Efficacy of glucocorticoids,chloroquine and vitamin A on cytokine release syndrome: a network pharmacology study
ZHANG Jing,ZHU Jingjing,HE Siqi,WANG Jianxun
ZHANG Jing,ZHU Jingjing,HE Siqi,WANG Jianxun,School of Life Sciences,Beijing University of Chinese Medicine,Beijing,China.
Abstract OBJECTIVE: To verify the efficacy of glucocorticoids,chloroquine and vitamin A in the treatment of cytokine release syndrome (CRS),and to investigate the underlying mechanisms,based on network pharmacology.METHODS: We used network pharmacology analysis and found 20 co-targeted genes of glucocorticoids,chloroquine,vitamin A and CRS.The pharmacological functions and therapeutic pathways of the genes were analyzed by gene ontology and Kyoto Encyclopedia of Genes and Genomes pathway enrichment.The candidate naturally bioactive compounds against the key genes were predicted by Traditional Chinese Medicine Systems Pharmacology Database and Analysis Platform.The anti-inflammatory activity of luteolin was assessed by real-time polymerase chain reaction.RESULTS: Among the 20 co-targeted genes of glucocorticoids,chloroquine and vitamin A,interleukin 10(IL-10),interleukin 2 (IL-2),interleukin 4 (IL-4) and tumor necrosis factor-α (TNF-α) were the key cytokines against CRS.The key pathway involved in the pharmacological mechanism could be cytokine-cytokine receptor interaction pathway,T cell receptor signaling pathway,Janus Kinase-signal transducer and activator of transcription signaling pathway and phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase-protein kinase B signaling pathway.Luteolin targeted by IL-10,IL-4,IL-2 and TNF-α could be one candidate drug for the treatment of CRS.CONCLUSION: This study comprehensively elucidates the pharmacological mechanism for the treatment of CRS and provides a new method for the discovery of drugs for this disease.
Keywords: glucocorticoids;chloroquine;vitamin A;cytokine release syndrome;inflammation;luteolin;network pharmacology
1.INTRODUCTION
Cytokine release syndrome (CRS) is a symptom complex associated with two main causations,including infectious diseases and immunotherapy.1,2The activation of immune cells and the releasing of large amounts of cytokines imbalance the immune homeostasis and cause immune injury.3,4Based on the evidence from patients of Middle East Respiratory Syndrome Coronavirus(MERS),severe acute respiratory syndrome (SARS) and SARS-2,CRS was the main cause of multiple organ and tissue damage and even death.5-7Meanwhile,with the development and optimization of Chimeric antigen receptor (CAR) T cells therapy,the side effects were significantly reduced.However,CRS still represented as one of the life-threatening adverse events with a high incidence.8,9
Early intervention of the over exuberant response is thought to be one of the efficient strategies for the control of CRS.Anti-inflammation drugs used in the treatment of CRS could be classified into two types,targeted and non-targeted drugs.Tocilizumab (Actemra) and siltuximab (Sylvant) could interfere the action of the cytokine interleukin-6.10,11However,glucocorticoids are among the most commonly used anti-inflammatory agents for a variety of diseases.12Other drugs like chloroquine and vitamin A also show anti-inflammatory activity in the treatment of autoimmune disease and infectious diseases,like SARS and corona virus disease 2019 (COVID-19).13-15Nevertheless,the major pharmacological molecular mechanism against CRS remains poorly understood.And,whether there exists a similar mechanism among glucocorticoids,chloroquine and vitamin A are still unknown.
Network pharmacology,a method based on the principles of systems biology and bioinformatics analysis,has been wildly applied in the discovery of therapeutic mechanism.16,17In the present study,we aimed to investigate and verify the efficacy of glucocorticoids,chloroquine and vitamin A in the treatment of CRS and the underlying mechanisms based on a network pharmacology.
2.MATERIALS AND METHODS
2.1.Identification of candidate genes associated with CRS
The GeneCards (https://www.genecards.org) were accessed to collect CRS-related genes using the search terms “cytokine release syndrome”.18The target genes of glucocorticoids,chloroquine and vitamin A were identified using the UniProt tool (https://www.uniprot.org/).19All the associated genes of CRS and target genes of glucocorticoids,chloroquine and vitamin A were subjected to intersection analysisviaan online platform with graphical output (http://bioinformatics.psb.ugent.be/webtools/Venn/) in the form of Venn diagrams.
2.2.PPI network construction and enrichment analysis
The intersection of CRS-related genes and candidate drugs associated genes were thought as potential therapeutic targets for CRS.The protein and protein interaction (PPI) network of these co-targeted genes was analyzed by the online tool (https://string-db.org/) and the interaction scores were ranked.20The Metascape online tool was used to thoroughly analyze enrichment information including gene ontology (GO) enrichment and Kyoto Encyclopedia of Genes and Genomes (KEGG)pathway analyses.GO and KEGG terms withP< 0.05 were considered significantly enriched.21
2.3.Screening of active compounds
The high-frequency interaction genes in the PPI network were considered as the most important candidate targets for the treatment of CRS and used as the queries to find potential drugs and natural products in the Traditional Chinese Medicine Systems Pharmacology Database and Analysis Platform (TCMSP,http://tcmspw.com/index.php).22
2.4.Validation of the anti-inflammatory response of macrophage by Luteolin
Macrophages was differentiated from THP-1 cells by the stimulation of phorbol 12-myristate 13-acetate (PMA)for 2 d.Then,the co-culture supernatant of anti-CD19 CAR-T cells and CD19 positive-Raji cells in our lab was used as the inducing factor of CRS of macrophages.In addition,Luteolin [MedChemExpress (MCE) (CAS:491-70-3)] was added to the culture and cultured for another 48 h.Then,the cells were harvested and total RNA was extracted using TRNzol Universal Reagent(Tiangen,China).Complementary DNA (CDNA) was obtained using PrimeScript? RT Master Mix (Perfect Real Time) for quantitative real-time polymerase chain reaction PCR (qRT-PCR) (Takara,CA,USA).QPCR was performed using SYBR? Premix Ex Taq? (Tli RNaseH Plus) (Takara,CA,USA) in Bio-Rad CFX96 PCR System (Bio-Rad,CA,USA).Primers were designed by the genscript online tool(https://www.genscript.com/tools/real-time-pcr-taqmanprimer-design-tool) (Table 1).Three independent experiments were performed and target gene expression was normalized to β-actin using the 2-ΔΔCtmethod of relative quantification.
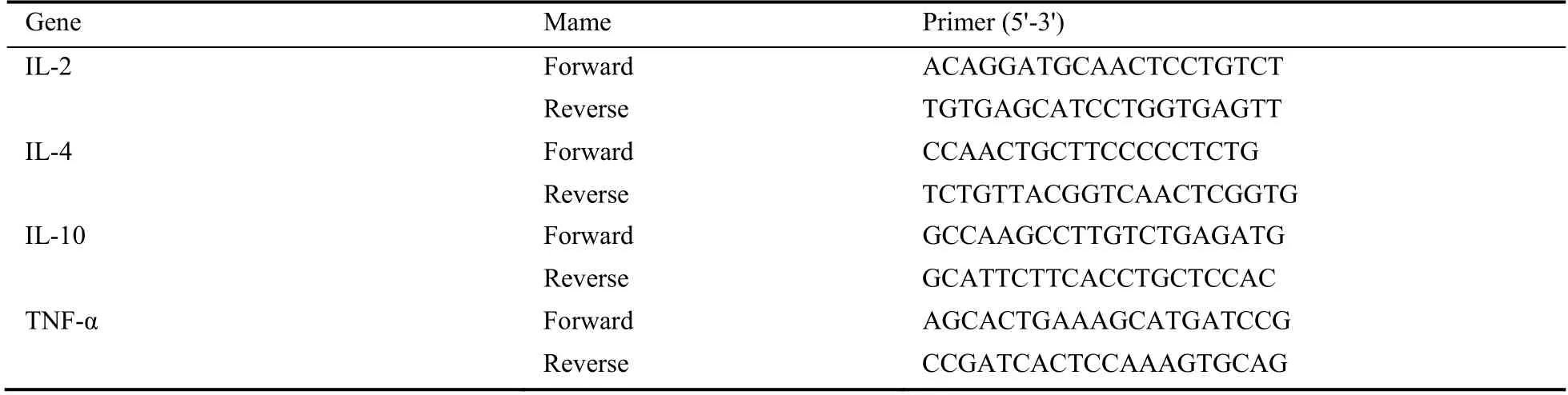
Table 1 Real-time reverse transcription-polymerase chain reaction primers sequences
3.RESULTS
3.1.CRS associated genes targeted by glucocorticoids,chloroquine and vitamin A
In order to determine the CRS-associated genes,we searched for “cytokine release syndrome” in GeneCards and obtained 2178 CRS-associated genes with relevance score ≥ 5.Then,the pharmacological action genes of glucocorticoids,chloroquine and vitamin A were identified using the UniProt tool.The common targeted genes among CRS and glucocorticoids,chloroquine and vitamin A were analyzed and shown in the Venn diagram.The results shown that 20 genes were found to be the common nod pharmacological genes for the treatment of CRS (Figure 1A),including BMP6,TNF-α,TNFRSF1A,IL-18,IL-10,IL-4,IL-1RN,IGFBP3,ALB,IL-1R1,CD4,HSPA4,ABCB1,ITGAM,IL-2RA,IL-2,TNFRSF1B,TLR4,IFNA1,CYP3A4.
3.2.Protein-protein interaction of the common genes
For further analysis of these common genes,the STRING database was used to construct the target-functionprotein interaction network.By setting the mediumconfidence ≥ 0.4 and enrichmentP-value < 1.0e-16,the PPI network of 19 genes was shown in Figure 1B.The interaction scores were ranked and TNF-α was the most associated genes in the 19 genes (Figure 1C).
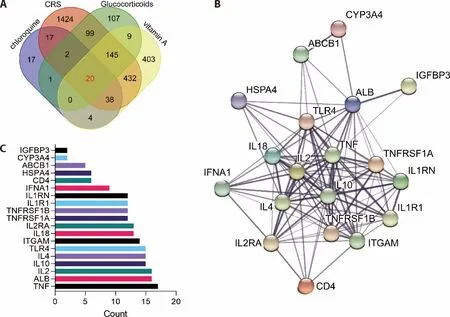
Figure 1 An association network of anti-inflammation drugs of glucocorticoids,chloroquine and vitamin A targeted genes associated with CRS
3.3.Enrichment analyses
GO enrichment analysis was used to elucidate the biological process (BP),cell composition (CC),and molecular function (MF) annotation of the 19 target genes.The top terms of BP,CC,and MF,which were ranked according to their adjusted p-value,are shown in Figure 2A.The GO enrichment analysis identified the regulation of production of molecular mediator of immune response (GO: 0002700),regulation of adaptive immune response based on somatic recombination of immune receptors built from immunoglobulin superfamily domains (GO: 0002822),regulation of adaptive immune response (GO: 0002819),regulation of leukocyte mediated immunity (GO: 0002703),regulation of inflammatory response (GO: 0050727),etc.
We conducted a KEGG pathway analysis to further understand the possible mechanism underlying the treatment of CRS by glucocorticoids,chloroquine and vitamin A.The results shown that 12 of the 19 target genes were enriched and yielded 35 pathways (P<0.001).These retrieved pathways could be clustered into 3 categories,signal transduction pathway,non-infectious diseases associated pathway and infection associated pathway: virus,bacteria and parasite (Figures 2B-2D).The results suggested that Cytokine-cytokine receptor interaction pathway,T cell receptor signaling pathway,Janus kinase-signal transducer and activator of transcription (JAK-STAT) signaling pathway and phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase-protein kinase B (PI3K-Akt)signaling pathway played a key role in the treatment of CRS.And,IL-10,IL-4,IL-2,TNF-α and IFNA1 were the key cytokines.
3.4.Drugs screening against the enriched targets
Traditional Chinese Medicine (TCM) has gained abundant experience in the treatment of diseases for thousands of years.TCM has been increasingly used in the last decades and become well known for its significant role in preventing and treating cancer and Inflammatory diseases.23In order to find TCM for the treatment of CRS,we retrieved the 5 key cytokines targeted herbs and analyzed the common ones.IFNA1 was excluded from analysis due to little drug information.The results shown that there are 142 kind s of herb with the common targets (Figure 3A).Then,we analyzed the common ingredients targeting IL-10,IL-4,IL-2 and TNF-α (Supplement 1).The results shown that luteolin was the only one ingredient targeting IL-10,IL-4,IL-2 and TNF-α (Figure 3B),which suggested that luteolin could be one candidate drug for the treatment of CRS.

Figure 2 Gene ontology analysis and Kyoto Encyclopedia of Genes and Genomes pathway analysis
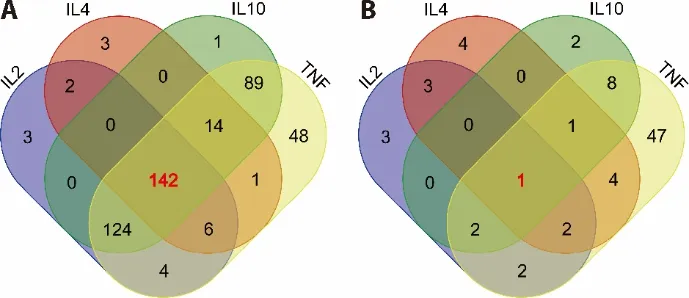
Figure 3 Venn diagram of drugs targeting IL-10,IL-4,IL-2 and TNF-α
3.5.Luteolin inhibit the inflammatory response of macrophage
In order to evaluate the anti-inflammatory activity of luteolin,the co-culture supernatant of anti-CD19 CAR-T cells and CD19 positive-Raji cells was used to stimulate macrophage-like cells,differentiated from the human monocytic cell line,THP-1 by PMA and the relative expression of IL-10,IL-4,IL-2 and TNF-α were detected by real-time PCR (Figure 4).The results shown that the co-culture supernatant of anti-CD19 CAR-T cells and CD19 positive-Raji cells could efficiently stimulate the inflammatory response of macrophage-like cells,which was consistent with researches in the mechanisms of CRS in CAR-T cells therapies.And,luteolin could inhibit the expression of IL-10,IL-4,IL-2 and TNF-α in a concentration-dependent manner.
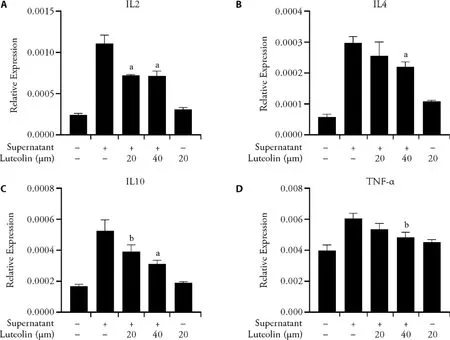
Figure 4 Regulation of expression of IL-10,IL-4,IL-2 and TNF-α in macrophages by Luteolin
4.DISCUSSION
CRS is the most common acute adverse event associated with CAR-T cell therapy,which could compromise therapeutic efficacy and even enhance toxicity.24Meanwhile,CRS is also seen in patients suffering a hyperimmune response to microbial infection,which was the principal mechanism of COVID19 associated pathological injury.25However,limited drugs could be chosen for the treatment of CRS.Glucocorticoid is wildly used to suppress the cytokine storm and have been used in the treatment of CRS.26The pharmacological mechanisms and action genes are not quite clear.
In this present study,a network pharmacology-based approach was applied to mine the targeted genes of glucocorticoids for the treatment of CRS.In the meantime,the other two wildly used anti-inflammation drugs chloroquine and vitamin A were used to narrow the scope of targeted genes.A total of 20 genes were targeted by glucocorticoid,chloroquine and vitamin A and associated with CRS.The PPI network analysis showed the interaction of each protein and indicated that IL-10,IL-4,IL-2,TNF-α and ALB were the core genes involved in the treatment of CRS.Apart from ALB,IL-10,IL-4,IL-2 and TNF-α are classic cytokines,which were considered as the hot targets in studies researching pathological mechanisms of CRS and identifying drugs.The role of ALB in the PPI network could be a transporter molecule involved in the carriage of endogenous molecules including hormones,fatty acids,and metabolites.
IL-10,a key anti-inflammatory cytokine,can negatively regulate inflammatory responses by inhibiting the production of proinflammatory cytokine.Numerous date has demonstrated that IL-10 was involved into the CRS of COVID-19 and significantly associated with disease severity.27,28The KEGG pathway enrichment analysis revealed that the top four enriched pathways associated with infection included Cytokine-cytokine receptor interaction pathway,T cell receptor signaling pathway,JAK-STAT signaling pathway and PI3K-Akt signaling pathway.It has been verified that IL-10 was associated with the JAK-STAT signaling pathway and PI3K-Akt signaling pathway.29,30In addition,one recent report shown that targeting JAK-STAT signaling pathway was one efficient strategy to control CRS in COVID-19.31Therefore,IL-10 might be one potential candidate gene for drug development.
Naturally bioactive compounds are attracting considerable attention,owing to the rich availability,efficacy and fewer side effects.Here,based on the identified targets for the treatment of CRS,naturally bioactive compounds targeting these genes were retrieved from database.Luteolin was found to be associated with IL-10,IL-2,IL-4 and TNF-α.Luteolin is a naturally-occurring flavonoid,with potential antioxidant,anti-inflammatory,apoptosis-inducing and chemopreventive activities.32And,some evidence indicates that luteolin could inhibits an endotoxinstimulated phosphorylation cascade and proinflammatory cytokine production in macrophages,which was supported by our research.33
In summary,the present study indicates that IL-10,IL-2,IL-4 and TNF-α were the key cytokines against CRS revealed by the bioinformatics analysis of the pharmacological targets of glucocorticoids,chloroquine and vitamin A.And,luteolin could inhibit inflammatory response in macrophages and have huge potential in the treatment of CRS.
 Journal of Traditional Chinese Medicine2022年1期
Journal of Traditional Chinese Medicine2022年1期
- Journal of Traditional Chinese Medicine的其它文章
- Development and evaluation of short form of constitution in Chinese medicine questionnaire: a national epidemiological survey data of 21 948 cases
- Registration of intervention trials of Traditional Chinese Medicine for four neurological diseases on Chinese Clinical Trial Registry and ClinicalTrials.gov: a narrative review
- Acupuncture for low back pain: a clinical practice guideline from the Hong Kong taskforce of standardized acupuncture practice
- Applying latent tree analysis to classify Traditional Chinese Medicine syndromes (Zheng) in patients with psoriasis vulgaris
- Mechanism underlying the effect of Liujunzi decoction (六君子湯) on advanced-stage non-small cell lung cancer in patients after first-line chemotherapy
- Correlation analysis between characteristics under gastroscope and image information of tongue in patients with chronic gastritis
