Importance of genetic data from type specimens:The questionable type locality of southern white-cheeked gibbon,Nomascus siki (Delacour,1951)
DEAR EDITOR,
Many historical descriptions of new species have included vague or inaccurate information about the type locality.This can lead to confusion in the study of the species and their geographic distributions,thereby hindering conservation efforts.One such example is the southern white-cheeked gibbon (Nomascus siki(Delacour,1951)).The type locality is given as Thua Luu in central Vietnam,which is located within the range of another crested gibbon species (N.annamensis)and more than 200 km south of the known range ofN.siki.To investigate the problematic type locality ofN.siki,we sequenced the mitochondrial genome of the holotype and compared its cytochromebgene sequence to those of other georeferenced crested gibbon samples.As expected from the phenotype,theN.sikiholotype clustered with the otherN.sikispecimens,but not with the parapatric or even sympatric samples of gibbons from the region close to its type locality(distance <5 km).This suggests that the type locality may not be the place where the specimen was collected in the wild.Our study highlights the importance of genetic data from name-bearing types,as they represent an important reference for taxonomic and biogeographic research.
Formal descriptions of new species are based on at least one specimen,namely the holotype (Sluys,2021).Descriptions normally entail physical information about the specimen itself,e.g.,sex,age (class),measurements,and external appearance,as well as its geographic provenance,i.e.,type locality.However,it is not uncommon to find that information regarding provenance is incorrect or unclear(Steinheimer &Dean,2007),leading to confusion in subsequent studies of the species and their geographic distributions.Likewise,it is often unclear whether the type locality provided is the site of collection in the wild or whether specimens were obtained third-hand at that place,e.g.,coastal harbor towns are sometimes mentioned as type localities.
Herein,we present the southern white-cheeked gibbon (N.siki) as one such example.According to the original description (Delacour,1951),theN.sikiholotype (Figure 1A)was collected by Jean Delacour and Pierre Jabouille on 4 February 1931 in “Thua-luu,au sud de Huê,Centre-Annam”(Delacour,1951:122) (=Thua Luu,South of Hue,central Annam=Thua Luu,Thua Thien-Hue Province,central Vietnam;N16°16′,E108°00′;Figure 1B) and later described as a new taxon (Hylobates concolor sikiDelacour,1951).Based on this and other specimens obtained in Hue (Thua Thien-Hue Province,Vietnam),Tourane (=Da Nang,Vietnam),Lao Bao(Quang Tri Province,Vietnam),Tchépone (=Xepon,Savannakhet Province,Laos),Napé (=Ban Nape,Bolikhamxai Province,Laos),and Nakai (Khammouane Province,Laos),Delacour (1951) concluded that the taxon occurs in central Annam (Vietnam) and neighboring Laos (Figure 1B).
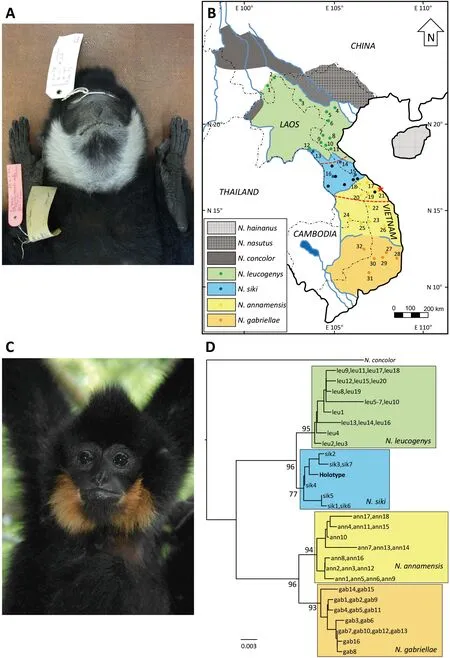
Figure 1 Photographs of N.siki and N.annamensis,distribution map of crested gibbons,and phylogeny of “l(fā)ight-cheeked” gibbons
Nomascus sikiis one of seven species belonging to the clade known as “crested gibbons” (genusNomascus)(Beauséjour et al.,2021;Mittermeier et al.,2013,Roos et al.,2014).Crested gibbons exhibit sexual dimorphism in fur coloration.Adult males are usually black,with the four southern species possessing white (N.leucogenys,N.siki) or yellow (N.annamensis,N.gabriellae) cheeks,hence collectively known as the light-cheeked gibbons.In contrast,adult females are yellowish or cream in body color,with a blackish crown patch or streak (Geissmann,1995,2007;Geissmann et al.,2000;Groves,2001;Mootnick,2006;Mootnick &Fan,2011).Thus,in addition to genetics(mitochondrial DNA sequence data) and vocalization(Geissmann et al.,2000;Konrad &Geissmann,2006;Monda et al.,2007;Roos et al.,2007;Ruppell,2010;Takacs et al.,2005;Thinh et al.,2010a,2010b,2011;Zhang,1997),pelage color pattern,particularly in males,is an important distinguishing characteristic of crested gibbon species(Geissmann,1995,2007;Geissmann et al.,2000;Groves,2001;Mootnick,2006;Mootnick &Fan,2011).
The type locality ofN.siki(Thua Luu) is close (<5 km) to Bach Ma National Park (N16°05–15′,E107°43–53′;Figure 1B,locality ID 21).Indeed,the holotype may have come from this park,as another museum specimen (NRM 8 747) collected by Bertil Bj?rkegren in March 1939 and stored in the Swedish Museum of Natural History,Stockholm,is labelled with the locality information “Bach Ma,Thua Luu” (Geissmann et al.,2000).However,the cheeks of this specimen are yellow rather than white,as found inN.siki(Geissmann et al.,2000).
In recent decades,it has been shown that gibbons from Bach Ma National Park and surrounding areas differ from typicalN.sikispecimens in phenotype (e.g.,yellow instead of white cheek patches) and vocalization (Geissmann,1995,2007;Geissmann et al.,2000;Konrad &Geissmann,2006;Ruppell,2010).Consequently,the validity of Thua Luu as the type locality ofN.sikihas been questioned (Duckworth,2008;Geissmann et al.,2000;Konrad &Geissmann,2006).Furthermore,during range-wide genetic and acoustic analyses of crested gibbons (Thinh et al.,2010b,2010c,2011) and a subsequent taxonomic revision of the genus,the gibbons of central Vietnam and neighboring areas in Laos,including the population of Bach Ma National Park,were identified as a new speciesN.annamensisThinh et al.,2010c (Figure 1C).As a result of this extensive research and classification,the putative type locality ofN.sikifell deep within the range ofN.annamensisand ca.200 km south of its southernmost known geographic limit (Thinh et al.,2010c).Delacour collected gibbons not only at the type locality but also at several other sites (see Figure 1 in Delacour (1951)).Except for the holotype and a specimen from the Danang vicinity and probably another one from Hue vicinity (if not the holotype),all other specimens mentioned by Delacour from Vietnam (Lao Bao) and Laos (Xepon,Ban Nape,and Nakai) are in the known range ofN.siki(Figure 1B).
In the absence of novel archival or historical information and to help elucidate the type locality ofN.siki,we sequenced the complete mitochondrial genome (mitogenome) of the holotype using next-generation sequencing methods and phylogenetically related the obtained sequence with a large set of available cytochromebgene sequences of known,georeferenced crested gibbon samples (Thinh et al.,2010b,2010c).We collected a small piece of skin (ca.5 mm×5 mm)of theN.sikiholotype (NHMUK ZD.1933.4.1.6(a);Figure 1A)stored at the Natural History Museum,London,United Kingdom (NHMUK).DNA was extracted in the ancient DNA laboratory of the German Primate Center using a columnbased method specifically designed to recover degraded DNA fragments (Dabney et al.,2013;Rohland et al.,2004).After extraction,DNA concentration was measured with a Qubit 4.0 fluorometer (ThermoFisher Scientific,USA),and DNA quality and degradation were checked using a Bioanalyzer 2 100(Agilent Technologies,USA).Genomic DNA (50 ng) was then used to construct a shotgun sequencing library with the NEBNext Ultra II DNA Library Prep Kit (New England Biolabs,USA) following standard protocols of the supplier (DNA fragmentation before library preparation was omitted).After end repair,adapter ligation,and ligation cleanup without size selection,the library was indexed with multiplex oligos and then cleaned with purification beads from the kit.Library concentration and size distribution were determined via Qubit and Bioanalyzer measurement,respectively,and molarity was quantified by quantitative polymerase chain reaction (qPCR)using the NEBNext Library Quant Kit (New England Biolabs,USA).Sequencing,together with 23 other libraries,was conducted on one lane of an Illumina HiSeq 4 000 sequencer(100 bp single-end read) by the core unit of NGS Integrative Genomics (NIG) at the University Medical Center Goettingen,Germany.Raw sequencing reads were demultiplexed with Illumina software.The subsequent bioinformatic analyses were performed with the Geneious Prime 2 021.2.2 package(https://www.geneious.com/).First,we trimmed and qualityfiltered reads with BBDuk v38.84 in the BBTools package(https://jgi.doe.gov/data-and-tools/bbtools/) and then removed duplicate reads with Dedupe v38.84 (BBTools package),both with default settings.We then mapped reads onto theN.sikireference mitogenome (GenBank accession No.NC_014051)using the Geneious Assembler with default settings (maximum five iterations).After trimming,quality-filtering,and duplicate removal,19 636 050 of the original 22 368 573 sequence reads remained,17 784 of which were mapped onto theN.sikireference mitogenome,resulting in a complete mitogenome of theN.sikiholotype,with a high average sequence depth of 94.6× and total length of 16 476 bp.The newly produced mitogenome was manually checked,annotated with Geneious,and submitted to GenBank (accession No.OM287160).Alignment was conducted using Muscle v3.8.31(Edgar,2010) in AliView v1.18 (Larsson,2014) with the cytochromebgene sequences (1 140 bp) of theN.sikiholotype and 61 other light-cheeked crested gibbons (N.leucogenys:n=20,N.siki:n=7,N.annamensis:n=18,N.gabriellae:n=16;for details see Supplementary Table S1 and Thinh et al.(2010b)).Nomascus concolorwas used as the outgroup.A maximum-likelihood tree was reconstructed with IQ-TREE v2.1.3 (Minh et al.,2020) with 1 000 ultrafast bootstrap replicates (Hoang et al.,2018) and the best-fit substitution model (TN+F+I) was automatically calculated with ModelFinder (Kalyaanamoorthy et al.,2017) in IQ-TREE according to Bayesian information criterion.
We obtained strong nodal support for all major clades(>70%) and found that light-cheeked gibbons initially diverged into white-cheeked (N.leucogenys,N.siki) and yellowcheeked (N.annamensis,N.gabriellae) forms,with further division into corresponding northern and southern species(Figure 1D),consistent with earlier studies (Thinh et al.,2010b,2010c).Corresponding to its phenotype (white cheeks),theN.sikiholotype was nested within theN.sikiclade and did not cluster with the para-/sympatric samples from Bach Ma National Park (samples ann5-7),which were clearly nested within theN.annamensisclade.The gibbons from Bach Ma National Park also exhibit the typical song repertoires and phenotypic traits of yellow-cheekedN.annamensis,rather than white-cheekedN.siki(Geissmann,1995,2007;Geissmann et al.,2000;Konrad &Geissmann,2006;Ruppell,2010;Thinh et al.,2010b,2010c,2011).Nevertheless,we were unable to locate the source population of theN.sikiholotype.Although mitochondrial sequence data can allow the taxonomic diagnosis of crested gibbon species,information on geographic structure cannot be determined as haplotypes are often shared among different local populations.This is likely because,in contrast to many other primate species,female gibbons are not philopatric (Brockelman et al.,1998;Matsudaira et al.,2018),thus contributing to the geographic mixing of matrilineally inherited mitochondrial haplotypes.
From our analysis,it is evident that the type locality ofN.sikiis problematic.Unfortunately,there is no information available on how Jean Delacour and Pierre Jabouille obtained the holotype specimen.Furthermore,the corresponding field notes are not traceable,either in NHMUK or any other natural history museum where Delacour’s field notes may exist.One explanation for the incorrect type locality may be that Delacour and Jabouille,like other collectors,received or purchased the specimen from local people who had kept the animal as a pet or for trade.Thua Luu is close to the Vietnamese coast and Vietnam’s Highway No.1,which has been the country’s major trading route for centuries (Logan,2002).Hence,the specimen may have arrived by trade from a wild origin other than Thua Luu.However,if the specimen was indeed collected at Thua Luu,various explanations are possible.First,the specimen may have been a previously released or escaped pet.Second,a small enclave population ofN.sikimay have existed historically (but not currently) near Thua Luu,surrounded by a larger population ofN.annamensis.Third,the historical geographic distribution of the two species may have differed substantially from current distributions,withN.annamensisreplacing a viableN.sikipopulation at Thua Luu/Bach Ma National Park in recent decades.However,the latter two explanations are unlikely as a yellow-cheeked specimen (NRM 8 747) was collected at the same (or nearly the same) site as the type specimen (“Bach Ma,Thua Luu”)only eight years after Delacour and Jabouille,indicating that a yellow-cheeked phenotype (N.annamensis) already existed at that time.Fourth,Thua Luu/Bach Ma National Park may be a natural hybridization zone betweenN.sikiandN.annamensis.However,this also seems unlikely as the distribution ranges ofN.sikiandN.annamensisare separated by large river barriers,as with most crested gibbon species.Hence,hybridization betweenN.sikiandN.annamensiscould only occur along the narrower upper river reaches,not 200 km away from such a barrier.Consequently,if the given type locality is correct,the specimen was most likely a released or escaped former pet or was obtained at the site from local people.
The debatable geographic record of the type locality has resulted in uncertainty regarding the number of extant crested gibbon species and their distribution ranges,thus hindering conservation for these (critically) endangered small apes.Notably,the geographic range ofN.sikiwas believed to be much larger,but the taxonomic revision of crested gibbons by Thinh et al.(2010c) reassigned several populations previously thought to beN.sikitoN.leucogenysorN.annamensis,significantly reducing the number ofN.sikipopulations(Nguyen et al.,2020).
Our study verified that genetic data from type specimens can help address long-standing taxonomic and biogeographic questions.In our example,a precise but likely incorrect type locality was provided with the original description of a new small ape species.In historical species descriptions,type locality information can be ambiguous or inaccurate,e.g.,providing only the name of the country where the specimen was collected or the harbor/trading town where the specimen was purchased (Roos et al.,2021).In such cases,genetic data can be an important tool for reassessing or rejecting the geographic origin of such specimens,or at least integrating them into valid taxa if comparable genetic information from conspecifics and congenerics is available.Even given accurate and correct type localities,genetic data can still be helpful,e.g.,when the type locality is close to a biogeographic barrier,such as a river,and the side from which the specimen was collected is unclear and needs to be more precisely determined (Boubli et al.,2021).Overall,genetic information from name-bearing types provides an important resource for taxonomic and biogeographic research and can inform conservation efforts.
SUPPLEMENTARY DATA
Supplementary data to this article can be found online.
COMPETING INTERESTS
The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
AUTHORS’ CONTRIBUTIONS
C.R.,T.N.,and V.N.T.conceived and designed the study.R.P.M.provided the holotype sample.C.R.analyzed the data.C.R.and D.Z.wrote the paper.All authors discussed the data and read and approved the final version of the manuscript.
ACKNOWLEDGEMENTS
We are grateful to Christiane Schwarz for laboratory work,Anna Barros for theN.sikiholotype photograph,Lawrence Heaney,Adam Ferguson,Cécile Callou,and Audrey Maille for investigating their archives,Douglas Brandon-Jones for help with tracing Delacour’s field notes,and four anonymous reviewers for helpful comments on an earlier version of the manuscript.
Christian Roos1,2,*,Roberto Portela Miguez3,Dietmar Zinner4,5,6,Tilo Nadler7,Van Ngoc Thinh8
1Gene Bank of Primates,German Primate Center,Leibniz Institute for Primate Research,Goettingen37077,Germany
2Primate Genetics Laboratory,German Primate Center,Leibniz Institute for Primate Research,Goettingen37077,Germany
3Natural History Museum,London SW7 BD,UK
4Cognitive Ethology Laboratory,German Primate Center,Leibniz Institute for Primate Research,Goettingen37077,Germany
5Leibniz Science Campus Primate Cognition,Goettingen37077,Germany
6Department of Primate Cognition,Georg-August-University,Goettingen37083,Germany
7Three Monkeys Wildlife Conservancy,Cuc Phuong Commune,Nho Quan District,Ninh Binh Province,Vietnam
8World Wide Fund for Nature (WWF) Vietnam,Nam Tu Liem District,Hanoi,Vietnam
*Corresponding author,E-mail:croos@dpz.eu
- Zoological Research的其它文章
- Zoological Research call for papers of Cavefish Special Issue
- Fuel source shift or cost reduction:Context-dependent adaptation strategies in closely related Neodon fuscus and Lasiopodomys brandtii against hypoxia
- Ecological study of cave nectar bats reveals low risk of direct transmission of bat viruses to humans
- Population and conservation status of a transboundary group of black snub-nosed monkeys (Rhinopithecus strykeri) between China and Myanmar
- Nucleus accumbens-linked executive control networks mediating reversal learning in tree shrew brain
- Europe vs.China:Pholcus (Araneae,Pholcidae) from Yanshan-Taihang Mountains confirms uneven distribution of spiders in Eurasia

