An investigation on hand hygiene cognition status and influencing factors of nursing workers in a third-grade a hospital during COVID-19 epidemic
Hong Chen, Su-Na Li, Xing-Tong Bao, Ling Tang
1Second breast surgery, Dongfang Hospital Beijing University of Chinese Medicine, Beijing, China; 2School of Nursing, Beijing University of Chinese Medicine, Beijing, China; 3Nursing Department, Dongfang Hospital Beijing University of Chinese Medicine, Beijing, China.
Abstract Objective:During the COVID-19 epidemic, the hand hygiene of nursing workers in a third-grade a traditional Chinese medicine hospital was investigated to find out existing problems and put forward management countermeasures.Methods: A cross-sectional questionnaire survey was conducted to investigate the hand hygiene cognitive status and influencing factors of 78 nurses in the hospital.Results: Through the early training, the nursing workers had a good grasp of the hand hygiene signs and related knowledge.Among the factors affecting hand hygiene, there are some problems in facilities and management factors.The cognitive factors of different categories of nursing workers have different influences on hand hygiene, especially the influence of length of service on hand hygiene is significantly different (P < 0.05); Nursing workers should be trained on how to use hand washing. Conclusion: Hand hygiene of nursing workers is of great significance for the prevention and control of hospital infection.Medical institutions at all levels and of various types should, in light of their own actual conditions, formulate operational and feasible hand hygiene management systems for various groups of people in hospitals, strengthen training and supervision, and improve compliance with hand hygiene, so as to prevent hospital infections and fight the battle against COVID-19.
Keywords: Nursing worker, Hand hygiene, COVID-19, Hospital infection
Introduction
COVID-19 is a new and highly infectious acute respiratory infectious disease to which the population is generally susceptible.It is mainly transmitted through respiratory droplets and close contact.Since the outbreak of the epidemic in December 2019, a series of prevention, control and medical treatment measures have been taken to contain the rising trend of the epidemic in China [1].As medical institutions at all levels and of all kinds begin to resume normal medical work, the most possible avoidance of hospital infection is the top priority in the current prevention and control work.Hand hygiene is an important link in the prevention of hospital infection, so the current situation of hand hygiene of all personnel in hospitals should be paid attention to [2].In accordance with the unified deployment of Beijing Municipal Health Commission and under the guidance of the hospital's COVID-19 prevention and control nursing expert team, our hospital has recently actively carried out COVID-19 protection knowledge training for non-health professionals on the job, including nursing workers, with hand hygiene as one of the key contents.Because of their nature and job characteristics, caregivers are one of the important vectors for COVID-19 hospital infection [3].The purpose of this study was to understand the hand hygiene cognition of nursing workers in our hospital, to explore the grasp of hand hygiene cognition of nursing workers in different situations, so as to improve the attention of managers to hand hygiene of them, and to take relevant management measures to prevent hospital infection caused by nursing workers.
Objects and methods
Subjects
The date is February 27, solstice March 2, 2020, and there are all 78 nursing workers taking care of patients in Dong Fang hospital of Beijing university of Chinese medicine.Inclusion criteria:nursing workers who provide care directly to patients; No mental disorders, and volunteered to participate in this survey.The investigator was a member of the COVID-19 in-hospital prevention and control nursing expert group.The investigator explained the purpose of the survey to each nursing worker, and explained the contents of the survey item by item, so that the nursing worker could fully understand and respond.A total of 78 nursing workers in the hospital were surveyed this time.The surveyors completed the questionnaire and collected it on the spot.A total of 78 questionnaires were sent out and 78 valid questionnaires were collected, with an effective recovery rate of 100%.
Survey methods
Cross-sectional questionnaire survey was adopted, and the self-designed Questionnaire on hand hygiene of COVID-19 Nursing Workers was adopted.The questionnaire included general information survey and hand hygiene survey of nursing workers.General data survey content includes gender, age, education, length of service, work departments and so on.The questionnaire for hand hygiene of nursing workers is designed according to the questionnaire for hand hygiene of nursing workers formulated by Liu Yan et al.[3], and the survey items are increased or decreased according to the actual situation of the hospital.The hand hygiene questionnaire is divided into four parts:(1) There are 13 indicators of hand hygiene, with a full score of 13.Answer “yes” or “no” to reflect the carers’ understanding of finger washing signs.1 point for correct answer; (2) Hand hygiene knowledge (12 items), reflecting the carers’ knowledge of hand washing, will be scored 1 point for correct or incorrect responses.(3) There are 21 factors affecting hand hygiene.Including 5 hand sanitation factors, 5 management factors, 6 cognitive factors and 5 other factors, with a “yes” or “no” response.(4) Hand washing methods:There are 12 items, with a full score of 12, reflecting the effect of hand washing performed by the nursing workers.The on-site demonstration is adopted, and one point is awarded for correct action standards.
Statistical Methods
SPSS 20.0 software was used for statistical analysis by Analysis of variance and t-test.
Results
General conditions of nursing workers
Of the 78 nursing workers, 22 were male and 56 were female.The patients were (52.12 ± 6.03) years old.Among them, 3 were from 31 to 40 years old, 30 were from 41 to 50 years old, and 45 were over 51 years old.The length of service is (6.34 ± 4.9) years, among which, 6 persons are less than 1 year, 18 persons are 1-3 years, and 54 persons are more than 3 years.Education:8 illiterates, 24 primary school students, 41 junior middle school students and 5 senior high school students; Department:Internal medicine ward (respiratory department,oncology department, Gastroenterology department, Neurology department, hematology department, nephrology department) 45 people, surgical department (surgery department, neurosurgery department, orthopedics department) 21 people, emergency department 7 people, critical care department 5 people.
Grasp of hand hygiene indications of nursing workers
Hand hygiene indications of the 13 items, there are two items (hand have a visible stain, after contact with patients) answer accuracy is 98.72%, the rest of the 11 items (contact patients before and after contact with the surrounding environment, in front of the clean operating, give patients before drinking or eating, go to the bathroom, after processing waste, before and after contact with body fluids patients after discharge, contact, contact patients after discharge, after picking gloves, hands after pollution from a patient's body parts to clean parts) are the correct answer is 100%.
Knowledge of hand hygiene of nursing workers
There are 12 items of hand hygiene knowledge, 8 of which are mastered by nursing workers at least 96%.The worst item is “The hand bacteria causing hospital infection are mainly temporary bacteria”, which is also 93.59%.See table 1.

Table 1:Nurses’ knowledge of hand hygiene (n = 78)
Factors affecting hand hygiene of nursing workers
Factors affecting hand hygiene of nursing workers include facility factors, management factors, cognitive factors and other factors.The proportion of "yes" in each item is shown in Table 2.Among the facility factors, items "not equipped with dry hand tissues" accounted for 71.79%, while some items of management factors, cognitive factors and other factors also accounted for a higher proportion.Compared with gender, age, education background and department, the length of service of nursing workers had a significant difference in influencing cognitive factors (P< 0.05), as shown in Table 3.

Table 2:Factors influencing hand hygiene of nursing workers (n = 78)
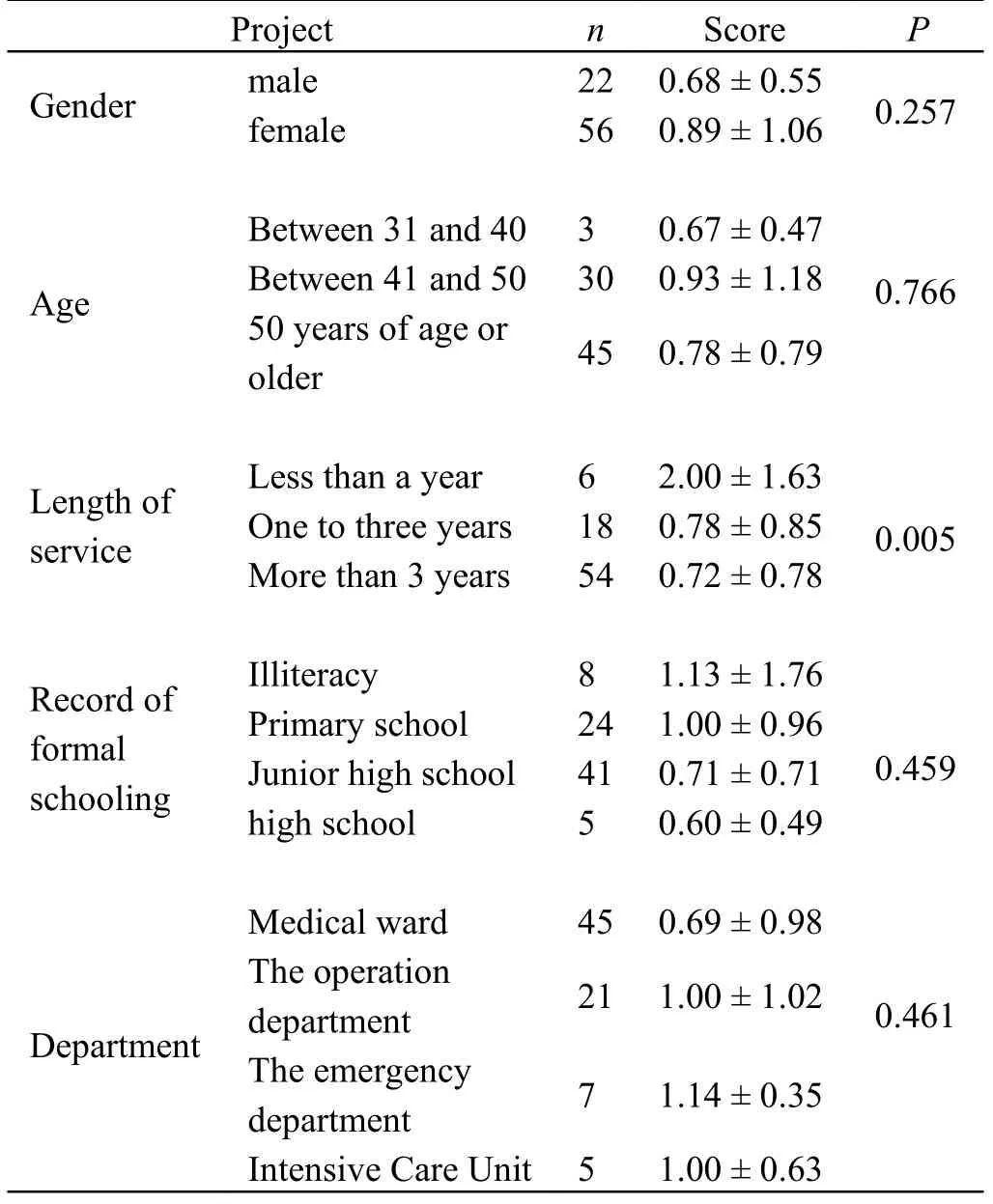
Table 3:Influence of cognitive factors of different categories of nursing workers on executive hand hygiene
Nursing workers’ mastery of hand washing methods
The questionnaire divided the process of hand washing into 12 points.Full marks were awarded for standardized on-site hand washing demonstration with no omissions, accounting for 69.23%.There were 17 mistakes, 6 mistakes and 1 mistake in the process of hand washing (Table 4).
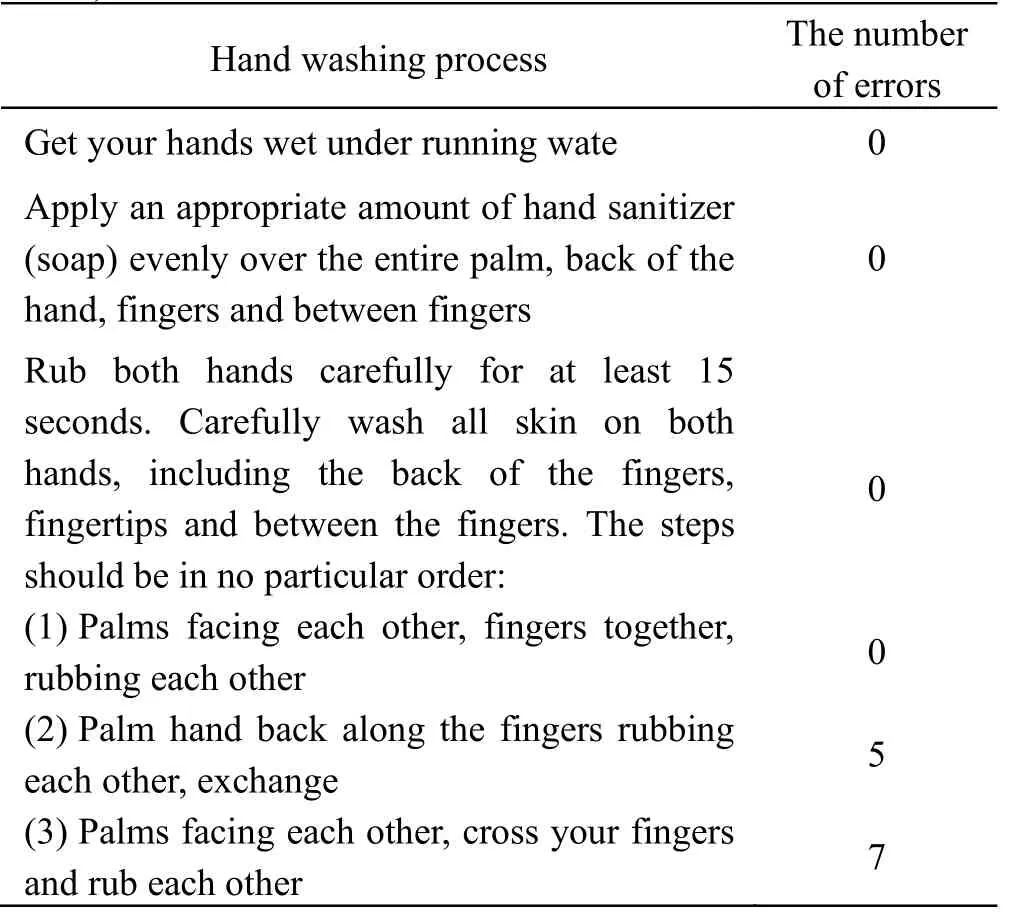
Table 4:Hand washing methods of nursing workers (n = 78)

(4) Bend the fingers so that the joints rotate and rub in the palm of the other hand, and the exchange occurs 20 (5) Hold the left thumb in the right hand, rotate and rub, and exchange 2 (6) Put the tips of five fingers together in the palm of the other hand, rotate and rub, and exchange 0 (7) Rotate and rub the wrist and forearm of the other hand until they reach the elbow 0 Rinse hands thoroughly under flowing water, wipe them dry, and apply proper amount of hand lotion to protect skin 0 Use paper towels when drying 0
Discussion
General conditions of nursing workers
From the survey results, the gender of nursing workers, female nursing workers account for as much as 70 percent, female nursing workers tend to take care of patients more careful and thoughtful, and for the need for certain physical labor, such as turning patients, assist patients activities, move patients, male nursing workers have more obvious advantages.Care of age, the average age of about 52, mainly concentrated in the 50 years of age or older, it shows that for a care of this work was hard to attract the young people, they are the advantages of rich life experience and experience, down-to-earth work, but thinking curing, accept new knowledge is more difficult, so the hand washing knowledge training to them not only to clear “to do”, but also speak “why” to understand, in order to better understand and accept them, hand hygiene to protect their own at the same time, also want to notice to protect patients.In terms of the length of service of nursing workers, the average length of service is about 6 years, with more than 3 years accounting for 69.32%, indicating that the nursing workers team of our hospital is relatively stable.It with the traditional thought is not very consistent, advantage is conducive to the ongoing training and management, but because in the same hospital working time is long, nursing workers are even relatives or fellow residents who know each other well.As a result, they are inevitably interconnected at work or in life, which greatly increases their mobility, and their hand hygiene can influence cross-infection in hospitals.Therefore, it is necessary to adopt regular training and assessment for hand hygiene knowledge to urge them to make correct hand hygiene a good habit in their daily life.In terms of the education level of the nursing workers, most of them are in junior or primary schools, which reflects that the education level of the nursing workers is generally low, and the low education level is a great obstacle for them to grasp the medical knowledge.Easy to understand comes first when they are trained in hand hygiene.
Cognitive status analysis of hand hygiene of nursing workers
In order to prevent clustered COVID-19 cases in hospitals, the Beijing municipal commission of health has made a unified deployment.On February 21, solstice February 26, 2020, non-health professionals working in medical and health institutions, including nursing workers, will conduct online learning, mainly to learn the work process of hospital escort for prevention and control of COVID-19.
Our hospital also carried out this survey in the first time to understand the hand hygiene situation of nursing workers, so as to organize and carry out targeted offline training and assessment in the next step to ensure the training effect.Hand hygiene knowledge includes hand hygiene indications.According to the survey results, the answer rate of health knowledge was high.Most of them are above 96%, especially the related items of the hand hygiene indication are basically 100%, which indicates that the daily training of our hospital for nursing workers and the online training of all staff of Beijing Municipal Health Commission have received the due effect recently.and hand hygiene related knowledge.However, whether the nursing workers can master it for a long time still needs to work hard from the perspective of understanding.Examples of hospital infection with COVID-19 can be used to educate people about the need and importance of hand hygiene, so that they can gain insight into the mind and improve long-term compliance with hand hygiene.
Analysis of factors affecting hand hygiene performed by nursing workers
Factors affecting hand hygiene of nursing workers include facility factors, management factors, cognitive factors and other factors, among the facility factors, “no dry hand tissue is equipped” is a common problem in all departments.Especially in the novel Coronavirus prevention and control period, hospitals and departments should increase the prevention and control fund, equip themselves with sufficient dry hand tissue and solve the problem of insufficient relevant facilities as soon as possible; Among the management factors, regular assessment and effective supervision are still necessary, and PDCA cycle quality management can be adopted for effective management of hand hygiene [4]; The measures of reward and punishment should be formulated, and the departments or individuals with excellent hand hygiene assessment should be praised and given material rewards, so as to stimulate the enthusiasm of nursing workers in hand hygiene implementation and nurses in nursing management.The cognitive factors of different categories of nursing workers have different effects on hand hygiene.According to the survey, the cognitive level of male nursing workers is slightly higher than that of female nursing workers, which may be related to their wide range of knowledge.In terms of age, the cognitive factors of nurses in different age groups are different, suggesting that relevant departments should carry out comprehensive hand hygiene education, and adopt different ways of education according to the characteristics of different age groups, so as to enhance the understanding of hand hygiene knowledge of nurses.The length of service of nursing workers has a significant difference in the impact on hand hygiene execution (P< 0.05), indicating that continuous learning and experience of nursing workers are of great help to hand hygiene execution, suggesting that the management department should increase the training and supervision of nursing workers less than one year into the job, so that they can master hand hygiene knowledge and perform hand hygiene earnestly as soon as possible.
The nursing workers’ mastery of hand washing methods
At the heart of hand hygiene is the ability to wash your hands properly.Through the hand washing process points and 12 steps to care for live demonstration of the inspection found that there are three errors of one worker, 2 errors of six people, 17, 1 item of human error shows that nearly seventy percent of the workers can correctly grasp the washing method, thus for training should be better to wash your hands to grasp details, knead to include washing hands back, fingertips and fingers, do comprehensive and effective.At the same time can wash hands down to seven steps essence, easy to understand, easy to remember, so as not to omit, such as ‘Inside Outside Clip Arch Big Vertical Wrist’:Inside, it is palm-to-palm, with emphasis on cleaning the palm; Outside, palm to palm back, internal and external interaction, focus on hand washing back; Clip, let the fingers crossed, wash is the side of the finger; Arch, bend your five fingers together and interlock them with your other hand, washing your fingers with emphasis; Big, palm around the thumb, wash the thumb; Vertical, five fingers stand up in the other palm rub, this is to wash the nail seam; Wrist, is washed around the wrist, washing the wrist.
Conclusion
Hand hygiene of nursing workers is of great significance to prevent and control hospital infection.Most of the nursing workers are surplus labor force from rural areas or people without formal jobs in cities and towns, and their family conditions are generally poor.Many of them have poor hygiene habits and low overall education level.These characteristics make them have poor learning ability of hospital infection prevention and control knowledge, and have very limited new knowledge.Due to the mobility of
hospitalized patients, the work characteristics of nursing workers, such as unstable work places and miscellaneous contacts, can easily lead to hospital infection if hand hygiene is not paid attention to [5].Therefore, during the critical period of COVID-19 prevention and control, it is extremely important to do a good job of hand hygiene of care workers, which should be paid high attention by hospitals and health management departments [6].Medical institutions at all levels and of all kinds should formulate operational and feasible hand hygiene management systems for different groups of people in hospitals according to their actual conditions.Training and supervision should be strengthened to improve compliance with hand hygiene, so as to ensure the unity of knowledge, trust and practice of hand hygiene, prevent the occurrence of hospital infections, protect the health of all hospital patients and staff, and fight the battle against COVID-19.
- Nursing Communications的其它文章
- Real experience among undergraduate nursing students in learning the course of geriatric nursing:a qualitative study
- Validity and reliability of the complementary and integrative health assessment for practitioners scale:CIHAPTR
- The relationship between academic adjustment and emotional intelligence among undergraduate students in Oman
- Analysis on the status quo and influencing factors of fear of disease progress in 120 patients’spouse after bladder cancer surgery

