same time, 10 μl MTT (5 mg/mL in PBS solution) was added to each well of the cell plate,and cultured at 37 ° C for 5 % CO2for 4h. After the supernatant was discarded, 100 μL of DMSO was added to each well,and the absorbance was measured at 570 nm after fully dissolved,to observe the cell survival rate.
Culture and identification of primary midbrain dopaminergic cells and drug treatment
The pregnant mice were sacrificed and transferred to a petri dish containing DPBS buffer, the mouse embryos were dissected, the midbrain was isolated, cut into small pieces and collected in DPBS buffer containing 2ml of 0.1% trypsin and 2ml 0.02% of DNase I. Incubate for 7 min in 37 °C water bath, and then add 2 ml of trypsin inhibitor at a concentration of 0.125 mg/ml, centrifugal the tissue at 100 x g for 4 min, and discard the supematant. Then, DMEM medium containing 0.02%DNase I was added, and the separated cells were resuspended in BM cell culture medium, seeded in polylysine-treated cell plates, and cultured at 37 °C, 5%CO2.On the 10th day of culture,10 μM MPP+was added to the cultured primary neuron cells for treatment, and then 50, 25, 12.5 μg/ml aqueous extract of Fomitopsis Pinicola was added for treatment at 37 °C, 5% CO2was cultured for 48 hours. On the 12th day of culture, some cells were used for the identification of dopaminergic neurons, and the cells were fixed with 4%paraformaldehyde at 4°C for 30 min,and then permeable for 30 min at room temperature with 0.4% Triton X-100.After rinsing with PBS buffer for 3 times, it was blocked with horse serum blocking solution for 90 min, then anti-TH primary antibody was added overnight, then biotinylated secondary antibody was added for room temperature for 90 min,and finally 3,3'-diaminobenzidine(DAB, 5 mg/ml) was developed. The cells positive for TH color were observed under the microscope as dopaminergic neurons.
Observation of nuclear morphology
MPP+ and drug-treated cells were fixed with 4%paraformaldehyde for 30 min, then ruptured with 0.4%Triton X-100 for 30 min,and then added with DAPI stain solution at a final concentration of 1 μg/ml for 5 min at room temperature. The morphology of the nucleus was observed under a fluorescence microscope.The excitation wavelength was 340 nm, and 4 fields were randomly selected for each well.
Detection of mitochondrial membrane potential
MPP+ and drug-treated cells were added to JC-1 dye at a final concentration of 10 μg/ml, and incubated at 37 °C for 15 min. The fluorescence intensity changes were observed by fluorescence microscopy at 488 nm and 568 nm excitation light respectively. The change in mitochondrial membrane potential was measured by the ratio of the fluorescence intensity at 568 nm to the fluorescence intensity at 488 nm.
ROS production test
MPP+ and drug-treated cells were added to C-DCDHF-DA dye at a final concentration of 10 mM,and after incubation at 37 °C for 30 min, the culture solution was discarded, and the cells were washed twice with a colorless DMEM medium. Fluorescence microscopy was used to observe the change of fluorescence intensity. The excitation wavelength was 488 nm, and 4 fields of view were randomly selected for each well. The time of exposure of the cells to the excitation light was not more than 5s.
Results
Antioxidant ability of Fomitopsis Pinicola
Fomitopsis Pinicola has obvious anti-oxidation effect,and its water extract has an antioxidant capacity of(165.80±7.13)μmol TEAC/g extract.
Anti-inflammatory effect of Fomitopsis Pinicola
After LPS induced BV2 cells, the release of NO was significantly increased, which was significantly different from that of the normal control group.After the aqueous extract of Fomitopsis Pinicola, the release of NO was significantly reduced, among which 100, 50, 25, there was a significant difference between the 12.5 μg/ml dose group and the LPS group (Fig. 1). After LPS induced BV2 cells, the cell survival rate was significantly lower than that of the normal control group.After the action of the aqueous extract of Fomitopsis Pinicola, the 100μg/ml dose group had a significant reduction in cell viability,and there was a significant difference compared with the LPS group. The 50, 25, 12.5 μg/ml dose group had no significant effect on cell viability(Figure 1,Figure 2).
Identification of midbrain dopaminergic neurons in fetal rats
After the specific TH staining of the cultured fetal rat midbrain neurons, the dopaminergic neurons showed a clear brownish yellow color, and the staining of the cell bodies and axons was clearly visible, which proved that the dopaenergic neurons were cultured successfully(Figure 3).
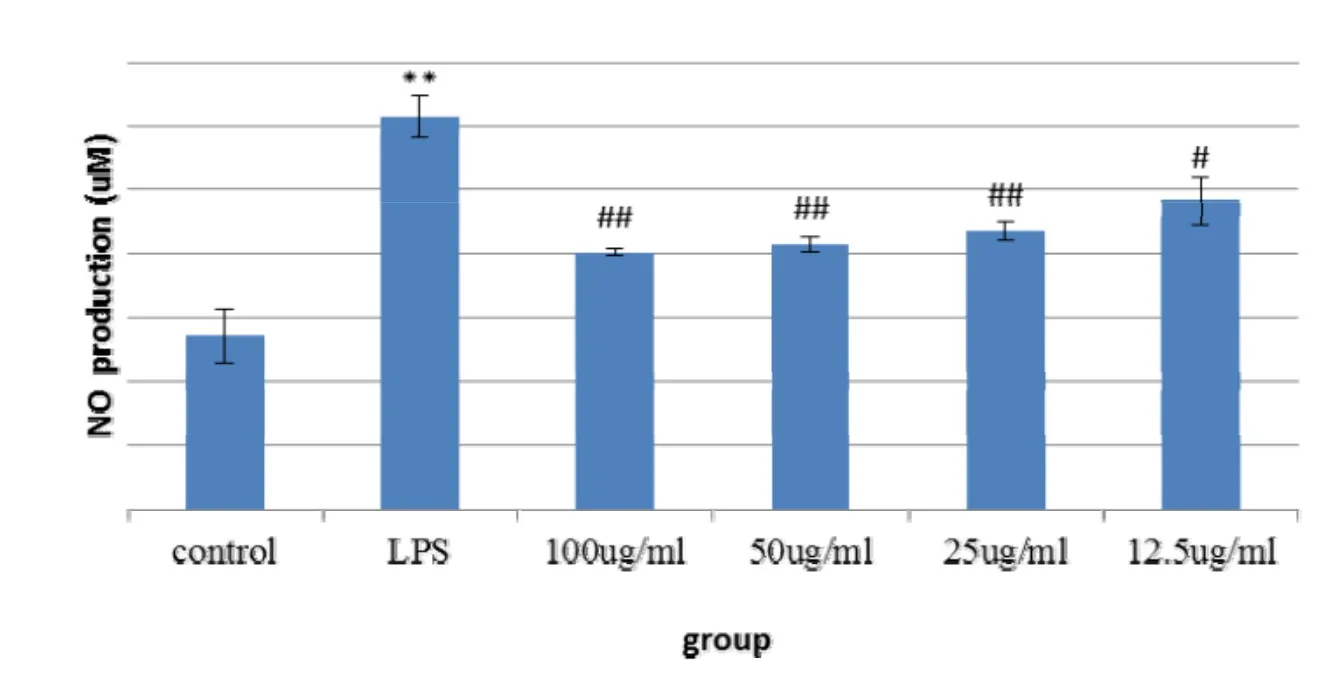
Figure 1 Effects of water extracts of Fomitopsis Pinicola on the release of NO in BV2 cells induced by LPS
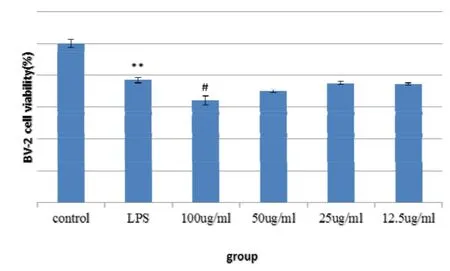
Figure 2 influence of water extract of Fomitopsis Pinicola on the survival rate of BV2 cells
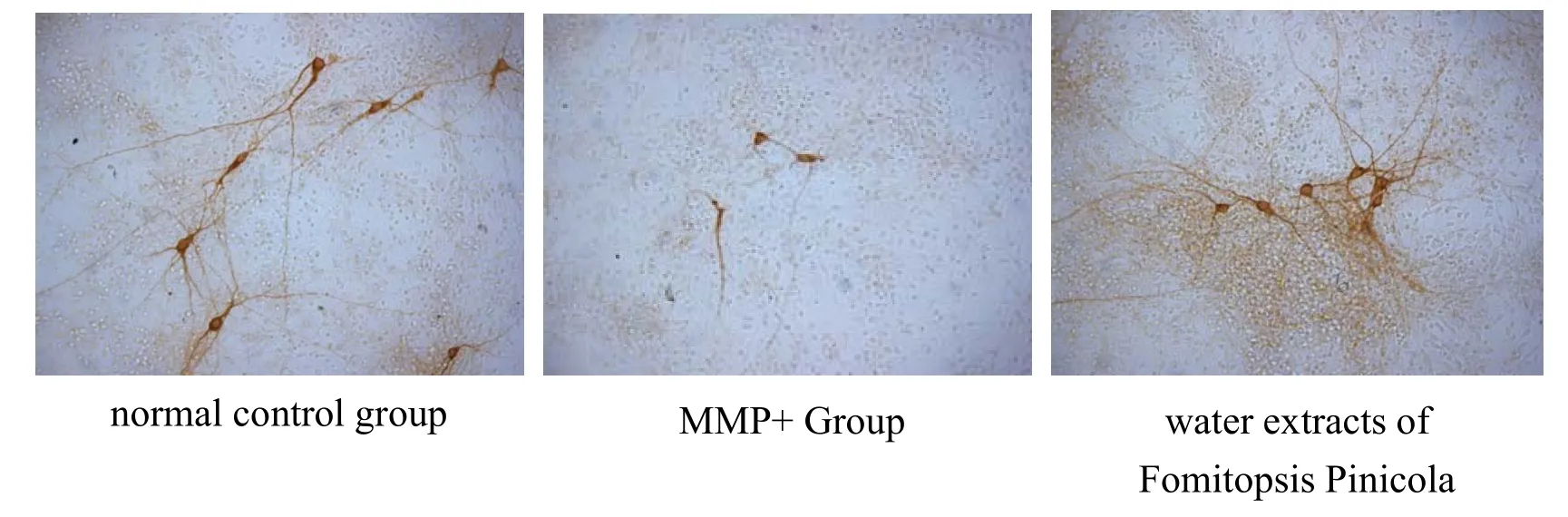

Figure 3 TH-labeled mesencephala DA neuron staining
Effect of Fomitopsis Pinicola on nuclear morphology
DAPI, 4',6-diamidino-2-phenylindole, is a fluorescent dye that penetrates the cell membrane and binds strongly to DNA. The results of this experiment showed that the nuclei of dopaminergic neurons in the normal control group remained almost intact and the chromatin was uniform. The MPP+ control group showed significant chromatin condensation, nuclear membrane lysis, and nuclear lysis. After the action of the aqueous extract of Fomitopsis Pinicola, the morphology of the nucleus was relatively intact, and the characteristics of apoptosis were reduced(Figure 4).
Effect of Fomitopsis Pinicola on Mitochondrial Membrane Potential
After MPP+ induction, the mitochondrial membrane potential of dopaminergic neurons decreased significantly,which was significantly different from that of the normal control group (P < 0.01).After the action of the aqueous extract of Fomitopsis Pinicola, the mitochondrial membrane potential decreased after MPP+ induction.There was a significant increase in mitochondrial membrane potential in the 50, 25, and 12.5 μg/ml dose groups compared with the MPP+control group(P<0.01,P<0.05)(Figure 5).
Effect of Pseudomonas sinensis on ROS production
After MPP+ induction, the ROS production of dopaminergic neurons was significantly increased, which was significantly different from that of the normal control group (P < 0.01).After the action of the aqueous extract of Fomitopsis Pinicola, the ROS increased after MPP+induction.The reduction of ROS production in the 50 and 25 μg/ml dose groups was significantly different from the MPP+control group(P<0.01)(Figure 6,Figure 7).
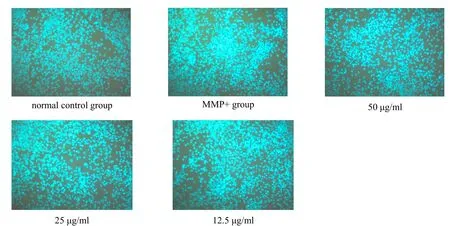
Figure 4.DAPI fluorescence staining imaging of DA neurons in the mesencephala
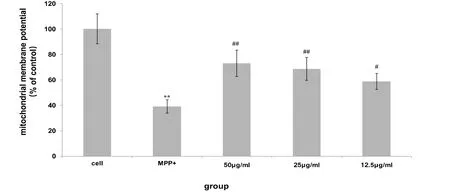
Figure 5 The effect of water extract of Fomitopsis Pinicola on MPP+-induced mitochondrial membrane potential of mesencephala DA neurons

Figure 6.C-DCDHF-DA fluorescence staining of DA neurons in the mesencephala
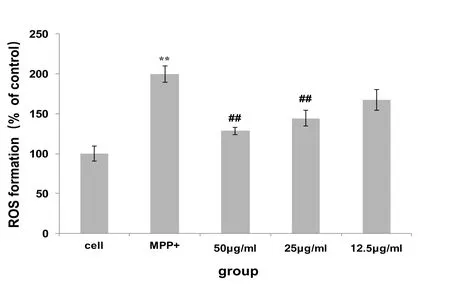
Figure 7 effects of water extracts of Fomitopsis Pinicola on MPP+-induced mesencephala DA neuron ROS production
Conclusion
The degeneration of dopaminergic neuron(DA neuron)in the midbrain is lost and The Lewy body in the cytoplasm of residual neurons is the main feature of Parkinson's disease. The clinical symptoms mainly include static tremor, bradykinesia, and hypermyotonia, posture instability, et al. At present, the treatment of Parkinson's disease is still dominated by dopamine replacement therapy. Although it can improve the symptoms of patients, it does not prevent the development of the disease. Long-term application will cause many adverse reactions[12],so the study of new therapeutic approaches is imperative. Studies have shown that oxidative stress and oxidized dopamine levels are important causes of selective damage of dopaminergic neurons [13], and some natural antioxidants such as quercetin, curcumin,tea polyphenols, et al have been confirmed to be dopamine caused by nerve agents. Neuronal damage has obvious protective effects [14 - 16], so it is promising to screen drugs for the treatment of Parkinson's disease from traditional Chinese medicines with antioxidant pharmacological effects.
In this study, FRAP was used to detect the antioxidant capacity of aqueous extracts of Fomitopsis Pinicola, using Trolox(6-hydroxy-2,5,7,8-tetramethylchroman) 2-carboxylic acid) was found to have significant antioxidant effects.The anti-inflammatory effect of aqueous extracts of
Fomitopsis Pinicola was detected by lipopolysaccharide-induced BV2 microglia release NO method, and there was no significant effect on cell viability at concentrations below 100 μg/ml, indicating that it was in glial cells have significant anti-inflammatory effects and have no significant effect on cell survival.
Oxidative stress refers to the imbalance between the production and elimination of oxygen free radicals in the body. It is an early event in the process of neuronal degeneration-apoptosis. Studies have shown that brain tissue is rich in phospholipids and unsaturated fatty acids,both of which are susceptible to oxidative stress. In patients with Parkinson's disease, Malondialdehyde, the lipid peroxidation index, in the striatum is significantly increased, while the concentration of polyunsaturated.fatty acids decreased significantly [17], the content of glutathione (GSH) decreased, and the function of mitochondrial respiratory chain complex enzyme I was impaired[18,19].MPP+ is a metabolite of the neurotoxic agent MPTP in the body,which can generate free radicals in the body, inhibit mitochondrial function, destroy DA neurons in the substantia nigra,and develop symptoms of Parkinson's disease in animal models. NO is also involved in the damage mechanism of MPP+. Excessive NO diffuses into DA neurons, which can nitrosation with the sulfhydryl site of the enzyme and inhibit mitochondrial respiratory chain complex enzyme I activity[20,21].
The results of this study showed that after MPP +induced primary cultured DA neurons, the nucleus showed obvious apoptosis, mitochondrial membrane potential decreased, and ROS production increased significantly, indicating that MPP+ can induce apoptosis of DA neurons Bby inhibiting mitochondrial oxidative stress. aqueous extract of Fomitopsis Pinicola a can improve the morphology of dopaminergic neurons after MPP+ induction, increase mitochondrial membrane potential, and reduce ROS production, indicating that water extract of Fomitopsis Pinicola inhibits the damage of midbrain DA neurons damaged by nerve agents,which may be related to its anti-oxidation and inhibition of NO production, and protect neurons by inhibiting mitochondrial oxidative stress.
1. Khan AU, Akram M, Daniyal M, et al. Awareness and current knowledge of Parkinson disease: A Neurodegenerative disorder. Int J Neurosci 2018, 8:1-64.
2. Klingelhoefer L, Reichmann H. Parkinson's disease as a multisystem disorder.J Neural Transm(Vienna)2017,124:709-713.
3. Choi DH, Cristóv?o AC, Guhathakurta S, et al.NADPH oxidase 1-mediated oxidative stress leads to dopamine neuron death in Parkinson's disease.Antioxid Redox Signal 2012,16:1033-1045.
4. Asaithambi A,Ay M, Jin H, et al. Protein kinase D1(PKD1) phosphorylation promotes dopaminergic neuronal survival during 6-OHDA-induced oxidative stress.PLoS One,2014,9:e96947.
5. Berndt N,Bulik S,Holzhütter HG.Kinetic Modeling of the Mitochondrial Energy Metabolism of Neuronal Cells: The Impact of Reduced α-Ketoglutarate Dehydrogenase Activities on ATP Production and Generation of Reactive Oxygen Species.Int J Cell Biol 2012,2012:757594.
6. Yan MH,Wang X,Zhu X.Mitochondrial defects and oxidative stress in Alzheimer disease and Parkinson disease.Free Radic Biol Med 2013,62:90-101.
7. Guo C, Sun L, Chen X, Zhang D. Oxidative stress,mitochondrial damage and neurodegenerative diseases.Neural Regen Res 2013,8:2003-2014.
8. Hao L, Sheng Z, Lu J, et al. Characterization and antioxidant activities of extracellular and intracellular polysaccharides from Fomitopsis pinicola.Carbohydr Polym,2016,141:54-59.
9. Shah F,Mali T,Lundell TK. Polyporales Brown Rot Species Fomitopsis pinicola: Enzyme Activity Profiles, Oxalic Acid Production, and Fe3+-Reducing Metabolite Secretion.Appl Environ Microbiol,2018,84:e02662-17.
10. Guo SS,Wolf D.Study on neuroprotective effects of water extract of Fomitopsis Pinicola on dopaminergic neurons in vitro.Chin J Pharmacovigil 2018,15:582-586.
11. Khaled Radad, Rudolf Moldzio, Wolf-Dieter Rausch .Toxicity Minocycline Protects Dopaminergic Neurons Against Long-Term Rotenone.Can J Neurol Sci 2010,37:81-85.
12. Rizek P, Kumar N, Jog MS.An update on the diagnosis and treatment of Parkinson disease.CMAJ 2016,188:1157-1165.
13. Crotty GF, Ascherio A, Schwarzschild MA.Targeting urate to reduce oxidative stress in Parkinson disease.Exp Neurol 2017,298:210-224.
14. Ay M, Luo J, Langley M, et al. Molecular mechanisms underlying protective effects of quercetin against mitochondrial dysfunction and progressive dopaminergic neurodegeneration in cell culture and MitoPark transgenic mouse models of Parkinson's Disease.J Neurochem 2017, 141:766-782.
15. Wang MS, Boddapati S, Emadi S, et al. Curcumin reducesalpha-synuclein induced cytotoxicity in Parkinson's disease cell model.BMC Neurosci 2010,11:57.
16. Weinreb O,Amit T,Mandel S,et al.Neuroprotective molecular mechanisms of(-)-epigallocatechin-3-gallate: a reflective outcome of its antioxidant, iron chelating and neuritogenic properties.Genes Nutr 2009,4:283-296.
17. Dawson TM, Ko HS, Dawson VL. Genetic animal models of Parkinson's disease. Neuron 2010, 66:646-61.
18. Bodis-Wollner. Retinopathy in Parkinson Disease. J Neural Transm(Vienna)2009,116:1493-1501.
19. Hisahara S, Shimohama S. Toxin-induced and genetic animal models of Parkinson's disease.Parkinsons Dis.2010,2011:951709.
20. Yang S, Liu T, Li S, et al. Comparative proteomic analysis of brains of naturally aging mice.Neuroscience 2008,154:1107-1120.
21. Gautier CA, Corti O, Brice A. Mitochondrial dysfunctions in Parkinson's disease. Rev Neurol(Paris)2014,170:339-343.
 TMR Modern Herbal Medicine2019年2期
TMR Modern Herbal Medicine2019年2期
- TMR Modern Herbal Medicine的其它文章
- Wenxin granule for cardiac arrhythmia:an overview of systematic reviews
- Terahertz spectral analysis of Yunpian Lurong
- Mechanism analysis of Traditional Chinese Medicine in treatment of Diabetic Nephropathy based on network pharmacology and Traditional Chinese Medicine inheritance support system
- Pharmacologic mechanisms mining and prediction of Xiaoer Qixing Cha Formulae in the treatment of infantile functional dyspepsia based on chemical analysis by UPLC-QTOF/MS and interactive network pharmacology
- Clinical research progress of ischemic heart failure and prospect of traditional Chinese medicine
