China National Standard—Test Method for Biodegradability of Surfactants (GB/T I5818—2006)
General Administration of Quality Supervision, Inspection and Quarantine of the People’s Republic of China Standardization Administration of the People’s Republic of China
Foreword
The national standard is the revision of GB/T 15818-1995 Testing Method for Biodegradability of Anionic and Nonionic Surfactants. It was issued on 21 August, 2006, and implemented on 1 January, 2007.
In comparison with GB/T 15818-1995, the significant changes of this national standard are as follows:
— Revision of the standard name
— Addition of the terms and definitions
— Revision of the calculation formula of biodegradability
— Revision of annex B.1 Determination of nonionic surfactants
— Addition of the method for determination of cationic and amphoteric surfactants
— Addition of the method for determination of alkyl polyglycosides
— Revision of annex B.2 Foam volume method
— Addition of DT-90 test
— Revision of the classification of sorbitan fatty acid esters
Annex A, B, C, D and E of this national standard are normative.
The national standard was proposed by China National Light Industry Council.
The national standard is under the jurisdiction of National Technical Committee 272 on Surfactant and Detergent of Standardization Administration of China.
The national standard was drafted by China Research Institute of Daily Chemical Industry and National Detergent Quality Supervision and Inspection Center (Taiyuan).
The main drafters of the standard are Zhao Yumei and Qin Yong.
This standard was issued first on December 8th, 1995, and this is the first time for adjustment.
The national standard will replace GB/T 15818-1995 from the implementation date of this standard.
Introduction
GB/T 15818-1995 Testing Method for Biodegradability of Anionic and Nonionic Surfactants is modified in relation to JIS K 3363-1990 Testing Method for Biodegradability of Synthetic Detergent. Fine chemical industry has made considerable progress in recent 10 years, promoting the development of many new types of anionic and nonionic surfactants. Furthermore, the production and consumption of amphoteric and cationic surfactants increase each year.In order to ensure the environment compatibility of such products, some newly developed analytical methods for the determination of these new surfactants have been added in the standard, and many other changes to the biodegradation test process as well as analytical procedure in the standard have been made in this revision.
Scope
The national standard specifies the test method for the determination of primary biodegradability of surfactants by aerobic micro-organisms.
The national standard is applicable to determination of biodegradability of
a) Anionic surfactants characterized by sulfate and sulfonate group
b) Polyoxyethylene nonionic surfactants characterized by single EO chain with EO number ranging from 3 to 40 or multi EO chains (2, 3, 4 EO chains) with total EO number ranging from 6 to 60
c) Alkyl polyglycoside surfactants
d) Cationic and amphoteric surfactants
e) Surfactants capable of producing rich foam during test.
The national standard is also applicable to determination of the biodegradability of above surfactants in detergents.
Normative references
The following normative documents contain provision which, through reference in this text, constitute provisions of this national standard. For dated references, subsequent amendments (excluding corrigendum contents), or revisions of, any of these publications do not apply. However,parties to agreements based on this section are encouraged to investigate the possibility of applying the most recent editions of the normative documents indicated below. For undated references, the latest edition of the normative document referred to applies.
GB/T 5173 Surface Active Agents and Detergents-Determination of Anionic-active Matter by Direct Twophase Titration Procedure (eqv ISO 2271:1989).
GB/T 5174 Surface Active Agents—Detergents—Determination of Cationic—active Matter Content (eqv IS0 2871.l:1988, IS0 2871.2:1990).
GB/T 5327 Surface Active Agents—Terms (idt ISO 862:1984).
GB/T 5328 Surface Active Agents—Simplified Classification (idt ISO 2123:1972).
GB/T 5560 Nonionic Surface Active Agents-Determination of Polyethylene Glycols and Nonionic Active Matter (adducts)—Weilbull Method (idt ISO 2268:1972).
GB/T 13173.1 Methods of Sample Division For Detergents (eqv ISO 607:1980).
GB/T 13173.2 Determination of Total Active Matter Content in Detergents.
GB/T 13173.3 Determination of Nonionic Surface Active Agents in Detergents-Ion Exchange Method (neq JIS K3362:1998).
GB/T 19464 Alkylpolyglycosides .
QB/T 2344 Amphoteric Surfactants—Fatty Alkyl Dimethyl Betaines.
Terms and definitions
For the purposes of this national standard, the following terms and definitions apply.
Biodegradability
Molecular breakdown of a chemical compound or organic matter by micro-organisms.
Primary biodegradability
Structural change (transformation) of a chemical compound by micro-organisms resulting in the loss of specific properties.
Disappear time DT- 90
The degradation time consumed to allow the biodegradability to reach 90 % of initial concentration of test sample.
Principle
The activated sludge, pre-adapted to surfactant test solution for 6 days, is inoculated and incubated in a synthetic medium containing 30 mg/L of test sample under shaking at a controlled temperature. Determine the elimination (reduction of concentration) of the test sample during the test cycle, and calculate the DT-90 and the biodegradability at a set time based on above determination.
Apparatus
Conical flask

Of capacity 1,000 mL, carefully cleaned, dried and sterilized at 170°C for 1 h to 2 h, covered with cotton stopper.
Shaking machine
Rotary shaker with amplitude of 24 to 51 mm and frequency of 200 to 250 rpm or reciprocating oscillation machine with amplitude of 50 to 100 mm and frequency of 100 to 130 rpm, equipped with automatic temperature control or used in a constant temperature room.
Autoclave
Rated temperature of 126℃, rated pressure of 0.14 MPa,and proper water.
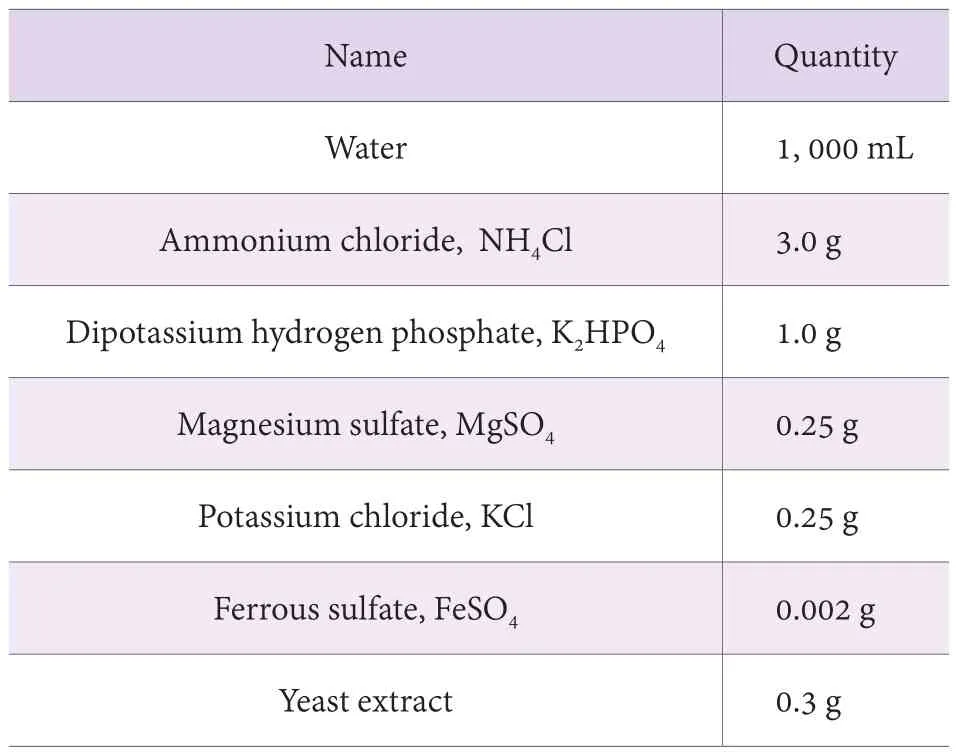
Reagents
Use only reagents of recognized analytical grade and only distilled water or deionised water or water of equivalent purity during analysis, unless otherwise specified.
1) Ammonium chloride, NH4Cl (GB/T 658);
2) Dipotassium hydrogen phosphate, K2HPO4(HG/T 3487);
3) Magnesium sulfate, MgSO4(GB/T 671);
4) Potassium chloride, KCl (GB/T 646);
5) Ferrous sulfate, FeSO4(GB/T 664);
6) Yeast extract (biochemical reagent);
7) Linear sodium dodecyl benzene sulfonate, purity>95 %,biodegradability>99 %;
8) Linear dodecanol polyoxyethylene ether (7EO),purity > 98 %, biodegradability>99 %;
9) Inoculum;
Collect a fresh sample of activated sludge from a properly working conventional sewage treatment plant.The suspended solids concentration of activated sludge shall be adjusted to 10,000 to 20,000 mg/L. It shall be used within 5 h after collection.
10) Formaldehyde (GB/T 685).

Test procedure
Preparation of test sample
In cases where the test sample was received as detergents or in form of any other mixture, it shall be pretreated in accordance with GB/T 5173, GB/T 13173.1, GB/T 13173.2,GB/T 13173.3 and purified from other ingredients as pure surfactant sample before biodegradation test.
The reference sample (6.7, 6.8) shall be neutralized (if necessary) and dissolved as 1 g/L solution.
The purified surfactant sample shall be neutralized (if necessary) and dissolved as 1 g/L solution.
Preparation of synthetic medium
Note-Yeast extract should be added before use.Sterilization at high pressure (0.11 Mpa to 0.13 MPa, 122℃to 125℃, for 20 min) by autoclave is necessary if the storage time of above synthetic medium (mixed with yeast extract) is more than 8 h, and the water for sterilization shall not contain any antimicrobial substances.
Preparation of test solution
Transfer 500 mL of synthetic medium to a 1,000 mL conical flask, and add proper volume of sample solution in it. The volume of which should be calculated to ensure the final concentration of test sample in medium is 30 mg/L.
As confirmation of test condition and running procedure,another conical flask with 500 mL of synthetic medium was prepared at the same time, and, appropriate volume of reference sample solution was added, ensuring that the concentration of reference sample in medium is 30 mg/L.
500 mL of blank synthetic medium without addition of test sample as inoculum control was prepared in parallel and run under the same condition as that of sample and reference.
Inoculation of activated sludge
Add, in each conical flask, 5 mL of activated sludge suspension.
Incubation
Place the conical flasks into the shaking machine,shake at 25 ± 3℃, and incubate for 72 h.
Adaptation
Transfer 500 mL of synthetic medium to 1,000 mL clean conical flasks. Pipette sample /reference solution as specified in. Add 5 mL of incubated solution as inoculum for adaptation. Leave one without addition of test sample as blank inoculum control. Shake at 25 ± 3℃ for 72 h as adaptation.
Biodegradation
Transfer 500 mL of synthetic medium to 1,000mL clean conical flasks. Pipette sample/reference solution as specified in. Add 5 mL of adaptation solution into each 500 mL of synthetic medium as inoculum for biodegradation. Leave one without addition of test sample as blank inoculum control. Shake at 25 ± 3℃ for 30 min first. Then, take appropriate volume of biodegradation liquor for analysis.
Determine the concentration of test sample in eachdegradation liquor including blank, by corresponding quantitative methods specified in annexes. This is the initial concentration of surfactant sample and reference.

Throughout the test, determine the concentration of test sample in each flask at appropriate time intervals to achieve the result of DT-90, or determine the remaining concentration of test sample in each flask at the end of day 7 and day 8 of biodegradation.The choice for determination method (in annex A, B,C, D and E) shall be based on the characteristics of test sample. The calculation of each concentration can be done by calibration curve or by regression equation y=a+bx.
If it is in evitable, store the anionic surfactant sample liquor by adding 1 mL of formaldehyde per 100 ml of sample. Surfactant samples other than anionic ones shall not be stored in this way due to the influence of formaldehyde on the accuracy of result.
Calculation
The degradation percentage of a sample at each time shall be calculated by the difference between the initial mass concentration (mg/L) /initial foam volume (mL) and the final mass concentration (mg/L) / final foam volume (mL)divided by the initial mass concentration (mg/L) / initial foam volume (mL), of test sample.
The biodegradability D, expressed as a percentage by mass, is given by the following formula, with results rounded to one decimal place.
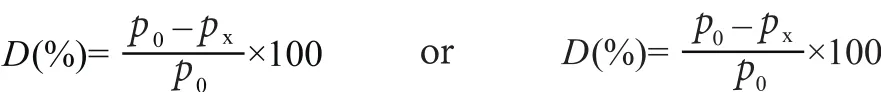
where
D is the biodegradability, in a percentage by mass, of test sample at time x;
p0is the mass concentration, in milligrams per litre, of initial test solution;
pxis the mass concentration, in milligrams per litre, of final test solution at time x;
V0is the volume, in milliliters, of foam in initial test solution;
Vxis the volume, in milliliters, of foam in final test solution at time x.
Validity of test
A test is considered invalid if either of these conditions is not met: a) The biodegradability of the reference compound linear sodium dodecyl benzene sulphonate≥ 97.5%or that of the reference compound linear dodecanol polyoxyethylene ether (7EO) ≥ 95.0%; b) The difference of biodegradability of the test surfactant at day 7 and at day 8 ≤ 2%.
Test report
The test results shall be reported as following:
The DT-90 reported as the time consumed for biodegradability of test sample to reach 90%, and/or the final degradation result reported as the calculated biodegradability at the end of day 7.
Annex A
(Normative)
Determination of Anionic Surfactants—Methylene Blue Method
A.1 Principle
The method is based on the fact that the cationic dye methylene blue forms blue salts with anionic surfactants (MBAS), which can be extracted with chloroform. The absorbance of the organic phase is measured photometrically at the wavelength of maximum absorption of 650 nm.
A.2 Scope
This method is applicable to anionic surfactants characterized by sulfate and sulfonate group.
A.3 Reagents
A.3.1 Surfactant standard stock solution and standard calibration solution
The purity of anionic surfactants can be measured according to GB/T 5173.
Weigh, to the nearest 0.001 g, the reference surfactant,about the equivalent of 1 g of 100% purity surfactant,dissolve in water, transfer to a 1,000 mL volumetric flask,dilute to the mark and mix well. The mass concentration of this stock solution is 1 g/L.
Pipette 10.0 mL of this stock solution into another 1,000 mL volumetric flask, dilute to the mark by water and mix. This is the standard calibration solution with anionic surfactant mass concentration of 0.01 mg/mL.
A.3.2 Concentrated sulfuric acid, H2SO4 (GB/T 625)
A.3.3 Sodium dihydrogen phosphate, NaH2PO4 (GB/T 1267)
Sodium dihydrogen phosphate solution—Dissolve 50g of sodium dihydrogen phosphate in water, add carefully 6.8 mL of concentrated sulfuric acid, dilute to 1,000 mL.
A.3.4 Methylene blue solution
Dissolve 0.10 g methylene blue (AR) in deionized water and dilute to 100 mL. Transfer 30 mL of this solution into a 1,000 mL volumetric flask. Dilute to the mark with sodium dihydrogen phosphate solution(A.3.3).
A.3.5 Chloroform (trichloromethane), CHCl3(GB/T 682).
A.4 Apparatus
Ordinary laboratory apparatus and Spectrophotometer,wavelength range from 360 to 800 nm, for measurement at 650 nm, with 10 mm cell.
A.5 Calibration curve
Pipette, accurately and respectively, anionic surfactant standard calibration solution (A.3.1, concentration 0.01mg/mL) 0 mL(blank), 3.0 mL, 6.0 mL, 9.0 mL, 12.0 mL,15.0 mL, into 250 mL separating funnels, and add water to ensure the total volume up to100 mL. Add 25 mL of methylene blue solution (A.3.4), mix and add 15 mL of chloroform (A.3.5) into each separating funnel. Shake the mixture for 30 s. Leave it to stand to allow phase separation. If the blue color in water layer disappears, add extra 10 mL of methylene blue solution (A.3.4). Shake for 30 s, and allow to stand at least 10 min for phase separation.
Run the chloroform layer into another 250 mL separating funnel (do not allow the floccule to pass through with chloroform layer). Repeat the extraction procedure till the chloroform layer becomes colorless.
Add 50 mL of sodium dihydrogen phosphate solution(A.3.3) into the combined chloroform extract. Shake the mixture for 30 s and allow to stand for 10 min. Pass the chloroform layer through a clean cotton-wool filter into a 100 mL volumetric flask. Add 5 mL of chloroform into the separating funnel. Repeat the extraction procedure till the chloroform layer becomes colorless. All the chloroform layer shall be filtered through cotton-wool filter to the 100 mL volumetric flask. Rinse the cottonwool filter with clean chloroform, dilute to the mark and mix well.
Measure the absorbance of the chloroform solution with a spectrophotometer at 650 nm in 10 mm cells against blank reference solution.
Plot the calibration curve as a linear function, with surfactant mass (μg) as x-axis and absorbance as y-axis,or calculate the slope and intercept by software based on the linear regression equation y=a+bx.
A.6 Determination of test surfactant concentration in biodegradation liquor
Pipette, accurately, appropriate volume (2 mL to 5 mL at beginning, up to 50 mL as appropriate during degradation process) of biodegradation liquor into a 250 mL separating funnel, and dilute to 100 mL with water. Then, follow the procedure “Add 25 mL of methylene blue solution… dilute to the mark and mix well” specified in A.5.
Determine the blank test solution following the same procedure.
Measure the absorbance of the chloroform solution with a spectrophotometer at 650 nm in 10 mm cells against blank test solution. Calculate the mass concentration of test surfactant via calibration curve or linear regression equationy=a+bx, with result expressed in μg/mL.
A.7 Calculation
The mass concentration of anionic surfactant, expressed in micrograms per milliliter, is given by the formula (A.1).

where
P is the mass concentration, in micrograms per milliliter, of anionic surfactant ;
m is the mass, in micrograms, of anionic surfactant in biodegradation medium via calibration curve.V is the volume, in milliliters, of sampled solution.
Annex B
(Normative)
Determination of Ethoxylated Nonionic Surfactants—Cobaltous Thiocyanate Method
B.1 Principle
Ethoxylated nonionic surfactants form complex with cobaltous thiocyanate, which is easy to be extracted with chloroform. The concentration of nonionic surfactants can be calculated based on the absorbance of complex measured by spectrophotometer.
B.2 Scope
This method is applicable to polyoxyethylene nonionic surfactants characterized by single EO chain with EO number ranging from 3 to 40 and multi EO chains (2, 3,4 EO chains) with total EO number ranging from 6 to 60,and polyethylene glycol (with molar mass from 300 g/mol to 1,000 g/mol) as well as polyether surfactants.
B.3 Reagents
B.3.1 Standard stock solution and standard calibration solution of ethoxylated nonionic surfactant
The purity of ethoxylated nonionic surfactants can be measured according to GB/T 13173.3.
Weigh, to the nearest 0.001 g, the reference surfactant,about the equivalent of 1 g as 100% purity, dissolve in water, transfer to a 1,000 mL volumetric flask, dilute to the mark and mix. The mass concentration of this stock solution is 1 g/L.
Pipette 25.0 mL of this stock solution into a 250 mL volumetric flask, dilute to the mark and mix. This is the standard calibration solution with ethoxylated nonionic surfactant mass concentration of 0.1 g/L.
B.3.2 Ammonium thiocyanate, NH4SCN (GB/T 660)
B.3.3 Cobalt nitrate hexahydrate, Co(NO3)2·6H2O (GB/T 15898)
B.3.4 Benzene, (GB/T 690)
B.3.5 Ammonium cobalt thiocyanate solution
Dissolve completely 620 g of ammonium thiocyanate(B.3.2) and 280 g of cobalt nitrate (B.3.3) in little water.Dilute to 1,000 mL after a thorough mixing. Extract twice with 30 mL of benzene (B.3.4) each time and keep in reserve.
B.3.6 Sodium chloride, NaCl (GB/T 1266)
B.3.7 Chloroform (trichloromethane), CH3Cl (GB/T 682)
B.4 Apparatus
Ordinary laboratory apparatus.
Ultraviolet spectrophotometer, wavelength range from 200 nm to 800 nm, for measurements at 319 nm, with 10 mm cells.
B.5 Calibration curve
Pipette, accurately and respectively, nonionic surfactant standard calibration solution (B.3.1, concentration 0.1 mg/mL)0 mL (blank), 5.0 mL, 10.0 mL, 20.0 mL, 25.0 mL, 30. 0 mL,35.0 mL into 250 mL separating funnels, and add some water to ensure the total volume up to100 mL. Add 15 mL of ammonium cobalt thiocyanate solution (B.3.5) and mix gently. Then add 35.5 g of sodium chloride (B.3.6)into each separating funnel. Shake the mixture vigorously for 1 min. Leave it to stand for 15 min. Add 15 mL of chloroform (B.3.7) and shake for 1 min. Allow to stand for 15 min for phase separation. Run the chloroform layer into a 50 mL volumetric flask (do not allow the floccule at the interface to pass through with chloroform layer).
Repeat the extraction procedure twice more times with chloroform. Collect the chloroform extract together,dilute to the mark with chloroform and mix well.
Measure the absorbance of the chloroform solution with an ultraviolet spectrophotometer at 319 nm in 10 mm cells against blank reference solution.
Plot the calibration curve as a linear function, with surfactant mass (μg) as x-axis and absorbance as y-axis,or calculate the slope and intercept by software based on the linear regression equation y=a+bx.
B.6 Determination of test surfactant concentration in biodegradation liquor
Transfer, accurately, 50 mL of biodegradation liquor into a 250 mL separating funnel, dilute to 100 mL with water(transfer directly 100 mL near the end of biodegradation without dilution with water). Then, follow the procedure“Add 15 mL of ammonium cobalt thiocyanate solution…dilute to the mark with chloroform and mix well”specified in B.5.
Determine the blank test solution following the same procedure.
Measure the absorbance of the chloroform solution with an ultraviolet spectrophotometer at 319 nm in 10 mm cells against blank test solution. Calculate the mass concentration of test surfactant via calibration curve or linear regression equationy=a+bx, with result expressed in μg/mL.
B.7 Calculation
The mass concentration of ethoxylated nonionic surfactant, expressed in micrograms per milliliter, is given by the formula (B.1)

where
P is the mass concentration, in micrograms per milliliter,of ethoxylated nonionic surfactant;
m is the mass, in micrograms, of ethoxylated nonionic surfactant in biodegradation medium via calibration curve ;
V is the volume, in milliliters, of sampled solution.
Note—The isolation of the test sample from anionic,cationic, amphoteric surfactants and polyethylene glycol is necessary before analysis by this method, as the presence of above chemicals may influence the accuracy of test result. The isolation procedure of test sample from polyethylene glycol is specified in GB/T 5560 and that of other surfactants is specified in GB/T 13173.3.

Annex C
(Normative)
Determination of Cationic And Amphoteric Surfactants-Orange-ⅡMethod
C.1 General
Buffer solution of pH=1 applies to cationic surfactants,amphoteric surfactants and mixture of both. Buffer solution of pH=5 applies to cationic surfactants only.For a sample containing both cationic surfactants and amphoteric ones, measure the absorbance of cationic surfactants at pH=5 and total absorbance at pH=1. The difference is the absorbance of amphoteric surfactants.
C.2 Determination of cationic surfactants
C.2.1 Principle
Cationic surfactants form complex with orange-Ⅱ,which is easy to be extracted with chloroform, in the presence of pH=5 buffer solution. The cationic surfactant content can be calculated based on the absorbance of complex measured by spectrophotometer.
C.2.2 Scope
This method is applicable to cationic surfactants.
C.2.3. Reagents
C.2.3.1 Hexadecyl trimethyl ammonium bromide standard stock solution and calibration solution
The purity test of hexadecyl trimethy ammonium bromide surfactants can be done by the method specified in GB/T 5174.
Weigh, to the nearest 0.001 g, the hexadecyl trimethy ammonium bromide, about the equivalent of 1 g as 100 %purity, dissolve in water, transfer to a 1,000 mL volumetric flask, dilute to the mark and mix. The mass concentration of this stock solution is 1 g/L.
Pipette 10.0 mL of this stock solution into another 1,000 mL volumetric flask, dilute to the mark and mix.This is the standard calibration solution with surfactant mass concentration of 0.01 mg/mL.
C.2.3.2 Orange-Ⅱ solution
Weigh 0.1g of Orange-Ⅱ (AR), dissolve in 100 mL of water and mix.
C.2.3.3 Acetic acid (GB/T 676)
0.2 mol/L acetic acid solution.
C.2.3.4 Sodium acetate, anhydrous (GB/T 694)
0.2 mol/L sodium acetate solution C.2.3.5 Buffer solution, pH = 5
Mix 59 mL of 0.2 mol/L acetic acid solution (C.2.3.3)with 141 mL of 0.2 mol/L sodium acetate solution (C.2.3.4).C.2.3.6 Chloroform, CHCl3(GB/T 682)
C.2.4 Apparatus
Ordinary laboratory apparatus.
Spectrophotometer, wavelength range from 360 to 800 nm, for measurements at 485 nm, with 10 mm cells.
C.2.5 Calibration curve
Pipette, accurately and respectively, cationic surfactant standard calibration solution (C.2.3.1,concentration 0.01 mg/mL) 0 mL (blank), 5.0 mL, 10.0 mL,15.0 mL, 20.0 mL, 25.0 mL, 30.0 mL, 35.0 mL, into 250 mL separating funnels, and add water to ensure the total volume up to 100 mL. Add 10 mL of pH=5 buffer solution(C.2.3.5) and 3 mL of orange-Ⅱ solution (C.2.3.2), and mix gently. Then, add 10 mL of chloroform (C.2.3.6)and shake for 30 s. Allow to stand at least 10 min for phase separation. Run the chloroform layer into a 50 mL volumetric flask (do not allow the floccule at the interface to pass through with chloroform layer).
Repeat the extraction procedure till the chloroform layer becomes colorless, dilute to the mark with chloroform,and mix well.
Measure the absorbance of the chloroform solution with a spectrophotometer at 485 nm in 10 mm cells against blank reference solution.
Plot the calibration curve as a linear function, with surfactant mass (μg) as x-axis and absorbance as y-axis,or calculate the slope and intercept by software based on the linear regression equation y=a+bx.
C.2.6 Determination of test surfactant concentration in biodegradation liquor
Transfer, accurately, 10 mL of biodegradation liquor into a 250 mL separating funnel, dilute to 100 mL with water. Then, follow the procedure “add water to ensure the total volume up to 100 mL ... dilute to the mark with chloroform, and mix well” specified in C.2.5.
Determine the blank test solution (7.3.3) following the same procedure.
Measure the absorbance of the chloroform solution with a spectrophotometer at 485 nm in 10 mm cells against blank test solution. Calculate the mass concentration of test surfactant via calibration curve or linear regression equation y=a+bx, with result expressed in μg/mL.
C.2.7 Calculation
The mass concentration of cationic surfactant,expressed in micrograms per milliliter, is given by the formula (C.1)

where
P is the mass concentration, in micrograms per milliliter,of cationic surfactant;
m is the mass, in micrograms, of cationic surfactant in biodegradation medium via calibration curve;
V is the volume, in milliliters, of sampled solution.
C.3 Determination of amphoteric surfactants
C.3.1 Principle
Amphoteric surfactants form complex with orange-Ⅱ,which is easy to be extracted with chloroform, in the presence of pH=1 buffer solution. The concentration of amphoteric surfactants can be calculated based on the absorbance of complex measured by spectrophotometer.
C.3.2 Scope
This method is applicable to amphoteric surfactants,cationic surfactants as well as mixture of both.
C.3.3 Reagents
C.3.3.1 Alkyl dimethyl betaine standard stock solution and calibration solution
The purity test of alkyl dimethyl betaine surfactant can be done by the method specified in QB/T 2344.
Weigh, to the nearest 0.001 g, the alkyl dimethyl betaine surfactant, about the equivalent of 1 g as 100 % purity,dissolve in water, transfer to a 1,000 mL volumetric flask,dilute to the mark and mix. The mass concentration of this stock solution is 1 g/L.
Pipette 10.0 mL of this stock solution into another 1,000 mL volumetric flask, dilute to the mark and mix.This is the standard calibration solution with amphoteric surfactant mass concentration of 0.01 mg/mL.
C.3.3.2 Orange-Ⅱ solution
The same as C.2.3.2.
C.3.3.3 Hydrochloric acid, HCl (GB/T 62)
0.2 mol/L hydrochloric acid solution.
C.3.3.4 Potassium chloride, KCl (GB/T 646)
0.2 mol/L potassium chloride solution
C.3.3.5 Buffer solution pH = 1
Mix 97 mL of 0.2 mol/L hydrochloric acid solution(C.3.3.3) with 53 mL of 0.2 mol/L potassium chloride solution (C.3.3.4), dilute to 200 mL and stir well.
C.3.3.6 Chloroform, CHCl3 (GB/T 682)
C.3.4 Apparatus
The same as C.2.4.
C.3.5 Calibration curve
The same as C.2.5.
C.3.6 Determination of test surfactant concentration in biodegradation liquor
The same as C.2.6.
C.3.7 Calculation
The same as C.2.7.
Annex D
(Normative)
Determination of Alkyl Polyglycoside Surfactants – Anthrone Method
D.1 Principle
Sugar group hydrolyzed from alkyl polyglycosides molecule can react with anthrone reagent to form a complex with green color in strong acidic medium under heating. The concentration of alkyl polyglycosides can be calculated based on the absorbance of complex measured by spectrophotometer.
D.2 Scope
This method is applicable to alkyl polyglycosides and sugar ester surfactants.
D.3. Reagents
D.3.1 Alkyl polyglycosides standard stock solution and standard calibration solution.
The purity test of alkyl polyglycosides can be done according to GB/T 19464.
Weigh, to the nearest 0.001 g, the alkyl polyglycosides,about the equivalent of 1g as 100% purity, dissolve in water, transfer to a 1,000mL volumetric flask, dilute to the mark and mix. The mass concentration of this stock solution is 1g/L.
Dilute 5.0 mL of this stock solution to 100 mL with water and mix. This is the standard calibration solution with alkyl polyglycosides mass concentration of 0.05 mg/mL.
D.3.2 Anthrone
D.3.3 Concentrated sulfuric acid (GB/T 625)
D.3.5 Anthrone— sulfuric acid reagent
Dissolve 0.08 g of anthrone in 100 mL of concentrated sulfuric acid. This reagent should be kept in refrigerator and refreshed for days after storage.
D.4 Apparatus
Ordinary laboratory apparatus and.
D.4.1 Spectrophotometer, wavelength range from 360 nm to 800 nm, for measurements at 625 nm, with 10 mm cells
D.4.2 Nashi colorimetric cylinder with glass stopper, of capacity 10 mL.
D.5 Calibration curve
Pipette, accurately and respectively, alkyl polyglycosides standard calibration solution (D.3.1 concentration 0.05 mg/mL) 0 mL (blank), 0.25 mL, 0.50 mL, 1.00 mL, 1.50 mL, 2.00 mL, into 10 mL nashi colorimetric cylinders (D.4.2), and add water to make the total volume up to 2.0 mL. Add dropwise 5.0 mL of anthrone sulfuric acid reagent (D.3.5). Cover and heat in boiling water bath for 5 min. Then, take out and cool immediately. Mix well and allow to stand for 50 min. Measure the absorbance with a spectrophotometer at 625 nm in 10 mm cells against blank reference solution.
Plot the calibration curve as a linear function, with surfactant mass (μg) as x-axis and absorbance as y-axis,or calculate the slope and intercept by software based on the linear regression equation y=a+bx.
D.6 Determination of alkyl polyglycosides concentration in biodegradation liquor
Pipette, accurately, 2.0 mL of biodegradation liquor in a colorimetric cylinder (D.4.2). Then, follow the procedure“Add dropwise 5.0 mL of anthrone sulfuric acid reagent ...Mix well” specified in D.5.
Determine the blank test solution following the same procedure.
Measure the absorbance with a spectrophotometer at 625 nm in 10 mm cells against blank test solution.Calculate the mass concentration of test surfactant via calibration curve or linear regression equation y=a+bx,with result expressed in μg/mL.
D.7 Calculation
The mass concentration of alkyl polyglycoside surfactant,expressed in micrograms per milliliter, is given by the formula (D.1)

where
P is the mass concentration, in micrograms per milliliter, of alkyl polyglycoside surfactant;
m is the mass, in micrograms, of alkyl polyglycoside surfactant in biodegradation medium via calibration curve;
V is the volume, in milliliters, of sampled solution.
Annex E
(Normative)
Foam Volume Method
E.1 Principle
A certain volume of testsolution is shook under described conditions to produce enough foam. The surfactant concentration corresponds to the foam volume produced during shaking.
E.2 Scope
This method is applicable to those surfactants capable of producing rich foam sufficient for the determination of concentration by foam volume method, while to which methods in annex A, B, C and D are not applicable.
E.3 Apparatus
Graduated cylinder with glass stopper, of capacity 100 mL,minimum scale 1 mL.
E.4 Determination
Add 50 mL of biodegradation liquor in a graduated cylinder (E.3), and cover with the stopper. Shake the cylinder up and down 50 times (2 times per second) and allow to stand for 30 s. Record carefully the total volume of liquor and foam, and conduct the test twice. Calculate the mean volume of duplicate test. Repeat the procedure for blank at the same time.
E.5 Calculation
The foam volume of test surfactant, in milliliters, is given by the formula (E.1)

where:
is the volume, in milliliters, of foam;
is the volume, in milliliters, of test surfactant(liquor + foam);
is the volume, in milliliters, of blank (liquor +foam).
 China Detergent & Cosmetics2017年1期
China Detergent & Cosmetics2017年1期
- China Detergent & Cosmetics的其它文章
- Are you ready to join in the ITP 2017 ?
- Environmentally Safe Surfactants in Cosmetic/Detergent Formulations:Risk of Microbial Contamination and Possible Solutions
- Regulatory Status of Wet Wipes Used on Human Body in Europe,United States, Canada, Australia and China
- Introduction to Technical Safety Standards for Cosmetics
- For Beauty — JALA Group are Here to You
- Development of Chinese Kids Toothpaste Market
