A Field Observation and Signifcant Range Extension of Manouria impressa in Myanmar
Saw HTUN and Steven G. PLATT
Wildlife Conservation Society, Myanmar Program, Offce Block C-1, Aye Yeik Mon 1st Street, Hlaing Township, Yangon, Myanmar
A Field Observation and Signifcant Range Extension of Manouria impressa in Myanmar
Saw HTUN and Steven G. PLATT*
Wildlife Conservation Society, Myanmar Program, Offce Block C-1, Aye Yeik Mon 1st Street, Hlaing Township, Yangon, Myanmar
Few records of the impressed tortoise (Manouria impressa) are available from Myanmar and most are based on historic accounts, old museum specimens, and shells obtained from villagers and wildlife traffickers. We herein report the observation of a living M. impressa in the Hukaung Valley Wildlife Sanctuary of northern Myanmar. Our observation extends the known distribution of M. impressa in Myanmar approximately 850 km northwards from previously reported populations in the Rakhine Hills of Magway Region.
conservation, Hukaung Valley Wildlife Sanctuary, impressed tortoise, Myanmar
The impressed tortoise (Manouria impressa) is a poorlystudied chelonian occurring from western Myanmar, eastwards to Thailand, Laos, Vietnam, Cambodia, and southern China, and south through Peninsular Malaysia (Iverson, 1992; Platt et al., 2001; Stuart and Platt 2004). Within Myanmar, the geographic distribution of M. impressa remains ill-defined; previous records include upland regions in Kayah, Kayin, and Shan States, and Magway and Bago Regions (formerly Division) (Smith, 1931; Iverson, 1992; Platt et al., 2001). However, with the exception of a living turtle captured by rural villagers in Shan State (Platt et al., 2001), most records of M. impressa from Myanmar are based on historic accounts and old museum specimens (Smith, 1931; Iverson, 1992) or shells obtained from rural villagers and wildlife traffckers (Platt et al., 2001). Field observations of living M. impressa from Myanmar and elsewhere within Southeast Asia are notable for their paucity in the published literature (Calame et al., 2013; but see Chan-ard et al., 1996). Herein we provide a recent feld observation of Manouria impressa in Myanmar and comment on the signifcance of this record.
This observation occurred in the Hukaung Valley Wildlife Sanctuary (HVWS) in Kachin State, Myanmar. HVWS encompasses 17,373 km2in northern Myanmar with elevations ranging from 94 to 3,440 m (Hla Naing et al., 2015). Lowlands are dominated by a mosaic of broadleaf forest and grassland, while hill forests, evergreen open forests, and temperate forests (depending on elevation) characterize higher elevation habitats (Hla Naing et al., 2015). On 22 May 2015 (ca. 1400 hr), one of us (SH) encountered an adult Manouria impressa (straight-line carapace length ca. 200 mm; Figure 1) along the Ledo Road between Namyun and Shinbweyan Villages (26.81345°N; 96.20468°E; India-Bangladesh datum). The tortoise was crossing the road (a dirt track) in an area of dense second-growth evergreen forest with an abundance of bamboo and ground cover at an elevation of 960 m in mountainous terrain (Figure 2). Heavy rains signaling the beginning of the annual monsoon (May through October) had fallen over the previous fve days, perhaps triggering activity by the tortoise (e.g., Smart et al., 2014). The tortoise was examined and photographed before being released into dense cover adjacent to the road. Voucher photographs (CUSC 2953) of the tortoise and habitat were later deposited in the Campbell Museum, Clemson University, Clemson, South Carolina, USA.
Our record extends the known distribution of M. impressa in Myanmar approximately 850 km northwardsfrom previously reported populations in the eastern Rakhine (formerly Arakan) Hills of Magway Region (Platt et al., 2001) (Figure 3). The distribution of M. impressa elsewhere in the uplands of western Myanmar remains unresolved. Platt et al. (2001) suggested M. impressa was likely present in the Chin and Naga Hills, contiguous mountainous terrain linking the Rakhine Hills with uplands in HVWS; however, surveys of this region have to date failed to confrm its occurrence (Platt et al., 2012, 2013). Collectively, our observation and those of Platt et al. (2001) represent the western-most records in the global distribution of M. impressa (Iverson, 1992). We speculate that high north-south trending mountain ridges in western Myanmar act as biogeographic barriers to dispersal and probably defne the distributional limit. Finally, our observation of M. impressa in an area of evergreen hill forests appears consistent with other reports describing the habitat of this tortoise (Chan-ard et al., 1996; Calame et al., 2013).

Figure 1 Manouria impressa found crossing the Ledo Road in the Hukaung Valley Wildlife Sanctuary, Kachin State, Myanmar on 22 May 2015.

Figure 2 Second-growth evergreen forest (elevation = 960 m) where a Manouria impressa was found crossing the Ledo Road in Hukaung Valley Wildlife Sanctuary, Kachin State, Myanmar.
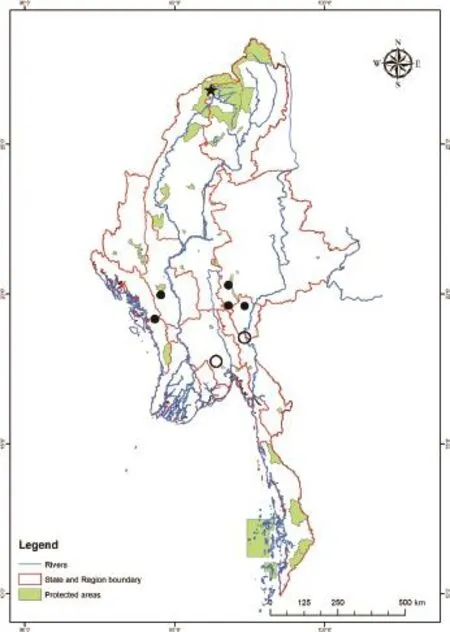
Figure 3 Map of Myanmar showing location where Manouria impressa was found in Hukaung Valley Wildlife Sanctuary (Star). Historic records (open circles) and more recent records (closed circles) from Iverson (1992) and Platt et al. (2001), respectively.
Manouria impressa is considered Vulnerable to extinction (http://www.iucnredlist.org) due to a combination of unsustainable subsistence harvesting, over-collecting for commercial wildlife markets in southern China, and widespread habitat destruction (Chan-ard et al., 1996; Platt et al., 2001; Calame et al., 2013). Because M. impressa is extremely difficult to maintain and propagate in captivity, in situ protection of wild populations is the recommended conservation option (Horne et al., 2012). Given its size, relatively low human population density, and widespread availability of suitable upland forest habitat (Hla Naing et al., 2015), HVWS could play a vital role in future efforts to protect M. impressa, although political and civil instability in the region has curtailed conservation efforts for the moment.
AcknowledgementsWe thank U Win TUN (Minister of Environmental Conservation and Forestry), Dr. NyiNyi KYAW (Director General, Forest Department), and U Win Naing THAW (Director, Nature and Wildlife Conservation Division) for granting us permission to conduct fieldwork in Myanmar. Voucher photographs were accessioned by Stanlee MILLER. Colin POOLE and U Than MYINT are also thanked for facilitating this project. Comments by Lewis R. MEDLOCK improved an early draft of this manuscript.
Calame T., Gray T. N. E., Hurley M., Timmins R. J., Thongsamouth K. 2013. Field observations of the Vulnerable impressed tortoise, Manouria impressa, from southern Laos and notes on local chelonian trade. Asian Herpetol Res, 4: 151–154
Chan-ard T., Thirakhupt K., van Dijk P. P. 1996. Observations on Manouria impressa at Phu Luang Wildlife Sanctuary, Northeastern Thailand. Chelon Conserv Biol, 2: 109–113
Hla Naing, Fuller T. K., Sievert P. R., Randhir T. O., Saw Htoo Tha Po, Myint Maung, Lynam A. J., Saw Htun, Win Naing Thaw, Than Myint. 2015. Assessing large mammal and bird richness from camera-trap records in the Hukaung Valley of northern Myanmar. Raffes Bull Zool, 63: 376–388
Horne B. D., Poole C. M., Walde A. D. 2012. Conservation of Asian tortoises and freshwater turtles: setting priorities for the next ten years. Recommendations and conclusions from the workshop in Singapore, February 21–12, 2011. Singapore: Wildlife Conservation Society, 32 pp
Iverson J. B. 1992. A revised checklist with distribution maps of turtles of the world. Richmond, Indiana: Privately Printed, 363 pp
Platt S. G., Win Ko Ko, Khin Myo Myo, Myint Shwe, Lay Lay Khaing, Holmstrom W., Rainwater T. R. 2001. Recent distribution records and a significant range extension for Manouria impressa in Myanmar. Hamadryad, 26: 362–364
Platt S. G., Win Ko Ko, Platt K., Khin Myo Myo, Me Me Soe, Rainwater T. R. 2012. Species inventory and conservation status of chelonians in Natma Taung National Park, Myanmar. Hamadryad, 36: 1–11
Platt S. G., Platt K., Khin Myo Myo, Kyaw Moe, Me Me Soe, Thet Zaw Naing, Naing Lin, Rainwater T. R. 2013. Noteworthy records of chelonians from the Chindwin River basin and Naga Hills of western Myanmar. Herpetol Conserv Biol, 8: 335–350
Smart V., Deepak V., Vasudevan K. 2014. Preliminary ethogram and in situ time-activity budget of the enigmatic cane turtle (Vijayachelys silvatica) from the western Ghats, South India. Herpetol Conserv Biol, 9: 111–122
Smith M. A. 1931. The fauna of British India, including Ceylon and Burma, Vol. 1, Loricata, Testudines. London: Taylor and Francis, 185 pp
Stuart B. L., Platt S. G. 2004. Recent records of turtles and tortoises from Laos, Cambodia, and Vietnam. Asiatic Herpetol Res, 10: 129–150
*Corresponding authors: Dr. Steven G. PLATT, from Wildlife Conservation Society-Myanmar Program, Yangon, Myanmar, with his research focusing on conservation of turtles and crocodilians in Southeast Asia.
E-mail: sgplatt@gmail.com
Received: 8 January 2016 Accepted: 27 February 2016
 Asian Herpetological Research2016年4期
Asian Herpetological Research2016年4期
- Asian Herpetological Research的其它文章
- Isolation and Characterization of 15 Microsatellite DNA Loci for the Alpine Stream Frog Scutiger boulengeri (Anura: Megophryidae)
- Major Factors Affecting the Distribution of Anuran Communities in the Urban, Suburban and Rural Areas of Shanghai, China
- Effects of Dietary Vitamins A, B2, and B6Supplementation on Growth and Feed Utilization of Juvenile Chinese Soft-shelled Turtle Pelodiscus sinensis according to an Orthogonal Array Experiment
- Effects of Feeding Time on the Growth Performance and Variation of RNA/DNA Ratio of the Chinese Soft-shelled Turtle, Pelodiscus sinensis
- Plasticity in Metamorphic Traits of Rice Field Frog (Rana limnocharis) Tadpoles: The Interactive Effects of Rearing Temperature and Food Level
- Pathological Changes in Andrias davidianus Infected with Chinese Giant Salamander Ranavirus
