Analysis on the status and influencing factors of undergraduate nursing students’ online learning engagement in the context of the pandemic
Lian-Di Ding, Ming-Jin Li
School of Nursing, Yanbian University, Yanji, Jilin, China
Abstract Objective:This project has mainly studied the online learning engagement of undergraduate nursing students and analyzes influencing factors of online learning and teaching mode during the Novel Coronavirus (COVID-19).This research has significant references for improving the efficiency and quality of the online learning mode of students.Methods: In this study, 212 undergraduate nursing students were selected from a comprehensive university in Jilin Province by combining convenience sampling and cluster sampling methods.And these students were conducted with a general information questionnaire, Online Academic Emotion Scale, and Online Learning Engagement Scale.The influencing factors of this teaching mode were analyzed by multiple linear stepwise regression.Results: The total score of online learning engagement of undergraduate students was 53.85 ± 7.38, which positively correlated with positive high arousal emotion and negative high arousal emotion, but weakly negatively correlated with negative low arousal emotion (r = 0.661, 0.246, -0.187, P < 0.001).Grade, type of online class, online learning time, and positively high arousal emotion were mainly affected the online learning engagement of undergraduate nursing students, which explained 78.5% of the total variation (P < 0.001).Conclusion: The online learning engagement of undergraduate nursing students was above the middle level under the background of the COVID-19 pandemic.Lectures and professors who teach undergraduate nursing students, should integrate the individuation characters of nursing students, and motivate their positively high arousal emotion to improve online learning engagement of students to ensure the quality of online teaching mode.
Keywords: Undergraduate nursing students; Online learning engagement; Online academic emotion; Root cause analysis
Introduction
The unexpected COVID-19 pandemic disrupted the original beginning of the term plan.For this serious situation, the Ministry of Education took an emergency measure "suspended class, ongoing teaching, and learning" [1].In China, colleges and universities have tried to start online teaching one after another for cooperating with this action.According to official data of the Ministry of Education, there were 2.3 billion people who participated in online learning and teaching mode until May 8, 2020 [2], which indicates that universities have experienced a classroom revolution of "Internet + teaching".However, some surveys have shown that large-scale online teaching did not connect with traditional classrooms perfectly [3], especially nursing majors.Due to the content of the class, the online teaching of nursing majors has been challenged unprecedentedly.On the one hand, teachers have different abilities to organize a class online, which cannot ensure that students get the same quality and level of online teaching; On the other hand, undergraduate nursing students are used to having class by face-to-face mode in specific environments, such as classrooms and laboratories.There was barrier-free communication and interaction between students and teachers.However, online learning engagement and emotion of students cannot be effectively monitored and dynamically adjusted, which undoubtedly become a sore point of online having the class of nursing students.Therefore, analyzing the current situation of undergraduate nursing students' online learning investment and factors that affect their online learning investment are important to improve the learning engagement of nursing students and optimize the online teaching design of nursing teachers.Meanwhile, this project will provide references to researchers for innovating the mixed teaching mode in the future.
Methods
Study design and participants
A total of 258 undergraduate nursing students were selected from a comprehensive university in Jilin Province by the method of convenience sampling and cluster sampling in this cross-sectional study.All participants were asked to complete the questionnaires from June 2020 to July 2020.We invited seven volunteers (one graduate, six undergraduates) from the comprehensive university."Wenjuan Xing" is a professional questionnaire survey platform.It was used to investigate the online learning engagement of participants through 6 Wechat groups.Inclusion criteria:(1) Participants were full-time unified enrollment of undergraduate nursing students from grades 1 to 3.(2) Participants have more than one month of online learning.(3) They are informed consent and participated voluntarily.Exclusion criteria:Participants are unable to take part in the survey due to sick leave during the survey.As a result, 212 participants answered the questionnaires effectively, the effective response rate was 82.2%.
Questionnaire
Demographic characteristicsGeneral information of questionnaire consists of gender, grade, residence, type of online courses, learning tools, and online learning time.
Online Academic Emotion ScaleIn this study, the Academic Emotion Questionnaire (AEQ) is applied, which was developed by Liu JL [4] and used to study the online academic emotional state of college students.The online academic emotional state was considered by three dimensions, such as positive high arousal emotion, negative high arousal, and negative low arousal.These three dimensions comprise 25 items.This questionnaire was answered on a 5-point Likert scale ranging from 1 (strongly disagree) to 5 (strongly agree), the total scores of the one-piece questionnaire would be ranging from 5 to 125.The Cronbach's α was 0.89 and the AEQ reliability was 0.861.
Data analysis
Data were analyzed by SPSS software version 25.0.Descriptive statistics were used to determine the distribution of demographic characteristics.The mean and standard deviations of participants' scores on online learning engagement and online academic emotion were calculated.Correlations between scores on online engagement and online academic emotion were assessed by Pearson's correlation.Stepwise multiple regression analyses were performed to assess how demographic characteristics and online academic emotions affecting each domain of participants' online learning engagement.A two-sidedP-value of less than 0.05 was considered statistically significant.
Results
Demographic characteristics
A total of 212 undergraduate nursing students were enrolled, and their demographic characteristics are summarized in Table 1.Most of the study participants were girls, accounting for 79.7% of the total.For these participants, 37.3% of them were freshman, 34.4% of them were sophomore, 28.3% of them were junior.In addition, 52.4% of participants had been living in the city, 62.7% of participants only had the nursing courses online, and participated students learned online for less than 3 hours were 13.2%.7.5% of these students usually used three kinds of online learning tools to have class.
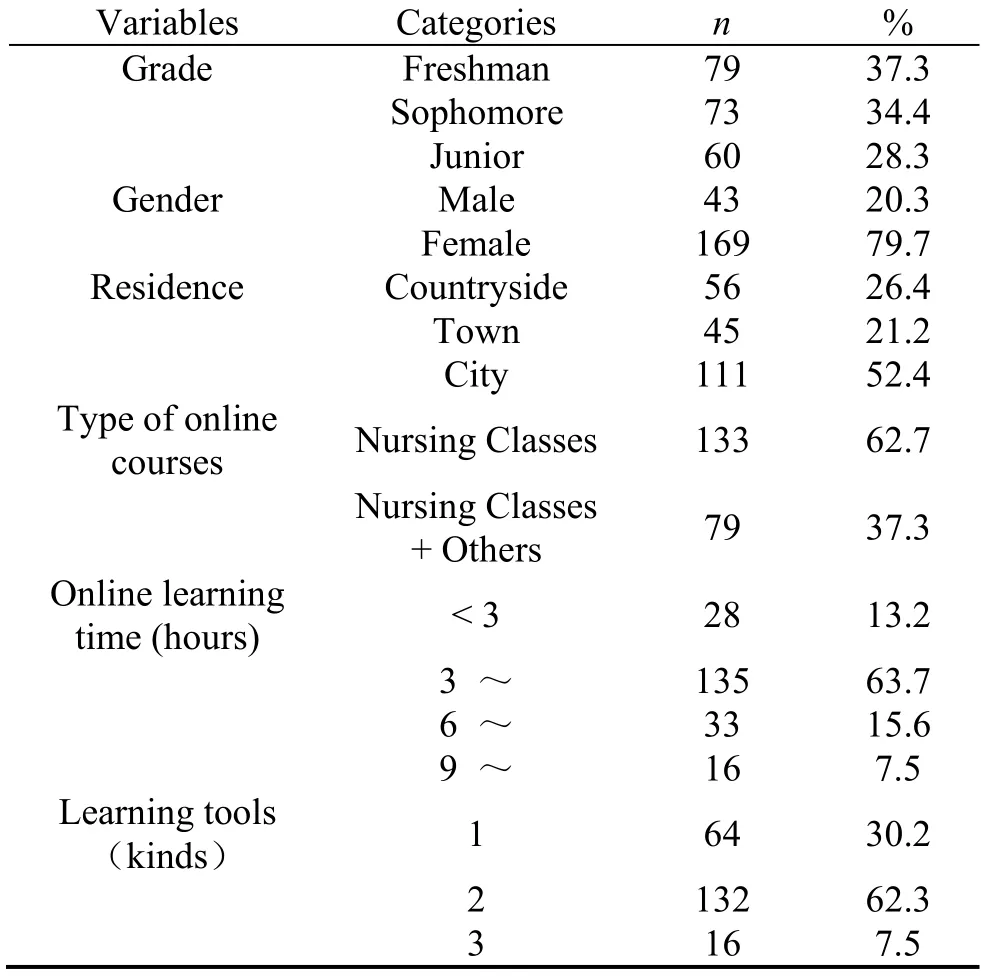
Table 1:Demographic characteristics of undergraduate nursing students (n = 212)
Online learning engagement and online academic emotion
The mean score (SD) of online learning engagement of undergraduate nursing students was 3.59 (SD0.49), which was above the average level.The mean score of online academic emotion was 3.02 (SD0.32), which was in the average level, and the positive high arousal emotion score was the highest (Table 2).
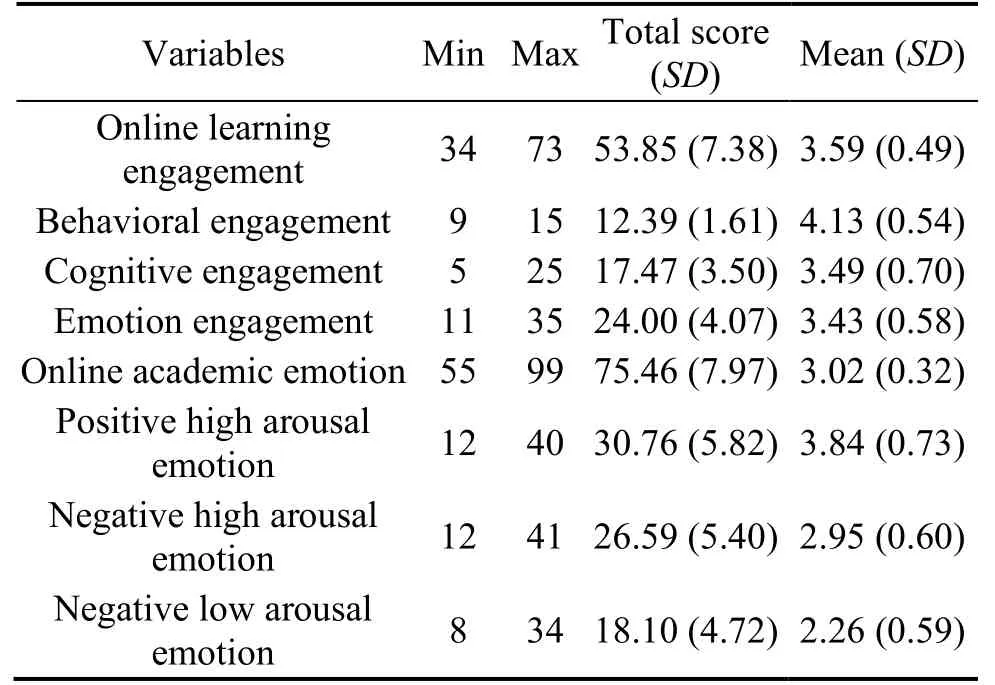
Table 2:Level of online learning engagement and online academic emotion
Correlations between online learning engagement and online academic emotion
Online learning engagement showed a positive correlation with online academic emotion (r= 0.540,P< 0.001).Positive high arousal emotion and negative high arousal emotion were positively related with each subscale of online learning engagement, while negative low arousal emotion was negatively correlated with online learning engagement (Table 3).
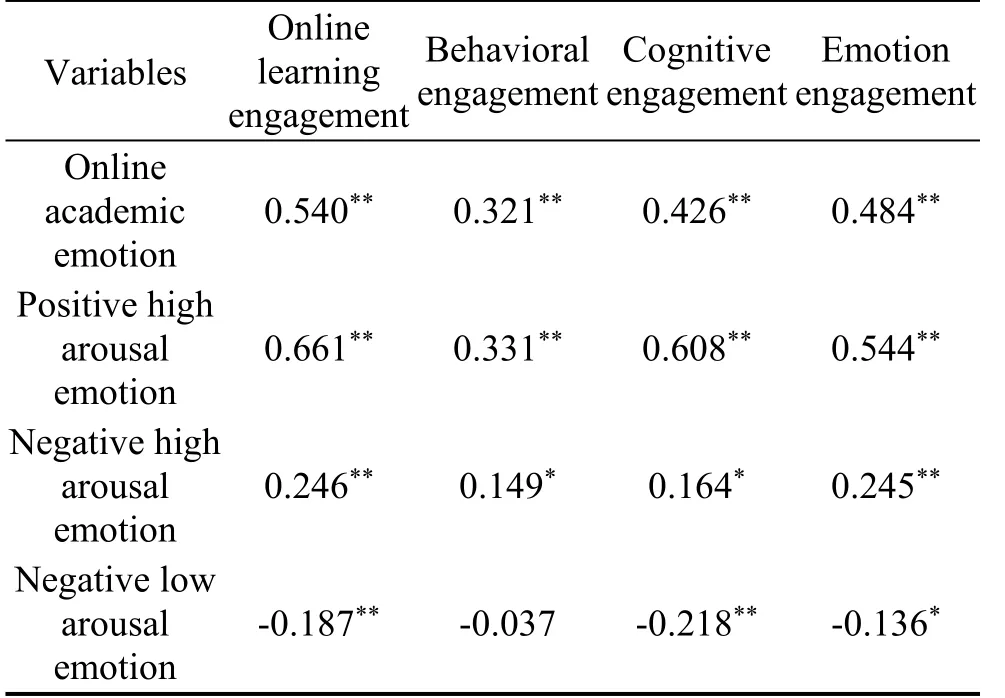
Table 3:Correlations between online learning engagement and online academic emotion
Factors influencing online learning engagement
Influencing factors of online learning engagement were grade (β= 0.132,P< 0.001), type of online courses (β= 0.224,P< 0.001), Online learning time (β= 0.289,P< 0.001), and positive high arousal emotion (β= 0.192,P< 0.001).The explanatory power of the model was statistically significant (78.5%, F =193.101,P<0.001) (Table 4).
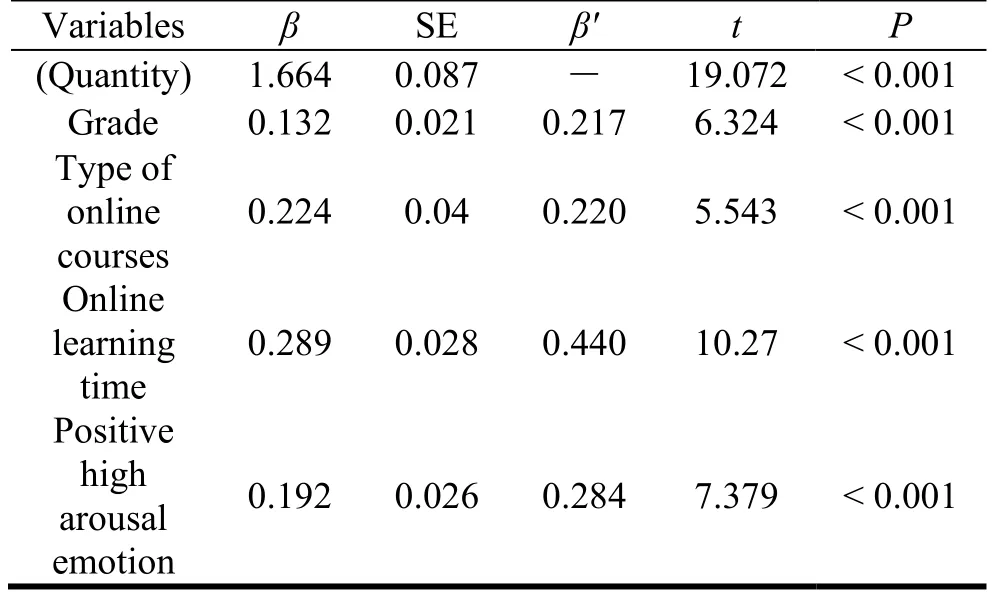
Table 4:Multiple regression analysis showing factors influencing online learning engagement.
Discussion
Several studies have shown that online learning engagement is the important variable to measure information literacy, evaluate academic emotion, and predict learning gains the satisfaction of learners in distance [7-10].In this study, the mean score (SD) of online learning engagement of undergraduate nursing students was 3.59 (SD0.49), which was above the average level and slightly higher than the theoretical meanM= 3.0 [11].This is similar to the research results of Zhou JR, et al.[12], while it is not consistent with the research results of Qin XH, et al.due to the full-time home-based online learning of nursing students in the context of epidemic prevention and control [13].Analyzing the three dimensions of online learning investment, the behavioral investment of nursing students is significantly higher than cognitive engagement and emotional engagement, and emotional engagement is the lowest.This suggests that although nursing students have completed credit-related activities or tasks in online courses, they lack internal motivation to learn independently.There are some reasons:first of all, the nursing student did not have clear goals and do sufficient preparation before having classes online, which would affect the adjustment of learning pace and strategy [14,15]; secondly, the teaching interaction of teachers and students would be delayed in the online classes, nursing students easily have negative emotions, such as loneliness, anxiety, boredom and so on.If the individual internal learning needs cannot be effectively met, the learning enthusiasm of students would be weakened; lastly, the self-control awareness and learning motivation of undergraduate nursing students are poor after classes [16], the learning engagement level is not ideal on the whole.Therefore,the teaching management department should improve the performance evaluation system of online learning and stimulate the external learning motivation of students majoring in nursing [17].Besides, teachers should take students as the main body and optimize the teaching design in the process of online teaching [9,11,15], which would provide sufficient independent and emotional support to students to maximize their personalized learning needs.Moreover, undergraduate nursing students should strengthen their professional identity, excavate internal learning motivation and cultivate network autonomous learning ability, these would improve their online learning engagement [12].
Back to Mom s to wrap the gifts. There were two separate boxes of hand-me-down clothes, sized, pressed and folded. Soon 10 grocery-store boxes, overflowing8 with holiday food, joined them.
Multiple linear stepwise regression analysis showed that grade, class type, online learning time, and positive high arousal emotion were the main influencing factors of online learning engagement of undergraduate nursing students.(a).The level of online learning engagement of senior nursing students is higher than that of junior nursing students.On the one hand, the adaptability of online learning of nursing students and the ability of online course perception is gradually enhanced with the increasing grade [18,19].On the other hand, the depth of nursing professional knowledge is gradually promoted from the professional characteristics, which requires senior nursing students to spend more time, energy and make effective efforts.(b).Compared with nursing students who only participate in nursing courses, nursing students who take part in both nursing professional courses and non-professional courses have a higher level of online learning engagement.Studies have shown that diverse learning activities and abundant learning resources are beneficial to gradually increase the degree of autonomy of learning motivation and improve integrating and adjusting of cognitive engagement, which would comprehensively improve the online learning engagement [17,20].(c).This study also proves that if the online learning time of students is longer, the level of online learning engagement is becoming higher, this trend is similar to the founding of Carver et al.[21].Most of the studies found that when nursing students spent long-time to focus on online learning, they would have a strong interest in learning tasks and then deepen their learning behavior [22,23].At the same time, the continuous online learning behavior of nursing students shows that the teaching design of teachers meets the inherent needs of individualized learning of students and highlights the student-centered teaching philosophy.d During online learning, positive high arousal emotion can positively predict online learning input.The emotions of learners are more positive, the level of online learning engagement is higher, which is the same with the research results of Gao J [8], who believes that maintaining positive emotions and enhancing online learning efficacy can improve online learning engagement.To sum up, undergraduate students of nursing major as the main body of online learning input, teachers taught courses nursing major should be student-centered,integrate the individualized differences of students, strengthen the ability of information teaching, carefully design online teaching [24-26], develop multi-interaction, give sufficient independent support and emotional support [11], stimulate and maintain nursing students to awaken academic mood, and then improve online learning engagement level and ensure teaching quality.
Conclusion
Under the background of COVID-19 pandemic, large-scale online teaching has promoted the classroom revolution in colleges and universities.Online learning engagement is an important indicator of ensuring the quality of teaching, which has become the main content of student development in this special period, and its subsequent impact continues to spread.At present,the online learning engagement of undergraduate nursing students is above middle level, and emotional engagement is the lowest.Grade, online class type, online learning time, and positively high arousal emotion were the main factors affecting online learning engagement of undergraduate nursing students.During the pandemic,teaching management departments, nursing teachers, and nursing students must open three-level linkage to perfect the evaluation mechanism, enrich the types of online courses, optimize the teaching design, stimulate, and maintain the positive emotions of nursing students, and cultivate the ability of network autonomous learning, to improve the level of online learning engagement of undergraduate nursing students.In addition, this study is limited by objective conditions and a small sample size.It is suggested that expanding the sample size and introducing information literacy to carry out in-depth research on online learning engagement in future research.
Reference
1.Su H.Give full play to the advantages of online education to achieve high-quality "no suspension of classes".CPPCC DAILY, 2020-03-25(006).
2.Higher Education Department of the Ministry of Education:the situation of online education in colleges and universities and the consideration of the next step.Mod Educ Technol 2020, 30(5):1.
3.Chen B.Online education:" inequality "between reality and ideal.China Science News, 2020-04-21(006).
4.Liu JL, Liu B, Zhang WL.The influences of academic emotions on collaborative problem solving of online learners.Chin Educ Technol 2019(7):82-90.
5.Yin R, Xu HY.The progress and prospects of online learning engagement research in foreign countries.Open Educ Res 2016, 22(3):89-97.
6.Sun CY, Rueda R.Situational interest, computer self-efficacy, and self-regulation:Their impact on student engagement in distance education.Brit J Educ Technol 2012, 43(2):191-204.
7.Zhai X, Chen C, Wang HR.Research on the influence factors of information literacy on college students' online learning engagement-taking the large-scale and long-term network teaching during the "epidemic Period" as an example.Mod Educ Technol 2020, 30(10):98-104.
8.Gao J.Impact of online academic emotion on learning engagement:A social cognitive perspective.Open Educ Res 2016, 22(2):89-95.
9.Li JJ, Fang F, Li MF, et al.A study on the influencing factors of online student engagement and learning outcome in preventive medicine undergraduates during COVID-2019 epidemic.J Shandong Univ 2021, 59(1):115-121.
10.Zhu LC, Wang N, Du YT.Research on the influencing factors and promotion strategies of online learning satisfaction of college students.J Natl Acad Educ admin 2020, (5):82-88.
11.Liu B, Zhang WL, Liu JL.Study on the effect of teacher support on online learners' learning engagement.e-Educ Res 2017, 38(11):63-68+80.
12.Zhou JR, Zhao L, Li QE.Analysis of the status and influencing factors of 825 undergraduate nursing students' engagement in online learning.J Integr Nurs 2020, 6(9):11-15.
13.Qin XH, Zhang LL, Lin JQ, et al.Online learning engagement of 200 intern nursing students.J Nurs 2018, 25(24):25-28.
14.Cho MH, Cho YJ.Instructor scaffolding for interaction and students' academic engagement in online learning:Mediating role of perceived online class goal structures.Int High Educ 2014, 21(3):25-30.
15.Rao RJ, Wan K.A Study on the Influence of online learning readiness on college students' online learning engagement.Educ Sci 2020, 36(2):31-38.
16.Zhang WJ, Zhou YF, Xuan XY, et al.University's online teaching and student development during the pandemic prevention and control:a case study on B university.Chin Higher Educ Res 2020, (6):64-71.
17.Gao J.The relationship between extrinsic motivation and online learning engagement:a self-determination theory perspective.e-Educ Res 2016, 37(10):64-69.
18.Li L, Liu YY.A study on online learning adaptability and learning effect of college students:based on data from 1698 questionnaires.J Changji Univ 2020, (3):100-105.
19.Feng XY, Hu Y, Li G.A research on the situation and influencing factors of college students' online learning engagement-In a case of H university in Henan during the epidemic prevention period.J Henan I Sci Technol 2020, 40(10):24-30.
20.Ryan RM, Deci EL.Self-determination theory and the facilitation of intrinsic motivation, social development, and well-being.Am Psychol, 2000 55(1):68-78.
21.Carver L, Mukherjee K, Lucio R.Correlation between grades earned and time in online courses.Online Learn 2017, 21(4):303-313.
22.Liu K, Tang SX, Nie SS.A study on the control mechanism of online learning effect of higher vocational college students under the background of epidemic prevention and control.Chin J ICT Educ 2020, (15):63-67.
23.Chen XY, Liu MC, Wu JW, et al.Towards a model for evaluating students' online learning behaviors and learning performance.Distance Educ Chin 2020(10):1-8+76.
24.Hew KF.Promoting engagement in online courses:What strategies can we learn from three highly rated MOOCS.Brit J Educ Technol 2016, 47(2):320-341.
25.Fang MM, Liu B.The influencing factors and strategies of student engagement in online learning.Digit Educ 2018, 4(1):40-44.
26.Hu LW.The influence of college students' online course learning and behavior intention-from the perspective of cognitive appraisal theory.Chin J Health Psychol 2021, 29(4):619-624.
- Nursing Communications的其它文章
- Research progress on career anxiety and influencing factors of nursing college students under the background of COVID-19
- Research progress on the application of attribution retraining in nursing education in China
- Outcome report of breast massage for lactational mastitis patients in early stage:A protocol for systematic review
- Spiritual care perceptions,spiritual health and their relationships with spiritual care competence among clinical nurses in China:A cross-sectional quantitative study

