Evaluation of Green Development Efficiency in Chongqing Municipality Based on Super-SBM and Malmquist Models
Zhang Yuefang
Party School of the CPC Hechuan District Committee
Abstract: The green development of Chongqing municipality is crucial in establishing a major ecological shield in the upper reaches of the Yangtze River.By developing a Super-SBM model and using the Malmquist index to analyze and calculate the green development efficiency and its influencing factors in Chongqing from 2011 to 2021,this study reveals an accelerating trend in the overall green development efficiency in Chongqing.The significant enhancement of green development efficiency in Chongqing is primarily attributed to changes in returns to scale.Pure technical efficiency and technological advancements have a considerable potential impact on improving green development efficiency in Chongqing.Furthermore,there are discernible disparities in green development efficiency among districts and counties in Chongqing,with different factors influencing these variations.Chongqing is suggested to promote clean and efficient energy utilization,bolster the application and commercialization of scientific and technological advancements,consistently advance ecological restoration and management,and elevate the quality of green development to a higher level.
Keywords: Chongqing,green development efficiency,super-efficiency,SBMMalmquist model
Introduction
The report to the 20th National Congress of the Communist Party of China (CPC) included pursuing green development and promoting harmony between humanity and nature.Located in the upper reaches of the Yangtze River and the heart of the Three Gorges Reservoir area,Chongqing shoulders an important mission in promoting green development and ecological advancement along the Yangtze River Economic Belt.In recent years,Chongqing has prioritized ecological conservation and pursued a green path to development by taking specific steps in building a land of natural beauty with lush mountains and lucid rivers.These efforts have consolidated its role as a major ecological shield in the upper reaches of the Yangtze River.“Green and low-carbon development” has become the main development goal of China’s 14th Five-Year Plan (2021-2025) for National Economic and Social Development and the Long-Range Objectives through the Year 2035.The Work Report of Chongqing Municipal People’s Government emphasized the importance of ecological advancement as one of the key objectives and tasks of significant improvement in six aspects for the next five years.To achieve this,Chongqing will enhance the policy and standard system to support green development and work towards the goals of carbon peak and carbon neutrality.In the process of achieving the goal of low carbon and green development,it is of great practical significance to evaluate the efficiency of green development in Chongqing.
Literature Review
International Research
The Emergence of Related Concepts
The essence of green development is a green economy,which inherits and develops the idea of sustainable development.It is a new economic concept put forward by economists when they reflect on the environmental issues facing humanity.The emergence of issues between humanity and the environment spans over 50 years.American marine biologist Rachel Carson’s bookSilent Spring(1962) first reminded humanity to pay attention to environmental problems.David Pearce,a British environmental economist,first used the concept of a green economy in his bookBlueprint for a Green Economy(1989) but did not fully define it.He only described the blueprint for a green economy from the perspective of the UK’s environmental policy: It explains the issues of environmental protection and improvements from the perspective of the environment.The green economy is a dynamic and evolving concept being applied in various countries and regions across the globe.As evidenced by the documents of international organizations and governments,there are 23 distinct definitions of a green economy.Until 2007,international organizations represented by the United Nations Environment Program published a report titledGreen Jobs:Towards Sustainable Work in a Low-Carbon World,which defined the green economy for the first time as “an economy that values nature and people and creates decent,well-paying jobs.” In 2010,the United Nations Environment Program has defined Green Economy as “one that results in improved human well-being and social equity,while significantly reducing environmental risks and ecological scarcities,” which has become a widely accepted interpretation of green economy.At the United Nations Conference on Sustainable Development,also known as Rio 2012,an important issue discussed was the important role of a green economy in sustainable development and poverty eradication.Around the greening of economic development,specific concepts such as a new green deal,green growth,and green investment emerged.McAfee (2016) proposed that the negative externalities of globalized capitalism on the environment can be mitigated by adopting a rationalized approach to economic development,commonly known as green development.
Evaluation of Green Development
There are two primary types of evaluation for green development: level evaluation and efficiency evaluation.Many countries and regions have built on the UN’s sustainable development index system as a framework for developing their own eco-city evaluation index systems.These systems typically draw upon the principles of the “society-economy-nature” complex ecosystem theory and utilize methods such as the projection pursuit regression,weighted summation method,and entropy method to evaluate the level of green development within their respective countries or regions.Following the introduction of the concept of eco-efficiency by Schaltegger and Sturm in 1990,many academics in the early 1990s began utilizing efficiency evaluation models such as the Data Envelopment Analysis (DEA) model,SBM model,and others to evaluate the green development efficiency of various countries,regions,and cities from different perspectives.Jacobs et al.(1991) argued that a green economy must prioritize increasing social organizational capital alongside the traditional production factors of labor,land,and artificial cost.Kahn (2009),meanwhile,explored the perspectives of different economic schools on a green economy,citing numerous global examples to highlight the importance of addressing environmental issues such as solid waste,sewage,noise,air pollution,and global warming for the sake of human survival.Weizsacker et al.(2009) proposed an ambitious goal for human society: reducing resource consumption by 80 percent while simultaneously improving global human welfare and achieving a comprehensive transformation of the world economy.In the field of green economic development evaluation,international research and practice have yielded noteworthy results.For instance,in 1998,the city of Seattle in the US established an indicator system framework based on the sustainable development of the city and the wider global community.This framework comprised 40 indicators selected from five key perspectives: environment,economy,people and resources,youth and education,and health and community.Yale University,in partnership with Columbia University,developed and published the Environmental Sustainability Index(ESI),which aims to address the long-term void of quantitative indicators for sustainable development.The ESI directly supports the United Nations’ Millennium Development Goals.In 2006,the Environmental Performance Index (EPI) was introduced as an improvement of the ESI,offering greater convenience and scientific rigor.The EPI encompasses 22 indicators that reflect key environmental,resource,and socioeconomic issues and contradictions.In 2011,the Chinese Ministry of Environmental Protection (now the Ministry of Ecology and Environment)collaborated with Yale University to apply the EPI at the provincial level in China.The EPI was used to assess various aspects of environmental performance,including air quality,climate change,biodiversity,agriculture,and forestry.The collaboration resulted in developing of a monitoring index system for environmental performance tailored to China’s unique national conditions,including 33 specific evaluation indicators and 12 environmental protection policies.
Research in China
Evaluation of Green Development Efficiency
Zhang (2002) provided a theoretical and practical perspective on China’s green economy,examining its current state,operational mechanisms,constraints,and coping strategies from the following four perspectives: green production,consumption,marketing,and markets.Xia et al.(2010) discussed the Chongqing model of building a green economy from two main perspectives:building a green economic industrial system and accelerating green scientific and technological innovation.In the evaluation of a green economy development,Tian and Su (2007) employed principal component analysis to calculate the index weight and conducted a comprehensive evaluation of the circular economy.Zhang (2011) utilized the analytic hierarchy process to evaluate the development of a green economy in the Changsha-Zhuzhou-Xiangtan city clusters.Xiao and Yuan (2013) analyzed and evaluated the degree of greening in China’s current economy using indicators such as the EPI,carbon dioxide emissions and energy consumption per unit of GDP,and economic growth modes.They concluded that China is still in the initial stage of green economic development.Wu and Zhu (2015) evaluated the green economic development of nine cities in Fujian province using a modified Technique for Order Preference by Similarity to Ideal Solution (TOPSIS) model with entropy weight and a linear regression model.Chen (2016)evaluated the current state of green economy development in Guigang,Guangxi province,using a green economy index system as the starting point.The study concluded that the city possessed potential advantages for a green economy development.Wu et al.(2020) evaluated,analyzed,and predicted the green development efficiency of 41 cities in the Yangtze River Delta by developing DEA and Malmquist models.Chen et al.(2022) employed the super-SBM model and Malmquist index to measure,analyze,and predict the green development efficiency of the Chengdu-Chongqing economic circle from 2007 to 2019.
Evaluation of Urban Eco-Efficiency
In China,the evaluation of ecological advancement is primarily divided into two categories.The first category is based on the perspective of complex urban ecosystems and their subsystems,with an index system constructed with three levels: economy,nature,and society.The other is based on the structural perspective of an urban integrated ecosystem.This approach involves constructing an index system based on three dimensions: structure,function,and coordination degree.The aim is to identify obstacles to urban development.Gao and Huang (2010) used the efficacy function method to construct an evaluation index system from four dimensions: growth mode,industrial structure,consumption mode,and ecological governance,and comprehensively evaluated the performance of ecological advancement in Jiangsu province from 2000 to 2007.Xiang et al.(2015) developed an evaluation index system for ecological advancement that encompasses five dimensions: ecological economy,environment,ecological human settlements,culture,and systems.They used the difference-driven method to compare and analyze the effects of ecological advancement in Jiangsu province and Guangdong province from 2010 to 2011.Wang et al.(2017) introduced an evaluation index system for ecological advancement using four main aspects: ecology-oriented economic development,ecology-oriented social development,efficiency of resources and utilization of the environment,and ecology-based development of culture and systems.They applied the attribute hierarchy model to assess the level of ecological advancement in prefecture-level cities of Guangdong province in 2013.Sun et al.(2018) constructed an index system from four dimensions: land and resources optimization,industrial structure optimization,ecological system development,and ecological culture publicity.The entropy method was applied to comprehensively evaluate the ecological advancement in Chongqing from 2004 to 2015.Tian et al.(2019) utilized the DEA model to evaluate the efficiency of ecological advancement in Shaanxi province from 2010 to 2016.Their findings suggest that the efficiency of ecological advancement in Shaanxi province generally improved over time,but there remained a significant gap between cities within the province.Xu et al.(2019) conducted a study on the Yangtze River Delta city clusters,utilizing entropy and TOPSIS models to evaluate changes in the ecological level of the cities within the region.They also used the obstacle degree model to identify the primary obstacles that affect the ecological level of the cities in the area.
Through research on green development and ecological advancement both in China and abroad,it is evident that many countries and regions are making progress in sustainable economic development through continuous exploration and evaluation of their models for green economic development.In assessing the current state of green development,both Chinese and international research institutions and scholars have utilized various evaluation methods to evaluate different regions.Green development has become the long-term development direction for all countries worldwide,and research in this area is expected to become increasingly more comprehensive and extensive.However,there are some inadequacies in the current studies on green development.First,some viewpoints on green development lack depth.Some simply understand it literally,while others equate it directly to sustainable economic development.Second,in the development of evaluation index systems for green development,subjective factors can have a significant influence,resulting in experimental results or conclusions that may not be sufficiently objective or comprehensive.Third,there is a lack of research into the efficiency of green development in Chongqing as a research subject.
Model Building and Data Sources
Research Methods
Super-SBM Model
The essence of green development is to maximize resource utilization and minimize energy consumption.The evaluation of green development efficiency has primarily utilized the index method in its early stages.However,the results of this method can be significantly influenced by subjective factors,leading to a certain degree of inaccuracy.Currently,the efficiency method is widely used and can be divided into two main categories: parametric and non-parametric methods.To minimize the impact of subjective factors,this paper utilized DEA to measure the efficiency of green development.DEA is a non-parametric method and does not require specific parameter settings,which can enhance the objectivity and accuracy of the measurement results.The early DEA model was radial,meaning that the measurement of inefficiency only included the proportion of all inputs (or outputs) that increased or decreased in equal proportion.However,even if the inputs (or outputs) that improved in equal proportion were removed,there would still be some invalid residues,resulting in slack variables.The efficiency improvement of decisionmaking units (DMUs) with invalid slack variables is considered non-radial.To address this issue,Tone (2001) proposed the Slack-Based Measure (SBM) model,which incorporates slack variables to deal with efficiency problems.However,the conventional SBM model for efficiency calculation generates results where the highest efficiency value is 1,making it impossible to distinguish and compare decision making units (DMUs) with identical efficiency values of 1.Moreover,if a large number of DMUs have efficiency values of 1,further analysis becomes even more difficult.To address this issue,Tone continued to refine the SBM model in subsequent work.This paper chooses the Super-SBM model proposed by Tone in 2002.The Super-SBM model can analyze decision-making units in a non-radial and non-angular manner and measure decision-making units whose efficiency value is 1.In addition,the model can compare the efficiency values to identify effective decision-making units,leading to more comprehensive measurement results.Tone did not provide a specific formula for the SBM model with unexpected output superefficiency.Thus,this paper refers to the formula introduced by Cheng (2014),which is:
In the formula (1),the green development efficiency value is represented,andm,S1,andS2represent the numbers of input variables,expected output,and unexpected output.x0,y0andz0respectively denote the three vectors of input,expected output,and non-expected output.xi0,yk0andzl0respectively represent the input vector of theith input factor,the output vector of thekth output factor,and the output vector of the 1th output factor.When ρ >1,the efficiency of green development is relatively effective,while when ρ <1,there is efficiency loss in the evaluation unit.To improve the efficiency of green development,adjustments can be made to the input,improvements can be made to the expected output,and the unexpected output can be controlled.The larger the value of ρ,the higher the efficiency of green development.
The Malmquist Index
The production technology and production scale of each DMU can change over time,making it difficult to analyze the contribution of production technology and production scale changes to the efficiency changes of DMUs by simply placing DMUs from different time periods on a unified production frontier for efficiency evaluation and comparison.Building upon the SBM model,F?re et al.(1992) introduced the concept of the Malmquist index,which decomposes efficiency changes into the change of technical efficiency and the change of technical progress.The Malmquist index,which uses radial distance,can be decomposed into three components: the pure technical efficiency change index (PEC),the scale efficiency change index (SEC),and the technical progress change index (TC),resulting in the multiplied Malmquist Total Factor Productivity (TFP) index.
Index Selection and Data Sources
Based on the current situation of Chongqing’s economic and social development,this paper selected capital input,land input,and energy input as input indicators in the development of the index system.Specifically,the investment in fixed assets of the whole society and the general public budget expenditure was selected as the input indicators,the construction area of housing was selected as the land input indicator,and the total energy consumption of industries above designated size was selected as the energy input indicators.Output indicators included expected output and unexpected output.The expected output indicators are represented by GDP,total retail sales of consumer goods,and green coverage area.The unexpected output indicators were measured by industrial wastewater discharges and industrial sulfur dioxide discharges,as shown in Table 1.This analysis measures the efficiency of green development in Chongqing and its influencing factors based on data from Chongqing municipality and its 38 districts and counties from 2011 to 2021.The paper also evaluated and analyzed the green development mode of Chongqing,and proposed a potential development path.The required data was primarily sourced from the statistical yearbooks of Chongqing municipality and its 38 districts and counties from 2012 to 2021,as well astheChongqing Ecological Environment Bulletinand the annual statistical bulletins of national economic and social development of each district and county.To maintain data consistency,the data from the Wansheng Economic and Technological Development Zone was included in the Qijiang district,and the data of the Shuangqiao district was included in the Dazu district.The data of Liangjiang New Area was calculated prior to its establishment and was not separately calculated.
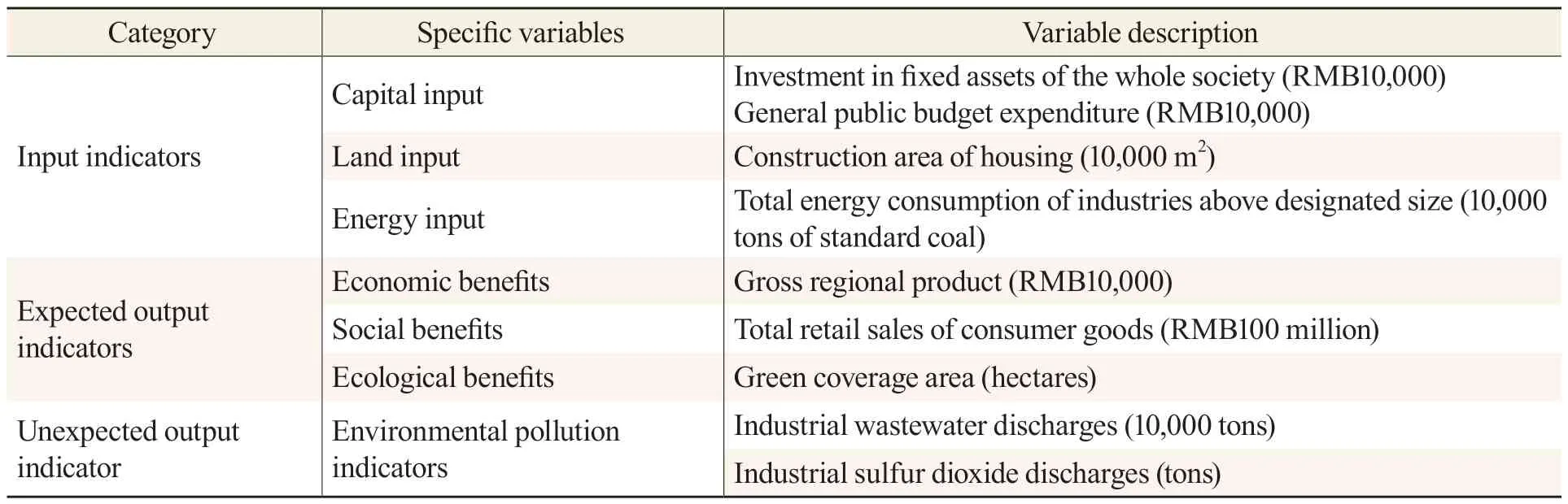
Table 1 Evaluation System of Green Development Efficiency in Chongqing
Measurement of Green Development Effciiency in Chongqing and Analysis of Infulencing Factors
Green Development Efficiency of Chongqing Based on the Super SBM Model
The green development efficiency of Chongqing municipality and its 38 districts and counties from 2011 to 2021 was measured using the super-SBM model.The resulting green development efficiency values for each region are presented in Table 2.Figure 2 displays the changes in green development efficiency for selected regions.
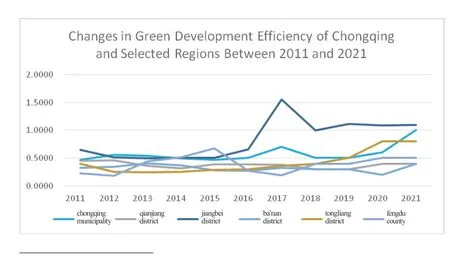
Figure 2 Changes in Green Development Efficiency of Chongqing and Selected Regions Between 2011 and 2021
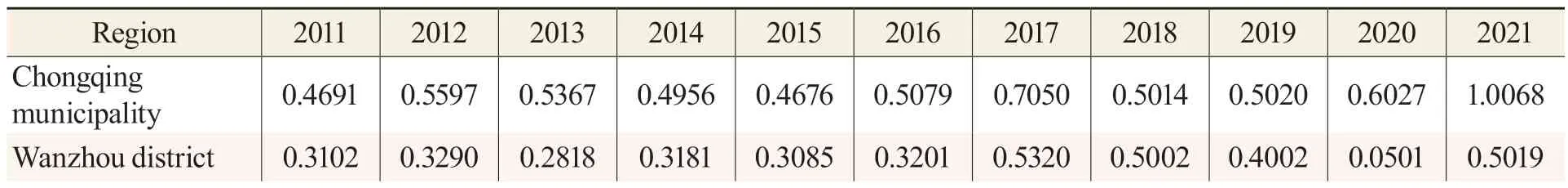
Table 2 Green Development Efficiency Value of Chongqing Between 2011 and 2021
Based on the results presented in Table 1,Figure 2,and Figure 3,the overall green development efficiency of all districts and counties in Chongqing has demonstrated a positive trend of slow improvement over the 11 years from 2011 to 2021.The green development of Chongqing reached its peak value of 0.705 in 2017,followed by a slow decline.However,since 2018,the trend has been upward with fluctuations.This can be primarily interpreted by a period of structural transformation of the national economy and the accelerating pace of green development after the 18th National Congress of the CPC.In 2016,Chongqing’s parallel progress in its growth strategies aligned with China’s national development goals contributed to the increasing green development in Chongqing.The level of green development in Chongqing has experienced a decline since 2018,which was partly due to the global economic weakness and the impact of the COVID-19 pandemic.However,since 2020,the situation has improved,indicating a positive trend in green development.According to the green development efficiency values of each district and county listed in Figure 3,the green development efficiency values of Yuzhong district (1.104),Chengkou county (0.973),Yubei district (0.930),Shapingba district (0.912),and Jiangbei district (0.835) were greater than 0.8,indicating that the green development level of these regions is relatively high and exceeds the overall level of Chongqing.The green development efficiency values of Liangping district (0.733),Shizhu county (0.710),Nan’an district (0.659),and Wulong district (0.603) were between 0.6 and 0.8,revealing that their green development efficiency level is in the medium development level.The efficiency values of green development in other regions were below 0.6,and the level of green development was relatively low,especially in the town clusters of the Three Gorges Reservoir area in Northeast Chongqing and the town clusters in the Wuling Mountains area in Southeast Chongqing,which failed to exhibit obvious strengths in green development.
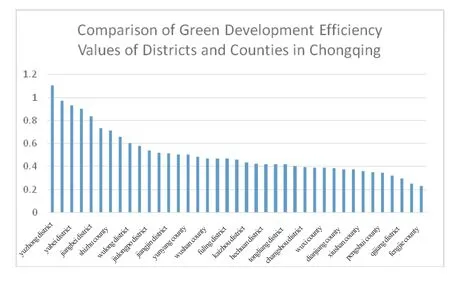
Figure 3 Comparison of Green Development Efficiency of Districts and Counties in Chongqing
Analysis of Dynamic Changes in and Influencing Factors of Green Development Efficiency in Chongqing Based on the Malmquist Index
This paper continued to analyze the green development efficiency of Chongqing and its influencing factors from 2011 to 2021 through the Malmquist index model to obtain the Malmquist index value and its decomposition index value.The results are shown in Table 3.
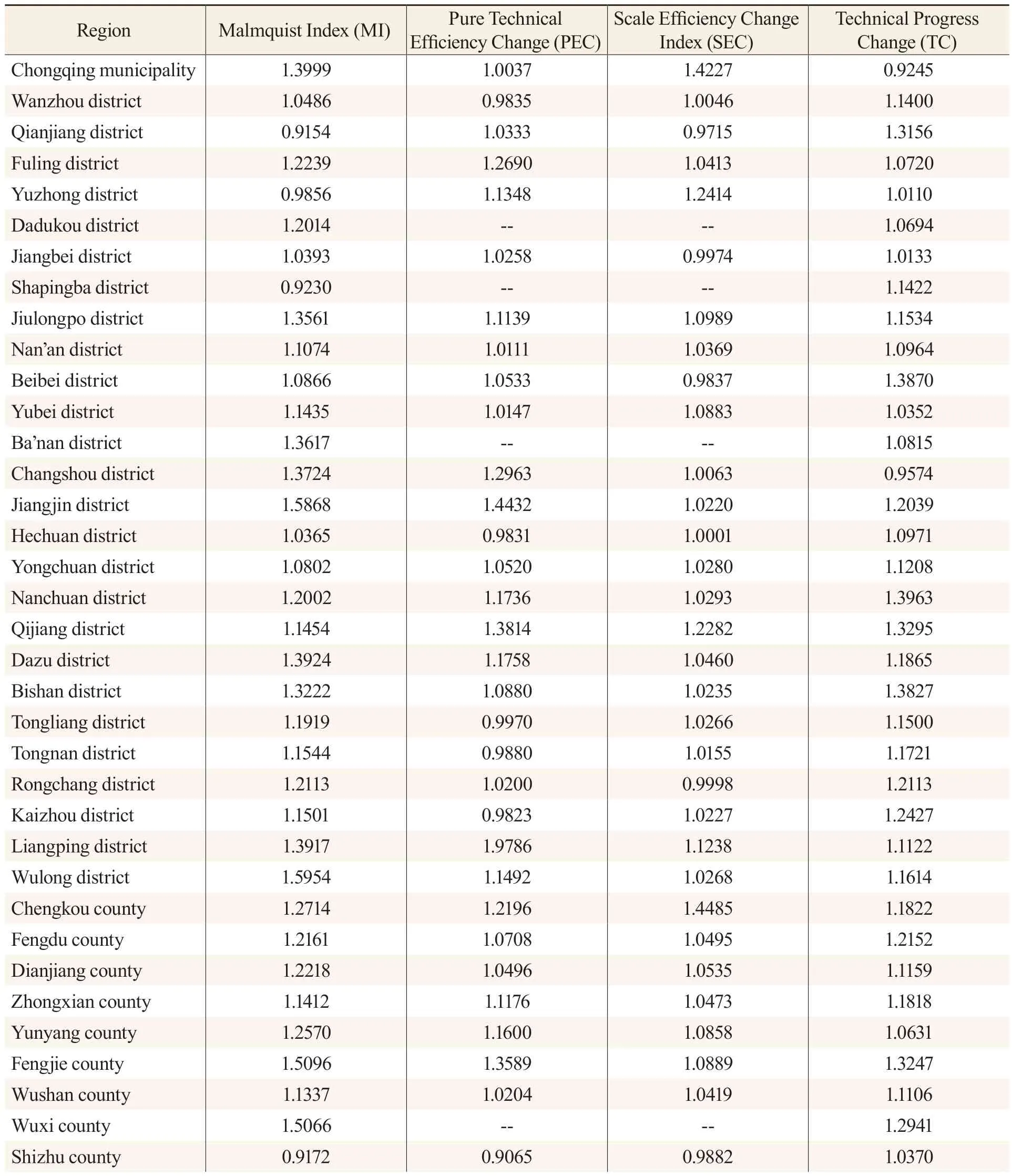
Table 3 The Malmquist Index and Its Decomposition of Chongqing Between 2011 and 2021
The following are the observations from Table 3:
First,the efficiency level of Chongqing’s green development improved rapidly from 2011 to 2021.The Malmquist index value of Chongqing was 1.3999,indicating an overall improvement in green development efficiency from 2011 to 2021.Among the 38 districts and counties,all but four showed Malmquist index values greater than 1,with the lowest being around 0.9.Wulong district achieved the highest level with a Malmquist index value of 1.5954.The other regions,including Jiangjin district,Youyang county,Wuxi county,Liangping district,Ba’nan district,and Jiulongpo district,significantly improved their green development efficiency.This indicates that the efficiency level of Chongqing’s green development is accelerating.The analysis using the super-SBM model suggests that the green development efficiency of Wulong district,Liangping district,Jiulongpo district,and Bishan district was characterized by “high efficiency and high growth,” while the green development efficiency of Fengjie county,Wuxi county,Dazu district,and Changshou district was characterized by “l(fā)ow efficiency and high growth.” The green development efficiency of Jiangbei district and Nan’an district was generally in the stage of “high efficiency and steady growth,” while the green development efficiency of Yuzhong district and Shapingba district was in the state of “high efficiency and low growth.”
Second,the rapid improvement of green development efficiency in Chongqing was mainly caused by the change in returns to scale.The Malmquist index decomposition of Chongqing indicates that the pure technical efficiency change value (1.0037) and the technical change value (0.9245) were both less than the Malmquist index value of 1.3999,while the scale efficiency (returns to scale) change value(1.4227) was greater than the Malmquist index value.This suggests that the greatest contribution to the improvement of green development efficiency in Chongqing came from the change of returns to scale,while the potential impact of pure technical efficiency change and technological change on the improvement of green development efficiency in Chongqing was significant.
Third,the efficiency of green development varies significantly across different districts and counties,and the factors influencing these changes are not uniform.The Malmquist index of Fuling district,Jiulongpo district,Nan’an district,Yubei district,Jiangjin district,and Yongchuan district was greater than 1,and their pure technical efficiency change value,scale efficiency change value,and technical progress change value were also greater than 1,which indicates that the change of green development efficiency was the result of the common influence of these three factors.The Malmquist index values of Wanzhou district,Beibei district,Changshou district,Hechuan district,Tongliang district,and Tongnan district were also greater than 1,and at least one of their pure technical efficiency change values and technical progress change values were greater than their Malmquist index values,indicating that the improvement of their green development efficiency level is mainly due to the pull of technological progress.The Malmquist index of Qianjiang district,Shizhu county,and other districts and counties was less than 1,and at least one of their pure technical efficiency changes and scale efficiency changes were less than 1,revealing that their technical factors or scale changes hindered the improvement of their green development efficiency levels.
Conclusions and Suggestions
By developing the super-SBM model and analyzing the Malmquist index,the author calculated the efficiency of green development in Chongqing from 2011 to 2021 and its influencing factors.The findings show that over the past decade,Chongqing has achieved a high overall level of green development,indicating a positive development trend characterized by overall acceleration and stable local growth.The scale effect has played a significant role in this progress,and the role of technology is starting to emerge.Chongqing has the potential to play an exemplary role in promoting green development along the Yangtze River Economic Belt.To achieve this,Chongqing should focus on optimizing and enhancing the efficiency of its green development efforts,thereby contributing to creating of an important ecological shield in the upper reaches of the Yangtze River.
Advancing Clean and Efficient Use of Energy
Chongqing should prioritize high-quality energy development by accelerating the energy supply revolution.The improvement of a diversified green supply system should serve as the starting point in vigorously promoting the development,construction,and application of new energy sources such as photovoltaic power generation,onshore wind power,hydropower generation,waste heat utilization,geothermal photothermal,and others.Chongqing should also accelerate the development of a smart multi-energy complementary system,laying out a multi-energy coordinated integrated energy network and actively advancing an energyintelligent dispatching system.This will ultimately increase the scale of clean,low-carbon energy supplies and ensure clean energy security.Additionally,Chongqing should accelerate the energy consumption revolution by controlling the total amount and intensity of fossil energy consumption,improving energy efficiency in key areas,and opening and establishing a thriving green consumption market.By fostering a new integrated consumption model,Chongqing can develop a new form of green consumption.
Strengthening the Application and Commercialization of Scientific and Technological Achievements
The transformation and application of green low-carbon technology are key to the green transformation of enterprises.It represents the core of this transformation.Chongqing,as an important traditional manufacturing powerhouse,is facing the competitive pressures of rapid technological upgrading and insufficient core competitiveness.This is particularly evident in the process of transforming a large number of traditional enterprises into new energy.The progress of transformation is relatively slow,with the commercialization of scientific and technological achievements being even more challenging.In exploring a new green development model for the Three Gorges region,Wanzhou,and northeastern Chongqing should leverage university resources to improve the government-led innovation mechanism of university and enterprise collaboration.This will involve building a platform for the technological R&D,commercialization,and application by industries,universities,and research institutions,increasing investments in R&D for green technology,and accelerating technological innovation.Cultivating energy technology and related industries will become new growth drivers to promote industrial upgrading and enhance the efficiency of transforming green technology into green development productivity.
Continuing to Deepen Ecological Restoration and Management
The Sichuan-Chongqing region is currently promoting the development of a green ecological corridor for the river system.This corridor will encompass the Yangtze River,Jialing River,Wujiang River,Minjiang River,Tuojiang River,and Fujiang River,along with other tributaries,lakes,reservoirs,and canals.This initiative is part of the development of the Chengdu-Chongqing economic circle and provides an opportunity for Chongqing to strengthen the protection and upgrading of the “Four Major Mountains” in the central urban area.Through this initiative,Chongqing can carry out ecological protection and restoration efforts.
The Yangtze River Basin is a whole.In the ecological management and restoration,Chongqing should prioritize the systematic and synergistic protection of the ecological environment.Additionally,it should pay attention to the division of labor and cooperation among districts and counties to ensure the effectiveness of collaborative efforts.All districts and counties in Chongqing should prioritize the protection of water resources and important rivers and lakes.This can be achieved through the science-based implementation of water resource protection and utilization measures,active exploration and promotion of industrial wastewater reuse and deep treatment,strengthening prevention and control of farmland non-point source pollution,and improving the treatment of urban and rural domestic sewage.Moreover,Chongqing should strengthen the protection of its urban and rural ecological environment,control pollution,and comprehensively restore the river basin ecosystem.
 Contemporary Social Sciences2023年5期
Contemporary Social Sciences2023年5期
- Contemporary Social Sciences的其它文章
- Reflections on Cultivating Critical Thinking in Foreign Language Courses in the Context of Integrating Ideological and Political Theories in All Courses
- Value Orientation and Dimension Expansion of City Image Communication: A Case Study of Chengdu
- A Literature Review on “Non-Marriage”: A Global Comparative Perspective
- Research on the Formation Mechanism for the Co-agglomeration of Producer Services and Manufacturing in the Guangdong-Hong Kong-Macao Greater Bay Area
- Research Methodology and Analysis of Innovative Pedagogical Models in Mechanical Engineering Courses for International Students at the School of Mechanical Engineering and Automation,Beihang University
- On the Ethical Dimensions of Literary Criticism in the Realm of We Media
