Comparison between Ophthalmologists and Community Health Workers in Screening of Shallow Anterior Chamber with Oblique Flashlight Test△
Yusoh Nuriyah,Xue-tao Ren,Li Jiang,Xi-pu Liu,2,and Yan-hong Zou,2*
1Department of Ophthalmology,Sekwa Eye Hospital,Beijing 100088,China
2Department of Ophthalmology,First Hospital of Tsinghua University,Beijing 100016,China
GLAUCOMA is the top cause of irreversible blindness worldwide.It affects approximately 66.8 million people around the world and among them 7.5 million have become blind.1Half of the cases belong to primary angle closure glaucoma(PACG).2PACG is the most common type of glaucoma in East Asia.It is predicted that the largest number of PACG will be found in China (47.5%).3
Shallow anterior chamber is a well known anatomic risk factor of PACG.It may lead to apposition of the peripheral iris to the trabecular meshwork and result in angle closure.Obstruction at the anterior chamber angle can induce increase of intraocular pressure and irreversible damage to optic nerve.4According to a population survey,the prevalence of occludable angle in Chinese people over 50 was about 10.2%.5By identifying this high risk population,occludable angle can be detected subsequently and the onset of PACG may be prevented.
There are a few techniques applied in clinics for detecting occludable angle,including gonioscopy,ultrasound biomicroscopy (UBM),and anterior segment optical coherence tomography (OCT).All of these techniques need intensive professional skills,and the latter two need expensive equipments.Therefore,they can not be considered as appropriate screening procedures.6,7
The oblique flashlight test is a fast,simple,and low cost method to detect shallow anterior chamber.8-10This test only requires the examiner to flash a penlight held at the temporal side of the examined eye,and then record the proportion of the bright area on the nasal part of the iris.It is not a routine procedure in ophthalmic clinics because ophthalmologists can observe the structure more precisely with slit lamp microscopes.However,a previous study which compared this technique with Schiotz tonometer,gonioscopy,and optic disc appearance found that it could detect occludable angle with high sensitivity (91.7%) and specificity (91.5 %).11
In recent years,community health service has become more and more important in disease prevention.We propose that oblique flashlight test may be applied as a first-step technique in screening of occludable angles by community health workers who are not ophthalmologists.The present study compared the performance of an ophthalmologist and two trained community health workers in screening shallow anterior chamber using oblique flashlight test in order to investigate the feasibility of this proposal.
SUBJECTS AND METHODS
Subjects
The study was carried out in a community health center in Desheng Area of Xicheng District,Beijing,China.The data was part of the records collected by Sekwa Eye Hospital which delivered the free eye examination.The included subjects were those who went to community clinics and registered to get the examination from November to December 2007,no matter whether they had any eye disease history.
Examination of anterior chamber depth (ACD) with oblique flashlight test
The ACD of each subject was examined and recorded by one ophthalmologist and two trained community health workers,both of whom had no experience in eye examination before (one nurse and one non-professional health worker who didn’t have any background in medical training).One-week training with 100 participants was delivered for the research team prior to the study,who were excluded from the final analysis.The obliqueflashlight test was performed as follows:a penlight was shone from the temporal side of the examined eye parallel to the iris,the distance between the subject and the examiner was kept at 30 cm.ACD was measured as grading level 1 to 4 based on the ratio of illuminated area to the full width of the nasal iris(Table 1).
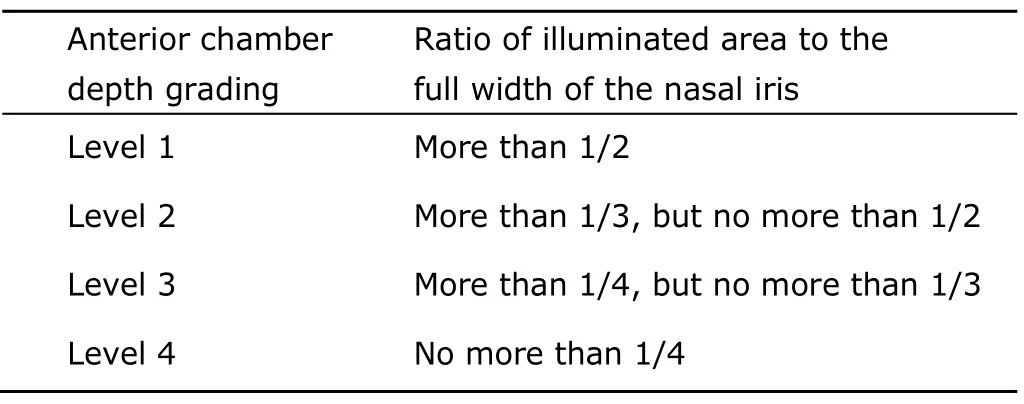
Table 1.Levels of anterior chamber depth recorded
Statistical analysis
A database was developed with EpiData software version 3.1.The data were coded and entered into the database on the day of examination.Data analysis was performed using R software version 2.6.1.Descriptive variables were summarized in frequencies and percentages.The agreement between the ophthalmologist and trained community health workers was analyzed using kappa statistic method.Kappa is a chance-corrected measure of proportional agreement,and its possible values range from +1 (perfect agreement)via0 (agreement by chance only) to-1(complete disagreement).APvalue of less than 0.05 was considered statistically significant.
RESULTS
Four hundred and twenty-five subjects were enrolled in this study,including 148 males (35%) and 277 females(65%).The mean age was 65 years (range,21-93 years).Their ophthalmic disease history showed that cataract was the most common disease (107 cases,80.5%) in this group,retinal diseases and glaucoma were ranked the second (16 cases,12%) and the third (15 cases,11.3%),respectively.
Resultsof ACD measurements by the ophthalmologist and community health workers are summarized in Table 2.The comparison between the performance of the ophthalmologist and that of the nurse showed a kappa statistic of 0.42 for both eyes (P<0.001).The kappa statistic between the ophthalmologist and the non-professional health worker was 0.54 and 0.52 for right and left eyes,respectively (P<0.001).The agreement between the nurse and the non-professional health worker was 0.49 and 0.38 for right and left eyes,respectively (P<0.001).
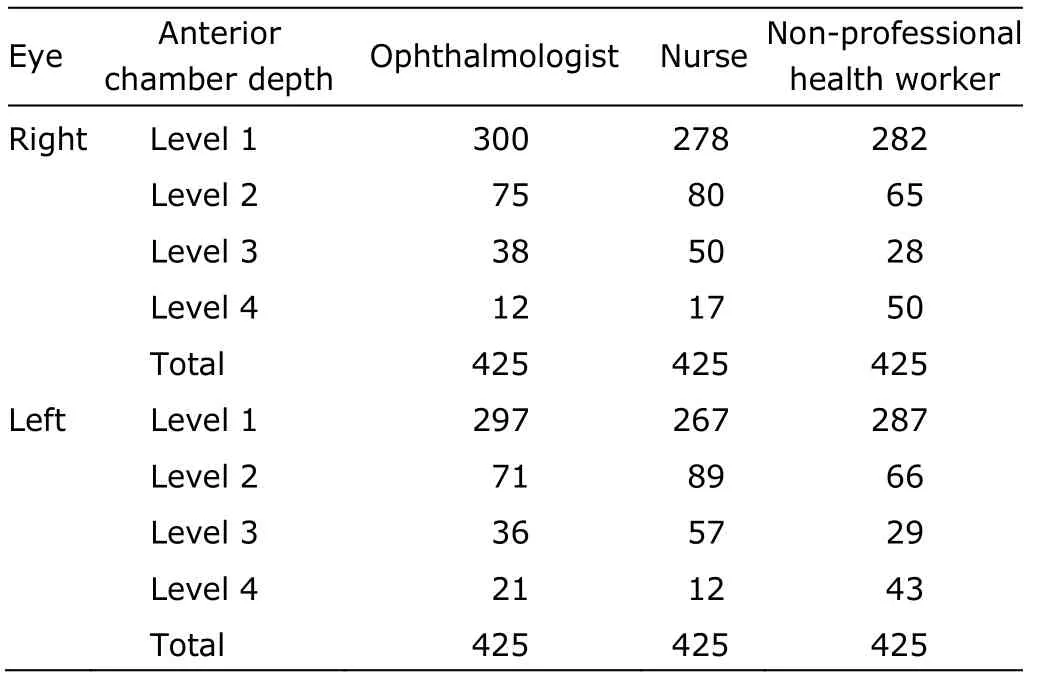
Table 2.Anterior chamber depth of both eyes recorded by the ophthalmologist and community health workers using oblique flashlight test
DISCUSSION
The agreement assessed by kappa statistic is considered to representexcellent,good,andmarginalif it showsK>0.75,0.4<K<0.75,and 0<K<0.4,respectively.The kappa value for the agreement between the ophthalmologist and community health workers was graded asgood,which means that it is possible for community health workers to use oblique flashlight test independently and effectively.
Using the results of the ophthalmologist as standard,the specificity in identifying the shallowest chamber (level 4) was quite satisfactory for the community health workers,which was more than 90% in each observer for each eye.That means the trained community health workers can correctly distinguish the non-risk population out,which was very important for a screening test.
However,the sensitivity was rather low,which means part of the people identified with level 4 may be not at high risk of PACG.Although previous studies showed that oblique flashlight test is a convenient,fast,and inexpensive method for screening PACG,9-12further eye examination is needed to confirm the diagnosis.Therefore,we propose a two-step strategy for PACG screening,first with oblique flash test in the community clinic and second in the ophthalmology clinic.
To put into place this prevention strategy,firstly we need to find a more effective way to improve the grading process.Secondly,we need to figure out how many people detected as shallow anterior chamber with oblique flashlight test are really glaucoma patients.Only after that can we promote this method in a larger population.
1.Quigley HA.Number of people with glaucoma worldwide.Br J Ophthalmol 1996;80:389-93.
2.Wang N,Wu H,Fan Z.Primary angle closure glaucoma in Chinese and Western populations.Chin Med J (Engl) 2002;115:1706-15.
3.Quigley HA,Broman AT.The number of people with glaucoma worldwide in 2010 and 2020.Br J Ophthalmol 2006;90:262-7.
4.Aung T,Nolan WP,Machin D,et al.Anterior chamber depth and the risk of the primary angle closure glaucoma in 2 East Asian populations.Arch Ophthalmol 2005;123:527-32.
5.He M,Foster PJ,Ge J,et al.Prevalence and clinical characteristics of glaucoma in adult Chinese:a population-based study in Liwan district,Guangzhou.Invest Ophthalmol Vis Sci 2006;47:2782-8.
6.Al-Mubrad TM,Ogbuehi KC.Smith-method assessment of anterior chamber depth for screening for narrow anterior chamber angle.Indian J Ophthalmol 2006;54:65-8.
7.Devereux JG,Foster PJ,Lee PS,et al.Anterior chamber depth measurement as a screening for primary angleclosure glaucoma in an East Asian population.Arch Ophthalmol 2000;118:257-63.
8.Krishnadas SR (Aravind Eye Hospital,Madurai,India).Clinical practice module:quality assurance in management of primary angle closure glaucoma [Internet].New Delhi:Ministry of Health &FW,Government of India;[cited 2009 Aug 1].Available from:http://laico.org/v2020resource/files/Closedangle_glaucoma.pdf
9.Yu Q,Li S,Ye T.Cost-effectiveness analysis of the screening strategies for primary angle closure glaucoma.Yan Ke Xue Bao 1997;13:202-9,185.
10.Yu Q,Li S,Ye T.The study of grading standard photos of oblique flashlight test.Yan Ke Xue Bao 1995;11:80-5.
11.Yu Q,Xu J,Zhu S,et al.A role of oblique flashlight test in screening for primary angle closure glaucoma.Yan Ke Xue Bao 1995;11:177-9.
12.Sparks BI 3rd.Tangential penlight angle estimation.J Am Optom Assoc 1997;68:432-4.
 Chinese Medical Sciences Journal2010年1期
Chinese Medical Sciences Journal2010年1期
- Chinese Medical Sciences Journal的其它文章
- Sex Hormones and Androgen Receptor:Risk Factors of Coronary Heart Disease in Elderly Men△
- Factors Influencing Pleural Effusion after Fontan Operation:an Analysis with 95 Patients
- Relationship between Carotid Atherosclerosis and Cerebral Infarction
- Expression of FLICE-inhibitory Protein in Synovial Tissue and Its Association with Synovial Inflammation in Juvenile Idiopathic Arthritis△
- A Case of Large“Silent”Extra-adrenal Retroperitoneal Paraganglioma Resected Laparoscopically
- Revascularization for Iliac-femoral Artery Pseudoaneurysm with Greater Saphenous Vein
