A review on the recent advances in the effects of exogenous substances in food on gut microbiota
Zhan Li ,Yong Yang ,Yue Liu ,Xiu-Hua Wu ,Zhan-Dong Li
1School of Biological and Food Engineering,Jilin Engineering Normal University,Changchun 130052,China.2Center of Digestive Endoscopy,Qianwei Hospital of Jilin Province,Changchun 130012,China.3School of Chemistry and Life Sciences,Changchun University of Technology,Changchun 130012,China.4Measurement Biotechnique Research Center,Jilin Engineering Normal University,Changchun 130052,China.
Abstract Gut microbiota is a large number of microorganisms closely related to human and animal health.The changes in the microbiota under different conditions directly reflect the health status of the host.As the main factor affecting the microbiota,the daily diet has attracted increasingly attention.Related studies have shown that in addition to the main endogenous components in food that interfere with the gut microbiota of human and other animals,other types of exogenous substances (e.g.,food additives,food condiments,and harmful chemicals produced in various food processing) can also cause changes in the gut microbiota.This paper systematically summarizes the recent advances in the effects of the exogenous substances,i.e.,food additives,food condiments,and food processing by-products,on gut microbiota.We further reviewed the changes of gut microbiota under the dietary intervention and the dietary habit adjustment from the perspective of weight loss,emphasizing the importance of a healthy diet and the weight loss method of balanced nutrition.Our study provided significant guidance for the investigation of gut microbiota in the field of a daily diet.
Keywords: gut microbiota;daily diet;exogenous substances;dietary habit;dietary intervention
Introduction
As a kind of microbial community widely existing in the gut of human and animals,the changes in the content and composition of gut microbiota can cause the deviation of micro-ecosystem in organisms,leading to inflammatory reactions and cascade effects,which have a certain impact on the normal operation of the body and related pathways and processes [1-3].In recent years,with the introduction and application of various organ-gut axis concepts,such as brain-gut axis [4] and lung-gut axis [5],the importance of gut microbiota has been further highlighted and the gut microbiota also has been used as a potential target for clinical treatment of certain diseases,which can intervene and affect the occurrence and development of certain diseases by regulating the contents and the composition of microbiota in the gut [6,7].For example,the supplement of some beneficial bacteria(e.g.,lactic acid bacteria)can not only increase the number of beneficial bacteria in the gut of mice but also assist the normal operation of the digestive system [8].In fact,the common microbial types in human gut can be roughly divided into three types.In addition to the beneficial bacteria mentioned above,there are also a large number of neutral bacteria (i.e.,conditional pathogenic bacteria) and harmful bacteria in the gut of human.The beneficial bacteria mainly include:Lactobacillus,Bifidobacterium,andAkkermansia muciniphila,and the harmful bacteria mainly include:SalmonellaandClostridium perfringens;the neutral bacteria are a kind of microbiota represented byE.coli,andEnterococcus,etc [9].Some changes and growth metabolism of gut microbiota can have a corresponding impact on the host body,and some activities of the host also affect the structure and composition of them,so they interact with each other [10].Although gut microbiota lives in closed gut organs of human and animals,it is vulnerable to external factors,such as environment and diet [11,12].The gut as the main organ for food digestion,and the main feeding source of gut microbiota is daily diet of the host.Due to the plasticity of gut microbiota,the dietary structure and eating habits of host will directly affect the survival and adaptability of them [11,13].In recent years,with the continuous improvement of scientific and technological advances and material conditions,the food processing industry has ushered in an unprecedented development opportunity.Various food-grade additives (e.g.,food additives and food condiments) are continuously identified,which effectively improves the flavor of food and prolongs their storage time.However,relevant research data show that although these exogenous additives can effectively improve food characteristics and facilitate specific populations,excessive or incorrect consumption may still have impact on human health [14,15].Besides,in addition to the food additives and food condiments,in the process of food processing and daily cooking,due to the characteristics of the food production process itself such as barbecue,fumigation,frying,and other operations,certain harmful by-products will be generated,and long-term exposure or intake may cause certain damage to the human body[16-18].Therefore,based on the influence of some exogenous substances in food on human body and the effectiveness of gut microbiota as an indicator for disease diagnosis,this paper systematically summarizes and reviews the advances in the influence of exogenous substances in food on gut microbiota.
Food additives
The development and application of food additives are a key link in the modern food processing industry.They are favored by the industry because they can effectively regulate food flavor and extend the shelf life.At present,various types of food additives represented by emulsifiers,preservatives,and sweeteners have emerged continuously.Its sources can be mainly divided into natural sources and chemical sources[19].Relevant studies have shown that common food additives contain many chemical components [20].The intake of food artificial sweeteners and food emulsifiers may cause gut homeostasis disorders,and can affect the health of animals or humans through the changes in gut microbiota [21,22].In the following,the effects of some common food additives on gut microbiota will be elaborated based on preservatives,sweeteners,and emulsifiers.
Food preservatives
The use of preservatives helps prolong the shelf life of food to delay food corruption,and more and more experimental data show that long-term or excessive intake of the substance has a certain impact on people's health [23].For example,the intake of propionic acid can affect the regulation of glucose metabolism related substances in animals [24].However,sodium benzoate has a certain impact on kidney and liver functions [25].Meanwhile,food preservatives have also been shown to bind to plasma proteins and affect human health[26].Sodium benzoate,potassium sorbate,sodium sulfite,and sodium nitrite are common types of food preservatives in daily life.Gut microbiota is highly sensitive to these exotic chemicals,and may respond to them even at a low level [27].Studies have shown that sodium benzoate can promote obesity by inhibiting gut microbiota[28].Yadav et al.[29]used the multi-omic approach to study the role of gut microbiota in the metabolism of sodium benzoate and found that the dominant bacteria wereBacteroidetes,Firmicutes,Actinobacteria,andProteobacteria,in that order.Nitrite is a common food preservative for meat products,which can effectively inhibit the growth ofClostridium botulinum,but excessive intake of nitrite may cause acute poisoning (>0.3 g) and even death (>3 g) [30,31].Therefore,the use of nitrite needs to comply with the corresponding food safety standards.In terms of gut microbiota,the study of Xu et al.[32] confirmed that high doses of nitrite can cause the increasing ofAlistipes,Prevotella,andRuminococcus.In addition,the migration of gut microbiota in normal mice can reduce the impact of nitrite on serum-related and colon-related indicators.For the dose intake range of sulfite,the results of Irwin et al.[33] provided detailed data support,showing that sulfite at a specific concentration may inhibit some beneficial bacteria in the gut after exposure for a certain time.For example,Lactobacilluswill be inhibited by bactericidal action under the conditions of exposure time of 4 h and concentration range of 1,000-3,780 ppm.However,when the exposure time was 6 h and the concentration of sodium sulfite was 2,000 ppm,theS.thermophiluswould be inhibited by bactericidal action.Potassium sorbate as an acidic preservative has certain inhibitory effect on mold,yeast,and aerobic bacteria [34].When compared with the impact of gut microbiota by sodium benzoate,potassium sorbate,and sodium nitrite at recommended levels,Nagpal et al.[35]found that the proportion ofBacteroides,Blautia,andRuminococcuswas increased in the gut of mice at benzoate group;the abundance ofFirmicutes,Turicibacter,andAlkaliphiluswas increased in the sodium nitrite group;however,the potassium sorbate group showed increased proportion ofParabacteroidesandAdlercreutzia.
Food sweeteners
Sweeteners (e.g.,aspartame,sucralose,saccharin,and cyclamate) are the products of the development of food processing technology,which were first used to regulate and improve the flavor of food.However,with the continuous improvement of living standards,obesity is widespread in the population,which is also the main cause of modern anxiety and physical sub-health state.The Fatty liver,“three high”diseases (i.e.,hypertension,hyperlipidemia,and hyperglycemia) and other diseases caused by obesity are threatening people's health.Various non-calorie or low-calorie sweeteners (i.e.,sugar substitutes)have been developed and applied to daily diets for weight loss and sugar intake reduction.According to relevant research data,incorrect or excessive intake of this substance may have a certain impact on human and animal health [36,37].For example,the intake of aspartame can increase the risk of cancer [38],and the sodium cyclamate has a certain inhibitory effect on the proliferation and differentiation of osteoblasts [39].In addition,some artificial sweeteners can promote the evolution of antibiotic tolerance of gut microbiota compared with ordinary glucose [40],and regulate the structure and species of gut microbiota[41].Zhang et al.[42]showed that sweeteners (saccharin sodium,stevioside,and sucralose) had the ability to increase the abundance ofMucispirillumandAlistipes,which was related to colitis.Besides,the change of host gut microbiota caused by some sweeteners has a certain intergenerational phenomenon that can extend from the mother to the next generation of the species [43,44].In the study of Wang et al.[44],it was found that the intake of aspartame and stevia could change the composition of gut microbiota and the metabolism of propionic acid and lactic acid in the cecum of dams offspring.Meanwhile,there is a certain positive and negative correlation between dams offspring health evaluation indexes (such as daily gain,liver weight,and body fat) monitored in the experiment and microorganisms involved in the process of succinic acid and propionic acid production.In the study of Bian et al.[45] on sweetener,i.e.,acesulfame-potassium (Ace-K),it was found that the consumption of this substance would disturb the gut microbiota of mice,and there were certain gender-specific effects on body weight and gut.In the study of sucralose on gut microbiota in mice carried out by Xu et al.[46],the change trend of gut microbiota in mice under different doses was showed.The results showed that this sweetener can not only affected the changes of microbiota,such as increasing the abundance ofActinobacteria,Proteobacteria,andBacteroidesand reducing the abundance ofClostridiumandRikenellaceae,but also inhibited the immune-related reactions in mice.In addition,theE.coli,a bacterium widely present in the gut of humans,may also be regulated by Aspartame and Ace-K [47].
Food emulsifiers
Emulsifier is an exogenous additive widely used in food and pharmaceutical processing industries,and relevant research data show that the substances can increase the permeability of intestinal cells to a certain extent and improve the bioavailability of pollutants in food[48].Natural or chemical food emulsifiers may lead to a variety of diseases and affect the gut micro-ecology of humans and animals[49-51].For example,glycerol monostearate can aggravate the testicular toxicity of phthalates [52],and polysorbate 80 (PS80) has cytotoxicity [53].Common emulsifiers in daily life are glycerol monolaurate (GML),carboxymethyl cellulose (CMC),polysorbate 80(P80),and κ-carrageenan(κ-CGN).In the study of the effect of GML on the gut microbiota of mice carried out by Mo et al.[54],this emulsifier showed advantages in maintaining the stability of gut microbiota and optimizing the structure of microbiota.It can positively regulate the beneficial bacteria (such asBarnesia,Vibrobacterium,andClostridiumXIVb),and inhibit harmful bacteria(such asAnaeroplasma).Meanwhile,this emulsifier at 150 mg/kg could also reduce the relative abundance of lipopolysaccharide-producing (LPS-producing) inhibitory bacteria(Akkermansia muciniphilaandLupinus luteus) in the gut of mice,and increase the relative abundance of LPS-producing bacteria(Bacteroides acidiciensandE.coli) [55].In Zhou [56] for κ-CGN research showed that the intake of this material could positively regulateBacteroidetesand reduce the content ofProteobacteria.In addition to GML and κ-CGN mentioned above,related studies also showed that CMC and P80,as two common emulsifiers,had a certain negative regulatory effect on gut microbiota in animals and humans,and affected the expression of related pro-inflammatory molecules [57].Chassaing et al.[58] showed the effect of CMC on the gut microbiota of subjects.The results showed that the intake of this substance increased postprandial abdominal discomfort and disorder of gut microbiota composition,reducing its diversity.Furuhashi et al.[59] showed that P80 could increase the abundance ofGammaproteobacteriaand reduce the α-diversity of small intestine.Meanwhile,the culture results of ileum contents under specific conditions showed that P80 could increase the number of colonies of sulfide-producing bacteria inProteus.
Other food additives
According to the relevant standards,food additives in China can be classified into 22 categories.In addition to the above three common types of additives,other types of food additives (such as acidity regulators and colorants/ food pigments) may also have certain effects on gut function and microbiota structure of humans and animals [60].Among them,the acidity regulator can be further divided into three categories: acidification agent,alkalization agent,and buffer [61,62].L-malic acid,as a common acidifier,can effectively improve the gut health of animals and produce positive guidance on gut inflammation [63].The study by Ma [64] confirmed the possibility of citric acid affecting three microorganisms(Bifidobacterium,Lactobacillus,andE.coli)in the duodenum and cecum of broilers.Liu et al.[65] obtained the intake range of alkalization agent-sodium bicarbonate in feed through the change of gut microbiota of laying hens.When the addition amount is less than 0.5%,the number of beneficial bacteria in the gut and the diversity index of gut microbiota will increase.When the addition amount was greater than 2.5%,the balance of gut microbiota would be damaged to some extent.For the impact of the buffer,the research of Zhang et al.[66] gives some experimental basis.Their experimental results showed that the buffer -sodium citrate had a certain effect on the β-diversity of gut microbiota in mice,changing the ratio ofFirmicutestoBacteroidetes.Meanwhile,high-dose sodium citrate intake can also cause the detection of related microorganisms (CorynebacteriumandStaphylococcus).In addition to the above three acidity regulators,there are some data showed that natural red pigment (such as tomato red,amaranth red,and sorghum red) [67],yellow pigment (such as sunset yellow) [68],and other pigments can also have a corresponding impact on the gut of animals.For example,the intake of tomato red,amaranth red,and sorghum red can increase the abundance ofDesulfovibrioandCoprococcus,and reduce the abundance ofLactobacillus,Clostridium,andParabacteroides[67].Sunset yellow has been proved to affect gut homeostasis by inhibiting and affecting the proliferation and differentiation of gut cells,and long-term or high intake of these substances may also increase the risk of gut inflammation [68].Meanwhile,different types of pigments also have their own unique effects,which can be involved in regulating the proportion of certain gut microorganisms and the structure of microbiota [67].In summary,for a large class of exogenous additives such as food additives,their effects on animal gut are diverse,but also subject to different conditions.The results may vary depending on the animal model or the type of disease/ inflammation,and may be affected by experimental conditions(e.g.,intake and time).In order to further understand these substances,it is necessary to continue to carry out more detailed experimental studies,increase and supplement the types of subjects,and update experimental data.The effects of some food additives on gut microbiota are listed in Table 1.
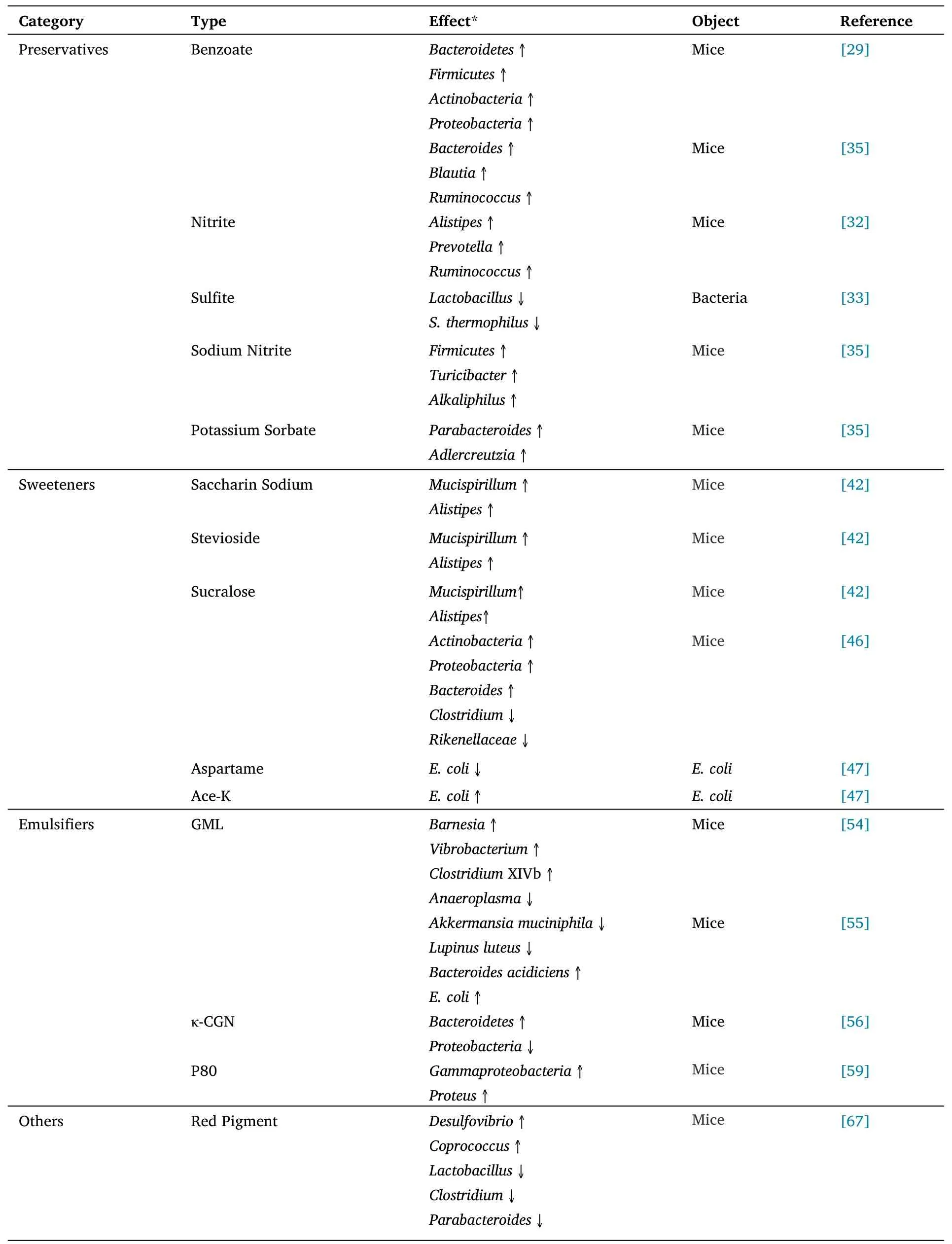
Table 1 The effects of food additives on gut microbiota
Food condiments
Food condiments are a kind of common substances that can effectively improve food flavor,including the common food condiments represented by salt,monosodium glutamate(MSG) and sugar,and the vegetable food condiments represented by pepper,ginger,and garlic.They can not only play a condiment role in diet and cooking,but also be used to supplement the lack of certain nutrients in human or animal bodies.For example,an adequate intake of iodized salt supplements the body's iodine requirements [69].However,similar to other exogenous additives,their intake may also affect the structure and composition of gut microbiota of human and animals.We here review the effects of some food condiments on gut microbiota according to two categories of vegetable food condiments and common food condiments.
Vegetable food condiments
The cuisine vegetable condiments represented by ginger,garlic,and pepper are common exogenous substances in people’s daily diet and family cooking.Different from salt,monosodium glutamate,soy sauce,and other common condiments,they not only can be eaten separately as dishes,but also can participate in the cooking of dishes as accessories or condiments to improve the sensory quality of dishes[70].Similar to other common vegetables,these condiments contain many flavonoids,phenols,and other foodborne components,such as capsaicin (CAP) in pepper [71] and allicin in garlic [72],which can affect the gut microbiota of human and animals to a certain extent.Garcia-Lozano et al.[73] carried out a practical study on the changes of gut microbiota ofDrosophila melanogasterin different backgrounds for the role of pepper in the gut.The results showed that pepper could increase the abundance ofLactobacillaceaeandAcetobacteraceae,and it was speculated that this change might be related to phenolic compounds in the pepper.In addition to phenolic compounds,pepper also contains abundant CAP,which can also effectively participate in the actual regulation of gut microbiota.In the research of Xiang et al.[71] for CAP,the result shows that when the dose of this material in mice is 60 or 80 mg/kg,it will cause some damage to the gastrointestinal tissue,and cause changes in hormone and substance levels.This change may be related to the regulation ofBifidobacterium,Lactobacillus,Faecalibacterium,andButyricimonasin the gut.Meanwhile,the research results of Kang et al.[74]also suggested that CAP may affect the microbiota which produce butyrate and LPS.Garlic is a common antibacterial vegetable,which contains rich active ingredients and can effectively inhibit inflammatory diseases caused by bacteria such asE.coli[75].In the study of the effect of garlic extract on gut microbiota in mice carried out by Jia et al.[76],the effects of alliin,garlicin,and garlic powder on some gut specific microorganisms were demonstrated.The results showed that three components could effectively increase the number ofLactobacillusandBifidobacterium,but had a negative effect onClostridium perfringens.The study of Panyod et al.[77] and Zhang et al.[78] also proved the reliability of the above conclusions.Trimethylamine-N-oxide is a metabolite of gut microbiota and has potential effects on atherosclerosis [79].Panyod et al.[77] suggested that allicin could reduce the production of trimethylamine-N-oxide by regulating gut microbiota,which had a beneficial effect on cardiovascular and cerebrovascular diseases.The results of Zhang et al.[78] suggested that the consumption of garlicin could affect the microbiota composition of small intestine and cecum,indirectly affect the genes in colon epithelial tissue,and have a certain impact on the immune system.Ginger is a kind of medicine and homologous food,which can be used as raw material for diet therapy to alleviate inflammation and gut microbiota imbalance [80],and can be used as seasoning to remove the bloody smell of meat [81].Ma et al.[82] confirmed the effectiveness of ginger decoction in the treatment of antibiotic-associated diarrhea and the recovery of gut barrier function,indicating that ginger can effectively participate in the improvement of the gut microbiota diversity,reduce the level ofEscherichia-Shigella,and improve the level ofBacteroides.Curcumin and gingerol,two main active ingredients in ginger,play roles in the regulation of gut microbiota.Xu et al.[83]and Feng et al.[84] studied curcumin and gingerol,respectively.The results of Xu et al.[83] showed that curcumin could positively guide the renal function and gut function of rats by regulating gut microbiota,which not only inhibited the excessive growth ofEscherichia-ShigellaandBacteroides,but also increased the abundance ofLactobacillusandLactococcus.The experimental results of Feng et al.[84] showed that 6-gingerol could improve and reduce the relative abundance ofBacteroidetesandFirmicutesrespectively,but further research was needed.
Common food condiments
Similar to the above kinds of vegetable condiments,salt,vinegar,wine,sugar,monosodium glutamate(MSG) and other commonly used condiments can improve the flavor of food,but also may have a certain impact on the gut microbiota of consumers [85].In the experiment of Dong et al.[86] on the effect of a high-salt diet on gut microbiota in rats,it was found that compared with the control group,the number ofLactobacillusandPrevotellaNK3B31 in the gut of rats in the high-salt group was decreased,while the number ofAlloprevotellaandPrevotella9 was increased.Besides,the results of Feng [87] on vinegar also proved the positive regulation of vinegar on gut probiotics (such asBifidobacteriumandLactobacillus) and the inhibition of harmful bacteria (such asEnterococcus,Clostridium,andDesulfovibrio).This is similar to the conclusion obtained by Shen [88],who found that the number of lactic acid-producing or acetic acid-producing bacteria (such asLactobacillus,Bifidobacterium,andEnterococcus faecalis) was increased and the number ofE.coliwas decreased in the feces of mice after 28 days of vinegar intervention,which confirmed that vinegar can play a role in colitis in mice by regulating gut microbiota and related reactions.Yellow rice wine,as a kind of wine variety with rich active ingredients,can play a deodorization role in the cooking process of meat food [89,90].Meanwhile,studies have shown that alcohol can also affect the gut microbiota of human or animals [91].The results of Qin et al.[92]showed that yellow rice wine could effectively inhibit the increase ofFirmicutesand the decrease ofBacteroidetescaused by high-fat diet in the gut of rats,so that the content and ratio of these microorganisms were closer to that of the blank control group,and the composition ratio ofAkkermansia muciniphilaandBacteroidetesin the gut of high-fat rats was improved and increased.The results of Wang et al.[93]showed that high-dose yellow rice wine could up-regulate the proportion ofAkkermansia muciniphila,andLactobacillus,and down-regulate the proportion ofBacteroides,Enterococcus,Clostridium,andProteus.In addition to the above three common condiments,MSG as a product of the food industry is also widely used in the process of food flavor regulation.Long-term or short-term consumption will have a certain impact on human and animal health.Nahok et al.[94]revealed the effects of MSG on gut microbiota and kidney liver,suggesting that MSG intake may lead to increasedFirmicutesand decreasedBifidobacterium.The results of Tang [95] showed that MSG could have a negative impact onClostridium ruminaliandVibrio desulphurizationi.Although the intake of MSG within a certain range can improve the abundance of gut microbiota,excessive MSG still causes certain damage to the intestinal tract of mice.The effects of some food condiments on gut microbiota are listed in Table 2.
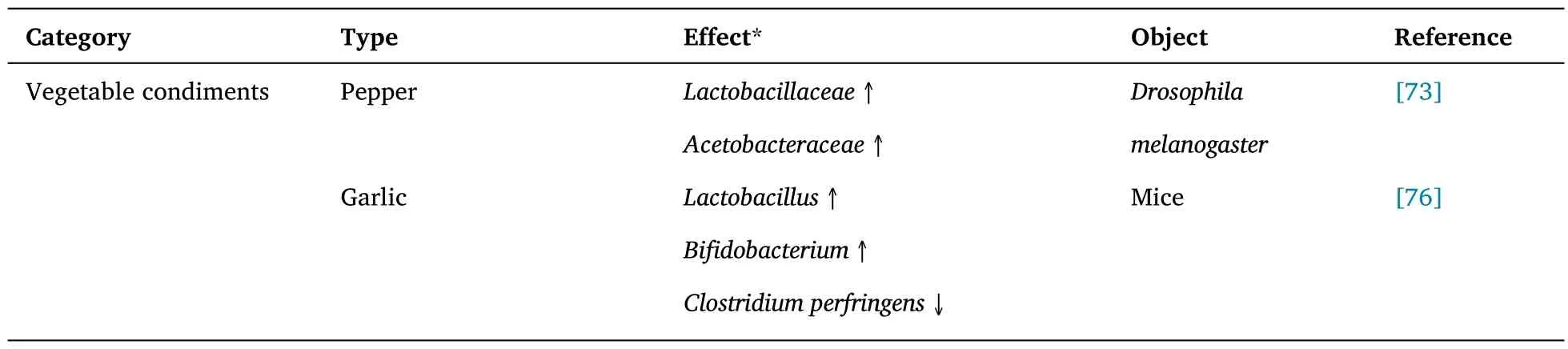
Table 2 The effects of food condiments on gut microbiota
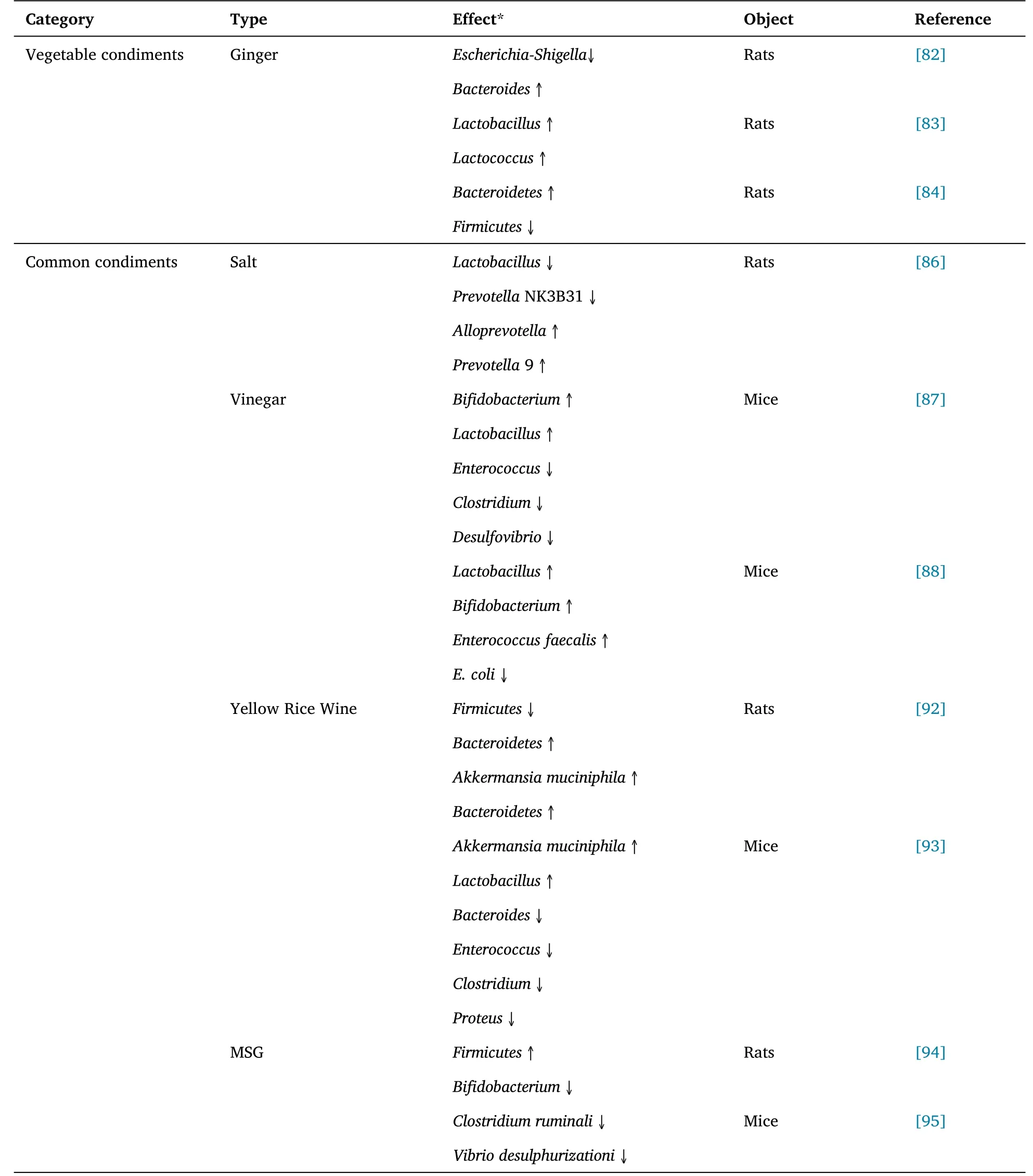
Table 2 The effects of food condiments on gut microbiota (Continued)
Food processing by-products
Food cooking is a conveninet means to improve food flavor and taste.Common cooking methods include: barbecue,frying,fumigation,etc.Studies have shown that different cooking methods can lead to changes in dietary composition and eventually lead to changes in gut microbiota [96].For example,due to the influence of temperature,time and other factors in the barbecue process,some components in meat will undergo chemical changes represented by Maillard reaction,producing a certain amount of polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons(PAHs) and heterocyclic aromatic amines (HAAs),increasing the risk of cancer and affecting the stability of gut micro-ecology [97,98].In the experiment carried out by Tang [99] on the interaction between the contents of camel digestive tract and HAAs(2-Amino-3-methylimidazo [4,5-f] quinoloneexists,IQ),it was found that the intake of HAAs could increase the abundance of microorganisms such asBacteroidetesandSphingobacteriiain camel gut.Zhang et al.[100] and Redfern et al.[101] showed the effects of another substance-PAHs on human and animal gut microbiota.Zhang et al.[100] showed that there was a negative correlation between microbiota (Bacteroidetes,Bacteroidia,andBacteroidales) and urinary hydroxyl PAHs (OH-PAH) levels under the influence of PAHs.The results of Redfern et al.[101]suggested that PAHs infection could affect the bacteria which contain sphingolipids in the gut of Atlantic killifish.benzo(a)pyrene(BaP)is a representative class of PAHs.In the study of young ginseng by Tao[102],the changes of gut microbiota inApostichopus japonicusexposed to BaP were revealed:the abundance ofPlanctomycetes,Proteobacteria,andBacteroideteswas increased,while the abundance ofFirmicuteswas decreased,which further revealed the toxic effect of BaP on gut health ofApostichopus japonicusand provided strong evidence for the study of PAHs.In addition to HAs and PAHs referred above,acrylamide (AA) produced by frying and baking are also potential carcinogens [103],and specific doses of intake may also have some impact on certain microorganisms in the gut [104,105].In the experimental study of the effect of AA on gut microbiota in mice carried out by Wang et al.[106],it was found that AA could reduce the abundance ofFirmicutesand increase the abundance ofBacteroidetes.The results of Petka et al.[104]confirmed the effect of this substance on the survival ability ofLactobacillus,such as beneficial effect onLactobacillus acidophilusLA-5 and harmful effect onLactobacillus plantarum.
In addition to the above common chemical derivatives,there are some other chemicals,such as: 1,2-dicarbonyl compounds (e.g.methylglyoxal,glyoxal) and advanced glycation end products (AGEs)[107-109],which may also affect the gut microbiota and cause intestinal diseases and metabolic disorders [110].Wang et al.[111]found that the intake of high-dose AGEs may reduce the number of butyrate-producing bacteria in the gut of mice (such asBacteroidales_S24-7,Ruminococcaceae,andLachnospiraceae).Theresults of Qu et al.[112] also showed that excessive intake of this substance may reduce the α-diversity of gut microbiota in mice and improve the level ofHelicobacterin the gut.Besides,Brighina et al.[113] suggested that over-processed foods rich in dicarbonyl compounds might reduce some important bacteria in human gut microbiota.Nitrite is widely used in meat processing,but under certain conditions,it can react with some substances in food (e.g.secondary amines,tertiary amines,etc.) to form N-nitrosamines (NAs,i.e.2A Carcinogen),which affect the health of human [31,114].In addition to meat processing sources,NAs are a by-product of tap water disinfection and relevant research data show that high-dose exposure of this substance will have a certain impact on the relative abundance ofFirmicutesandBacteroidetesin the gut of mice,and can improve the relative abundance ofAlistipesandRumenococcus[115].In fact,the effect of exogenous chemicals passively accepted by the body can be mediated by the host's gut microbiota,and improved by fecal transplantation or supplementation of some probiotics to alleviate related diseases and inflammatory reactions [116,117].For example,the supplement ofEubacterium halliican participate in the degradation of HAs[118,119],andLactobacillus casei SB27is involved in reducing the toxicity of NAs to IEC-6 cells [114].Meanwhile,previous studies have also confirmed that the participation of probiotics (such asBifidobacteriumandLactobacillus)and their metabolites can play a role in the degradation and inhibition of harmful chemicals and have acertain beneficial impact on human and animal health [117,120].For example,Urlithin A can inhibit the production of AGEs [121],while Lactobacillin tablet can improve the structure of human gut microbiota and promote the alleviation of related inflammation[122].The effects of some food processing by-products on gut microbiota are listed in Table 3.
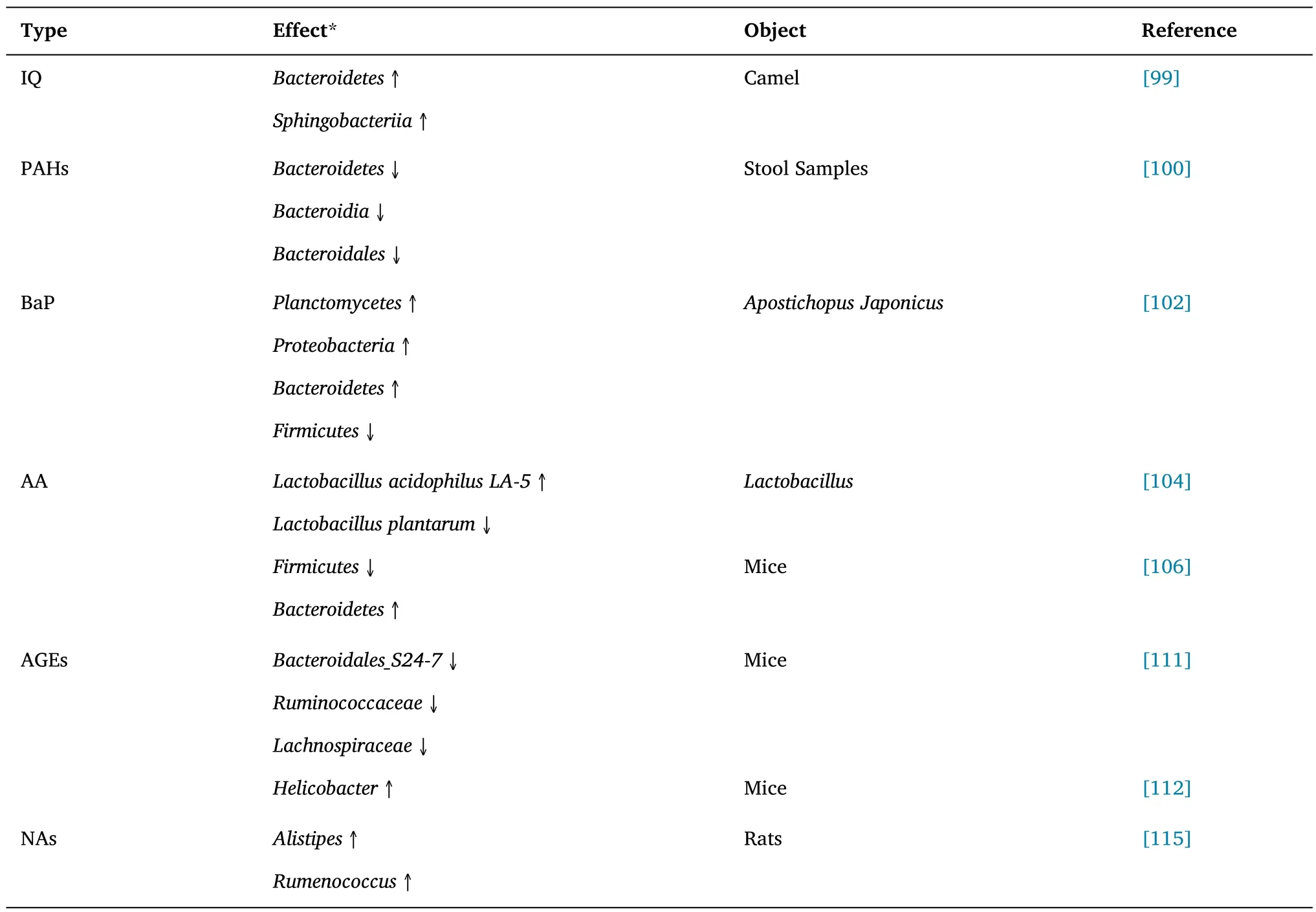
Table 3 The effects of food processing by-products on gut microbiota
Dietary intervention and gut microbiota
Dietary intervention is an important way to improve gut micro-ecology.There may be some differences in the structure and composition of gut microbiota of humans and animals under different living and dietary habits (e.g.,participation in exercise and eating lightly) [123-125].Obesity,as a common health problem,is the main research object of diet intervention therapy.The synergistic effect of diet and gut microbiota is one of the influencing factors of obesity and its complications [126].Therefore,the change of gut microbiota is also considered an important target in this regulation process[127-129].Related studies have shown that long-term or excessive intake of high fat and high calorie food will cause obesity and the two factors (fat and calories) can also affect gut microbiota [130-132].Therefore,in daily life for our own health,we should pay attention to the regulation of eating habits,consciously control the intake of heat and fat.The study of Sbierski-Kind et al.[132] showed the changes of gut microbiota and fat accumulation in mice under heat control.The results showed that some microbes in the gut of obese patients under specific conditions (800 kcal/day for 8 weeks) were transplanted into mice,which not only reduced fat accumulation and improved glucose tolerance,but also reduced the abundance ofClostridium ramosum,Hungatella hathewayi,Alistipi obesiand other microorganisms to a certain extent.Ketogenic diet is a widely used diet in the fields of obesity,diabetes,and other diseases in recent years.This method refers to the user by eating the diet with high fat content,low carbohydrate content,and the suitable proportion of other substances,so that the organism's energy supply was transferred from glucose to ketone body,so as to further promote the catabolism of fat,showing a certain adjuvant therapeutic effect [133].However,this extreme eating habits with nutritional imbalance may have a positive impact on many diseases,but its long-term application may still induce organ damage and inflammatory reaction,and has a certain impact on the rhythm and metabolism of gut microbiota [134-137].Therefore,we should choose a more healthy lifestyle for weight control,such as a Mediterranean diet (MED),and compared with ketogenic diet,this method has slower effect on weight loss of specific population and needs longer time,but it has certain advantages in energy balance and other aspects.MED,as a healthy and classical diet,can effectively regulate gut microbiota,improve physical condition,and reduce the risk of many diseases [138,139].Rinott et al.[140] found that both the intervention of green Mediterranean diet (Green-MED,i.e.increasing the proportion of plant foods based on the MED) and MED could alter gut microbiota in patients with abdominal obesity and dyslipidemia,but the changes caused by the improved Green-MED were more pronounced,including enrichment ofPrevotellaand reduction ofBifidobacterium.In addition to the above common dietary interventions,obesity and its complications can also be effectively improved by transplanting or“eating” some beneficial bacteria[141].Gao et al.[142] used metagenomic analysis to study 40% of high-fat-resistant cynomolgus monkeys screened during high-fat diet,and found that the relative abundance ofMegasphaerain the gut of these monkeys was significantly increased,and the possibility of this microbial-assisted host blood lipid phenotype change was demonstrated by fecal transplantation.The results of Liu et al.[143]confirmed thatLactobacillus paracasei24 could alleviate the lipid accumulation of obese mice induced by high-fat diet and regulate the bacterial community structure of mice by reducing the number ofFirmicutesand increasing the abundance ofAkkermansia muciniphila.
Conclusion and prospect
In summary,as an important indicator of human and animal health,it is significant to study the impact of exogenous substances in food on gut microbiota.At present,based on the relevant literature and application examples worldwide,some exogenous substances,including food additives,food condiments,and food processing by-products,can affect the composition and structure of microorganisms in human and animal gut to a certain extent.Furthermore,this influence or change from exogenous factors is sometimes constrained by material intake dose.Although some scholars have verified the intake range of some additives and their specific effects by experimental methods,which has promoted the research and development of some exogenous substances to a certain extent,there is still a problem of less experimental data on the whole,and further research should be continued.In addition,these so-called effects are sometimes good or bad.Some vegetable condiments,such as ginger,garlic,pepper and so on,are similar to other plant foods.They contain rich endogenous active substances,which can play a role in some functions or activities of the body and improve human health.But for some synthetic chemicals or chemical derivatives produced during cooking,they can increase the risk of cancer,gastrointestinal diseases,and other diseases,and can also cause the disorders of gut microbiota.And the above research also shows that the natural extracted food additives may also have a certain impact on the changes of gut microbiota.At present,researchers have studied more in the field of food additives,environmental pollutants,and some endogenous active substances,but less in the field of condiments.As a common food additive,condiments will help improve the quality of products by studying their effects on human and animal gut microbiota.In summary,the measurement and evaluation of exogenous food additives by studying the changes of gut microbiota can help us fully understand the impacts of these substances on humans and animals,standardize the development and application of new products,and promote the development of food industry.
Data availability statement
This paper is a review,and the data used in this review are all from the references at the end.The relevant data can be obtained by visiting the doi or web address of corresponding references.
- Food and Health的其它文章
- Probable beneficial effects of black seeds (Nigella sativa) in the management of langya henipavirus infection
- Anxiety disorder:definition,symptoms,causes,epidemiology and treatments
- Investigation physico-chemical characterization of jaggery from different sugarcane varieties
- Research progress of metal chelating peptides
- Comment on"The association between dairy products and the risk of COVID-19"

