Scheme to measure the expectation value of a physical quantity in weak coupling regime?
Jie Zhang(張杰), Chun-Wang Wu(吳春旺), Yi Xie(謝藝), Wei Wu(吳偉), and Ping-Xing Chen(陳平形),?
1Department of Physics,College of Liberal Arts and Sciences,National University of Defense Technology,Changsha 410073,China
2Interdisciplinary Center for Quantum Information,National University of Defense Technology,Changsha 410073,China
Keywords: weak measurement,expectation value,trapped ions
1. Introduction
Quantum measurement, involving a wide range of content of quantum mechanics, is difficult to be understood but also one of the most interesting basic research directions.[1]The study of quantum measurement can be summarized as two aspects, one is the understanding of the nature of quantum measurement,such as how quantum states collapse,[2]and the other is the application of quantum measurement. Here we focus on the latter. The applications of quantum measurement include three aspects: to obtain the information of the measured quantum state;[3]to obtain the value of the physical quantity of the measured system;[4,5]and to sense the information of the external environment,[6,7]such as sensing the intensity of the external magnetic field, etc. A basic model of quantum measurement is von Neumann measurement, which regards the measurement as the interaction between the measured system and measuring pointer.[2]If the interaction is strong enough so that the different states of the pointer corresponding to the eigenvalues of the measured system are orthogonal to each other, one can get the measurement results from the pointer states, which can be described by projective measurement. If the interaction is too weak to discriminate the pointer states completely,the measurement is modeled by the weak measurement scheme, which was proposed by Aharonov, Albert, and Vaidman (AAV) in 1988.[8]AAV also showed that the weak value amplification (WVA)effect[9-15]can be observed by an appropriate postselection in the weak measurement, which would be useful in quantum sensing.[16,17]Here is the question that under the weak measurement condition (the pointer states are not orthogonal to each other), how can we obtain the expectation value? In this paper we propose a scheme to measure the expectation value under weak coupling condition inspired by, but not using,WVA technique.
The structure of this paper is organized as follows. In Section 2,we will introduce the theoretical model of our measurement scheme. A proof of principle of our scheme using trapped ion is shown in Section 3. Finally,we give the discussion and conclusion of this paper.
2. Theoretical model of the measurement scheme
In this section,we introduce the theoretical model of the new measurement scheme. Suppose a general measurement described by the von Neumann’s measurement model, and the interation between the measured system and measuring pointer can be written as

where g is the coupling strength, ?A and ?p are the operators of the measured system and measuring pointer, respectively.The evolution of the system at time t with the initial state and the deviation comes from the instable experimental parameters and limited data points for reconstruciton of the wave packet.

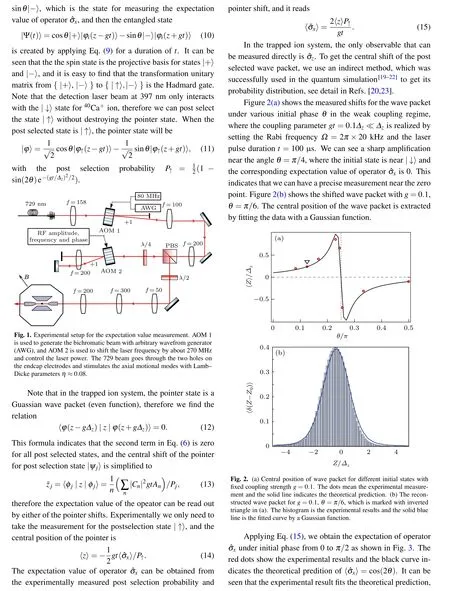
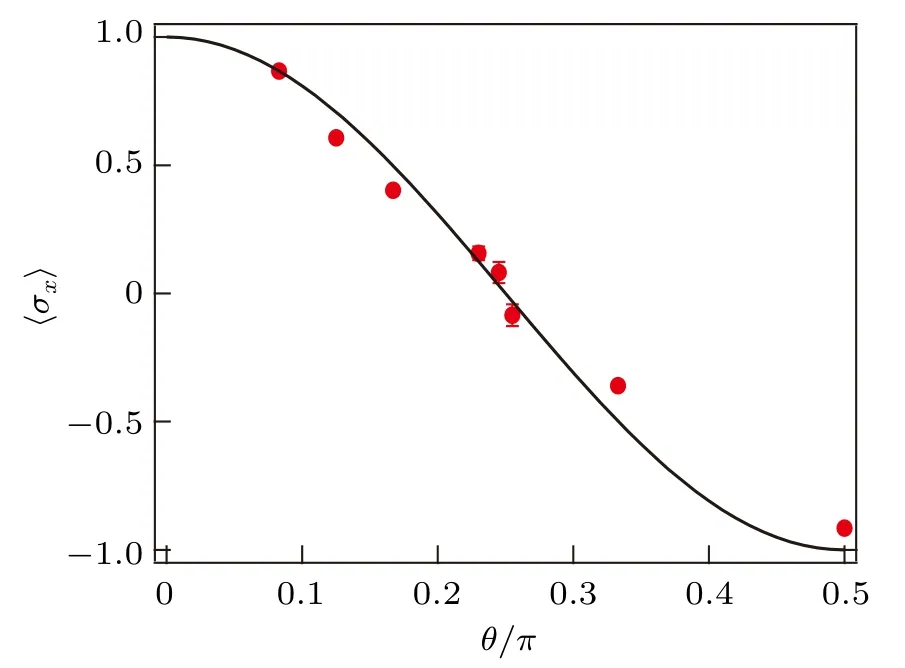
Fig.3. Expectation value measurement for different initial states with coupling parameter gt =0.1Δz. The solid line indicates the theoretical prediction of operator 〈?σx〉=cos(2θ) with initial state cosθ|+〉+sinθ|?〉 and the dots mean the experimental measurement.
4. Discussion and conclusion
It is interesting to compare the weak value with the expectation value in the weak coupling regime. Firstly, the expectation value has a different definition from the weak value as shown in Ref. [8]. Secondly, to get a useful weak value,one should choose an appropriate postselected state according to the initial state. On the contrary,to get the expectation value one may always choose the postselected state as shown in Eq.(4)in spite of the initial states.
In conclusion, we proposed a useful method for measuring the expectation value of a weak coupling system and demonstrated the scheme by taking advantage of a single trapped40Ca+. This scheme provides an effective method to extract the expectation value for the weak coupling system.The good agreement between the theoretical prediction and experimental results shows that the scheme may be useful in quantum sensing.
- Chinese Physics B的其它文章
- Transport property of inhomogeneous strained graphene?
- Beam steering characteristics in high-power quantum-cascade lasers emitting at ~4.6μm?
- Multi-scale molecular dynamics simulations and applications on mechanosensitive proteins of integrins?
- Enhanced spin-orbit torque efficiency in Pt100?xNix alloy based magnetic bilayer?
- Soliton interactions and asymptotic state analysis in a discrete nonlocal nonlinear self-dual network equation of reverse-space type?
- Discontinuous event-trigger scheme for global stabilization of state-dependent switching neural networks with communication delay?

