Effect of foot reflexology on pain and physiological indicators in postoperative patients:A systematic review and meta-analysis
Li Tian,Mengyuan Li,Ling Yan
1School of Nursing,Tianjin University of Traditional Chinese Medicine,Tianjin,China
2Department of Brain Cancer,Tianjin Medical University Cancer Institute&Hospital,Tianjin,China.
3Department of Nursing,Tianjin Medical University Cancer Institute&Hospital,Tianjin,China.
Abstract Aim:To determine the effect of foot reflexology intervention on pain and physiological indicators in postoperative patients. Data resources: The Cochrane library, PubMed, EMBASE, MEDLINE, SCOPUS, CINAHL, China National Knowledge Infrastructure (CNKI), VIP, and Wan Fang Data were searched from inception until January2020. Review methods: Studies were screened according to the PICOS principle.The methodological quality was assessed with Cochrane Risk of Bias Tool.Meta-analysis was performed using RevMan 5.3 software.Results: 5 randomized clinical trials involving 318 participants were included in the meta-analysis .There were significant differences in pain and heart rate in postoperative patients between the two groups.Conclusion:The foot reflexology intervention decrease the postoperative pain and heart rate for the postoperative patients.It can be considered to be an effective non-pharmaceutical therapy to reduce the postoperative pain and heart rate.The evidence is not enough to prove the effectiveness of reducing postoperative blood pressure, respiratory rate, pulse rate and oxygen saturation using the foot reflexology.
Keywords: Footreflexology,Postoperativepatients, Pain, Physiological indicators, Nursing, Systematic review and meta-analysis Abbreviations:RCT,Randomized controlled trial;CI,Confidence interval;SMD,Standardized mean difference.
Introduction
More than 200 million operations are performed worldwide each year[1],postoperative pain has been a serious problem for all of the patients who undertook the surgery.80%patients report the moderate to severe different degrees of pain [2], caused by the incision of the surgery, tracheal intubation [3].Postoperative pain can bring a variety of negative consequences to the postoperative patients,such as leading to the emotional instability,activity limitation,length of stay in hospital,increased medical burden, and even chronic post-surgery pain or persistent postsurgical pain[4-6].What's more, the stimulation of pain and unstable mood will cause the increase of physiological indexes such as blood pressure, respiratory pulse and heart rate[7].Thus, management of postoperative pain is of great importance for the postoperative patients.
Nowadays,Analgesics are still the most common and effective way to relieve pain of the patients [8].However, excessive analgesics can result in many side effects, including drowsiness, respiratory depression,nausea, vomiting, intestinal irritation and severe addiction [9-11].Besides, many mild pain patients do not have to use analgesics because of the medication management principle for pain.
Therefore, researchers shift their attention to the non-pharmacological therapies, such as complementary and alternative medicine.A body of studies have shown that the combinations of complementary and alternative medicine have favorable significant effects on reducing the dose of analgesics and relieving the pain compared to analgesics alone [12, 13].Complementary and alternative medicine to relieve pain include acupuncture, Yoga, music therapy, aromatherapy,guided imagery, reflexology [14-17].Reflexology is one of the most popular and safest therapy [18], which affects the whole body by placing pressure on the hands, feet, and ears [19].The feet are most common part to apply pressure on account of its' good operability, larger reflective area and better intervention effects to reduce postoperative pain and anxiety [20].Foot reflexology is designed to reduce pain by pressing the specific reflective areas in the feet corresponding to the various organs of the body,glands and other parts of the body to releasing natural analgesic called “endorphins” [21, 22].What's more,pressing through the reflex area contributes to better blood circulation, which can relax the patients and lower the relevant physiological indicators.In this regard, foot reflexology appears to be easier and patient-acceptable and no special equipment is required except hands without side effects.
Although a few systematic reviews showed the positive effects of the foot reflexology on the healthy people, breast cancer patients and the chronic patients[23-25], it is unclear whether foot reflexology is more effective for postoperative patients than routine care,no interventions or simple foot massage.In addition,previous research has focused on the effects of foot reflexology on pain, but those subjects were not aimed at the postoperative patients and the included studies were not randomized controlled trials [26].Thus my study is the first systematic review and meta-analysis on the effect of foot reflexology on the pain and physiological indicators in postoperative patients.It is considered that the finding of this meta-analysis will serve as a guide on whether it is effective for nurses to relieve pain and reduce the physiological indicators in postoperative patients through the foot reflexology.
Methods
Aim
The aim of systematic review and meta-analysis was to analyze the effect of foot reflexology on pain and physiological indicators in postoperative patients.
Design
This was a systematic review with meta-analysis concerning foot reflexology on pain and physiological indicators in postoperative patients.The systematic review and meta-analysis was carried out with the guideline of Cochrane Collaboration[27].
Search methods
The Cochrane Central Register of Controlled Trials,PubMed, EMBASE, MEDLINE, SCOPUS, CINAHL,China National Knowledge Infrastructure(CNKI),VIP,and Wan Fang Data were searched from inception to January2020.The studies were limited to publish in English and Chinese.The following combinations of mesh terms or subject headings were used: “foot reflexology”, “zone therapy”, “foot reflexotherapy” ,“foot reflex zone massage”,“foot massage”,“postoperat*”,“operat*”,“perioperative”or"s urg*"“surgery”,“operation”,“postoperation”“perioperat ion ”and “randomized controlled trial” The reference lists of eligible trials were also searched extensively for potential trials.According to PICO principle, we carried out the inclusion and exclusion criteria for the literature.
The inclusion criteria were as follows
PopulationPatients had to have undergone any kind of surgical procedure at any age or in any gender.
InterventionPatients had to have received foot reflexology alone without other treatments.Intervention duration and frequency were not restricted.
ComparisonPatients could undergo no intervention,usual care or other ways that are different from foot reflexology;
OutcomesThe primary outcomes were pain and the secondary outcomes included physiological indicators,such as systemic blood pressure, diastolic blood pressure, respiratory rate, pulse rate, heart rate, mean arterial pressure, oxygen saturation.The study had to have assessed at least one of the outcomes investigated in this meta-analysis.
Study designRandomized controlled trails.
The exclusion criteria were as follows
PopulationPatients could have foot problems (such as callus, corn, fungal skin infection, previous scars,diabetic foot or known neuropathy).
InterventionPatients could receive more than just a foot reflexology intervention,they had received hand reflexology, ear reflexology or other combined interventions.
ComparisonPatients could receive hand reflexology or ear reflexology.
OutcomesThe data of outcomes were incomplete.Study design:non-randomized controlled trials.
Search outcomes
The process of study selection is shown in the Flow chart (Fig.1).A total of 1264 relevant articles were retrieved from 9 databases, 320 of which were duplicate.After removing the duplicates,the remaining 944 studies needed screening for further evaluation.879 studies were excluded after the screen of titles and abstracts.65 articles were included for an assessment of the full texts, 60 of which are excluded for the following reasons (the incomplete data, unrelated outcome indicators, inconsistent study design and unavailable full text).Finally, 5 records met the all criteria and were left in the final meta-analysis.
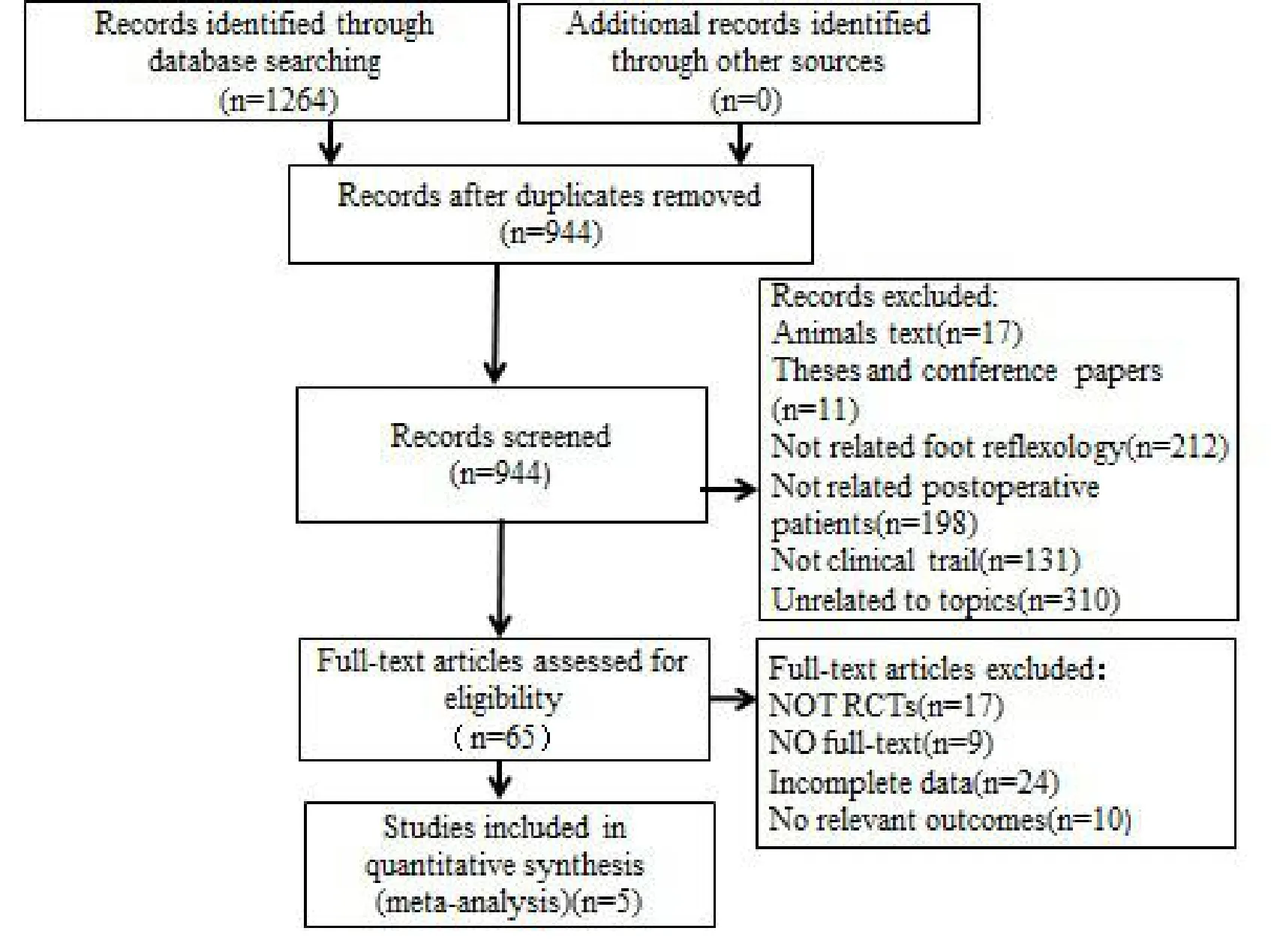
Figure 1:Flow diagram of literature retrieval and study selection
Quality appraisal
The methodological quality of the included studies was assessed independently by two reviewers using Cochrane Collaboration Risk of Bias Tool [27].Each study was scored as high, low or unclear risk for the following seven items: random sequence generation,allocation concealment, blinding of participants and personnel,blinding of outcome assessment,incomplete outcome data, selective reporting and other bias.Any disagreement was settled by discussing with the third reviewer.
Data abstraction
Two researchers extracted the following data for the included trials independently:general information(e.g.language, location, year of publication), characteristics of patients (e.g.age, sample size, type of procedure),Information about the control and intervention (e.g.intervention methods, duration and frequency) and the outcomes.Any disagreement was solved through discussion or arbitration by the third researcher.The outcome measures were presented as the mean with 95%confidence interval(CI).We calculated the change of means and SD for the two groups according to the following formula.
change in mean=Mean post-Mean pre
Synthesis
Revman 5.3 software was used for data analysis and the I2 was used to test the heterogeneity of the included studies.We divide heterogeneity into "low","moderate" and "high" according to the result of I2.When I2<25% ,it means low statistical heterogeneity;The values over 25% and less 50%were considered to be moderate in heterogeneity; If I2>50%, it means high statistical heterogeneity; A fixed-effects model was used to Integrate the data If I2>50%.Otherwise,a random-effects model was used [27].For dichotomous data, risk ratio (RR) and odds ratio (OR) was included in the Forest plot.For continuous data, it is a must for us to use the weighted mean difference method(WMD)when the measurement standards are consistent.Otherwise, a standardized mean difference method(SMD)was used.
If there are enough included studies,the source of heterogeneity can be explained by subgroup analysis.Meta-analysis cannot be carried out if there are not valid data or effective methods to determine the source of heterogeneity.Otherwise, descriptive analysis is a good idea.Sensitivity analysis will be applied to judge the stability of the result by exclusion of each study one by one.
Results
Characteristics of the included studies
The characteristics of the 5 [29-33] included randomized controlled trials are presented in Table 1.All of the trails were carried out in Iran.The five papers included in the review were all published in English between 2015 and 2020.The sample size ranged from 20 to 116 with a total size of 318,composed separately by 159 patients in the control and experiment group.In the 5 studies included,participants had received different operations: cardiac surgery (N=4 trails) and caes are an section surgery(N=1 trail).The time and frequent of the interventions were different among all the 5 trail .The time of the interventions ranged from 5 minutes to the 20 minutes:5 minutes (N=1 trail), 20 minutes (N=3trails) and 18minutes (N=1 trail).The frequency of intervention also differed among the studies: single session (N=4 trails) and five sessions (N=1 trail).As for the outcomes, 3 studies reported the pain measured by visual analogue scale (VAS).And physiological indicators were measured by systemic blood pressure( N=4 trails), diastolic blood pressure (N=4 trails), respiratory rate(N=4 trails), pulse rate (N=2 trails), heart rate (N=2 trails), mean arterial pressure(N=2 trails)and oxygen saturation(N=2 trails).
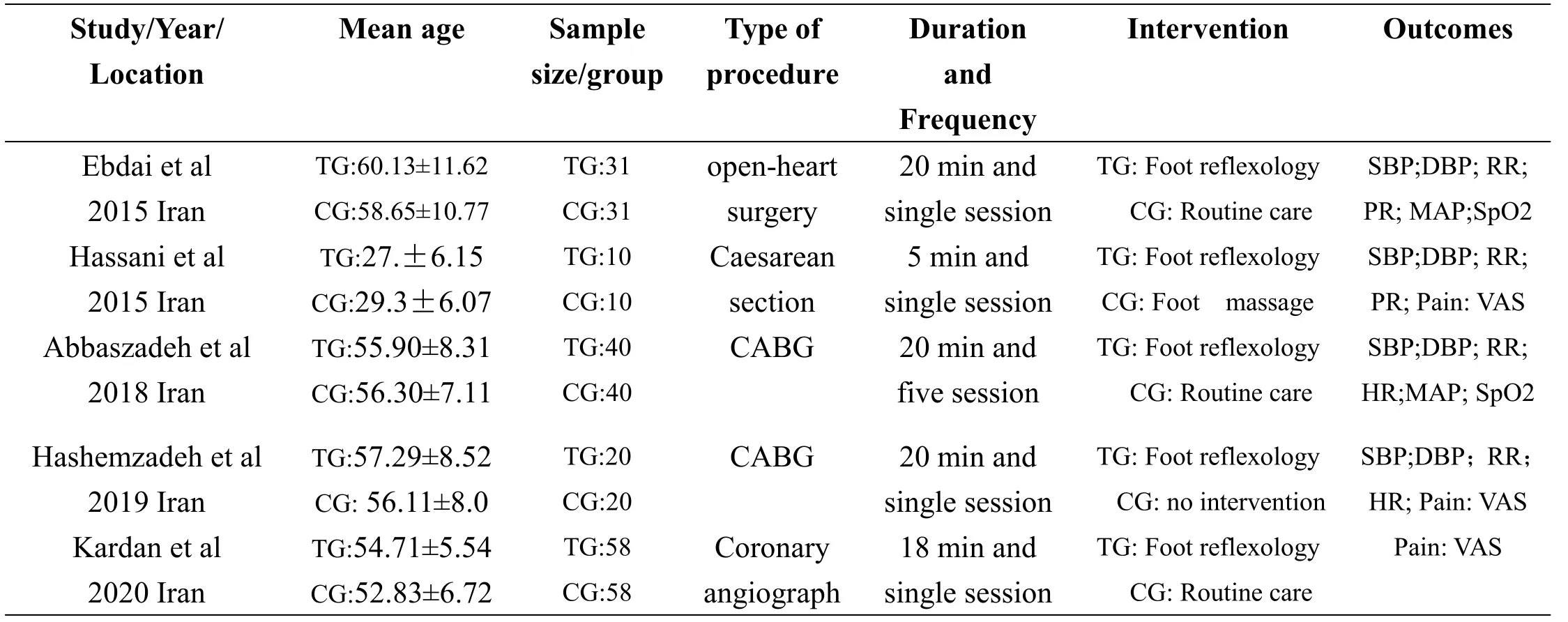
Table 1:Basic features of the included literature
Risk of bias
The risk of bias assessment of the included 5trails was shown in the Fig.2 and Fig.3 .Of the 5 trials included in the review, all the patients were randomly assigned to the intervention group and control group,but only 2 trails [31, 32] described the detailed random sequence generation.And only 1 trail [31] described allocation concealment .2 studies [29, 31] reported that blind to the patients and the investigators and 1 trail [29]reported that blind to the outcome evaluator.All the 5 studies reported intention to treat approach.As for the selective reporting bias, we judged that expected outcomes were stated in all trials.
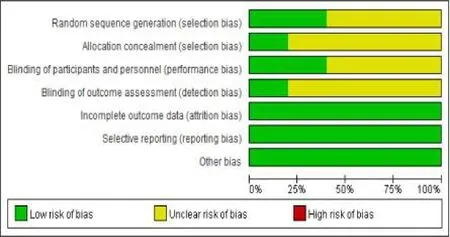
Figure 2:Risk of bias graph
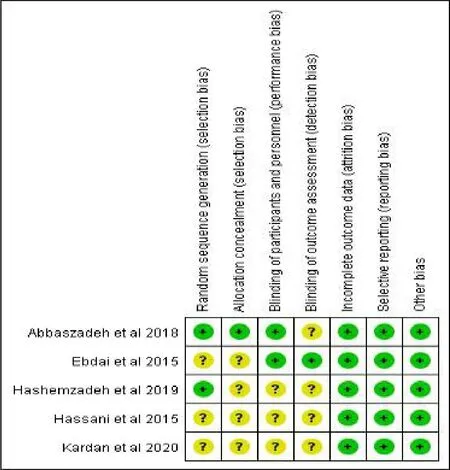
Figure 3:Risk of bias summary
Effects of the foot reflexology
Effects of foot reflexology on postoperative pain
Three studies [30, 32, 33] with 176 patients were measured postoperative pain using visual analogue scale (VAS).MD and the fixed-effect model was used in analyzing the data on account of a moderate heterogeneity (P=0.23, I2= 32%).The meta-analysis showed that foot reflexology had significant effects on decreasing postoperative pain when compared with control group [MD= -1.19, 95% CI (-1.60, 0.78), p<0.00001](Fig.4)
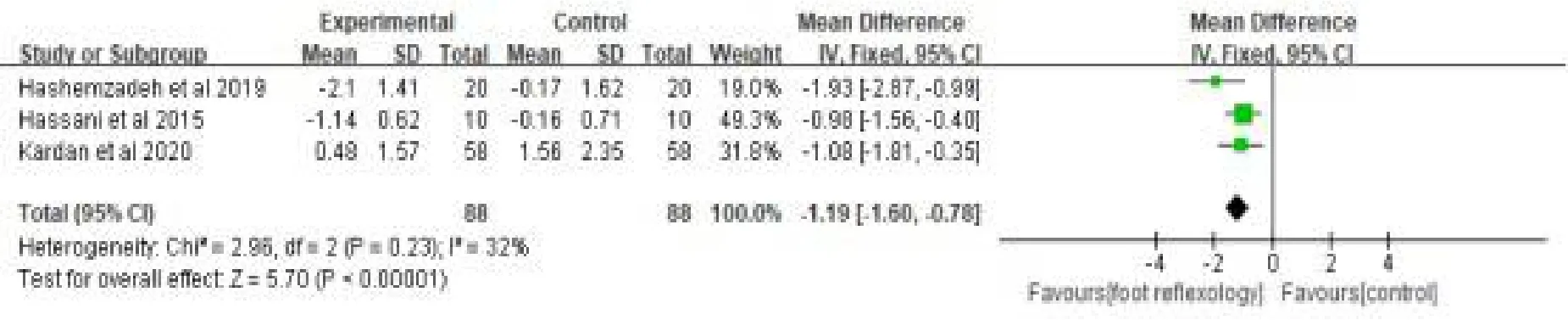
Figure 4:Effects of foot reflexology on postoperative pain
Effects of foot reflexology on systemic blood pressure
Four studies [29-32] with 202 patients were measured systemic blood pressure.A random-effect model was used in analyzing the data on account of a high heterogeneity (P=0.04, I2= 64%).The meta-analysis indicated that foot reflexology had no significant effects on decreasing systemic blood pressure when compared with control group[MD=-3.65, 95% CI(-8.10, 0.80), p=0.11] ( Fig.5).The sensitivity analysis was carried out to identify the sources of heterogeneity by excluding the literature one by one.There existed no heterogeneity(P=0.65,I2=0%),when the study by Hashemzadeh K was removed from the study.However, the foot reflexology still showed no improvements on the systemic blood pressure (MD=-1.24,95%CI(-3.01,0.54),p=0.17)((Fig.6).
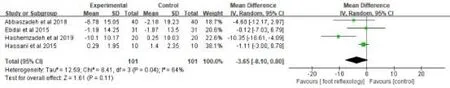
Figure 5:Effects of foot reflexology on systemic blood pressure
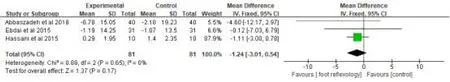
Figure 6:Sensitivity analysis of the effect of foot reflexology on systemic blood pressure
Effects of foot reflexology on diastolic blood pressure
Four studies [29-32] compared the effects of effects of foot reflexology intervention on diastolic blood pressure in 202 patients.A random- effect model was used in analyzing the data on account of a high heterogeneity (P=0.008, I2= 82%).The meta-analysis suggested that foot reflexology had no significant effects on decreasing systemic blood pressure when compared with control group[MD=-2.54, 95% CI(-7.46, 2.39), p=0.31] (Fig.7).Literature was eliminated one by one to find the source of heterogeneity and the study by Hashemzadeh K was found to be the main cause of the heterogeneity.But no significant result was found between the two group[MD= 0.52, 95% CI (-0.47, 1.52), p=0.30] with no heterogeneity (P=0.83, I2= 0%) (Fig.8) after removing the study.
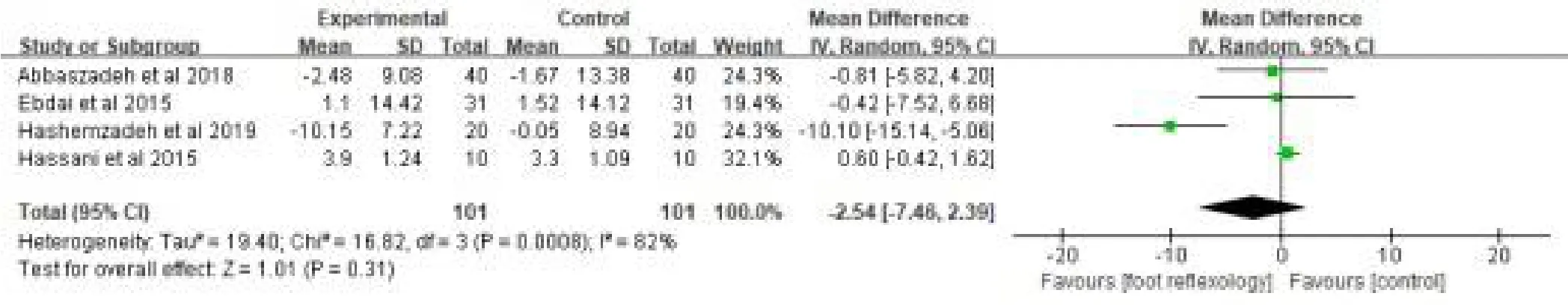
Figure 7:Effects of foot reflexology on diastolic blood pressure

Figure 8:Sensitivity analysis of the effect of foot reflexology on diastolic blood pressure
Effects of foot reflexology on respiratory rate
Four studies [29-32] compared the effects of foot reflexology intervention on respiratory rate in 202 patients.A random-effect model were used in analyzing the data due to a high heterogeneity(P=0.03,I2= 67%).The results suggested that there were no significant differences in respiratory rate between the foot reflexology intervention and control groups[MD=-0.15, 95% CI (-1.34, 1.04), p=0.81] (Fig.9).We conducted the sensitivity analysis and found the study by Hashemzadeh K was the source of the heterogeneity.Heterogeneity was decreased from the 67% to 17%after the exclusion of this study .Also a significant result was found between the two group [MD= -0.65,95%CI(-1.25,-0.06),p=0.03](Fig.10).
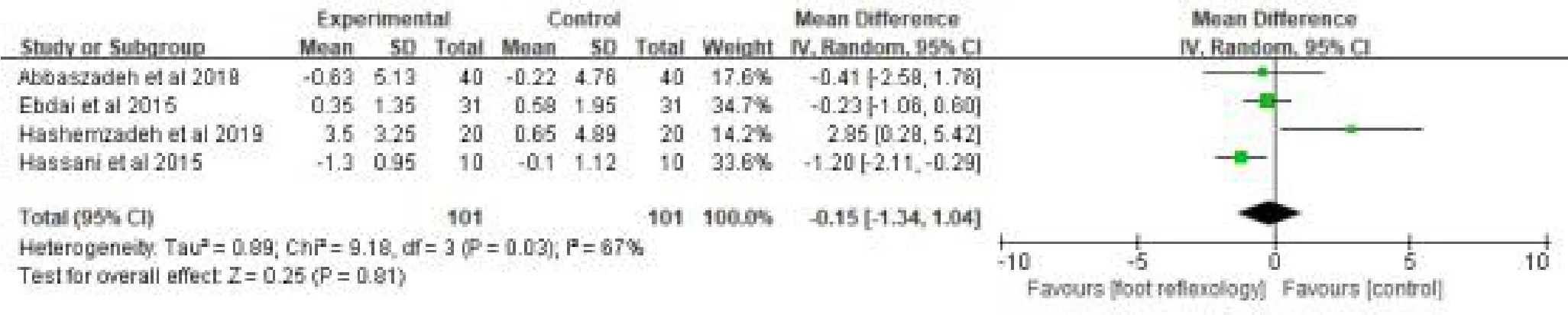
Figure 9:Effects of foot reflexology on respiratory rate
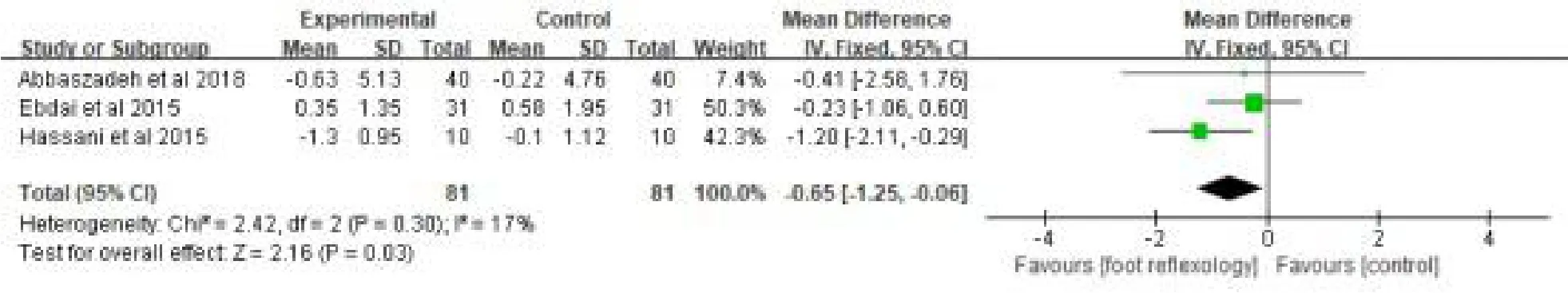
Figure 10:Sensitivity analysis of the effect of foot reflexology on respiratory rate
Effects of foot reflexology on pulse rateTwo studies[29, 30] compared the effects of foot reflexology intervention on pulse rate in82 patients.The heterogeneity of the studies was moderate(P=0.17,I2=48%),thus we use a fixed-effect model to analysis the data.However, the results showed that the control group was more effective than the foot reflexology intervention group[MD=5.89,95%C I(0.82,10.97),p=0.02](Fig.11).
Effects of foot reflexology on heart rateThe effects of foot reflexology on heart rate was reported in 2 trials [29, 32] with 60 patients, and the results suggested that foot reflexology had favorable significant effects on decreasing postoperative heart rate when compared with control group [MD=-7.0 ,95%CI (-11.29, -2.07), p=0.005]( Fig.12)with a fixed-effect model.
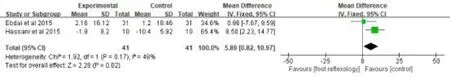
Figure 11:Effects of foot reflexology on pulse rate
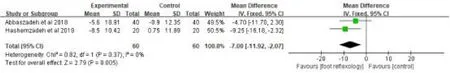
Figure 12:Effects of foot reflexology on heart rate
Effects of foot reflexology on mean arterial pressure
The effects of foot reflexology on mean arterial pressure was reported in 2 trials [29, 31] involving 71 patients.There was no heterogeneity between the two studies (P=0.67, I2=0%), so a fixed- effect model was applied to analyze the relevant data.The results showed that there were no significant differences in mean arterial pressure between the intervention and control groups [MD =-1.35, 95% CI (-5.34, 2.64), P=0.51](Fig.13).
Effects of foot reflexology on oxygen saturation
Two trails [29-31] involving 71 patients assessed the effects of foot reflexology on oxygen saturation.A fixed-effect model was applied to analyze the relevant data as there was no heterogeneity between the two studies (P=0.68, I2= 0%).The meta-analysis showed no significant difference between the two groups [MD=-0.04,95%CI(-0.76,0.68),P=0.91](Fig.14).
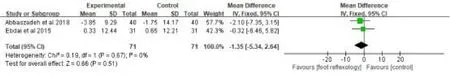
Figure 13:Effects of foot reflexology on mean arterial pressure
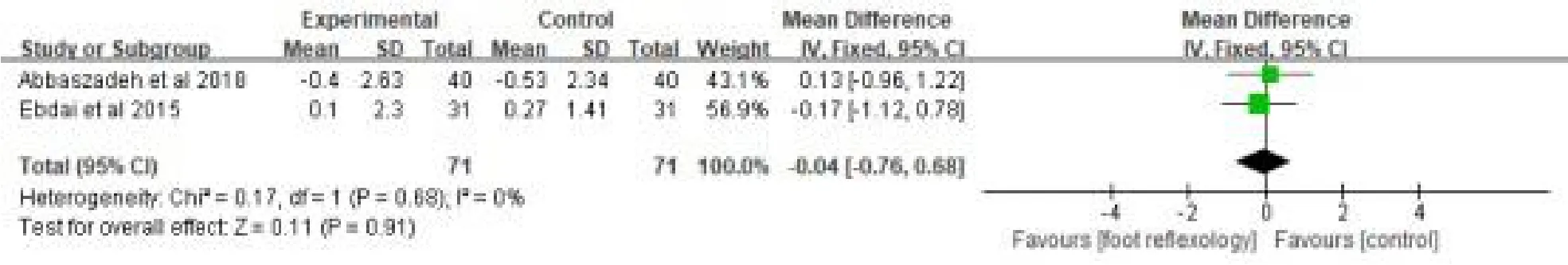
Figure 14:Effects of foot reflexology on oxygen saturation
Discussion
It is known that the first review and meta-analysis appraising the effect of foot reflexology on the pain and physiological indicators in the postoperative patients.Though previous reviews showed that the effect of foot reflexology on pain and physiological indicators, the research design of the included studies was not RCTs and the meta-analysis was not carried out [34, 26, 35].In addition, some studies have been contradictory in discussing the effects of foot reflexology on physiological indicators, which made it necessary for us to conduct a comprehensive systematic review and meta-analysis to study the specific effect of on physiological indicators.The result revealed foot reflexology significantly relieved the postoperative pain and heart rate but showed no improvements in blood pressure,respiratory rate, pulse rate,and oxygen saturation.
The combined results of the three included studies showed that foot reflexology could significantly reduce pain for postoperative patients, measured by visual analogue scale (VAS) scores.That was, the foot reflexology treatment method could indeed be used as an effective and significant complementary and alternative method to the analgesic treatment in addition to being a non-invasive and safe procedure.This was similar to the results of some studies[36,37],which also demonstrated the effectiveness of foot reflexology for pain management.The mechanism of foot reflexology on pain relief is not yet understood,however, it is conjectured that the following mechanism might explain the how the foot reflexology reduce the pain.Nourmohammadi thought that foot reflexology involved deep pressure on the foot reflex area corresponding to the body's organs, stimulating nerve endings and released a natural analgesic called endorphin,which could reduce the feeling of pain[22].In addition, reflexologist, poole , considered pressure on certain reflex points in the soles destroyed the calcium crystals accumulated in nerve endings after the operation, opening the blocked nerve pathways, and speeded up blood flow throughout the body and relieved pain [38].The neuromatrix pain theory suggested that the pain was prevented from transmitting by transmitting afferent impulses and closing the neural gates in the dorsal horn of the spinal cord in the reflexology therapy [39].In foot reflexology, pressure stimulated blood circulation throughout the body,causing the decline in pain,which relaxed the whole body and improved the physiological indicators.Physiological indicators include many aspects, such as blood pressure,respiratory rate, heart rate, pulse rate and oxygen saturation.Some documents also demonstrated that the foot reflexology had a positive effect on physiological indicators [36, 40].However, foot reflexology was found to have a positive and significant effect only on heart rate in our review and meta-analysis, with regard to the blood pressure, respiratory rate, heart rate, pulse rate and oxygen saturation, foot reflexology did not make a good improvement compared with the control group.It could be explained for the following several reasons: the number of studies included in the meta-analysis was not enough, ranging from 2 to 4,which caused the small sample size.The type of surgery and the age of the participants caused the difference in sensitivity for the patients to foot reflexology.Thus, it was highly suggested that more high-quality and large-sample randomized controlled trials on the effect of foot reflexology on the physiological indicators for the postoperative patients in different types of surgery should be conducted in the future,especially the studies on the effect on the blood pressure, respiratory rate, pulse rate and the oxygen saturation.
In addition, there was high heterogeneity in the results of systemic blood pressure ,diastolic blood pressure and respiratory rate.Thus a sensitivity analysis for the three results was carried out.It was found that the study by Hashemzadeh K was the sources of heterogeneity, when the study by Hashemzadeh K was removed, the new data suggested the foot reflexology intervention could reduce respiration rate in postoperative patients.But the new data also suggested foot reflexology intervention might have no significant effect on the systemic blood pressure and diastolic blood pressure .The control group received no intervention in the removed study but the control group had at least one intervention measure in other studies, which might explain why the results of the removed study were different from other studies.
This systematic review and meta-analysis adopted five latest studies after retrieving comprehensively from 3 Chinese databases and 6 English databases.And all of the included studies were RCTs, which is important in the meta-analysis.However, there were some inevitable limitations in this systematic review.Firstly, the methodological quality of the included studies is moderate.Three studies didn't mention the detailed random sequence generation,causing potential selection bias to some extent.What's more, there were performance bias and attrition bias in the 4 studies,which had a bad impact on the integration of results.Secondly,the included trails were all conducted in Iran,which might lead to potential selection bias to a certain degree.And it was unclear whether the foot reflexology was applied in other countries.Thirdly,subgroup analysis was not conducted because the number of studies was small to analyze the effect of the foot reflexology one by one.In addition, the small sample size reduced the credibility of merged results.Fourthly, there were some unavoidable heterogeneity due to the variations in the studies themselves(duration and frequency of the interventions, the interventions in the control group, type of procedure and age of the patients), which might lead to certain restrictions on the validity of the interpretation of the results.
Conclusion
In a word, the systematic review and meta-analysis showed that foot reflexology intervention reduced the postoperative pain and heart rate with fewer side effects, but made no difference in the blood pressure(systemic blood pressure, diastolic blood pressure,mean arterial pressure), respiratory rate, pulse rate and oxygen saturation .However, the current data was insufficient to ensure the effect of foot reflexology on the physiological indicators as a result of the limited number of included literature.Thus high-quality,large-sample and multi-center randomized controlled trials needed to be conducted to study the effect of foot reflexology on physiological indicators in the future.In addition, the definite standard (e.g.timing and frequency) for the foot reflexology should be established in the future.
- Nursing Communications的其它文章
- Electronic cigarettes-The Unvarnished Truth
- Focal Point of Nursing Management of PTSD Related to COVID-19 Infection,Quarantine,and Curfew
- Effectiveness of structured teaching programme on knowledge regarding therapeutic nurse-patient communication among the staff nurses
- Bibliometric analysis of researches of Orem self-care model in China based on BICOMB

