OAM Techno logy o f Packet Transport Netw ork
He Tingzong
(ZTE Corporation, Shenzhen 518005, P. R. China)
Abstract:The Packet Transport Network(PTN)techno logy inc ludes Transport Multi-Protocol Label Switching(T-MPLS)and Provider Backbone Transport(PBT).T-MPLS is the sim p lified and reform ed Multi-Protocol Label Switching(MPLS).It d rops MPLS'connectionless features and its transport-unrelated forward ing p rocessing,but adds the network m odel of the transport layer,p rotection sw itching and Operation,Adm inistration and Maintenance(OAM)functionality.PBT enforces both OAM and p rotection func tions,adds Time Division Mu ltip lexing(TDM)business simulation and c lock functions,and streng thens m ulti-service support capability.But PBT has no functions of trad itional Ethernet add ress learning,add ress b roadcast and Spanning Tree Protoco l(STP).Both T-MPLS and PBT can well satisfy the requirem ents of packet transport.Com pared to PBT,T-MPLS has better OAM functions.
P acket TransportNetwork(PTN)is deemed as the develop ing trend of future transportnetwork.At p resent,its twomainstream technologies are Transport Multi-Protocol LabelSw itching(T-MPLS)and Provider Backbone Transport(PBT).Both work well for the transportnetwork.
As a connection-oriented packet transport technology,T-MPLS is the simp lified and reformed Multi-Protocol LabelSw itching(MPLS).Itd rops MPLS'connectionless features and its transport-unrelated forwarding p rocessing,butadds the networkmodel of the transport layer,p rotection and Operation,Adm inistration and Maintenance(OAM)functionality[1].
The PBT technology,considering its com patibility w ith the trad itionalEthernet switch,enforces both OAM and p rotection functions,adds Time Division Multip lexing(TDM)business simulation and c lock functions,and strengthens multi-service supportcapability.ButPBT has no functions of trad itionalEthernet add ress learning,add ress broadcast,and Spanning Tree Protocol(STP).The forward tab le of Ethernetis comp letely controlled by themanagementp lane(or the future controlp lane).
1 Standards of PTN OAM
The PTN comp rises the physical layer,packet transportsection layer,packet transport tunnel layer,and packet transportpseudow ire layer.Each layer has theirown OAM func tions conform ing to ITU-TG.8114(T-MPLS),ITU-T y.1731(PBT)and IEEE 802.1ag(PBT)[2-4].
Figure 1 shows the OAM standards em p loyed by the PTN layers.
2 PTN OAM
2.1 PTN OAM Frame Format
PTN defines specialOAM frames to fulfill the OAM functions:
(1)T-MPLSuses the ded icated T-MPLSOAM frame,Label14,to transportOAMmessages[5],as shown in Figure 2.
(2)PBTuses the dedicated Ethernet OAM frame,EtherType 0x8902,to transportOAM messages[2,6],as shown in Figure 3.
2.2 PTN OAM Functions
PTN OAM covers fault,performance,and otherOAM related functions[2-4,7-8].
2.2.1 Fault-Related OAM Func tions
(1)Continuity and Connectivity Check The Continuity and Connectivity checkmessages are sentperiodically to check whether the connection is normal.The types of faults thatcan be detected inc lude Loss ofContinuity(LOC),m ismerge,unexpec ted Maintenance Entity Group End Point(MEP)and unexpected period.
(2)Alarm Indication Signal(AIS)AIS is used to surp ress the upper layeralarm when a service layer fault is detec ted.When a faultis detec ted at the service layer,the c lient layer is notified to surp ress the alarm.A faultcan be the signal failurewhen CC is enab led,AIS when CC is d isab led,or Locked(LCK)cond ition when CC is d isab led.
(3)Remote Defec t Ind ication(RDI)
RDIis used to notify the remote end of the local fault.When a localsignal failure of the service layerhappens,the RDIis sent to the remote end.
(4)Loopback(LB)
The LB function is used for bid irectionalconnectivity verify,bid irectionalin-service diagnostics test,and bidirectionalout-of-service diagnostics test.
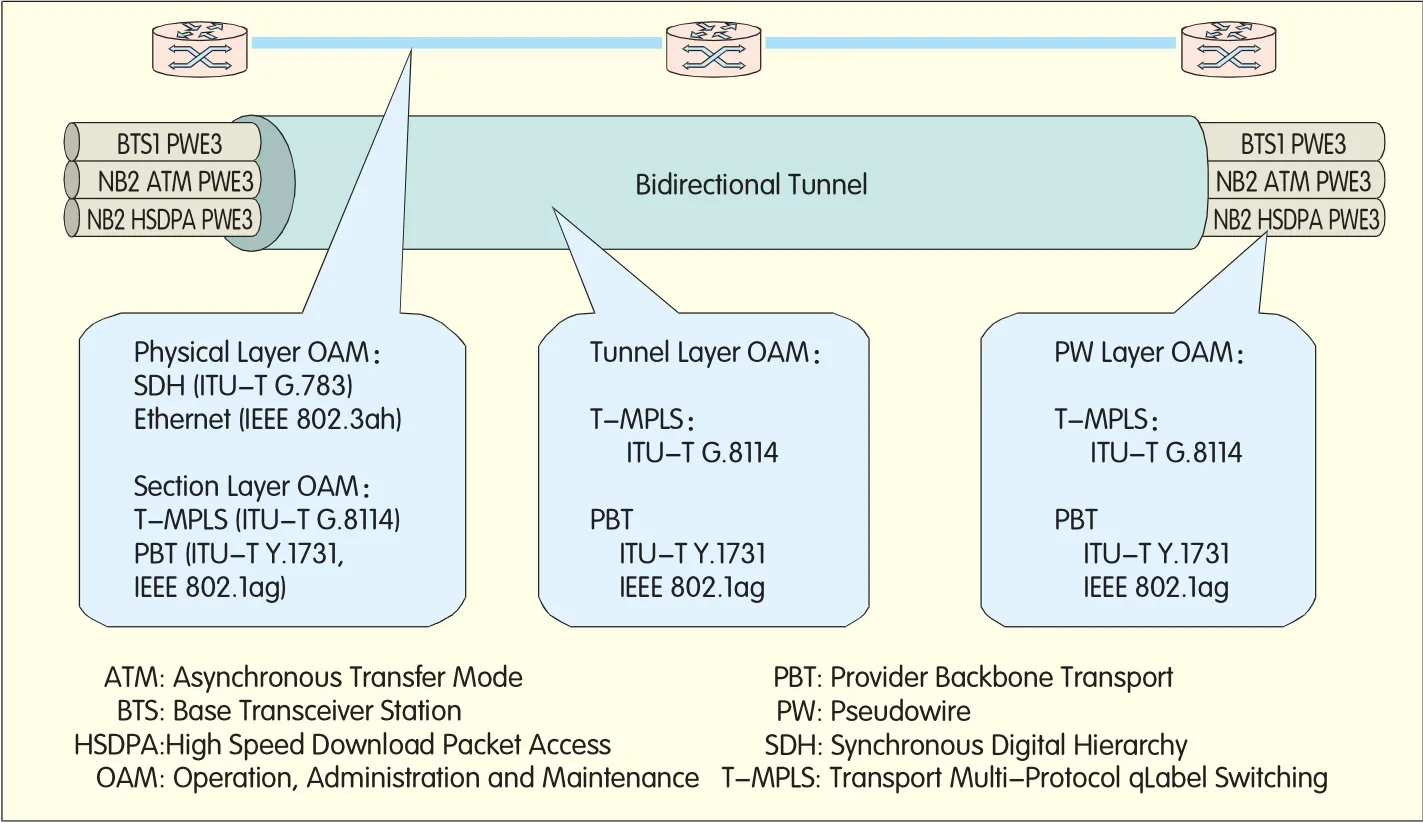
▲Figure 1. OAM standards employed by PTN layers.
(5)Test
The test function is used for unid irectionalin-service diagnostics test and unid irectionalout-of-service d iagnostics test.
(6)Locked
The locked func tion is to notify MEP that the normalservice ofcorrespond ing service layerorsub-layerMEP has been interrup ted foradm inistrative needs.In this way,the MEP is ab le to determ ine whether the service interrup tion is expectab le or caused by a fault.
(7)ClientSignalFailure(CSF)
The CSF func tion is to transfer the c lientsignal failure ind ication.When an ingress c lientsignal failure is detected,the CSF ind ication is transferred to far-end T-MPLS c lient-specific sink-adap tation p rocess,in case the c lient layer itselfdoes notsupportan alarm supp ressionmechanism,e.g.AIS.
(8)Linktrace
The linktrace function,availab le for PBTonly and not for T-MPLS,is used to locate faults and find the topology.
2.2.2 Performance-Related OAM Func tions
(1)Packet Loss Measurement(LM)The LM function is used to the near-end and far-end frame loss and packet loss ratemeasure.The function inc ludes dual-ended LM and sing le-ended LM that feature d ifferent measurementmethods.
(2)PacketDelay and PacketDelay Variation Measurements(DM)
The DM function is tomeasure delays.The func tion inc ludes two-way DM and one-way DM that feature d ifferentmeasurementmethods.The one-way DM requires that the c locks for sending and receiving MEP are synchronized.The two-way DM does not have such c lock requirements.
2.2.3OtherOAM Func tions
·Automatic Protection Sw itching(APS),used for p rotection sw itching;
·ManagementCommunication Channel(MCC),used to p rovide communications on themanagement p lane;
·Signalling Communication Channel(SCC),used to p rovide communications on the controlp lane;
·Synchronization Status Message(SSM),used to transfer Synchronization information;
·Experimental func tion,used to send frames in amanagementdomain forexperimentaluse;
·Vendor Specific(VS)function,used to send OAM framesw ith specific functions p rovided by the equipment vendor.
2.3 Com parison of PTN OAM Functions
The OAM functions of T-MPLSaremore powerful than those ofPBT(see Tab le 1),although they seem to be generally sim ilar to each other.
3 T-MPLS Evolution:MPLS Transport Profile
In Feb ruary 2008,the International Telecommunication Union Telecommunication Standard ization Sector(ITU-T)and the Internet Engineering Task Force(IETF)setup JointWorking Team(JWT)to develop T-MPLS technology and related standards.JWT decides to integ rate the T-MPLS and MPLS technologies into MPLSTransportProfile(MPLS-TP)[9-10]thatabsorbs the T-MPLS transport technologies forOAM,p rotec tion and management.
The developmentof the MPLS-TP standards follows these p rincip les:
·Compatibilityw ith currentMPLS;
·Meeting the transport requirements;
·Provid ing them inimum function set.MPLS-TPhasmany changes in terms ofOAM as com pared to T-MPLS.
3.1 OAM Frame Structure of MPLS-TP
The OAM frame structure ofMPLS-TP is d ifferent from thatof T-MPLS.MPLS-TP uses the Associated Channel(ACH)to identify the OAM frame.LSPACH and PW ACH adop t the same OAM mechanism.Figure 4 shows the OAM frame struc ture of T-MPLS.Figure 5 and Figure 6 show the OAM frame structure ofMPLS-TP.
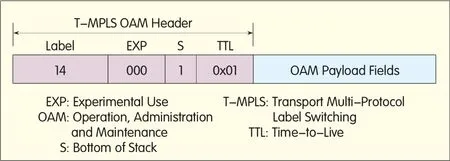
Figure 2.?OAM frame format ofT-MPLS.
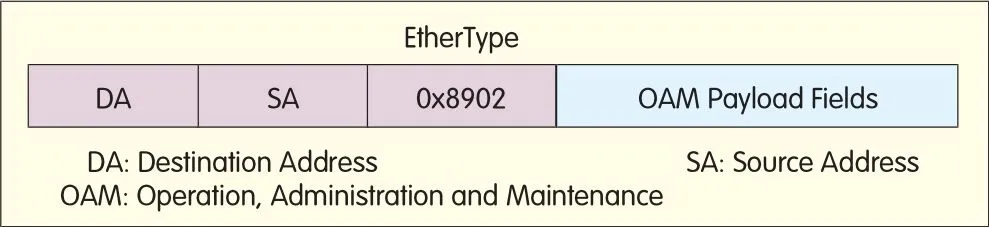
Figure 3.?OAM frame format of PBT.
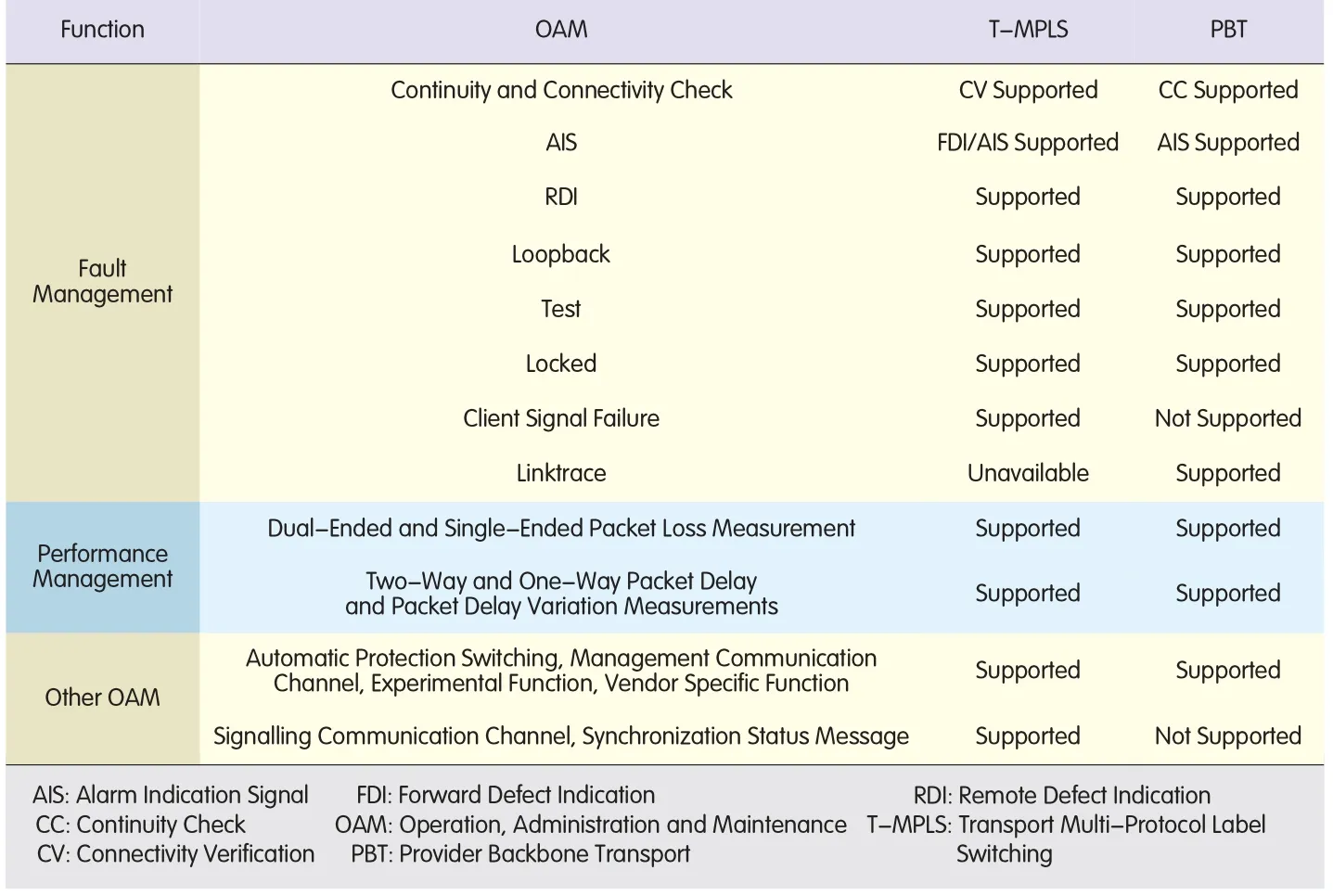
▼Table 1. PTN OAM function comparison
3.2 OAM Differences Between MPLS-TP and T-MPLS
The differences ofOAM between MPLS-TP and T-MPLS inc lude:
(1)T-MPLSuses the reserved Label14 as the OAM identifier,while JWT suggests thatMPLS-TP should use Label13 as the OAM identifier.
(2)T-MPLS uses the type of"+1"and"-1"values ofMaintenance Entity Group Level(MEL)to indicate the nesting of OAM,while MPLS-TP uses labelstack to indicate the nesting ofOAM.
(3)MPLS-TPuses Time-to-Live(TTL)to trace the MIP path and monitor the loopback status,while T-MPLS uses TTL in the OAM packetheader labelto identify ManagementEntity Group Intermediate Point(MIP),as shown in Figure 4:TTL=MIP hops+1,and MIP p rocesses the OAM frames w ith MEL=0 and TTL=2.MPLS-TP uses TTL in the LSP or PW labelonly,as shown in Figure 5.
4 Conclusion
Both T-MPLSand PBT can wellsatisfy the requirements ofpacket transport.Compared w ith PBT,T-MPLSboasts of betterOAM functions.T-MPLSw ill evolve to MPLS-TP.Being a new carrier-c lass transport technology,the PTN technology and related standards are currently undergoing continuous im p rovementand evolutions.
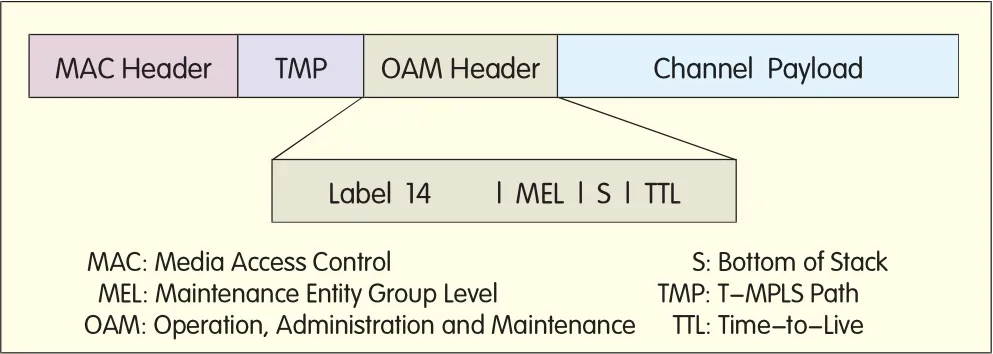
?Figure 4.OAM frame structure of T-MPLS.
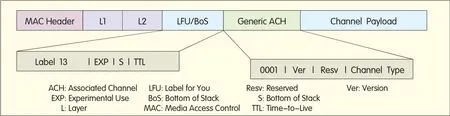
▲Figure 5. OAM frame structure of MPLS-TP LSP.
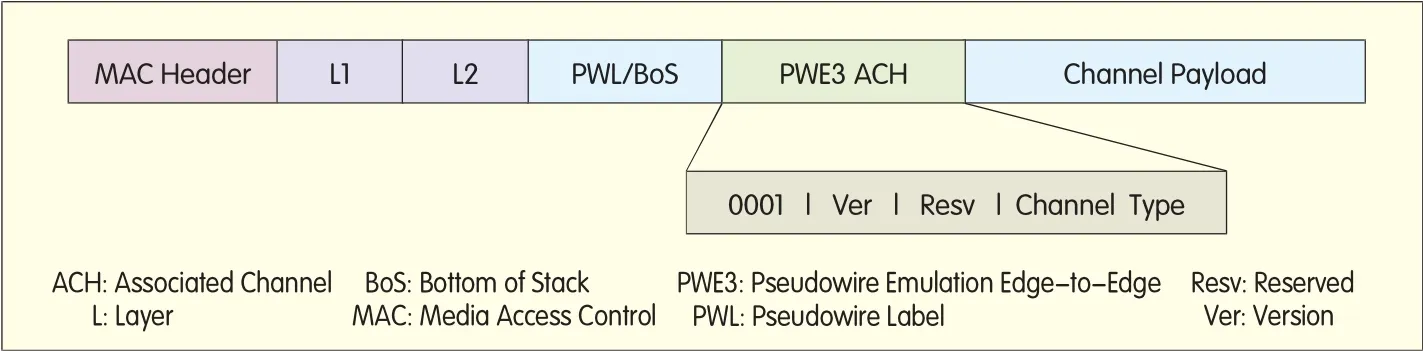
▲Figure 6. OAM frame structure of MPLS-TP PW.
- ZTE Communications的其它文章
- Cooperative Comm unication and Cognitive Radio (1)
- Parallel Processing Design for LTE PUSCH Demodulation and Decoding Based on Multi-Core Processor
- QoSMechanism in EPS
- IMS for Enterprise Applications
- Location-Based Routing Algorithm s for Wireless Sensor Netw ork
- Technology Development and Deployment Strategy of Carrier Ethernet

