Effects of electroacupuncture on uterine prostaglandin F2α, cyclooxygenase 2 and nuclear factor κB in rats with primary dysmenorrhea
Liu Yu (劉余),Tang Wen-jing (唐文靜),Wang Yi-qin (王乙欽),Tang Biao(唐標(biāo))Medical School,Hunan University of Chinese Medicine,Changsha 410028,China
Abstract
Keywords: Acupuncture Therapy;Electroacupuncture; Dysmenorrhea; Prostaglandins F; Cyclooxygenase 2; NF-kappa B;Rats
Primary dysmenorrhea (PD) is defined as cramping pain in the lower abdomen occurring just before or during menstruation, in the absence of pelvic pathology.It is often accompanied by back pain, nausea, vomiting and diarrhea, seriously affecting women's daily study,work and life[1].
The pathological mechanism of PD is mainly related to the increased synthesis and release of prostaglandin(PG)and other factors in the endometrium.Prostaglandin F2α(PGF2α) can cause increased uterine muscle activity, uterine spasm and contraction, tissue ischemia,hypoxia,and pain[2-4].Cyclooxygenase 2(COX-2) is a key factor regulating the synthesis of PG.Under normal circumstances, COX-2 is extremely low in cells. However, body damage can stimulate monocytes,macrophages, fibroblasts, vascular smooth muscle or endothelial cells to induce the production of COX-2,which in turn catalyzes the conversion of arachidonic acid to PG, thereby enabling tissues to synthesize and release a large amount of PG[4].The production of COX-2 is regulated by nuclear factor κB (NF-κB). When bodily stimulation is perceived,NF-κB is phosphorylation-activated and translocated into the mucleus,regulating the transcriptional expression of COX-2[5].Studies have shown that NF-κB/COX-2 pathway plays a vital role in the pathological mechanism of PD[4,6-7].
Electroacupuncture (EA) is an effective intervention method for PD[8]. Studies have shown that EA plays an analgesic effect in PD by regulating the level of PGF2G[9-10].However, the specific mechanism of EA in regulating the synthesis and release of PGF2αin PD is still unclear.
In this experiment, a PD rat model was established to observe the effects of EA on PGF2α, COX-2 and NF-κB in rat’s uterine tissues,and explore the underlying mechanism in EA intervening PD.
1 Experimental Materials and Methods
1.1 Experimental animals and groups
Forty SPF grade healthy female adult Sprague-Dawley rats weighing 220-250 g,2-3 months old,were purchased from Hunan Slack Jingda Experimental Animal Co.,Ltd.,China[Certificate No.:SYXK (Xiang)2013-0004].Before the formal experiment,7 d of adaptive ordinary feed was required.The ambient temperature was kept at 20-25℃. All the rats were maintained on the normal phase of the light-dark cycle and given free access to water and food.This experimental protocol has been approved by the Ethics Committee of Hunan University of Chinese Medicine.The disposal of animals during the experiment complied with theGuiding Opinions on the Treatment of Experimental Animalsissued by Ministry of Science and Technology of the People’s Republic of China in 2006.The rats in this experiment were randomly divided into a blank group, a model group, an EA group and an ibuprofen group by random grouping method,with 10 rats in each group.
1.2 Experimental instruments and reagents
1.2.1 Experimental instruments
TGL20M desktop high-speed refrigerated centrifuge(Changsha Xiangzhi Centrifuge Instrument Co.,Ltd.,China); electrophoresis instrument, transfer membrane instrument and gel imaging system(BIO-RAD,USA);Hwato SDZ-V EA apparatus (Suzhou Medical Products Factory Co., Ltd., China); filiform needles (0.30 mm in diameter and 13 mm in length,Ma'anshan Bond Medical Equipment Co., Ltd., China).
1.2.2 Experimental reagents
Ibuprofen (State Food and Drug Administration (SFDA)Approval No.:H10900089,300 mg/tablet,Sino-US Tianjin Shike Pharmaceutical Co., Ltd., China); estradiol benzoate (SFDA Approval No.:H12020529, 2 mg/mL,Guangzhou Baiyunshan Mingxing Pharmaceutical Co.,Ltd.,China);oxytocin(100 mg,Shenggong Bioengineering Co.,Ltd.,China);radio immunoprecipitation assay (RIPA)lysate (Shanghai Biyuntian Biotechnology Co.,Ltd.,China);protease inhibitor cocktail (Bimake, USA); phosphatase inhibitor cocktail(A and B tubes,100×,Bimake,USA);polybutylcyanoacrylate (bicinchoninic acid, BCA) protein quantification kit (Thermo,USA);polyvinylidene fluoride (PVDF) membrane (26.5 cm×3.75 m, 0.22 μm,Shanghai Biyuntian Biotechnology Co.,Ltd.,China);NF-κB p65 antibody, phospho-NF-κB p65 antibody and COX-2 antibody (Cell Signaling Technology,USA);ultra-sensitive enhancer chemiluminescent substrates(ECL)kit (Shanghai Biyuntian Biotechnology Co.,Ltd.,China); goat anti-rabbit secondary antibody and goat anti-mouse secondary antibody (Merck Millipore,Germany);hematoxylin-eosin(HE)stainingkit(Shanghai Biyuntian Biotechnology Co.,Ltd.,China);PGF2αenzyme-linked immunosorbert assay detection kit (Cayman Chemical, USA).
1.3 Establishment of animal models
Except the blank group, PD rat models using estradiol benzoate combined with oxytocin were established in the other 3 groups refers to the previous study[11]. On day 1, 6:00 p.m., the rats were injected with estradiol benzoate subcutaneously in the thigh.Estradiol benzoate (0.5 mg/rat) was injected subcutaneously on the first day, 0.2 mg/rat on the 2nd to 9th days, and 0.5 mg/rat on the 10th day. On the 11th day, oxytocin was intraperitoneally injected 2 U/rat (mixed with normal saline,at a concentration of 500 mg/L,namely 5 U/mL).Rats in the blank group were injected with normal saline subcutaneously at the same time once a day for 10 consecutive days.On the 11th day,an equal volume of normal saline was injected intraperitoneally.The criterion for successful PD rat model was the writhing reaction after injection of oxytocin[10].
1.4 Intervention methods
1.4.1 Blank and model groups
The rats in the blank group and model group were grabbed moderately during the intervention period without any intervention.
1.4.2 EA group
The modeling method was as described above.EA treatment started on the first day of modeling.The rats were fixed in a homemade cloth cover. Guanyuan(CV 4)and bilateral Sanyinjiao (SP 6)were selected.The location of acupoints in rats was carried out with reference to previous studies[11].
Sanyinjiao(SP6):10 mm above the tip of the medial malleolusof the hind limbs.
Guanyuan(CV 4):25 mm below the umbilicus (the umbilicus is positioned at the lower 1/4 between the sternoclavicular joint and pubic symphysis).
After routine disinfection of each acupoint,acupuncture was performed with disposable sterile acupuncture needles of 0.30 mm in diameter and 13 mm in length.The needle was perpendicularly inserted into the skin by 5 mm at Sanyinjiao (SP6)and 2 mm at Guanyuan(CV 4)respectively.The positive electrode of the EA lead was connected to the needle,and the negative electrode clamped the skin beside the acupoint.The continuous wave was selected,the frequency was 50 Hz, and the stimulation intensity was such that the local muscles at the acupoints were slightly twitched and the rats could tolerate.The intervention schedule was once a day,20 min each time for 10 consecutive days.The acupuncture was completed by one same person.
1.4.3 Ibuprofen group
After the rats were grasped and fixed,they were given ibuprofen intragastrically (mixed with normal saline at a concentration of 1.25 g/L), 0.8 mL/rat,once a day for 10 consecutive days.
1.5 Observation items and detection methods
1.5.1 Number of writhing
After the injection on the 11th day,the number of writhing in each group of rats within 30 min was observed and recorded.The writhing reaction manifested as the appearance of a concave abdomen,extension of the trunk and hind limbs,and internal rotation of unilaterallimb in the rat[10].
1.5.2 Uterine PGF2αdetection
Five rats were randomly selected from each group,and the rats were anesthetized by intraperitoneal injection of 10% chloral hydrate at 3.5 mL/(kg·bw).The uterine tissues of each group of rats were quickly removed on an ice tray,and the right uterine horn was taken.The uterine tissues were homogenized and centrifuged, and the supernatant wastaken. The diluent standard solution was prepared according to the kit instructions.After adding the samples,incubated plate overnight at 4 ℃.After washing the plate,added Ellman's Reagent and left it in the dark at 4 ℃for 60 min.Signal was measured on fluorometer at 412 nm to determine the absorbance of each well. The standard curve was drawn based on the absorbance value of the standard hole and its corresponding concentration,and the concentration of PGF2ain the supernatant of the uterine homogenate of each group was calculated.BCA method was applied for the protein quantification.Firstly,the gradient standards were prepared and the samples were added.After the working solution was added,the plate was incubated at 37℃ for 30 min.Finally,the absorbance at 562 nm wasdetected under a microplate reader.The standard curve was drawn based on the absorbance value of the standard hole and their corresponding concentrations.The concentration of samples of uterine homogenates in each group was calculated according to the standard curve.The relative content of PGF2αwas represented by the ratio of the PGF2acontent of the uterine homogenate supernatant to the total protein content of the uterine homogenate supernatant.
1.5.3 Uterine phospho-NF-κB p65,NF-κB p65 and COX-2 protein expressions detection
The rest 5 rats in each group were anesthetized by intraperitoneal injection of 10% chloral hydrate at 3.5 mL/(kg·bw).The uterine tissue of each group was quickly taken on an ice tray. Accurately weighed 100 mg of uterine tissue from the right uterine horn of each group of rats,added 1 mL lysis buffer containing 10 μL protease and phosphatase inhibitors,and lysed the protein on ice for 10 min.After homogenization,centrifuged at 12 000 r/min at 4 ℃for 10 min,and took out the supernatant containing total tissue protein.Protein quantification was carried out according to the instructions of the BCA protein quantification kit.After the protein standard curve was drawn,the protein concentration was calculated.After adding the sample buffer,placed the protein in boiling water for 10 min for full degeneration.Western blot was carried out to determine the protein expression in uterine tissues.Electrophoresis,membrane transfer and blocking were performed.Phospho-NF-κB p65(1:1 000),NF-κB p65(1:1 000),COX-2(1:1 000)andβ-actin(1:5 000)primary antibodies were added and incubated overnight at 4 ℃,and then washed with Tris-buffered saline with Tween(TBST)buffer.Diluted secondary antibody (1:10 000)was added and incubated on a shaker at room temperature for 60 min.ECL was chosen for Western blot detection.Quantitative image analysis was performed using Quantity One grayscale analysis software to determine the relative opticaldensity (ROD)of the target protein.Withβ-actin as the internal reference protein,the ratio of the target protein RODto the internal reference protein ROD was calculated,and the relative content of the target protein was obtained.
1.6 Statisticalmethods
All data were statistically processed by SPSS version 22.0 software.The measurement data were first tested for normality,and those conforming to the normal distribution were expressed as mean± standard deviation(±s).For multiple comparisons,the oneway analysis of variance with a completely random design was used.For comparison between groups,the least significant difference method was used if the variance was homogeneity;the Dunnett T3 was used if the variance was uneven.P<0.05 was considered statistically significant.
2 Results
2.1 Effects of EA on the number of writhing in PD rats
Within 30 min of injection of oxytocin, no writhing reaction was observed in the blank group,while writhing reaction was observed in the model group,which was significantly different from the blank group(P<0.01),indicating that the model was successful;compared with the model group,the numbers of writhing in the EA group and the ibuprofen group were reduced within 30 min (bothP<0.01), and there was no significant difference in the number between the EA group and the ibuprofen group (P>0.05), (Table 1).
Table1. Comparison of the number of writhing in each group ( ±s, number)
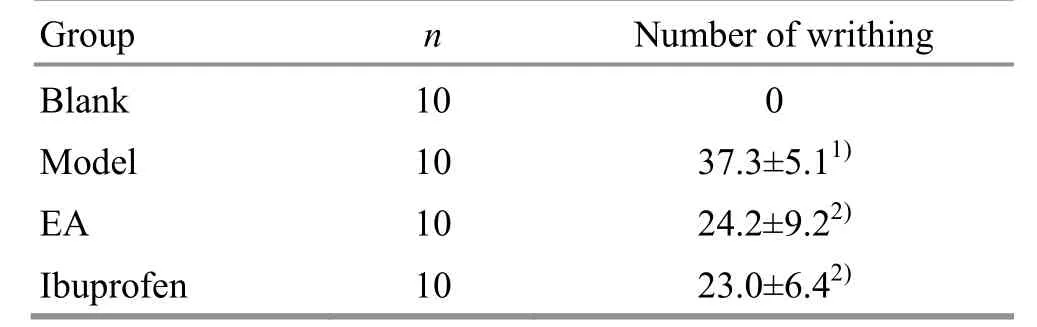
Table1. Comparison of the number of writhing in each group ( ±s, number)
Note:Compared with the blank group,1)P<0.01;compared with the model group, 2) P<0.01
Group n Number of writhing Blank 10 0 Model 10 37.3±5.11)EA 10 24.2±9.22)Ibuprofen 10 23.0±6.42)
2.2 Effects of EA on uterine PGF2α in PD rats
Compared with the blank group, the level of PGF2αin uterine tissues of the model group was significantly increased (P<0.01); compared with the model group,the levels of PGF2αin uterine tissues of the rats in the EA group and ibuprofen group were significantly reduced(bothP<0.01); and there was no significant betweengroup difference in the level of PGF2αin uterine tissues between the EA group and ibuprofen group (P>0.05),(Figure 1).
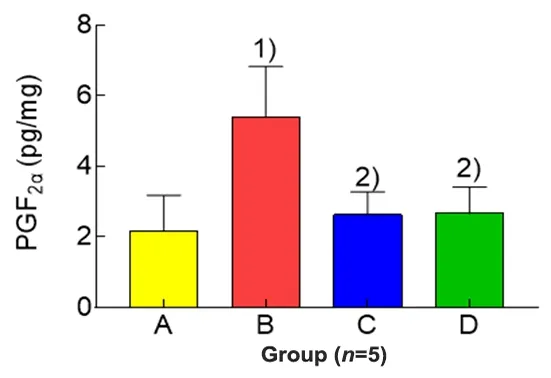
Figure 1.Comparison of the uterine PGF2α in each group
2.3 Effects of EA on uterine COX-2 protein expression in PD rats
The expression level of uterine COX-2 protein of rats in the blank group wasvery low and cannot be detected by Western blot.Compared with the blank group,the level of COX-2 in the model group was significantly increased(P<0.01);compared with the model group,the levels of COX-2 in the EA group and the ibuprofen group were significantly reduced(bothP<0.01);and there was no significant difference in the level of COX-2 between the EA group and the ibuprofen group(P>0.05),(Figure 2 and Figure 3).
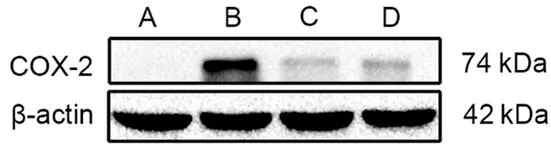
Figure 2.Comparison of the uterine COX-2 in each group (Western blot results)
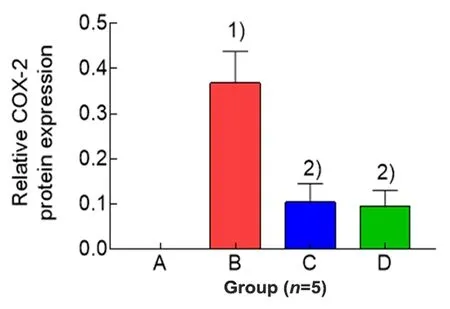
Figure 3.Comparison of the expression level of uterine COX-2 protein in each group
2.4 Effects of EA on the expression levels of uterine phospho-NF-κB p65 and NF-κB p65 proteins in PDrats
Compared with the blank group,the expression levels of phospho-NF-κB p65 and NF-κBp65 proteins in uterine tissues of the model group were significantly increased(bothP<0.01).Compared with the model group,the expression level of phospho-NF-κB p65 protein in uterine tissues in the EA group was significantly reduced (P<0.01), while the level of NF-κB p65 protein was not statistically different between the two groups (P>0.05).The protein expression levels of phospho-NF-κBp65 and NF-κBp65 in uterine tissuesof rats in the ibuprofen group were not statistically different from those in the model group(allP>0.05).Compared with the ibuprofen group,the phospho-NF-κB p65 level in uterine tissuesof rats in the EA group was significantly reduced(P<0.01),while there was no significant difference in the level of NF-κB p65 protein between the two groups(P>0.05),(Figure 4-Figure 6).
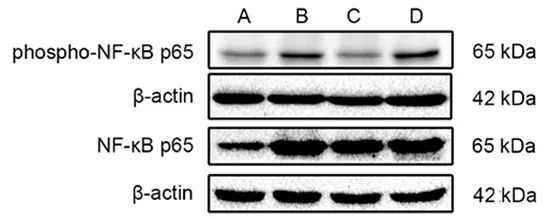
Figure 4. Comparison of the uterine phospho-NF-κB p65 and NF-κB p65 in each group (Western blot results)
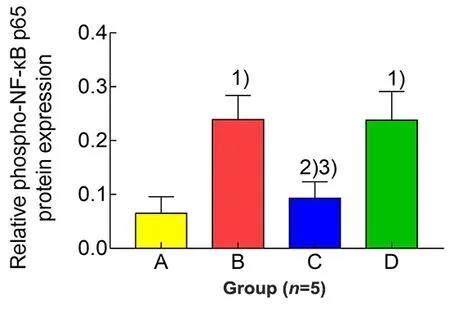
Figure 5. Comparison of the expression level of uterine phospho-NF-κB p65 protein in each group
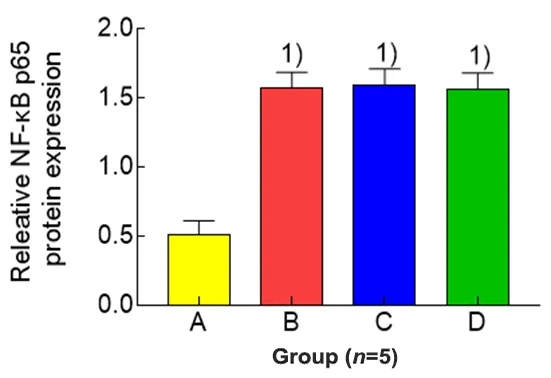
Figure 6.Comparison of the expression level of uterine NF-κB p65 protein in each group
3 Discussion
At present,oral non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs(NSAIDs)such as ibuprofen or contraceptives are still the first-line medicinesfor PDin clinic, while studies have shown that long-term use of such drugs has great damage to kidneys and liver, and many more adverse reactions have been observed[12-13].Clinicalstudieshave shown that EA has a positive short-term and long-term effect in the treatment of PD.It provides a therapeutic advantage of faster pain relief,better curative effect,and in absence of adverse reactions[8,14-15].
Dysmenorrhea,also known as‘a(chǎn)bdominal pain during menstruation’in traditional Chinese medicine,is usually caused by various pathogenic factors during or after menstruation.For example,due to the stasis or cold blocking the Thoroughfare Vessel and the Conception Vessel resulting in‘pain due to blockage’,or‘pain due to the malnourishment’caused by deficiency of liver and kidney and insufficient qi and blood.Sanyinjiao(SP 6)is the crossing point of the three yin meridians of foot.The liver,spleen,and kidney are the most closely related to the occurrence of dysmenorrhea.Guanyuan(CV 4)is the place where women store blood.Qi and blood of the Thoroughfare Vessel and the Conception Vessel can be smoothed by the coordination of the two points,so as to achieve the purpose of easing menstruation and pain relief.The previous research of our group revealed that EA at Sanyinjiao(SP 6)and Guanyuan(CV 4)alleviated the pain of PD model rats and improved the pathological damage,which showed acupoint specificity[11].The results of this study showed that EA and ibuprofen had equivalent efficacy in reducing the number of writhing in PD modelrats.
Studies have shown that PGF2αsynthesized in the endometrium of non-pregnancy can cause uterine muscle contraction,thereby aggravating the pain of PD[3].Clinical and experimental studies have revealed that acupuncture treatment of PD was achieved by regulating the synthesis and secretion of PGF2αin uterine tissues[9-10,16].The results of this experiment showed that the content of PGF2αin uterine tissues was significantly increased in the model group,while significantly decreased in the EA group and ibuprofen group,indicating that both EA and ibuprofen can regulate the synthesis and secretion of PGF2α.
COX-2 is the rate-limiting enzyme in the process of prostaglandin synthesis.Inflammatory damage can promote the synthesis of COX-2,which in turn promotes the production of a large amount of PG in tissues[4].Studies have shown that under normal physiological conditions,the content of COX-2 in the body is very low,and it increases before menstruation.At the same time,it catalyzes the synthesis of PG from arachidonic acid,which in turn causes cramping pain in the uterus.Studies have shown that NSAIDs such as ibuprofen can inhibit the activation of COX-2,reduce the level of PG,so as to achieve the purpose of treating PD[4,17-18].The results of this study showed that the expression level of COX-2 protein in uterine tissues of rats in the blank group was very low,while it was significantly increased in the model group,indicating that the COX-2 protein level was increased in PD rats.After the intervention of EA or ibuprofen,the level of COX-2 protein was significantly reduced,indicating that both EA and ibuprofen down-regulated the expression levelof COX-2 protein in uterine tissues of PDrats.
NF-κB is an important transcriptional regulator.It regulates the expression and activity of COX-2. And the activation of NF-κB is found in PD[19].This study found that the levels of phospho-NF-κBp65 protein and NF-κB p65 protein in uterine tissues of PD rats increased significantly, indicating that the phosphorylation levelof NF-κB in uterine tissues of PDrats increased and NF-κB was activated.The level of phospho-NF-κBp65 protein decreased after the intervention of EA,while the level of phospho-NF-κB p65 protein in uterine tissues of rats in the ibuprofen group did not change significantly,suggesting that EA can inhibit the phosphorylation of NF-κB in uterine tissues of PD rats,thereby inhibiting the activation of NF-κB.
To sum up,the results of this study suggested that the mechanism of EA at Sanyinjiao(SP6)and Guanyuan(CV 4)for PD rat,may be related to inhibiting NF-κB phosphorylation,reducing the COX-2 level,and regulating the PGF2αlevel.
Conflict of Interest
The authors declare that there is no potential conflict of interest in thisarticle.
Acknowledgments
This work was supported by National Natural Science Foundation of China (國(guó)家自然科學(xué)基金項(xiàng)目,No.82004490);Hunan Provincial Innovation Foundation For Postgraduate (湖南省研究生科研創(chuàng)新項(xiàng)目,No.CX2018B515);Open Fund of the Domestic First-class Discipline Construction Project of Chinese Medicine of Hunan University of Chinese Medicine (湖南中醫(yī)藥大學(xué)中醫(yī)學(xué)一流學(xué)科開(kāi)放基金,No.2018ZYX05);First-level Discipline Basic Medicine Construction Project During the 13th Five-year Plan Period of Chinese Medicine of Hunan University of Chinese Medicine (湖南中醫(yī)藥大學(xué)“十三五”一級(jí)學(xué)科基礎(chǔ)醫(yī)學(xué)建設(shè)項(xiàng)目, No.06).
Statement of Human and Animal Rights
The treatment of animals conformed to the ethical criteria in thisexperiment.
Received:28 October 2019/Accepted:13 March 2020
 Journal of Acupuncture and Tuina Science2020年6期
Journal of Acupuncture and Tuina Science2020年6期
- Journal of Acupuncture and Tuina Science的其它文章
- The role of microglia in thalamic reticular nucleus in acupuncture regulating cognitive deficits in insomnia rats
- Study on the acupoints belonging to the three yin meridians of foot reflecting the variation pattern of uterine qi and blood in women with moderate constitution
- Effect of moxibustion at sensitized-acupoints on quality of life in patients with chronic superficial gastritis
- Research advances in the brain mechanisms of acupuncture effects based on the BOLD-fMRI technology
- Effects of intradermal needle therapy plus pinaverium bromide on gastrointestinal hormone levels in irritable bowel syndrome-diarrhea patients
- Clinical observation on acupoint massage plus Vitalstim electrical stimulation for deglutition disorder after stroke
