Effect of three tongue needles acupoints Lianquan (CV23) and Hegu(LI4) combined with swallowing training on the quality of life of laryngeal cancer patients with dysphagia after surgery
ZHU Xuewei,LIU Minghui,ZONG Minru,CHEN Qianqian,WANG Jianfeng
ZHU Xuewei,Department of otolaryngology head and neck surgery,China-Japan Union Hospital of Jilin University,Changchun 130033,China
LIU Minghui,Department of Chinese traditional Medicine,China-Japan Union Hospital of Jilin University,Changchun 130033,China
ZONG Minru,Department of rehabilitation,China-Japan Union Hospital of Jilin University,Changchun 130033,China
WANG Jianfeng,CHEN Qianqian,Department of Radiotherapy,China-Japan Union Hospital of Jilin University,Changchun 130033,China
Abstract OBJECTIVE:To evaluate the effect of acupuncture therapies administered in combination with swallowing training on the quality of life of laryngeal cancer patients with dysphagia after surgery.METHODS:Seventy-one postoperative patients with laryngeal cancer participated in this study.The patients diagnosed with swallowing dysfunction by video fluoroscopic swallowing examination (VFSE) were randomly divided into experimental group (n= 36) and control group (n= 35).Patients in both groups were provided swallowing training and rehabilitation consultation.Patients in the experimental group were additionally provided with acupuncture therapies.All patients were evaluated using VFSE and MD Anderson dysphagia inventory (MDADI) and Quality of Life Questionnaire-core 30 (QLQ-c30) score immediately after surgery and three months later.RESULTS:The effective rate of 97.1% (n= 35) and the complete remission rate of 36.1% (n= 13) in the experimental group were higher than those in the control group of 60% (n= 21) and 14.3% (n= 5) (P <0.01).The scores of VFSE,MDADI and QLQ-c 30 in the experimental group and the control group at three months after therapies were significantly improved compared with those before therapies (P <0.05).The scores of VFSE,MDADI and QLQ-c30 in the experimental group at three months after therapies were significantly improved compared with the control group.The improvement in the intervention group was significantly better than that in the control group.There were no adverse reactions in two groups.CONCLUSIONS:Acupuncture therapies combined with swallowing training can improve the swallowing function and the quality of life of laryngeal cancer patients with dysphagia after surgery.
Keywords:laryngeal neoplasms;deglutition disorders;acupuncture;swallowing training;quality of life
1.INTRODUCTION
Dysphagia is one of the common complications in laryngeal cancer patients after surgery.Approximately 30%-50% of patients have variable degrees of dysphagia due to tumor invasion and surgery.Dysphagia affects the intake of energy,protein and water,leading to complications such as dehydration,malnutrition and aspiration pneumonia,which have a serious impact on the therapeutic efficacy and the quality of life (QoL) of those patients.1,2
At present,scholars have realized the harm of dysphagia and carried out training of swallowing function in head and neck cancer patients.Swallowing training is the basic method to treat swallowing disorders and improves swallowing function and depression in postoperative tongue cancer patients.But it is still a weak link in postoperative rehabilitation.3,4
Acupuncture has been used in Traditional Chinese Medicine (TCM) for more than 3000 years as a therapeutic method for many types of health problems such as pain,dysphasia and so on.5Acupuncture is widely used in the therapies of swallowing dysfunction after stroke,and is considered to be simple,safe and effective.6,7Previous studies have suggested that acupuncture can accelerate restoration of swallowing function by establishing new synaptic connection.8
The adverse effect of dysphagia in patients with laryngeal cancer patients and the functional improvement brought by acupuncture therapies is a focus area for research.Acupuncture therapies for patients with dysphagia have also evoked considerable attention.However,the effect of acupuncture therapies administered in combination with swallowing training on the clinical outcomes is not well characterized.Therefore,in this study we aimed to evaluate the effect of acupuncture therapies combined with swallowing training on the QoL of laryngeal cancer patients with dysphagia after operation.
2.MATERIALS AND METHODS
2.1.Participants
Clinical materials:71 patients with dysphagia after laryngeal cancer diagnosed in the China-Japan Union Hospital of Jilin University from January 2020 to June 2021 were selected.
The inclusion criteria:(a) after total laryngectomy,pathologically confirmed as squamous cell carcinoma;(b)diagnosed as swallowing dysfunction by VFSE;(c)Karnofsky score ≥ 70;(d) able to understand and answer the questionnaire correctly;(e) patients and their families were informed of this study and signed the informed consent.
The exclusion criteria:(a) existence of cognitive dysfunction;(b) severe cardiovascular and cere-brovascular complications;(c) other diseases affecting swallowing function;(d) cannot tolerate acupuncture therapies and rehabilitation training;(e) mental illness.
The study protocol was approved by the Institutional Review Board of the China-Japan Union Hospital of Jilin University (No.201907027).The patients were divided into the experimental group (n=36) and the control group (n=35) by random number table method.The general data of two groups of patients,such as gender,age,stage,education level,family income,was not statistically significant (P>0.05) (Table 1).
Table 1 Comparison of general data of patients in 2 groups before training ()

Table 1 Comparison of general data of patients in 2 groups before training ()
Notes:experimental group:treated with swallowing training,rehabilitation consultation and acupuncture therapies;control group:treated with swallowing training and rehabilitation consultation.CNY:China Yuan.
2.2.Interventions
Research team members included oncological physician,rehabilitation physician,nutritionists,acupuncturist and speech therapist agreed with the protocol.The study started two weeks after surgery.VFSE,health counseling,and questionnaire were regularly accomplished by an oncology physician and a rehabilitation physician who had greater than 3 years of clinical experience on screening and management of dysphagia.Swallowing training and acupuncture were performed by a speech therapist and an acupuncturist who have received professional clinical training respectively.Both groups received rehabilitation guidance and swallowing training,and the experimental group added acupuncture therapies on this basis.The procedure was conducted once a day,over 3 months of therapies.
2.3.Rehabilitation guidance
Rehabilitation guidance included health consultation and nutrition education,once a week,30 min each time.According to the type and degree of the patient’s swallowing dysfunction,to help the patients to develop an individualized diet plan,conduct a diet analysis to calculate the daily intake of energy and nutrients.The target feeding amount is 6-7 kJ·kg-1·d-1for total energy and 1.2-1.5 g·kg-1·d-1for total protein.When the dietary intake does not reach the target,oral nutritional supplements or nasogastric tube treatment was given to achieve the target requirement.
2.4.Swallowing training protocol
The swallowing training protocol was designed based on the experience of the research team in order to improve swallow function.Two training options were available:indirect and direct.Indirect training was to strengthen muscles related to swallowing activities,included tongue resistance,tongue base retraction,mendelson manoeuvre,supraglottic swallow and jaw exercises.Direct training included to choose feeding environment,swallowing position,different textures and tastes of food,the most suitable amount of swallowing,removal of pharyngeal residues and so on.The therapy was conducted for 30 min once a day,7 d a week for three months.
2.5.Acupuncture therapies
The acupuncture procedure was conducted as follows.After normal disinfection of the acupoints,three tongue needles and Hegu (LI4) on both hands were punctured respectively.The three tongue needles acupoints are located at Lianquan (CV23) point in the depression on the upper edge of the hyoid bone and the 0.8cunpoints on both sides.The method of operation is to slightly tilt the needle tip and the 4.0cm filamentary needle tip (0.25 mm × 40 mm) to a depth of 0.8-1cun.Hegu (LI4)acupoint is located in the depression between the first and second metacarpal bones of the hand.Puncture straight 1cun.It is best to feel sour and swelling.These 5 points were evenly supplemented and reduced.The needles were pulled after the De Qi.The entire therapy was conducted for 3 months,once a day for 30 min.
2.6.Efficacy and safety assessment
Before therapies and 3 months after therapies,the swallowing function was evaluated by VFSE and MD Anderson Dysphagia Inventory (MDADI);QoL was evaluated by Quality of Life Questionnaire-Core 30(QLQ-C30).To observe the symptoms of cough,expectoration and choking in two groups,and conduct chest CT to understand the rate of pulmonary infection if necessary.The occurrence of subcutaneous congestion,hematoma,pain,syncope,arrhythmia and other adverse reactions in acupuncture therapies group were observed.VFSE has a high sensitivity in comprehensive evaluation of oropharyngeal swallowing efficiency (includes silent aspiration and post-swallow pharyngeal residue) and the therapeutic efficacy.The process of swallowing is recorded as a video.Score range is 0-12,0 is normal,1-4 is mild,5-8 is moderate,9-12 is severe.The higher the score is,the more severe dysphagia is.Decreased scores indicate that therapies are effective.9
MDADI represents the most widely employed patientreported outcome metric for the assessment of swallowing through questions directed at the emotional,functional,and physical impact of patient-perceived function.The MDADI is a 20-item self-administered questionnaire that quantifies swallowing-related QoL.Each item is scored on a 5 point Likert scale.The MDADI quantifies an individual’s global,physical,emotional,and functional perceptions of their swallowing ability.10
QLQ-C30 is the most validated questionnaire of life tool in oncology and widely used all over the world.It consists of three sections as general health status scale,functional scale,and symptom scale,and with 30 questions in total.11
2.7.Data analysis
The data were processed with SPSS 20.0 (IBM Corp.,Armonk,NY,USA) by independent statisticians.Thettest for continuous data was conducted after the Kolmogorov-Smirnov test for normality.A pairedsamplest-test was used for intra-group comparison,while an independent-samplest-test was used for comparison among groups.Non-normal data were subjected to nonparametric test.Ranked data were compared using a rank-sum test.Enumeration data was identified by the χ2test.Pvalues less than 0.05 were considered statistically significant.
3.RESULTS
The effective rate was 97.1% (n=35) and the complete remission rate of 36.1% (n=13) in the experimental group were higher than those of the control group of 60% (n=21) and 14.3% (n=5) (P<0.01).The comparison of VFSE before and after treatment was shown in Figure 1.
Figure 1 Comparison of VFSE before and after treatment
3.1.Efficacy evaluation
The scores of VFSE,MDADI and QLQ-c 30 were presented in Table 2.Before therapies,there was no significant difference in scores of VFSE,MDADI and QLQ-c 30 between two groups (P>0.05).The scores of VFSE,MDADI and QLQ-c 30 in two groups at 3 months after therapies were significantly improved compared with those before therapies (P<0.05).The scores of VFSE,MDADI and QLQ-c 30 in experimental group at 3 months after therapies were significantly improved compared with the control group(P<0.05).There was a significant difference between two groups with respect to the scores obtained at 3 months after surgery in Table 3.
Table 2 Scores of VFSE,MDADI and QLQ-c 30 before therapies and 3 months after therapies in two groups (scores,)
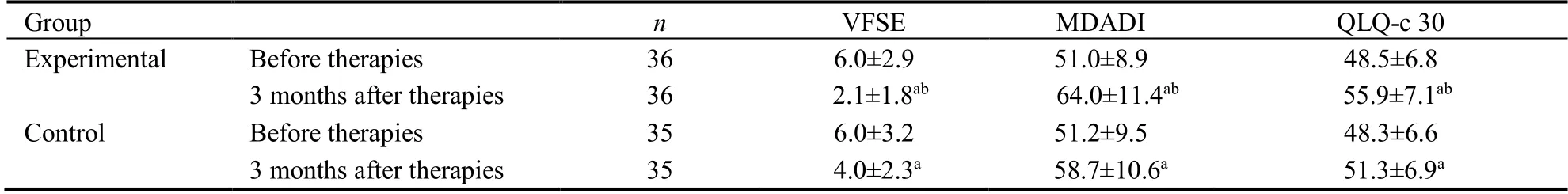
Table 2 Scores of VFSE,MDADI and QLQ-c 30 before therapies and 3 months after therapies in two groups (scores,)
Notes:experimental group:treated with swallowing training,rehabilitation consultation and acupuncture therapies;control group:treated with swallowing training and rehabilitation consultation.VFSE:video fluoroscopic swallowing examination;MDADI:MD Anderson dysphagia inventory;QLQ-c30:qQuality of life questionnaire-core 30.Compared with the same group,aP <0.05,compared with the control group,bP <0.05.
Table 3 Difference between before therapies and 3 months after therapies on VFSE,MDADI,QLQ-c 30 scores in two groups (scores,)

Table 3 Difference between before therapies and 3 months after therapies on VFSE,MDADI,QLQ-c 30 scores in two groups (scores,)
Notes:experimental group:treated with swallowing training,rehabilitation consultation and acupuncture therapies;control group:treated with swallowing training and rehabilitation consultation.VFSE:video fluoroscopic swallowing examination;MDADI:MD Anderson dysphagia inventory;QLQ-c30:quality of life questionnaire-core 30.Compared with the control group,aP <0.05.
3.2.Safety evaluation
There were no pulmonary infections in two groups;there were no adverse reactions such as subcutaneous congestion,hematoma,pain,syncope,and arrhythmia after acupuncture therapies.
4.DISCUSSION
Swallowing is a complex process involving multiple muscles,cranial nerves and reflexes,and requires the coordination of the oral cavity,pharynx,larynx and esophagus.Due to tumor invasion and surgery,dysphagia is very common in laryngeal cancer patients after laryngectomy.Dysphagia causes dehydration,malnutrition due to difficulties and fear of taking food,seriously affects the therapeutic effect and reduces the QoL.12,13
In this study,in order to find the laryngeal cancer patient with dysphagia,the patients undergo VFSE two weeks after the operation.This helps us to find patients who need rehabilitation treatment early.Swallowing training was used as the basis for rehabilitation of patients with dysphagia after laryngeal cancer surgery.14The functional training of the lips,tongue,and mandible is to increase muscle strength,improve the ability to control food,alleviate the retraction of the tongue base,and enhance the ability to drive food movement.Stimulation on the throat with frozen cotton swab can increase the sensitivity of swallowing reflex on the pharynx and soft palate.Mendelssohn manipulation can significantly improve the throat elevation.Swallowing training can obviously promote the blood circulation of the swallowing organs,to improve the coordination and flexibility of the pharyngeal muscles,and form a normal swallowing process that avoids aspiration.Kraaijengaet al15found that the training intervention of the lips,mandible,tongue and swallowing muscles improves the activity of the tongue and oropharyngeal muscles,and improves swallowing function.Gaoet al16showed that swallowing training for patients with head and neck tumors can improve swallowing function,and increase their nutritional intake.This study found that swallowing rehabilitation training played a positive role,and the swallowing function of patients with dysphagia after laryngeal cancer surgery was significantly improved.
The receptors in the soft palate and pharynx are stimulated by food;the impulse is transmitted to the medulla oblongata.Muscles controlled by the cranial nerves,such as the face nerve,the tongue nerve,the vagus nerve,and hypoglossal nerve,complete the swallowing.Therefore,local stimulation is of great significance to the treatment of this disease.Acupuncture can not only directly stimulate the swallowing muscles,but also effectively stimulate the glossopharyngeal nerves,improve the excitability of the medulla oblongata,and promote the recovery of the swallowing reflex arc.17-19
Lianquan (CV23) acupoint is a point of Renmai,distinguished with sublingual and glossopharyngeal nerve branches,is mainly used to treat dysphagia,tongue weakness,sublingual swelling and pain.Hegu (LI4)acupoint is one of the four general acupoints,is a commonly used acupoint for the treatment of facial and oropharyngeal diseases.Acupuncture is a simple,safe and economical method for treatment of dysphagia.The effective rate of acupuncture to treat neurogenic dysphagia is about 80%-100%.20,21Acupuncture therapy and rehabilitation training therapy are highly complementary.This study shows that acupuncture combined with swallowing rehabilitation training is more effective than swallowing rehabilitation training alone.
The quality of life has become an important criterion for evaluating the therapeutic effect of malignant tumors.Swallowing dysfunction in patients with head and neck tumors will reduce the patient’s appetite,reduce dietary intake,lead to malnutrition,decline in physical and social activities,and reduce the patient’s quality of life.22
Compared with other head and neck tumors and hemilaryngoectomy,the quality of life of patients after total laryngectomy is poor,and comprehensive rehabilitation therapy has played a positive role in improving the quality of life of patients.23Acupuncture treatment can reduce the olfactory disturbance and pain of head and neck cancer patients,and is a treatment option to improve the QoL.24This study found that acupuncture therapies combined with swallowing training improved the patient's quality of life.
In conclusion,acupuncture therapies combined with swallowing training can better improve the swallowing function and QoL of laryngeal cancer patients with dysphagia after surgery,is a safe and reliable solution and is worthy of clinical application.
5.REFERENCES
1.Hasan Z,Dwivedi RC,Gunaratne DA,et al.Systematic review and Meta-analysis of the complications of salvage total laryngectomy.EJSO 2017;43:42-51.
2.Terlingen LT,Pilz W,Kuijer M,et al.Diagnosis and therapies of oropharyngeal dysphagia after total laryngectomy with or without pharyngoesophageal reconstruction:systematic review.Head Neck-J SCI 2017;40:2733-48.
3.Mancopes R,Smaoui S,Steele CM.Effects of expiratory muscle strength training on videofluoroscopic measures of swallowing:a systematic review.AM J Speech-Lang PAT 2020;29:335-56.
4.Zhang LP,Huang ZS,Wu H,et al.Effect of swallowing training on dysphagia and depression in postoperative tongue cancer patients.Eur J Oncol Nurs 2014;18:626-9.
5.Sheng RY,Yan Y,Linh Dang HH.Acupuncture for hot flashes:a literature review of randomized controlled trials conducted in the last 10 years.World J Tradit Chin Med 2021;7:397-407.
6.Lu YY,Chen Y,Huang DT,et al.Efficacy of acupuncture for dysphagia after stroke:a systematic review and Meta-analysis.Ann Palliat Med 2021;10:3410-22.
7.Xu J,Zhang J,Wang J.The application of Traditional Chinese Medicine against the tumor immune escape.J Transl Intern Med 2020;8:203-4.
8.Djaali W,Simadibrata CL,Nareswari I.Acupuncture therapy in post-radiation head-and-neck cancer with dysgeusia.Med Acupunct 2020;32:157-62.
9.Frowen JJ,Cotton SM,Perry AR.The stability,reliability,and validity of videofluoroscopy measures for patients with head and neck cancer.Dysphagia 2008 23:348-63.
10.Chen AY,Frankowski R,Bishop-Leone J,et al.The development and validation of a dysphagia-specific quality-of-life questionnaire for patients with head and neck cancer:the MD.Anderson dysphagia inventory.Arch Otolaryngol Head Neck Surg 2001;127:870-6.
11.Aaronson N,Ahmedzai S,Bergman B,et al.The European Organization for Research and Therapies of Cancer QLQ-C30:a quality-of-life instrument for use in international clinical trials in oncology.Natl Cancer 1993;85:365-76.
12.Baijens LWJ,Walshe M,Aaltonen LM,et al.European white paper:oropharyngeal dysphagia in head and neck cancer.Eur Arch Oto-Rhino-L 2021;278:577-616.
13.Loyo M,Espinoza S,Giraud P,et al.Early and severe dyspnea after supracricoid partial laryngectomy.Ann Otol Rhinol Laryngol 2014;123:53-7.
14.Agrawal D,Kern M,Lynch SM,et al.Effect of swallow strength training on oropharyngeal swallow function and deglutitive biomechanics in patients with oropharyngeal dysphagia after therapies for head and neck cancer.Gastroenterology 2020;158:1082-2.
15.Kraaijenga SAC,Molen LV,Stuiver MM,et al.Efficacy of a novel swallowing exercise program for chronic dysphagia in longterm head and neck cancer survivors.Head Neck 2017;39:1943-61.
16.Gao JX,Zhou HF.Therapeutic effect of nape cluster acupuncture combined with swallowing function training on post-stroke dysphagia.Zhong Guo Zhen Jiu 2020;40:586-90.
17.Li LX,Deng K,Qu Y.Acupuncture therapies for post-stroke dysphagia:an update Meta-analysis of randomized controlled trials.Chin J Integr Med 2018;24:686-95.
18.Zheng HD,Wang ZQ,Li SS,et al.Effect of acupoints on acupuncture-moxibustion and its therapeutic mechanism.World J Tradit Chin Med 2020;6:239-48.
19.Chen KX.Academician kai-xian chen talks about the development of Traditional Chinese Medicine and global medicine.World J Tradit Chin Med 2020;6:1-11
20.Liu XP,Chen FY,Chu JM,et al.Effects of nape acupuncture combined with swallowing rehabilitation on dysphagia in pseudobulbar palsy.J Tradit Chin Med 2018;38:117-24.
21.Lu YY,Chen Y,Huang DT,et al.Efficacy of acupuncture for dysphagia after stroke:a systematic review and Meta-analysis.Ann Palliat Med 2021;10:3410-22.
22.Bressan V,Stevanin S,Bianchi M,et al.The effects of swallowing disorders,dysgeusia,oral mucositis and xerostomia on nutritional status,oral intake and weight loss in head and neck cancer patients:a systematic review.Cancer Treat Rev 2016;4:105-19.
23.Bat?o?lu-Karaalt?n A,Binbay Z,Yi?it ?,et al.Evaluation of life quality,self-confidence and sexual functions in patients with total and partial laryngectomy.Auris Nasus Larynx 2017;44:188-94.
24.Djaali W,Simadibrata CL,Nareswari I.Acupuncture therapy in post-radiation head-and-neck cancer with dysgeusia.Med Acupunct 2020;32:157-62.
 Journal of Traditional Chinese Medicine2022年4期
Journal of Traditional Chinese Medicine2022年4期
- Journal of Traditional Chinese Medicine的其它文章
- Editorial Board Listing
- Mixed methods research in complementary and alternative medicine:a scoping review
- Herbal anthelmintic agents:a narrative review
- Factors influencing physician's behavioral intention to use Traditional Chinese Medicine to treat coronavirus disease 2019 based on the theory of planned behavior
- Identification of novel biomarkers and therapeutic target candidates for stasis-heat symptom pattern of acute intracerebral hemorrhage by quantitative plasma proteomics
- Effectiveness of auricular point acupressure with magnetic plate for pain management in acute postpartum cesarean section patients in Thammasat University Hospital:a randomized clinical controlled trial
