Chemical Composition of Fruit of Embelia undulata (Wall.) Mez
Ling CHAI, Jiantong YUAN, Mingsheng CHEN, Buming LIU
Guangxi Key Laboratory of Traditional Chinese Medicine Quality Standards, Guangxi Institute of Chinese Medicine & Pharmaceutical Science, Nanning 530022, China
Abstract [Objectives] To study the chemical constituents of the fruit of Embelia undulata (Wall.) Mez. [Methods] Silica gel column chromatography, gel column chromatography, recrystallization, high-performance preparative liquid chromatography and other modern separation methods and techniques were used to separate and purify the chemical components of the ethyl acetate fraction of the fruit of E. undulata (Wall.) Mez, and based on the physical and chemical properties and spectral data, their structure was identified. [Results] Six compounds were isolated from the fruit of E. undulata (Wall.) Mez, including trimethyl citrate (1), vanillic acid (2), 5-hydroxymethylfurfural (3), 1,5-dimethyl citrate (4), 1,6-dimethyl-5-ethyl citrate (5) and 3,4-dihydroxybenzoic acid (6). [Conclusions] Compounds 1-6 are all isolated from E. undulata (Wall.) Mez for the first time.
Key words Embelia undulata (Wall.) Mez, Fruit, Ethyl acetate fraction, Chemical constituent
1 Introduction
Embeliaundulata(Wall.) Mez (Myrsinaceae:Embelia) is mainly distributed in the moist shrubs, marginal hillsides and dense forests in Guangxi, Guangdong, Fujian and Guizhou[1]. Fruit ofE.undulata(Wall.) Mez can be eaten directly, tastes sweet and sour, and has the effect of repelling roundworm. As a characteristic plant of Guangxi,E.undulata(Wall.) Mez has a certain history of use in the folk. Longzhou, Daxin, Jingxi and Napo in Guangxi have a large amount of resource forE.undulata(Wall.) Mez[2], with good prospects for being developed as a national medicine. However, there are few researches on the pharmacology ofE.undulata(Wall.) Mez and its fruit at present, and there is no relevant report on the chemical composition ofE.undulata(Wall.) Mez and its fruit at home and abroad. In order to clarify the chemical substance basis of the fruit ofE.undulata(Wall.) Mez, this study used silica gel column chromatography, gel column chromatography, recrystallization, high performance preparative liquid chromatography and other methods to systematically study the chemical composition of the ethyl acetate fraction of the fruit ofE.undulata(Wall.) Mez. Using modern spectroscopy technology, the structure of the monomer compound was identified, and 6 compounds were obtained, including trimethyl citrate (1), vanillic acid (2), 5-hydroxymethylfurfural (3), 1,5-dimethyl citrate (4), 1, 6-dimethyl-5-ethyl citrate (5) and 3,4-dihydroxybenzoic acid (6). The structural formulas are shown in Fig.1.
2 Instruments and reagents
Finnigan Trace DSQ quadrupole mass spectrometer (Thermo Fisher, USA); Bruker Dre-500, AVANCE-800 MHz nuclear magnetic resonance system (Bruck, USA); Waters 2545-2489-2707 high performance preparative liquid chromatograph (Waters, USA); Agilent 1260 high performance liquid chromatograph (Agilent, USA); EV311 rotary evaporator (Beijing LabTech Instruments Co., Ltd., PRC); SH-III circulating water multi-purpose vacuum pump (Zhengzhou Greatwall Scientific Industrial and Trade Co., Ltd., PRC). Column chromatography silica gel was produced by Qingdao Ocean Chemical Plant (PRC); Sephadex LH-20 gel was produced by Pharmacia Corporation (USA); SUN-Fire Prep C18preparative column (150 mm×19.0 mm, 5 μm) was produced by Agilent Technologies Inc. (USA); ZORBAX SB-C18chromatography column (250 mm×4.6 mm, 5 μm) was produced by Agilent Technologies Inc. (USA).
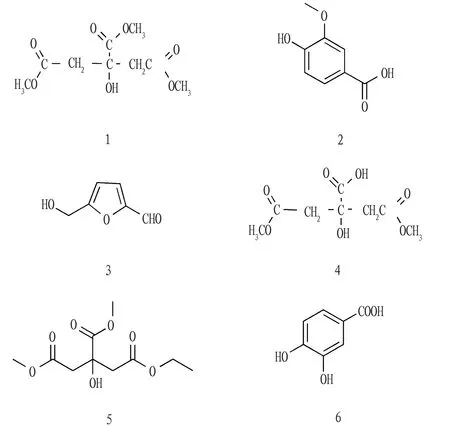
Fig.1 Structural formulas of compounds 1-6
The fruit ofE.undulata(Wall.) Mez, identified by Associate Researcher Huang Yunfeng from Guangxi Institute of Chinese Medicine & Pharmaceutical Science, was picked from Napo, Guangxi. After being picked, the fruit was naturally air-dried, crushed and passed through a No.3 sieve for later use.
Reagents such as petroleum ether, chloroform, ethyl acetate, n-butanol, methanol,etc.for separation were of analytical grade and were purchased from Guangdong Guanghua Technology Co., Ltd. Methanol and acetonitrile were chromatographically pure, and were purchased from Thermo Fisher Scientific (China) Co., Ltd. The water used was ultrapure water.
3 Methods and results
3.1 Extraction and separationCoarse powder of fruit ofE.undulata(Wall.) Mez (4.8 kg) was extracted by methanol percolation, concentrated into thick paste, suspended with 1.0 L of water, and extracted with petroleum ether (4 L×5 times), ethyl acetate (4 L×5 times), and n-butanol (4 L×5 times) successively, and the solvent was concentrated in vacuum to yeild to obtain extract of each extraction fraction. The mass of the petroleum ether fraction, ethyl acetate fraction and n-butanol fraction was 116.6, 135.0 and 178.0 g, respectively.
The extract of ethyl acetate fraction (90.0 g) was separated with silica gel (200-300 mesh, 2.5 kg) column chromatography, eluted gradiently with dichloromethane-methanol (50∶1→0∶100), and identified using thin-layer chromatography. A total of 20 sub-fractions (Fr.1-Fr.20) were obtained. From Fr.3, compound 1 (50.35 mg) was obtained after Sephadex LH-20 gel chromatography and recrystallization. From Fr.4, compound 2 (4.16 mg, tR11.50 min) was obtained after Sephadex LH-20 gel chromatography and high performance preparative liquid chromatography (methanol-0.1% glacial acetic acid aqueous solution, 30∶70, 5 mL/min). From Fr.5, compound 3 (20.13 mg, tR6.17 min) was obtained after Sephadex LH-20 gel chromatography and high performance preparative liquid chromatography (acetonitrile-0.1% glacial acetic acid aqueous solution, 20∶80, 5 mL/min). From Fr.6, 4 sub-fractions were obtained after Sephadex LH-20 gel chromatography. From sub-fraction 2, compound 4 (5.36 mg) was obtained after recrystallization. From sub-fraction 3, compound 5 (10.12 mg, tR7.96 min) was obtained after high performance preparative liquid chromatography (methanol-0.1% glacial acetic acid aqueous solution, 40∶60, 5 mL/mn). From Fr.9, compound 6 (12.66 mg, tR6.53 min) was obtained after Sephadex LH-20 gel chromatography and high performance preparative liquid chromatography (methanol-0.1% glacial acetic acid aqueous solution, 20∶80, 5 mL/min).
3.2 Structure identification
3.2.1Compound 1. White granular crystal (methanol), m.p. 74-76 ℃. ESI-MS (m/z): 235 [M+H]+.1H-NMR (500 MHz, DMSO-d6)δ: 5.75 (1H, s, 3-OH), 3.64 (3H, s, H-7), 3.56 (6H, s, H-8, 9), 2.87 (2H, d,J=15.1 Hz, H-2), 2.73 (2H, d,J=15.1 Hz, H-4).13C-NMR (125 MHz, DMSO-d6)δ: 43.0 (C-2, 4), 51.5 (C-8, 9), 52.1 (C-7), 73.1 (C-3), 169.7 (C-1, 5), 173.1(C-6). The above spectral data was basically consistent with the literature[3], and compound 1 was elucidated as trimethyl citrate.
3.2.2Compound 2. White needle crystal (methanol), m.p. 211-212 ℃. ESI-MS (m/z): 169 [M+H]+.1H-NMR (500 MHz, DMSO-d6)δ: 7.43 (1H, d,J=8.6, 3.1 Hz, H-2), 7.42 (1H, d,J=3.1 Hz, H-6), 6.83 (1H, d,J=8.6 Hz, H-5), 3.80 (3H, s, OCH3).13C-NMR (125 MHz, DMSO-d6)δ: 112.7 (C-2), 114.9 (C-5), 123.4 (C-6), 129.6 (C-1), 147.1 (C-4), 150.9 (C-3), 167.4 (COOH), 55.5 (OCH3). The above spectral data was basically consistent with the literature[4], and compound 2 was elucidated as vanillic acid.
3.2.3Compound 3. Yellow oily. EI-MS (m/z): 126 [M]+.1H-NMR (500 MHz, CDCl3)δ: 9.54 (1H, s, CHO), 7.21 (1H, d,J=3.7 Hz, H-3), 6.50 (1H, d,J=3.7 Hz, H-4), 4.69 (2H, s, H-5).13C-NMR (125 MHz, CDCl3)δ: 57.6 (2-CH2OH), 110.1 (C-4), 123.3 (C-3), 152.4 (C-5), 160.9 (C-2), 177.9 (CHO). The above spectral data was basically consistent with the literature[5], and compound 3 was elucidated as 5-hydroxymethylfurfural.
3.2.4Compound 4. White granular crystal (methanol), m.p. 90-92 ℃. ESI-MS (m/z): 221 [M+H]+.1H-NMR (500 MHz, Pyridine-d5)δ: 3.59 (6H, s, H-7, 8), 3.49 (2H, d,J=14.9 Hz, H-2), 3.39 (2H, d,J=14.9 Hz, H-4).13C-NMR (125 MHz, Pyridine-d5)δ: 44.4 (C-2, 4), 51.8 (C-7, 8), 74.5 (C-3), 171.4 (C-1, 5), 177.1 (C-6). The above spectral data was basically consistent with the literature[6], and compound 4 was elucidated as 1,5-dimethyl citrate.
3.2.5Compound 5. White granular crystal (methanol), m.p. 115-117 ℃. ESI-MS (m/z): 249 [M+H]+.1H-NMR (500 MHz, DMSO-d6)δ: 4.02 (2H, q,J=7.1 Hz, H-8), 3.64 (3H, s, H-10), 3.56 (3H, s, H-7), 2.86 (2H, dd,J=15.1, 4.4 Hz, H-4), 2.71 (2H, dd,J=15.2, 10.2 Hz, H-2), 1.23 (1H, s, 3-OH), 1.15 (3H, t,J=7.1 Hz, H-9).13C-NMR (125 MHz, DMSO-d6)δ: 14.0 (C-9), 43.1 (C-2), 43.3 (C-4), 51.5 (C-10), 52.1 (C-7), 60.1 (C-8), 73.1 (C-3), 169.2 (C-5), 169.7 (C-1), 173.1 (C-6). The above spectral data was basically consistent with the literature[7], and compound 5 was elucidated as 1, 6-dimethyl-5-ethyl citrate.
3.2.6Compound 6. Yellow oily. EI-MS (m/z) 154 [M]+.1H-NMR (800 MHz, DMSO-d6)δ: 7.35 (1H, brs, H-2), 7.27 (1H, brd,J=8.2 Hz, H-5), 6.60 (1H, brd,J=8.2 Hz, H-6).13C-NMR (200 MHz, DMSO-d6)δ: 121.6 (C-1, 6), 116.9 (C-2), 144.7(C-3), 149.3(C-4), 115.0 (C-5), 169.3 (C-7). The above spectral data was basically consistent with the literature[8], and compound 6 was elucidated as 3,4-dihydroxybenzoic acid.
4 Discussion
Six compounds were isolated from the ethyl acetate fraction of the fruit ofE.undulata(Wall.) Mez, among which, three citrate compounds were identified as trimethyl citrate, 1,5-dimethyl citrate, 1,6-dimethyl-5-ethyl citrate; two phenolic acid compounds were identified as vanillic acid and 3,4-dihydroxybenzoic acid; and one aldehyde compound was identified as 5-hydroxymethylfurfural. The six monomer compounds were all isolated from this plant for the first time.
Studies show that citrate compounds have a certain antioxidant effect. They are widely used in the food industry, and are a food additive that is safe to the human body and easily biodegradable[9]. Vanillic acid (4-hydroxy-3-methoxybenzoic acid) is an oxidized form of vanillin. It is a commonly used food and drug additive, and has anti-oxidant[10], anti-inflammatory[11-12], antibacterial[13], myocardial protection[14], anti-cancer[15]and many other pharmacological activities. 3,4-dihydroxybenzoic acid (protocatechuic acid) is a phenolic substance widely found in nature. It is the main phenolic metabolite of plant polyphenols such as anthocyanins, and is one of the secondary active products of polyphenols that exert their physiological functions in the body, with anti-oxidant[16], anti-inflammatory[17], antibacterial[18], anti-virus[19-20], liver and kidney protection[21]and other biological activities. 5-hydroxymethylfurfural is a small molecule compound of aldehydes. It has a variety of pharmacological activities such as anti-oxidation[22], anti-tumor[23], hypoglycemia[24]and neuroprotection[25].
According to the above literature reports, it could be concluded that the six compounds isolated in this study all have a variety of activities and have good research and development prospects. This study can provide a basis for the research on the effective material basis ofE.undulata(Wall.) Mez and lay the foundation for more in-depth pharmacological research on quality standards of medicinal materials as well.
- Medicinal Plant的其它文章
- Potential Preventive and Therapeutic Effects of Traditional Chinese Medicine Compound Prescription and Traditional Chinese Medicine Products on COVID-19
- Review of Modern Research on Toxicity of Traditional Chinese Medicine Aconm Lateralis Radix Praeparaia
- Advances in Research of Pharmacological Action and Mechanism of Tibetan Medicine Ranasampel
- Research Progress of External Treatment of Acute Gouty Arthritis with Traditional Chinese Medicine
- Study on Pharmacological Effects of Harmine Hydrochloride
- Research Progress in the Application of Network Pharmacology in Traditional Chinese Medicine and Compound Prescriptions

