Clinical observation of Tiao Shen Tong Du Tuina in promoting neuropsychological development of premature infants
CHEN Jie (陳杰), LⅠ Xueli (李雪莉), CHONG Yuexian (種月先), YANG Lihong (楊麗紅), YⅠN Zhongxin (尹中信),ZHANG Ping (張平), GUO Zhankun (郭戰(zhàn)坤), ZHANG Ning (張寧)
1 Baoding Maternal and Child Health Hospital, Hebei Province, Baoding 071000, China
2 Hospital of the 82nd Group Army, Baoding 071000, China
Abstract
Keywords: Tuina; Massage; Pediatric Massage (Tuina); Infant, Premature; Child Development
In China, the development of perinatal medical techniques has brought up the survival rate of premature infants. Due to the immaturity of organs at birth, premature infants may develop various complications later especially neurodevelopmental impairment such as cognitive impairment, motor dysfunction, and long-term behavioral disorders[1]. In recent years, the neuropsychological development of premature infants has attracted attention in clinical and healthcare fields[2-4]. Early identification and targeting intervention can encourage the infant’s mental development, effectively avoiding or reducing damage to the premature infant’s nervous system and elevating their quality of life (QOL). Tuina (Chinese therapeutic massage), a traditional Chinese medicine (TCM) therapy,can improve muscle function, increase muscle force,down-regulate muscle tone, mitigate respiratory and digestive functions, and reduce recurrent respiratory tract infections by regulating the functions of Zang-Fu organs, Qi, and blood. Tuina therapy can also increase the compliance of the infants and their parents with the rehabilitation training and produce better neurodevelopment result in high-risk infants, especially premature infants[5-6].
The five spiritual beings reside in, modulate, and nourish the five Zang organs. However, due to prenatal insufficiency and improper feeding after birth,premature infants usually suffer from disordered five spiritual beings and irregular Qi activities of the five Zang-organs, which affect their growth. Guided by the theory of “the five Zang-organs storing the spiritual beings”, this study retrospectively summarized the treatment of premature infants using Tiao Shen Tong Du (regulating the mind and unblocking the Governor Vessel) Tuina by observing the impact of this therapy on the infant’s neuropsychological development, to provide evidence that Tuina improves the short-term and long-term prognosis of the nervous system and intellectual development.
1 Clinical Materials
1.1 Diagnostic criteria
A premature infant refers to an infant born prior to 37 weeks of gestation[7].
1.2 Inclusion criteria
Born with a gestational age ≥28 weeks but <37 weeks;with complete follow-up information; age ≤12 months.
1.3 Exclusion criteria
Congenital genetic metabolic diseases; severe congenital malformations; severe asphyxia; a history of surgery during the neonatal period; serious skin lesions or skin being too delicate to receive Tuina.
1.4 Statistical processing
The data were processed using SPSS version 23.0 software. The normally distributed measurement data were expressed as mean ± standard deviation (±s),and their comparisons were analyzed byt-test. The enumeration data were checked using the Chi-square test. Statistical significance was recognized asP<0.05.
1.5 General data
This study was approved by the Ethics Committee of Baoding Maternal and Child Health Hospital, Hebei Province. Informed consent was obtained from the primary guardian of each kid. This study recruited 115 premature infants who underwent regular health examinations and established rehabilitation files at the Rehabilitation Outpatient of Baoding Maternal and Child Health Hospital, Hebei Province between July 1, 2019 and June 1, 2020 and retrospectively analyzed their clinical data. They were divided into a control group (59 cases) and an observation group (56 cases) based on different interventions. The control group received physical therapy and conventional early-stage intervention, and the observation group received additional Tiao Shen Tong Du Tuina therapy.Eighteen cases were lost to the one-year follow-up,including 10 cases in the observation group and 8 cases in the control group. The general data were statistically equal between the two groups (P>0.05),suggesting comparability (Table 1).
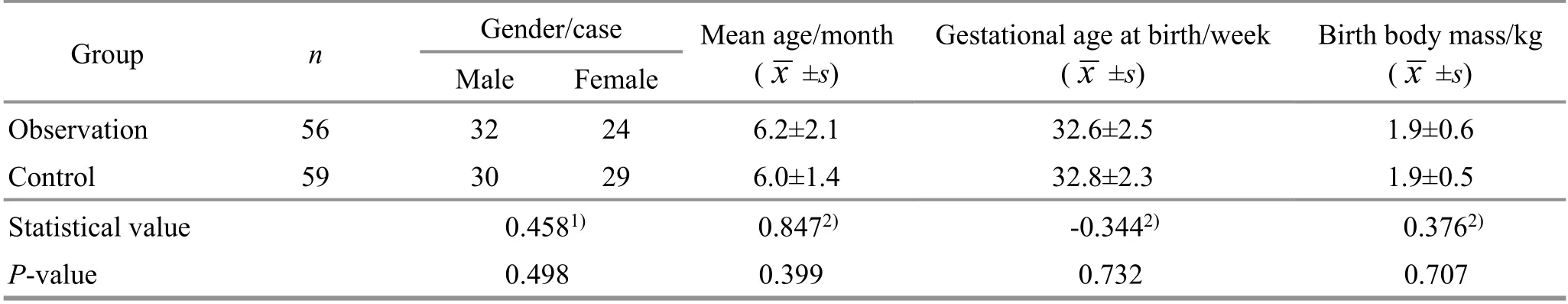
Table 1 Comparison of the general data between the two groups
2 Methods
At the initial visit, a file was established for each infant to collect their gestational age, birth weight,and medical histories during the hospital stay, along with the mother’s health status during gestation and information about the primary caregiver. The infants were assigned to a control or observation group according to the guardian’s will after the first Gesell assessment.
2.1 Control group
The conventional early-stage intervention regime was designed according to the assessment, including visual stimulation training, auditory stimulation training, tactile stimulation training, kinesthetic stimulation training, vestibular function training,posture control, parent-child interaction, infant touch,etc.
Bobath therapy was used as the principal physical therapy to help premature infants hold up their heads,raise their heads in a prone position, turn over their bodies, and keep balance in a sitting position, assisted standing, or independent standing.
2.2 Observation group
Infants in the observation group received Tiao Shen Tong Du Tuina treatment in addition to the same intervention as in the control group[8-9].
Head and neck: Dian-Digital An-Pressing Shenting(GV24), Baihui (GV20), and Sishencong (EX-HN1),10-20 times each point (Figure 1); finger Rou-Kneading Taiyang (EX-HN5) and Dazhui (GV14),50-100 times each point (Figure 2).
Hand and foot: Bu-Reinforcing Shenjing and Pijing,100-300 times each point (Figure 3); Rou-Kneading Zusanli (ST36), Chengshan (BL57), and Yongquan (KI1),50-100 times each point (Figure 4).
Abdomen: Rou-Kneading Zhongwan (CV12),Tianshu (ST25), and Guanyuan (CV4), 50-100 times each point (Figure 5); palm-root Mo-Rubbing and Zhen-Vibrating the abdomen for 15 min (Figure 6).
Back: Gun-Rolling along the Governor Vessel and Bladder Meridian for 5 min (Figure 7); Nie-Pinching the spine from Guiwei (Extra) till Dazhui (GV14)5-7 times, where Feishu (BL13), Pishu (BL20), and Shenshu (BL23) were heavily lifted (Figure 7).
The Tuina treatment was performed once daily,30 min each session, 5 d a week, with 3 months as one intervention cycle.

Figure 1 Dian-Digital An-Pressing head points
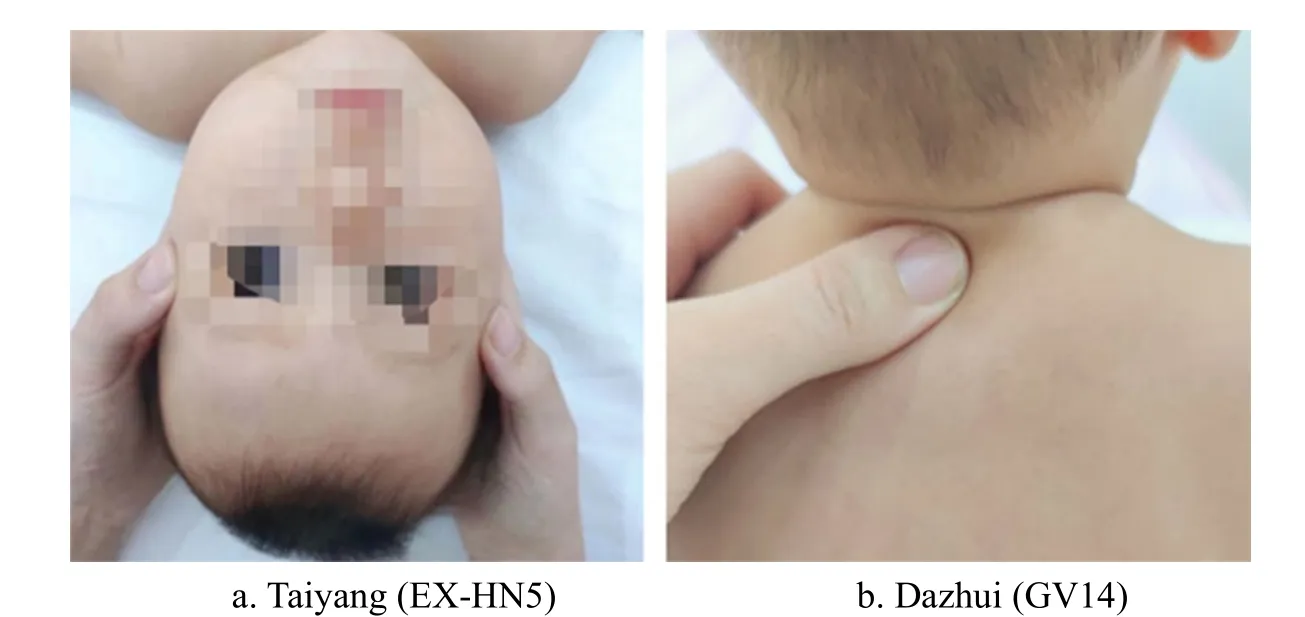
Figure 2 Finger Rou-Kneading Taiyang (EX-HN5) and Dazhui (GV14)
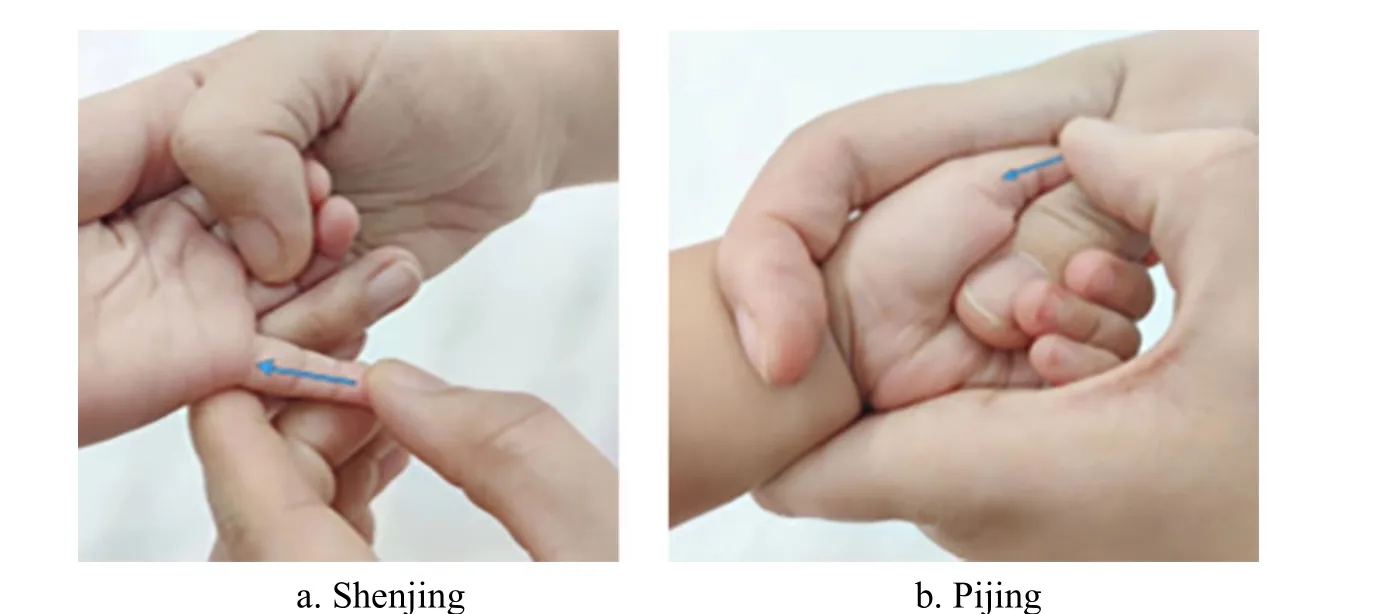
Figure 3 Bu-Reinforcing Shenjing and Pijing
Figure 4 Rou-Kneading lower-limb points
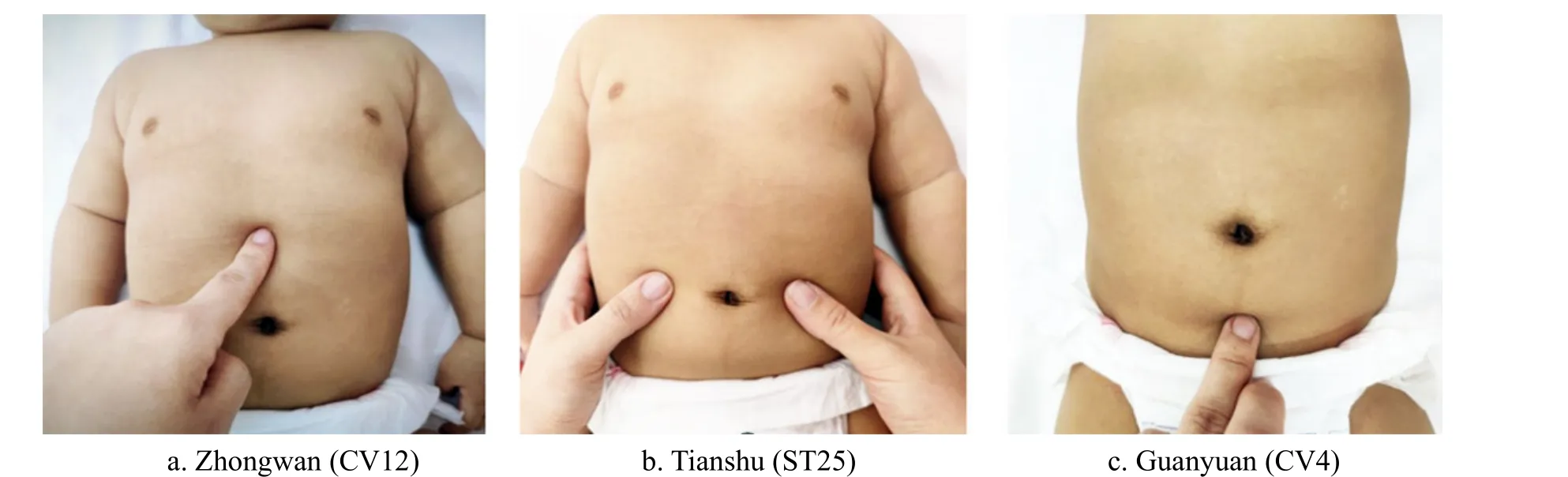
Figure 5 Rou-Kneading abdominal points
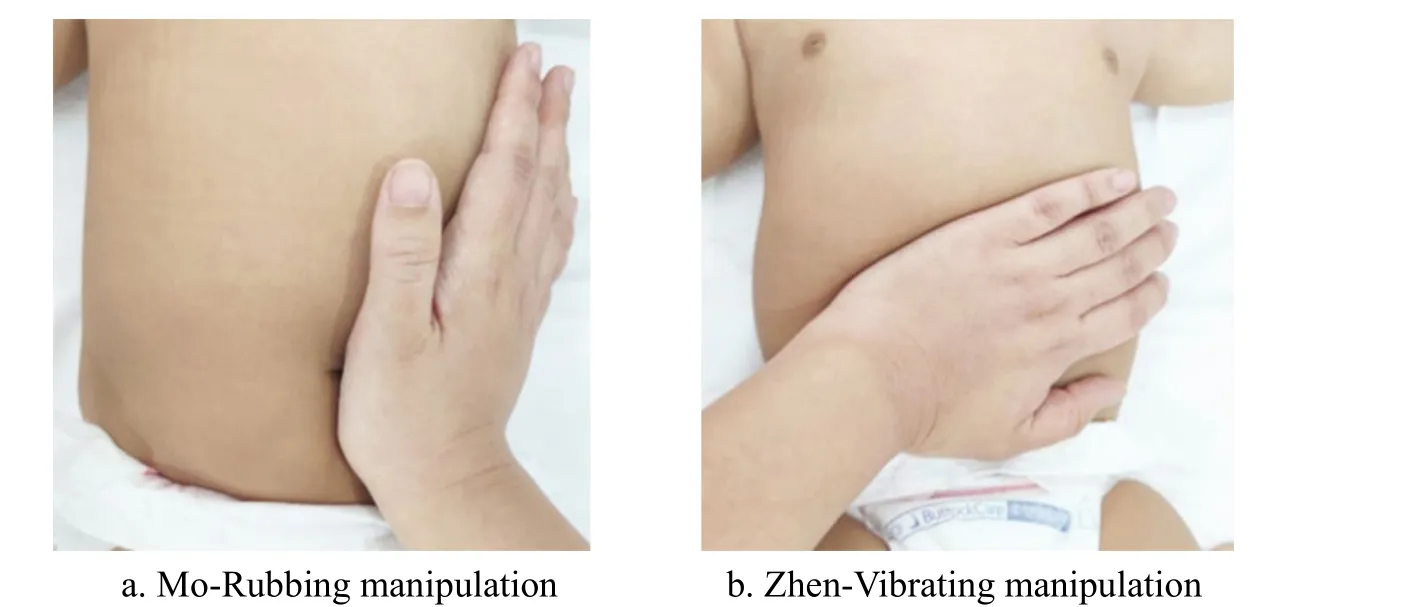
Figure 6 Mo-Rubbing and Zhen-Vibrating the abdomen
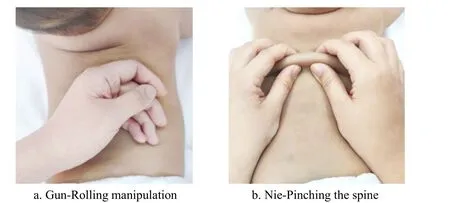
Figure 7 Gun-Rolling manipulation and Nie-Pinching the spine
3 Efficacy Observation
3.1 Outcome measures
The Gesell developmental schedule was adopted to evaluate the infant’s mental development level and structure in five domains: gross motor, fine motor,adaptive, language, and personal-social[10].
Evaluation criteria: for each domain, the development quotient (DQ) ≥86 points is considered normal; DQ ≥76 but <86 points, borderline state; DQ≥55 but <76 points, mild developmental delay; DQ≥40 but <55 points, moderate developmental delay;DQ ≥25 but <40 points, severe developmental delay;DQ <25 points, extremely severe developmental delay.
3.2 Results
3.2.1 Comparison of the DQ score
There were no statistically significant differences in each Gesell domain DQ between the two groups before treatment (P>0.05), suggesting comparability.After treatment, there were improvements in every Gesell domain DQ in both groups, and the intra-group differences were statistically significant (P<0.01). The gross motor DQ was higher in the observation group than in the control group after the intervention,showing statistical significance (P<0.05). The details are presented in Table 2-Table 4.
3.2.2 Comparison of the DQ at the one-year follow-up At the one-year follow-up, the observation group was higher than the control group in comparing each Gesell domain DQ, showing statistical significance(P<0.01 orP<0.05). The details are presented in Table 5.
Table 2 Comparison of the development quotients of gross motor and fine motor ( ±s) Unit: point
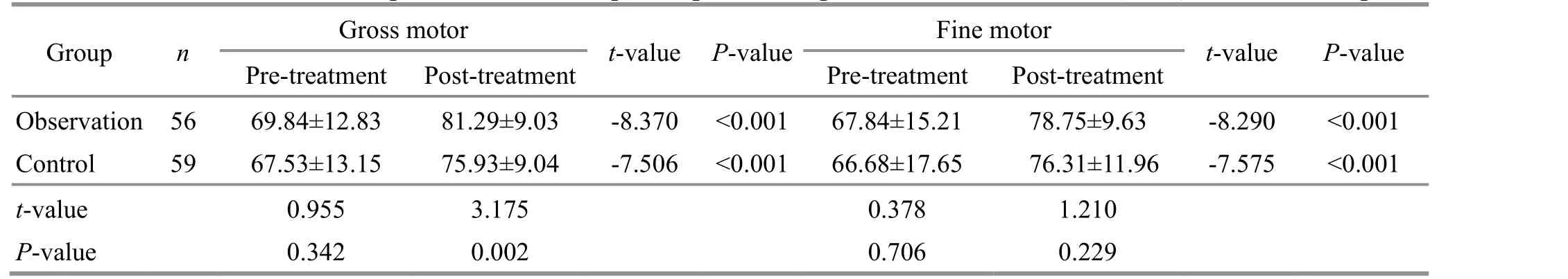
Table 2 Comparison of the development quotients of gross motor and fine motor ( ±s) Unit: point
t-value 0.955 3.175 0.378 1.210 P-value 0.342 0.002 0.706 0.229
Table 3 Comparison of the development quotients of adaptive and language domains ( ±s) Unit: point
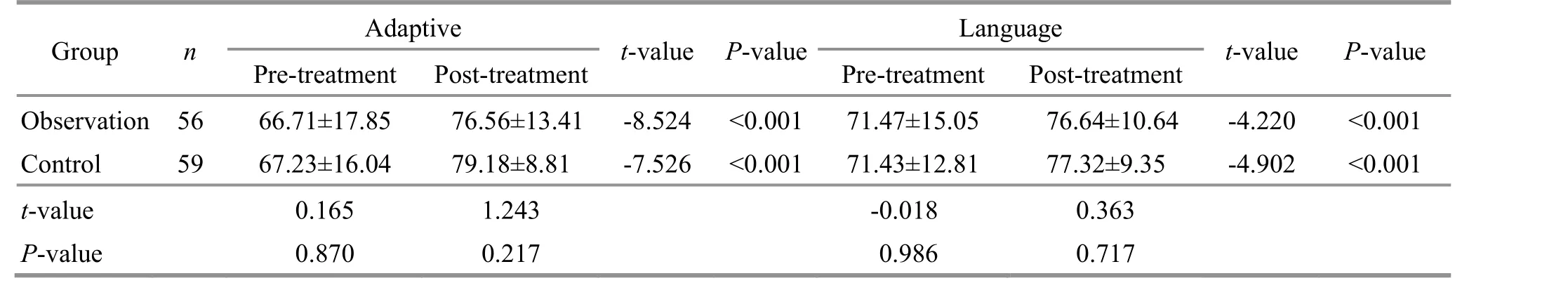
Table 3 Comparison of the development quotients of adaptive and language domains ( ±s) Unit: point
t-value 0.165 1.243 -0.018 0.363 P-value 0.870 0.217 0.986 0.717
Table 4 Comparison of the personal-social development quotient ( ±s) Unit: point
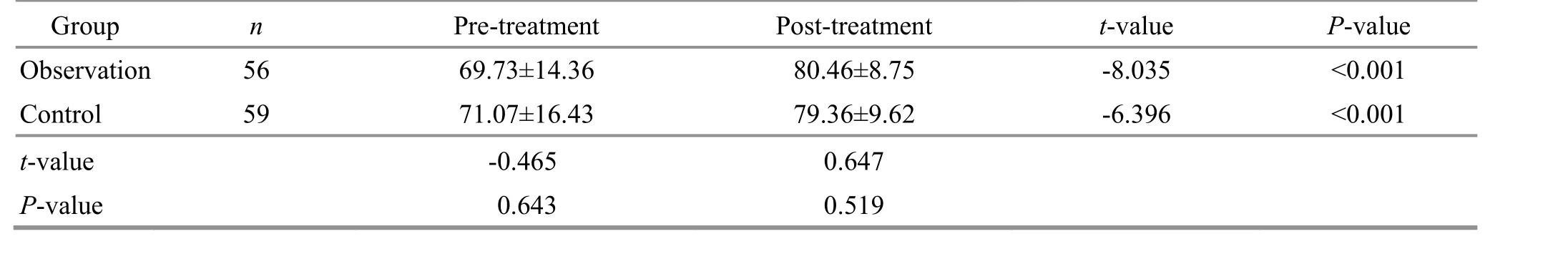
Table 4 Comparison of the personal-social development quotient ( ±s) Unit: point
t-value P-value-8.035 <0.001-6.396 <0.001
Table 5 Comparison of the development quotients at the one-year follow-up ( ±s) Unit: point
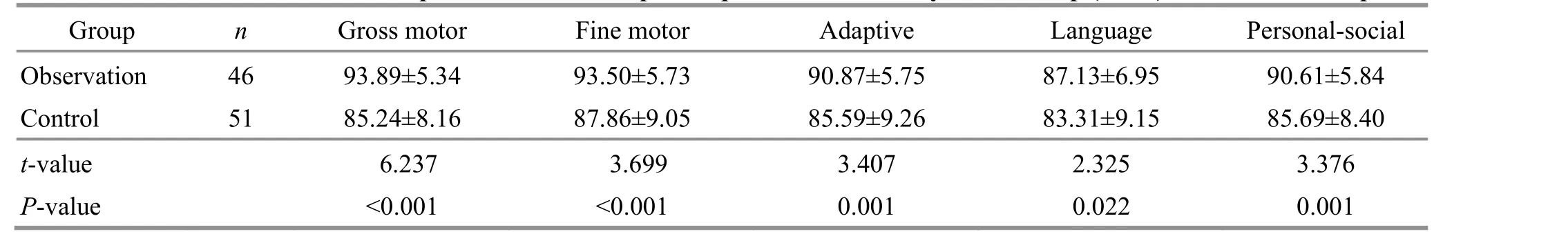
Table 5 Comparison of the development quotients at the one-year follow-up ( ±s) Unit: point
Language Personal-social 87.13±6.95 90.61±5.84 83.31±9.15 85.69±8.40 2.325 3.376 0.022 0.001
4 Discussion
Premature infants usually have short stature and incomplete Zang-Fu organ or Qi development due to poor innate endowment. In TCM, they are diagnosed as “fetal debility” or “congenital weakness”[11].According to TCM, premature delivery has complicated etiology and pathogenesis. Infants’original spirit roots in the father’s essence and the mother’s blood, taking nutrients from the mother as the foundation and, at the same time, influenced by medications and moods during gestation.You Ke Fa Hui(Elaboration on Pediatrics) states that the development of congenital weakness is closely associated with the parents’ constitution. The variety of the five Zang-organs’ excess and deficiency will result in different symptoms in kids after birth: lung insufficiency will present thin withered hair; heart Qi insufficiency will show a pale complexion; spleen insufficiency will lead to weak muscles; liver-kidney deficiency will cause flaccidity[12]. Therefore, there is a close link between congenital weakness and parents’essence and blood. The insufficient essence and blood in parents will lead to weakness of original spirit in infants, alongside the deficient sea of marrow,inadequate nutritional supply of essence and blood to Zang-Fu organs, limbs, muscles, bones, and tendons during growth, finally leading to five retardations and five flaccidities manifested as developmental delay,cerebral palsy, etc. Besides, research also shows that premature birth is related to autism and is the leading cause of language disturbance in children with autism spectrum disorder[13-14].
Taking parents’ essence and blood as the root, a person’s normal original spirit function depends on the regulation of the “five spirits-original spirit”axis[15]. Under the guidance of the theory that “the five Zang-organs house the five spirits”, abdominal Tuina was taken as the main part of Tuina treatment in this study, assisted by Tuina on the back, head, and limbs. Tuina manipulations such as Rou-Kneading,Mo-Rubbing, and Zhen-Vibrating were used to supplement the deficiency, nourish the five spirits,and help them return to their places. Tuina manipulations also benefited the five Zang-organs so that the body could display its normal physiological functions, which is a forward adjustment. Rou-Kneading and An-Pressing manipulations aimed to unblock meridians and collaterals to dissipate stasis,which is a backward adjustment. Consequently, the harmony between Yin and Yang was regained, the five Zang-organs got enough fuel, and the five spirits returned to their places through the forward and backward adjustments. The original spirit is the root,the five spirits are the origin, and meridians, Qi, and blood are the pivot. Different Tuina manipulations work at various levels to modulate disordered spiritual activities[16].
The final gestational stage is the critical stage for brain development. However, premature infants miss this stage because they leave the womb too early.Compared to full-term infants, premature infants have a smaller, lighter brain with fewer and shallower sulci, larger gyri, decreased proliferated nerve cells,and dysplasia of sulci, gyri, and myelin sheaths[17]. The maldevelopment of brain structure and other organs due to premature birth in premature infants, along with complications such as infection, hypoglycemia,and respiratory distress syndrome, will damage brain function and then affect both short- and long-term neuropsychological development in the infants.According to the 2019 systemic review, the global incidence of premature infants is 10.6%, which is about 6.9% in China[18]. Gesell developmental schedule reveals significantly lower DQs in all five function domains in extremely preterm infants compared with mid-late preterm infants at 6 months of the corrected age despite the gestational age(P<0.001)[19], and their growths in the five function domains are still retarded at one year old of the corrected age[20]. Regarding long-term neuropsychological development, premature infants run a higher risk than full-term infants, mainly manifested as cerebral palsy, language disturbance, visual and auditory impairments, attention deficit, and cognitive impairment, which will affect their cardiovascular and metabolic systems[21-22].
In this study, the two different early-stage intervention methods both boosted neuropsychological development in premature infants.After the intervention, the observation group had a higher DQ in the gross motor domain compared with the control group, suggesting that Tiao Shen Tong Du Tuina can effectively improve the infants’ gross motor function in the short term. At the one-year follow-up,the five domains’ DQs were all higher in the observation group than in the control group,indicating that Tiao Shen Tong Du Tuina can produce satisfactory long-term efficacy in boosting neuropsychological and language developments in premature infants. ZHANG Y,et al[23]found that the language function was retarded compared with other domains in premature infants. The retardation rate was 14.63% and 5.91% in six-month-old high-risk and low-risk premature infants, respectively; the rate reached 47.15% and 26.60% at 12 months and 18.70% and 10.34% at 24 months. Language development is influenced by multiple factors,including biological and environmental factors.Gestational age, disease severity, increased neonatal morbidity, hospital stay, hearing status, gender, age,socioeconomic risk factors, and feeding difficulties all may negatively impact language development[24].However, the current study failed to observe the language development level at 24 months old in most of the kids as they have not reached that age even after the 3-month treatment and 1-year follow-up.Therefore, we can extend the observation duration to further study the effect of Tiao Shen Tong Du Tuina on language development in the future.
In brief, this trial has revealed that Tiao Shen Tong Du Tuina plus conventional intervention can boost neuropsychological development in premature infants,manifested as a significant advantage in the shortterm gross motor function, and gross motor function,fine motor function, adaptive behaviors, language,and personal-social behaviors in the long run.
Conflict of Interest
There is no potential conflict of interest in this article.
Acknowledgments
This work was supported by the Science and Technology Plan Project of Baoding City, Hebei Province (河北省保定市科技計(jì)劃項(xiàng)目, No. 2041ZF142).
Statement of Informed Consent
Ⅰnformed consent was obtained from the guardians of the recruited children in this study.Received: 15 August 2021/Accepted: 1 December 2021
 Journal of Acupuncture and Tuina Science2022年6期
Journal of Acupuncture and Tuina Science2022年6期
- Journal of Acupuncture and Tuina Science的其它文章
- Efficacy of electroacupuncture for patients with dry eye syndromes: a randomized controlled trial
- Clinical observation of acupuncture combined with sitting-position knee-adjustment manipulations for patellofemoral arthritis
- Clinical observation of acupuncture and moxibustion for functional dyspepsia due to Yang deficiency of the spleen and stomach
- Clinical study of acupuncture combined with medication for the elderly with Alzheimer disease
- Effects of herbal cake-partitioned moxibustion on the expression of thyroid autophagy-related factors LC3B and Beclin-1 in rats with autoimmune thyroiditis
- Effects of Tuina on serum creatine kinase and skeletal muscle mitochondria in delayed onset muscle soreness model rats
