Detection of Listeria monocytogenes in Dairy Food by Loop-mediated Isothermal Amplification(LAMP)
Xiao CHENG,Yongxin WANG,Juanjuan LIU,Bo ZHANG,Chen XU,Zhen JIA,Hong AN
Anhui Inspection and Research Institute for Food and Drug/China National Center for Quality Supervision and Test of Agriculturalavocation Processed Food,Hefei 230051,China
Listeria monocytogenesis a type of gram-positive bacteria growing in cells facultatively.It has strong pathogenicity,and can cause listeriosis in humans and animals.Listeria monocytogenesis an important pathogen for foodborne zoonotic diseases.It can be spread through food(such as milk and dairy products,vegetables,aquatic products and meat),and is still able to grow at low temperature(such as 4℃).So,Listeria monocytogeneshas great harm.Since the 1980s,Listeria monocytogeneshave outbroken frequently in Canada,Switzerland and other countries.In China,the food monitoring results also show thatListeria monocytogenescontamination is prevalent in food.In Yunnan,Fujian,Zhejiang and other provinces,it has even been reported thatListeria monocytogenesoutbreaks among livestock and humans.At present,the international community attaches great importance to the research onListeria monocytogenes.As early as in the 1990s,Listeria monocytogeneswas listed as one of the four food pathogens[1].Therefore,it is very necessary to establish a method for the rapid and accurate detection ofListeria monocytogenes.
Currently,in the field of food safety,the detection ofListeria monocytogenesmainly depends on traditional national standard method,immunological method,gene probes and PCR assay.The traditional isolation and identification method is tedious and time-consuming,and is not suitable fordaily rapid detection.Although PCR assay is characterized by rapidness and high accuracy,it has high requirements for costs and equipment,limiting its wider application.Loop-mediated isothermal amplification(LAMP)isa newly-developed nucleicacid amplification method[2].Targeting at the 6 regions in the target gene,two pairs of specific primers are designed.After tens of minutes of isothermal re-action using BstDNA polymerase at about 65℃,the high-efficiency amplification of nucleic acids is achieved.
At present,LAMP technology has been widelyused in detection of pathogens in food, includingSalmonella,ShigellaandEscherichia coli[3-7].Rich nutrients in dairy products may lead to false positive detection results and other issues.In order to further improve the detection accuracy ofListeria monocytogenesin dairy products,in this study,one set of LAMP primers targeting at hlyA gene that encodes listeriolysin O inListeria monocytogeneswere designed for detectingListeria monocytogenesin dairy food[8].Moreover,comparative analysisof sensitivity was carried out between established LAMP and real-time fluorescentquantitative PCR.Through comparing with the traditional detection method,the reliability of established LAMP method for detectingListeria monocytogenesin dairy food was determined.
Materials and Methods
Strains
Total nine strains were used in this study,including one standardListeria monocytogenesstrain,five other types of Listeria trains and three non-Listeriastrains.The strains were all preserved by the China National Center for Quality Supervision and Test of Agricultural-Avocation Processed Food.
Instruments and reagents
Main instrumentsThe used instruments and equipment included PCR instrument (Bio-Rad,USA),highspeed desktop centrifuge(Sigma,USA),nucleic acid and protein electrophoresis(Bio-Rad,USA),gel imaging system (Bio-Rad,USA)and fluorescent quantitative PCR instrument(ABI,USA).
Main reagentsThe various molecular biology reagents and kits were all purchased from the TaKaRa Biotechnology(Dalian)Co.,Ltd.
Methods
Preparation of DNA templateIn this study,total nine strains were sued,including one standardListeria monocytogenesstrain and 8 non-Listeria monocytogenesstandard strains.The standardListeriamonocytogenesstrain was first inoculated in the TSAYE and incubated at 30℃overnight.From the TSA-YE,one loop of activatedListeria monocytogeneswas selected,and inoculated in another fresh and sterile TSA-YE liquid medium and incubated at 30℃overnight for use.The other stains were all preserved in sealed tubes in the form of lyophilized powder.They were activated in nutrient agar medium and incubated at 37℃overnight.And then,one loop of each of the strains was inoculated in nutrient broth and cultured at 37℃overnight.Subsequently,the strains weretransferredto liquid medium containing emulsion for use.The genomic DNA of all the strains was all extracted using genomic DNA extraction kit(Takara).
Design of primersBased on the sequence ofhlyAgene registered in the NCBI database,the LAMP-specific oligonucleotide primers were designed for detectingListeria monocytogenesusing Primer Explorer V4 software(http://primerexplorer.jp/). Totaltwo outer primers (F3,B3)and two inner primers(FIP,BIP)were designed.
Optimization of LAMP reaction systemThe LAMP reaction system(25 μl)was as follows:F3 primer 0.04 μmol/L,B3 primer 0.04 μmol/L,FIP primer 0.5 μmol/L,BIP 0.5 μmol/L,Bst polymerase 8 U,dNTP 1.6 mmol/L and reaction buffer 2.5 μl.The amplification time was 90 min.Using the extracted DNA fromListeria monocytogenesin emulsion as a template,the concentration of dNTP that greatly influenced the amplification efficiency was optimized.
Specificity test of LAMP method
The genomic DNA ofListeria monocytogenes,Listeriagrayi,Listeriaivanovii,Listeria mulTayi,Listeria welshimei,Listeria innocua,Salmonella,StaphylococcusaureusandEnterobacter sakazakiiin the emulsions was extracted respectively.The extracted DNAs were used as templates for LAMP reaction,and the LAMP reaction was performed in accordance with the optimized conditions.After adding SYBR Green I,the amplification results were inspected by naked eye(whether the color turned green).And then,the amplification products were examined by 2%agarose gel electrophoresis.The electrophoresis results were analyzed using gel imaging system.
Sensitivity test of LAMP method
The standardListeria monocytogenesstrain was inoculated in fresh and sterile TSB-YE liquid medium and incubated at 37℃overnight(theOD600was adjusted to about 0.5).The population of cultivatedListeria monocytogeneswas counted by diluted plate.The broth was diluted gradiently by 10 times with sterile physiological saline.A certain amount(1 ml)of broth at each of the concentrations was used for DNA extraction,and the extracted DNA was used as template for LAMP.After adding SYBR Green I,the amplification results were inspected by naked eye (whether the color turned green).And then,the amplification products were examined by 2%agarose gel electrophoresis.The electrophoresis results were analyzed using gel imaging system.
Comparative analysis of sensitivity between LAMP method and realtime fluorescent quantitative PCR
The detection sensitivities of LAMP method and real-time fluorescent quantitative PCR were compared.Based on the sequence ofhlyAgene fromListeriamonocytogenes,the primers and probe were designed.The reaction system(25 μl)was as follows:forward primer(0.2 mmol/L)1.0 μl,reverse primer(0.2 mmol/L)1.0 μl,probe(0.2 mmol/)0.5 μl,PremixTaq12.5 μl,genomic DNA ofListeria monocytogenes1.0 μl,ddH2O 9 μl.The reaction parameters were shown in Table 1.
Detection ofListeria monocytogenesindairyfoodbyLAMP methodTotal 50 dairy products samples were collected from the market,including 10 adult milk powder samples,10 pasteurized milk samples,10 yogurt samples and 10 baby milk powder samples.Total 5 parts ofListeria monocytogeneswere added to each of the samples by hand.After adding fresh and sterile TSB-YE liquid medium,the 50 samples were incubated at 37℃for 24 h.A certain amount(1 ml)of each of the samples was used for DNA extraction.In addition,theListeria monocytogenesin each of the samples was detected using GB 4789.30-2010.
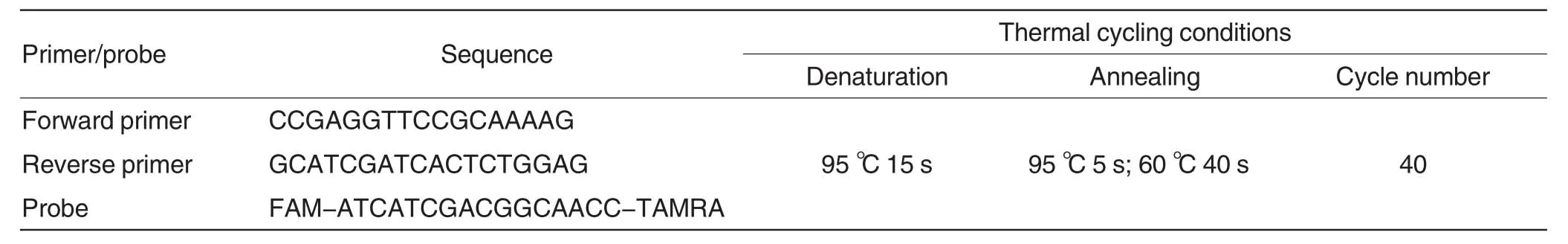
Table 1 Sequences of primer/probe for real-time fluorescent quantitative PCR
Results and Analysis
Optimization ofLAMP reaction system
As shown in Fig.1,when the dNTP concentrations were 1.2,1.6 and 2.0 mmol/L,obvious amplification bands were obtained.When the dNTP concentration was 1.6 mmol/L,the LAMP amplification effect of genomic DNA fromListeriamonocytogeneswas best,so the optimum dNTP concentration in the reaction system was 1.6 mmol/L.
Specificity of LAMP method
The specificity ofestablished LAMP was examined with the genomic DNA of the 9 strains.After adding SYBR Green I into the post-amplification tubes,only the amplification product in the first tube turned bright green(Fig.2).The electrophoresis results also showed that only the sample inoculated withListeria monocytogenes,but not the other samples inoculated with non-Listeriamonocytogenesstrains,showed bright bands(Table 3).It suggests that the established LAMP method can be used for specific detection ofListeria monocytogenes.
Sensitivity of LAMP method
The initial concentration ofListeria monocytogenesin the suspension was calculated as 1.60×1011cfu/ml through plate counting.The suspension was diluted 100,101,102,103,104,105,106,107,108,109and 1010times,respectively,and the genomic DNA ofListeria monocytogenesin suspension at each of the concentrations was extracted using genomic DNA extraction kit for LAMP amplification.After the amplification,SYBR Green I was added to each of the tubes.As shown in Fig.4,the amplification product in the 2ndtube turned bright green,while in the 12thtube turned orange.Subsequently,the amplification products were examined by 2%agarose gel electrophoresis(Fig.5).The electrophoresis results showed thatstep-likebandswere shown in Lane 2-11,implying that the detection limit of established LAMP method was 1.60×102cfu/ml.
Comparative analysis of sensitivity between LAMP method and realtime fluorescent quantitative PCR
The DNA template was diluted gradiently as described above to compare the detection sensitivities between established LAMP method and real-time fluorescent quantitative PCR.The DNA template at each of the concentration was amplified by PCR respectively.The results showed that the detection limit of fluorescent quantitative PCR was 1.60×102cfu/ml(Fig.6),which was equivalent to that of LAMP method.
Detection results of Listeria monocytogenes in dairy food by LAMP method
Afteradding fresh and sterile TSB-YE liquid medium,the 50 dairy food samples were incubated at 37℃for 24 h.A certain amount(1 ml)of each of the dairy food samples was used to extract the genomic DNA ofListeriamonocytogenesforLAMP amplification. Simultaneously, theListeriamonocytogenesin the 50 samples was detected by traditional bacterialisolation and identification method.Table 2 showed that the detection results were exactly the same between the two methods,indicating that the LAMP method can accurately detect the existence ofListeria monocytogenesin various dairy products.
Discussion
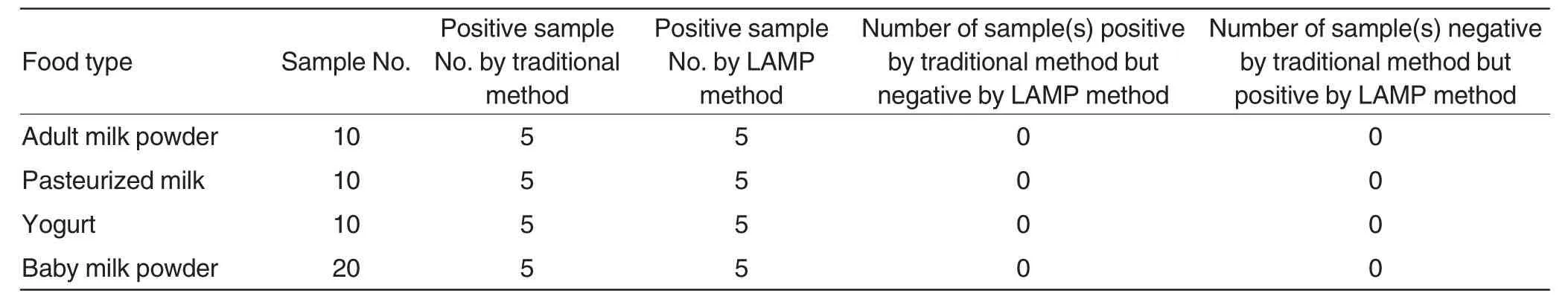
Table 2 Detection results of Listeria monocytogenes in artificially polluted dairy food samples
The traditional detection ofListeria monocytogenesin dairy products requires isolation and cultivation and multiple smear tests and hemolysis tests,consuming time and labor.As the theory and technology of molecular biology mature,the nucleic acid probe hybridization,conventional PCR,multiplex PCR and real-time fluorescent quantitative PCR and other molecular biology methods have been widely applied,bringing the detection ofListeria monocytogenesto a new stage.Molecular biotechnology has advantages of high specificity,high sensitivity,and it solves the shortcomings of consuming time and labor.However,mostmolecularbiologicalmethods have higher requirements for instruments and equipment,test environment and operating techniques,limiting their application and development to some extent.
Based on the analysis on fulllength sequence of hlyA gene in previously published literatures,a LAMP method was successfully established for detectingListeria monocytogenesin dairy products in this study.After the pure culture,the genomic DNA ofListeria monocytogeneswas extracted using genomic DNA extraction kit.The sensitivity test was performed using gradient dilution method.The results showed that the detection limit of established LAMP method was 1.60×102 cfu/ml,indicating thatthe LAMP method has a high sensitivity.In addition,various non-Listeria monocytogenesstrains were detected by the established LAMP method.The results showed that the established LAMP method has a high specificity.Moreover,the detection efficiency ofListeria monocytogenesin dairy products by LAMP method was equivalent to that by real-time fluorescent quantitative PCR.The LAMP method doesn’t require PCR instrument or expensive reagents,but it has high specificity.After high-efficiency amplification,the positive amplification product can turn apparent bright green by adding SYBR Green I,which can be directly identified by naked eye.Therefore,LAMP is an ideal method for detection ofListeria monocytogenesin dairy products in emergency situations.
[1]LI Y(李郁),WEI J(魏建),WANG GJ(王桂軍).Research advances inListeria monocytogenes(產(chǎn)單核李斯特菌的研究進(jìn)展)[J].Chinese Journal of Health Laboratory Technology(中國(guó)衛(wèi)生檢驗(yàn)雜志),2005,15(8):1018-1020.
[2]NOTOMI T,OKAYAMA H,MASUBUCHI H,et al.Loop-mediated isothermal amplification of DNA [J].Nucleic Acids Research,2000,28(12):63.
[3]WU YS(吳陽(yáng)升),LUO SP(羅淑萍).A novel high efficiency,rapid,isothermal nucleic amplification-LAMP method(一種新的高??焖俸怂岷銣?cái)U(kuò)增方法—LAMP法)[J].Biotechnology(生物技術(shù)),2004,14(4):76-78.
[4]XIAO B(肖斌),ZHU YH(朱永紅),ZOU QM(鄒全明).A new simple and sensitive gene diagnose technology:loopmediated isothermal amplification(簡(jiǎn)便敏感的環(huán)介導(dǎo)等溫?cái)U(kuò)增基因診斷新技術(shù))[J].Chinese Journal of Laboratory Medicine(中華檢驗(yàn)醫(yī)學(xué)雜志),2005,28(7):761-763.
[5]MORI Y,NAGAMINE K,TOMITA N,et al.Detection of loop-mediated isothermal amplification reaction by turbidity derived from magnesium pyrophosphate formation[J].Biochemical and Biophysical Research Communications,2001,289(1):150-154.
[6]AKIHIRO Y,SHIORI N,TOSHIHIRO A,et al.Loop-mediated isothermal amplification method for rapid detection of the periodontopathic bacteriaPorphyromonas gingivalis,Tannerella forsythiaandTreponema denticola[J].Journal of ClinicalMicrobiology,2005,43(5):2418-2414.
[7]JIN LL(金莉莉),WANG F(王芳),GUO ZK (郭振坤),et al.Advances in detection ofListeria monocytogenesin food(食品中單核增生李斯特氏菌檢測(cè)研究進(jìn)展)[J].Journal of Microbiology(微生物學(xué)雜志),2001,21(2):36-38.
[8]GIAMMARINI C,ANDREONI F,AMAGLIANI G,et al.Purification and characterization of a recombinant Listeriolysin O expressed inEscherichia coil and possible diagnostic applications[J].Journal of Biotechnology,2004,109(1-2):13-20.
 Agricultural Science & Technology2015年8期
Agricultural Science & Technology2015年8期
- Agricultural Science & Technology的其它文章
- Simplified Cultivation Technology of Hua’an No.513——A New Summer Maize in Suixi County
- Research Progress on Heavy Metals Detoxification in Human Body
- The Strategies of Rainfall Accumulation and Utilization in New Countryside
- Advances in the Study of Protein Quality Traits and Main Influencing Factors of Wheat in China
- DNA Extraction from Half-grain Wheat Seeds without Using Chloroform
- Purification and Antimicrobial Assay of an Antimicrobial Protein from a Biocontrol Bacterium Strain K2-1 against Aquatic Pathogens
