Research on the Correlation Between Physical Examination Indexes and TCM Constitutions Using the RBF Neural Network
LUO Yue, LIU Yu-Nn, LIN Bing, WEN Chun-Bio*
a.School of Medical Information Engineering, Chengdu University of Traditional Chinese Medicine, Chengdu, Sichuan 611137, China
b.Affiliated Hospital of Chengdu University of Traditional Chinese Medicine, Chengdu, Sichuan 610075, China
Keywords
TCM constitution
Physical examination index
Correlation model
RBF neural network
ABSTRACT
Objective To establish correlation models between various physical examination indexes and traditional Chinese medicine(TCM)constitutions, and explore their relationships based on the radial basis function (RBF)neural network.
Methods The raw data of physical examination indexes and TMC constitutions of 650 subjects who underwent a physical examination were cleaned, classified and sorted, on the basis of which valid data were retrieved and categorized into a training dataset and a test dataset.Subsequently, the RBF neural network was applied to the valid samples in the training set to establish correlation models between various physical examination indexes and TCM constitutions.The accuracy and the error margin of the correlation model were then verified using the valid samples in the test set.
Results Of all selected samples, the highest accuracy rates were 80% for the blood lipid index - TCM constitution model; 100% for the renal function index - TCM constitution model; 100% for the blood routine (male)index - TCM constitution model; 88.8% for the blood routine (female)index - TCM constitution model;84.1% for the urine routine index - TCM constitution model; and 100% for the blood transfusion index - TCM constitution model.
Conclusions The samples selected in this study suggested that there is a strong correlation between physical examination indexes and TCM constitutions, making it feasible to apply the established correlation models to TCM constitution identification.
1 Introduction
In Traditional Chinese Medicine (TCM), constitution refers to an individual’s comprehensive and relatively stable inherent uniqueness with regards to structural,physiological and psychological aspects caused by inherited and acquired influences[1].On the contrary,as a quantitative indicator of western medicine,physical examination indexes refer to several physical and chemical parameters that demonstrate the health status of the examinee.
Combining physical examination indexes with TCM constitutions and exploring the correlation between the two facilitate an objective and quantitative analysis of TCM constitution.Multiple studies have investigated the correlation between physical examination indexes and TCM constitution types.For example, LIU et al.[2]discovered that for patients with type 2 diabetes, an increased BMI, an enlarged waist circumference, as well as escalating cholesterol and triglyceride indexes are all risk factors of the constitution of phlegm-dampness, whereas a decreased BMI and waist circumference are risk factors of the constitution of Yin deficiency.Moreover, the contents of fibrinogen and D-dimer are risk factors of the constitution of blood stasis.Alternatively, an investigation by LI et al.[3]suggested that the constitution of phlegm-dampness was associated with blood glucose levels and blood lipids (TG, TC, HDL-C and LDLC).By analyzing the correlation between physical examination indexes and the TCM constitutions of hypertension patients, DENG et al.[4]found that for these patients, the constitution of Yin-Yang harmony was related to myocardial ischemia and electrocardiogram (ECG)conduction indexes, whereas the constitutions of phlegm-dampness and damp-heat were associated with renal function indexes.Other studies,such as those conducted by ZHANG[5]and LI et al.[6],focused on the analysis of a certain type of patients.Amout of studies indicated that TCM constitution was related to certain physical examination indexes of western medicine, climate, or individual factors such as personality and psychology[5-21].However,the above studies only investigated the correlation between some physical examination indexes and certain types of TCM constitutions.
Artificial intelligence (AI)has also been applied to exploring the correlations between physical examination indexes and TCM constitutions.For example,some studies adopted the back propagation (BP)neural network to investigate subjects who underwent physical examinations and their corresponding TCM constitution types.By establishing neural network correlation models between physical examination indexes and TCM constitutions, they found that there was a certain correlation between the two[22-25],and in addition the established BP neural network correlation model between comprehensive physical examination indexes and TCM constitutions demonstrated the highest accuracy at 53%[21].The prediction ability of the correlation model was not optimal due to BP neural network’s dismal generalization and approximation capabilities as well as the “overfitting”problem.
On the contrary, in addition to a superior clustering and classification capability, the radial basis function (RBF)neural network also exhibits a better generalization capability as well as a higher approximation accuracy than the BP neural network.Therefore,in this study, five types of physical examination indexes, including blood routine, urine routine, blood lipid, renal function, and blood transfusion indexes,as well as the corresponding TCM constitutions, were collected.Subsequently, these data were used to train the RBF neural network to build correlation models between various physical examination indexes and TCM constitutions.The purpose of the study was to build a highly accurate correlation model between the two by integrating AI with multiple TCM and western medicine subjects and, on this basis, further realize the automatic modelling of different correlations, thereby providing new methods for TCM constitution identification.
2 Research Subjects
2.1 Raw data source
In total, 650 subjects who underwent a physical examination between January 2016 and March 2017 at Affiliated Hospital of Chengdu University of Traditional Chinese Medicine, were included as research subjects.All subjects signed Informed Content Form.
2.2 Inclusion and exclusion criteria
Subjects were included in the study if their physical examinations conducted by modern medical equipment indicated no abnormal physical indexes or organic diseases.
2.3 Constitution classification criteria
The patients’ constitution types were classified according to the “Classification and Determination of TCM Constitutions” criteria proposed by the China Association of Chinese Medicine[26].Nine constitution types were analyzed, including Yin-Yang harmony, Qi deficiency, Yang deficiency, Yin deficiency, phlegm-dampness, damp-heat, blood stasis, Qi stagnation, and inherited special constitution type.
2.4 Data samples
The physical examination indexes were selected according to the physical examination index standards proposed by the Physical Examination Center of Affiliated Hospital of Chengdu University of Traditional Chinese Medicine.Details of the selected indexes are listed below.
(1)Blood routine indexes (20 indexes in total, including white blood cell counts, neutrophil counts,lymphocyte counts, monocyte counts, eosinophil counts, basophil counts, and neutrophil percentage,etc.).
(2)Urine routine indexes (20 indexes in total, including pH, urine specific gravity, white blood cell counts, and red blood cell counts, etc.).
(3)Renal function indexes (including urea nitrogen, creatinine, uric acid, glucose, and carbon dioxide combining power).
(4)Blood lipid indexes (including cholesterol,triglyceride, high-density lipoprotein cholesterol, and low-density lipoprotein cholesterol).
(5)Blood transfusion indexes (10 indexes in total,including hepatitis B surface antigen, hepatitis B surface antibody, hepatitis Be antigen, hepatitis Be antibody, hepatitis B core antibody, and preS1 antigen of hepatitis B virus, etc.).
Valid samples were created after the collected raw data were cleaned and classified.These included the respective blood routine indexes from 45 male examinees and 193 female examinees, urine routine indexes from 536 examinees, blood lipid indexes from 188 examinees, renal function indexes from 254 examinees, blood transfusion indexes from 212 examinees, as well as their corresponding TCM constitutions.In addition, each valid sample group covered all nine types of TCM constitutions investigated.The distributions of the nine TCM constitution types in the 254 examinees whose renal function indexes were collected are shown in Figure 1.
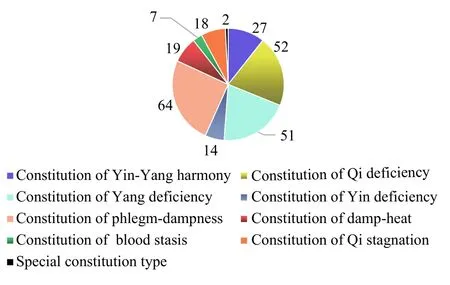
Figure1 Distributions of the nine TCM constitution types in the 254 examinees whose renal function indexes were collected
3 Research Methods
3.1 Sample data index quantification
3.1.1 Quantification of TCM constitution type data
Before the TCM constitution data could be used to train the neural network algorithm, they were first digitalized.The digitization of the TCM constitutions is shown in Table 1.
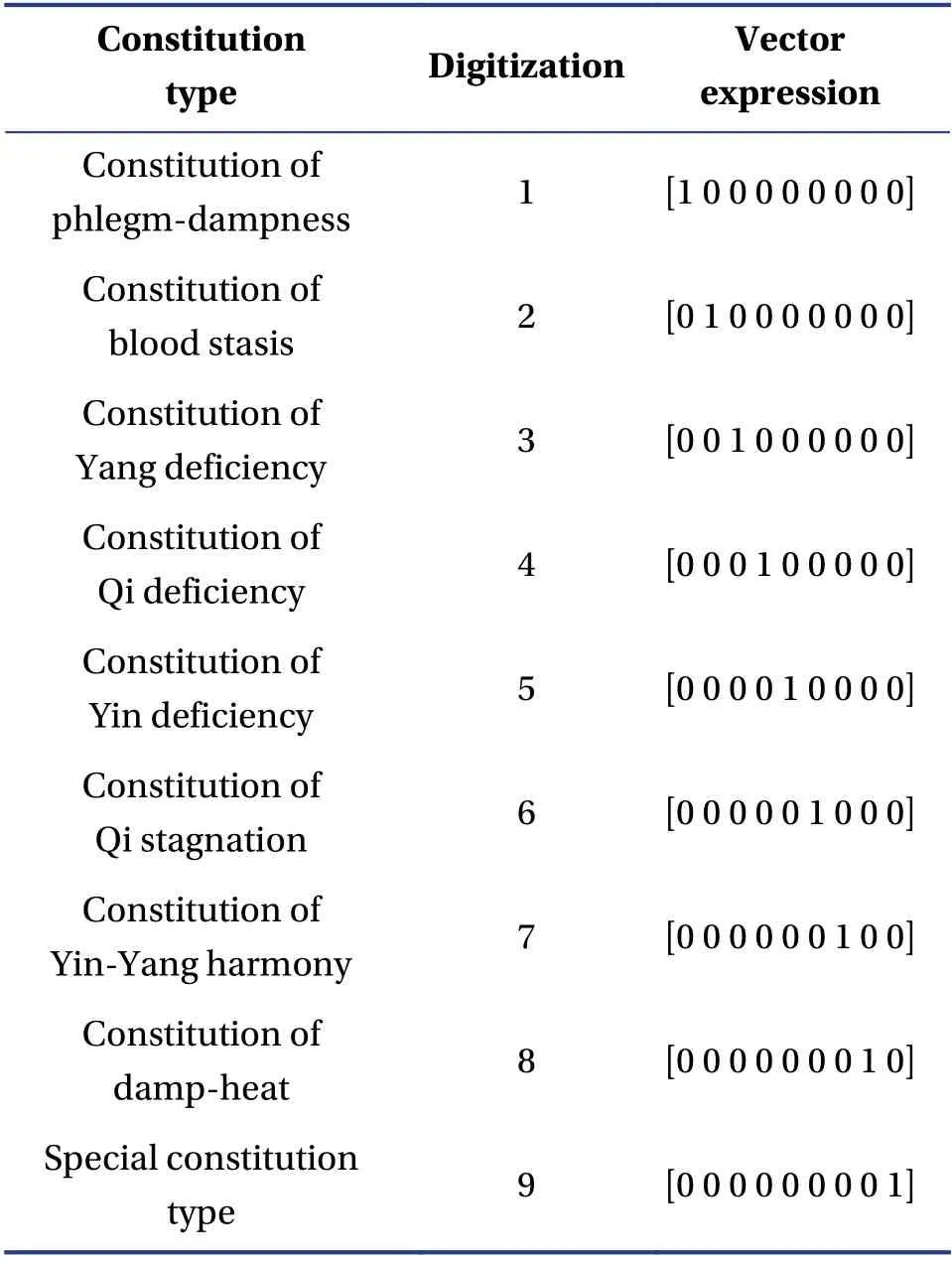
Table1 Digitization of TCM constitutions
3.1.2 Digitization of physical examination indexes
As the physical examination indexes were already quantified numbers, they needed to be standardized before they were input into the neural network algorithm.The digitization of the physical examination indexes was performed by matrices.For example, the quantification of the renal function indexes is, where the rows denote all renal function indexes of a sample,while the columns denote a certain renal function index (such as urea nitrogen)of all samples.For renal function indexes in particular, the size of the matrix is 254 × 5.
3.2 Algorithm design
Although the correlations between physical examination indexes and TCM constitutions are nonlinear,as a feedforward artificial neural network[27], the RBF neural network is capable of approximating arbitrary nonlinear functions[28].Therefore, the adoption of the RBF neural network to establish correlation models between physical examination indexes and TCM constitutions makes it possible to potentially explore the correlation strength between the two.The RBF neural network is composed of three layers: the input layer, the hidden layer, and the output layer.The correlation model between the physical examination indexes and TCM constitutions based on the RBF neural network is shown in Figure 2,where the physical examination indexes are the inputs and the TCM constitution types are the outputs.While the conversion from the input layer of the model to the hidden layer is nonlinear, that from the hidden layer to the output layer is linear.Therefore, the weight of the network can be directly solved by linear equations.
In this study, a supervised learning RBF neural network algorithm was used.SupposeG(X,Ti)is the output of theithunit on the hidden layer,Xis thepdimensional input vector,Tiis the basis function center of theithunit on the hidden layer, σiis the normalization parameter of theithhidden node, i.e., the width,and ωiisthe connectionweightbetweenthe hiddenandtheoutput layers.Nisthe numberof samples, andOis the expected output.During the training phase, the parameters that need to be determined by the network model includeTi,σiand ωi.If the Gaussian function is selected as the basis function, then we have
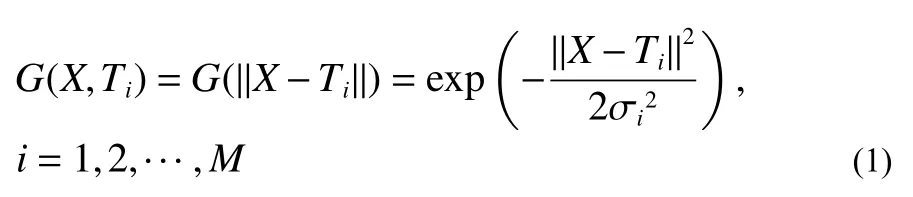
The algorithm process (model construction and testing)[29,30]is
1)Initialization: after normalizing the sample input data, preset ωi,Ti, σi, and the target error, as well as the learning steps η1, η2, η3.
2)Calculateej.
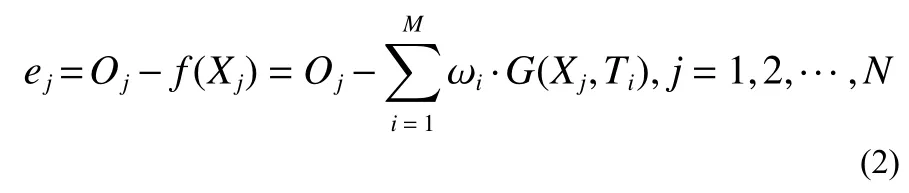
3)Calculate the weight change of the output unit.
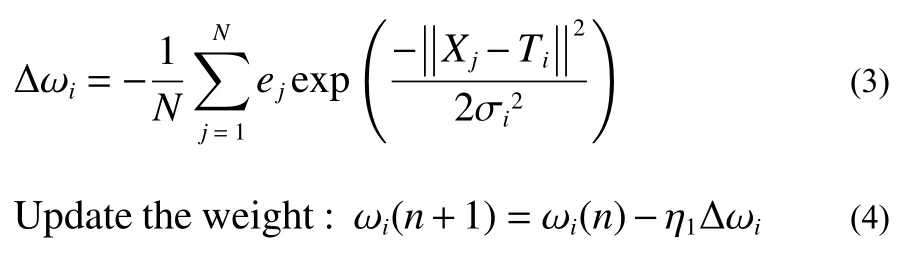
4)Calculate the center change of the hidden layer unit.

5)Calculate the change in width of the basis function.
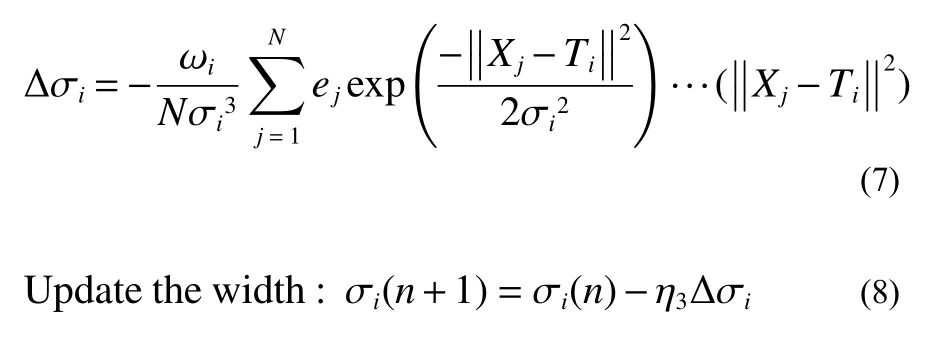
6)Calculate the objective function.

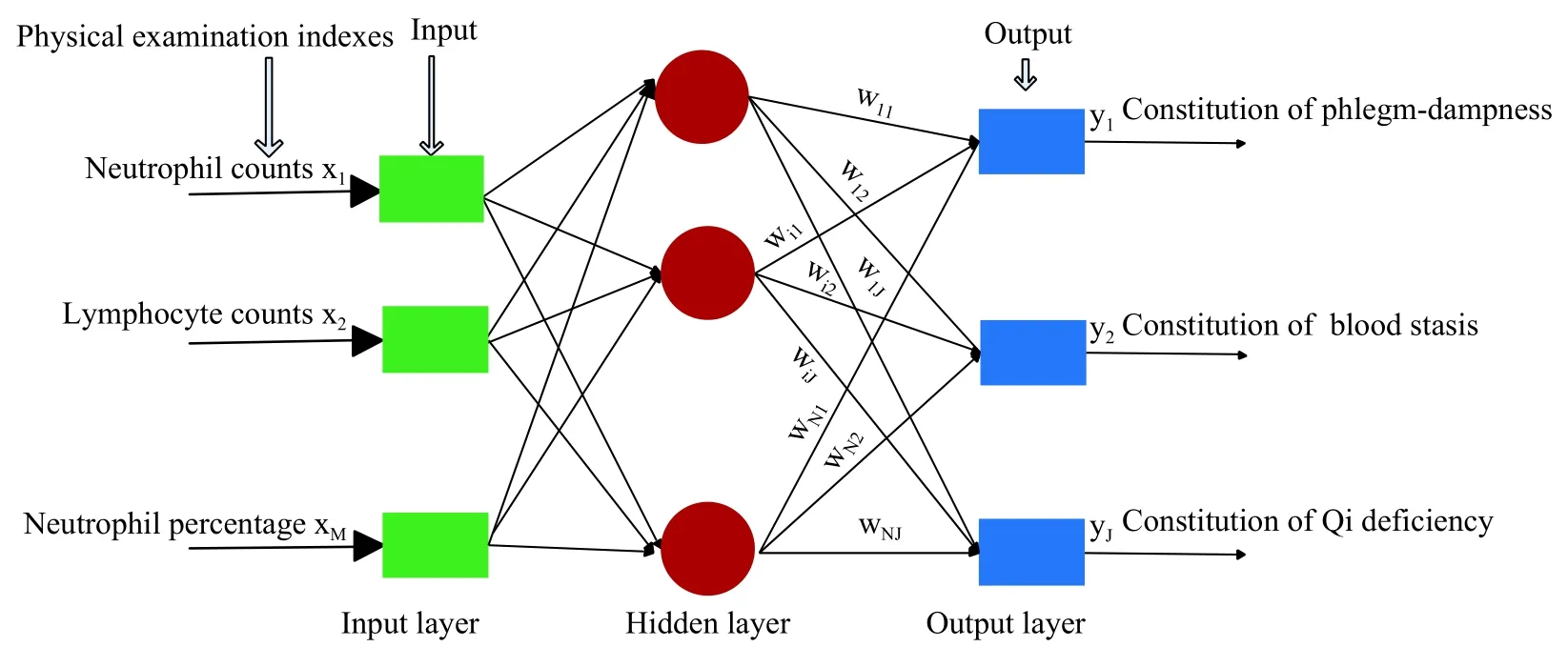
Figure2 Neural network algorithm for the correlation model between physical examination indexes and TCM constitutions
7)Determine the difference between the calculation error and the target error.When the calculation error is larger than the target error, repeat steps 2)to 7)until the former is smaller.If the calculation error cannot reach the target error, then repeat the process until the preset maximum number of trainings is hit.At this point, the training process is over, and the model has been established.
8)Import the physical examination indexes of the test dataset as input data into the established model and calculate the output.
9)Compare the calculated output with the expected output to identify the accuracy rate and the error.
3.3 Algorithm implementation
In this study, MatlabR2016a software was used to implement the RBF neural network.The configuration of the experimental environment was as below.
(1)Hardware environment: RAM 4.00 GB, hard disk 500 GB, Intel? Core? i5-3230M@2.60 GHz.
(2)Software environment: Operating system:Windows 7/64 bit.
4 Results and Discussion
The valid data of the blood routine, urine routine,blood lipid, renal function, and blood transfusion indexes, as well as their corresponding TCM constitutions, were categorized into a training dataset and a test dataset.Our preliminary algorithm test indicated that when the ratio between the number of samples in the training set and the test set was either 95% : 5% or 90% : 10%, the accuracy rates of the corresponding correlation models did not differ significantly.However, when this ratio was 70% : 30%,the accuracy rate of the correlation model was smaller than that of 80% : 20% but larger than that of 60% : 40%.Therefore, four different training set and test set sample number ratios, i.e., 95% : 5%, 80%: 20%,60% : 40%, and 50% : 50%, were used to build the correlation models and analyze the results.Of the valid data samples, the training set and the test set of all physical examination indexes and TCM constitutions consistently covered all nine types of constitutions.The prediction results of the renal function index-TCM constitution correlation model are shown in Table 2 for a ratio between the number of samples in the training set and the test set of 95% : 5%.
The prediction results of the blood routine index -TCM constitution correlation model, the urine routine index - TCM constitution correlation model,the renal function index - TCM constitution correlation model, the blood lipid index - TCM constitutioncorrelation model, and the blood transfusion index -TCM constitution correlation model at respective ratios of 95% : 5%, 80% : 20%, 60% : 40% and 50% : 50%are listed in Table 3.
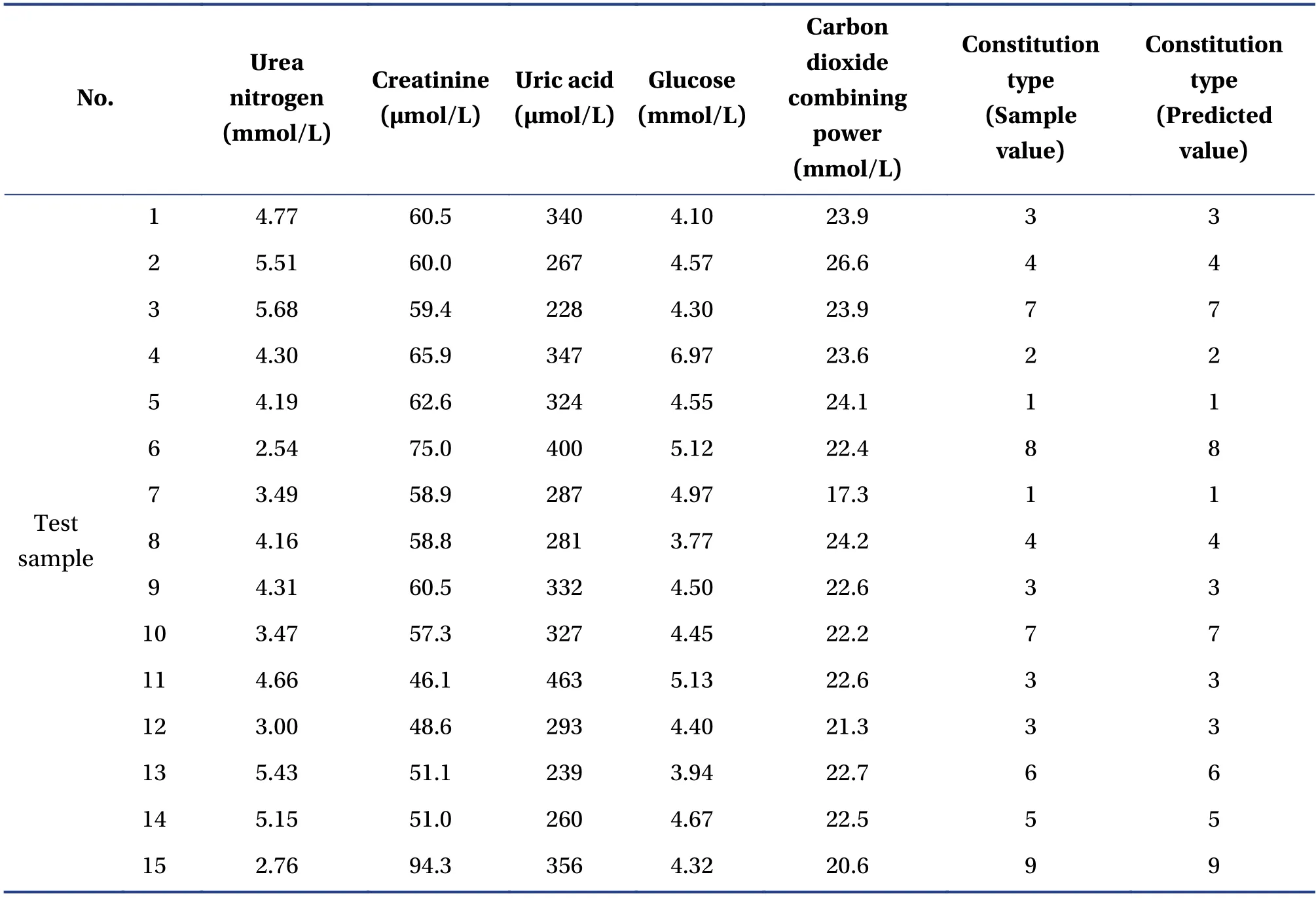
Table2 Prediction results of the renal function index – TCM constitution correlation model at a ratio of the number of samples in the training and the test sets of 95% : 5%
Figure3, 4 and 5 illustrate that with an increasing sample proportion of the training dataset, the accuracy rate of the physical examination index - TCM constitution correlation model improves, whilst the number of errors of the model prediction decreases.Alternatively, Figure 6, 7 and 8 indicate that when the sample proportion of the test dataset declines, the number of errors of the model prediction also decreases.In addition, although the accuracy rate of the model fluctuates, the overall trend is positive.Lastly,Figure 3 to 8 suggest that there is a correlationbetween the physical examination indexes and the TCM constitution types in the sample data analyzed in this study.Furthermore, the proportion of the number of samples between the training set and the test set affects the accuracy rate and the number of errors of the model prediction.The higher the proportion, the higher the accuracy rate and the smaller the error.
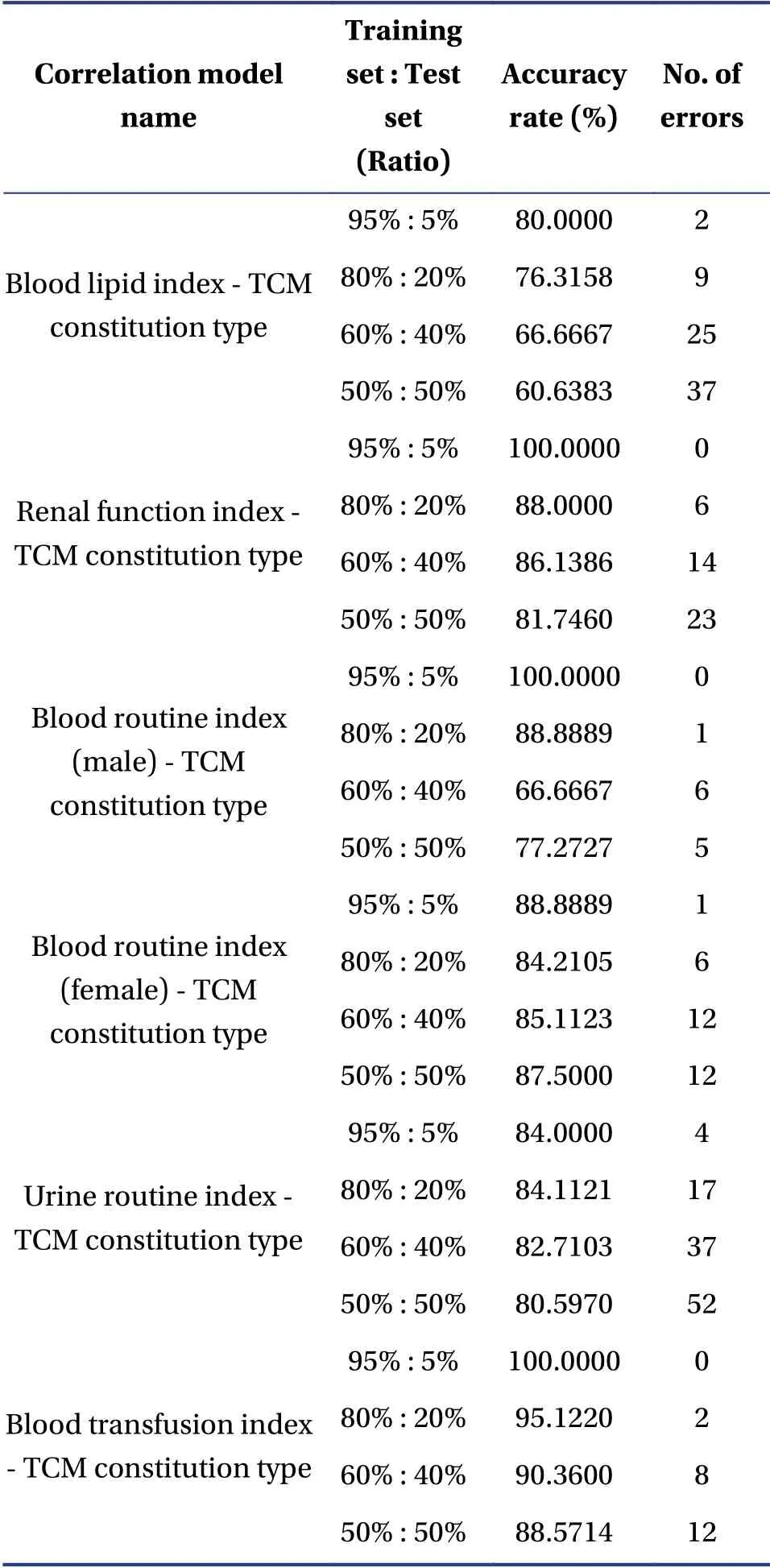
Table3 Verification results of the six types of physical examination indexes - TCM constitution correlation models
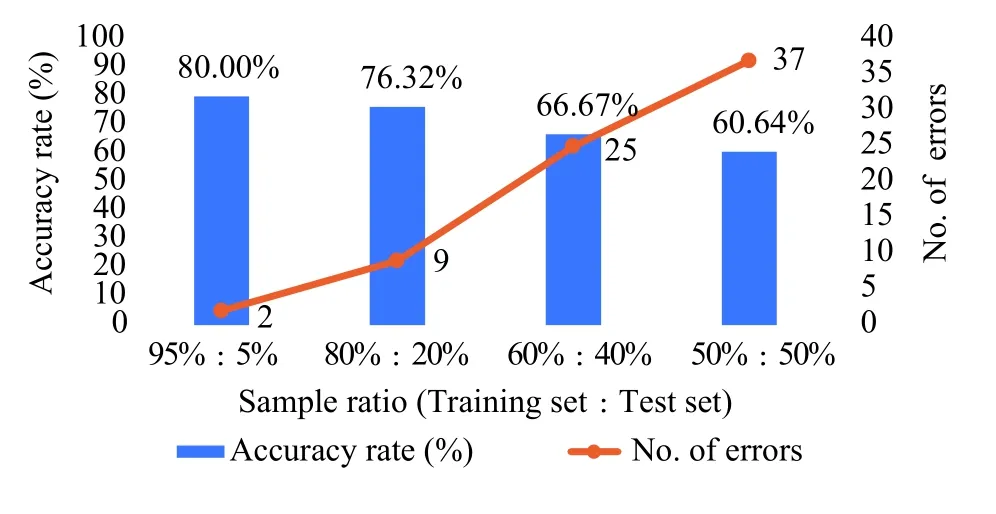
Figure3 Accuracy rate and number of errors of the blood lipid index - TCM constitution correlation model with four different ratios
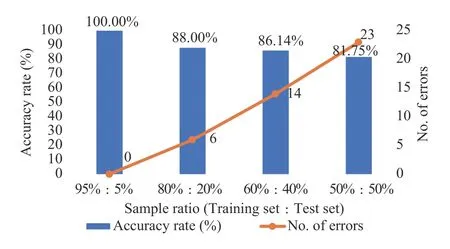
Figure4 Accuracy rate and number of errors of the renal function index - TCM constitution correlation model with four different ratios
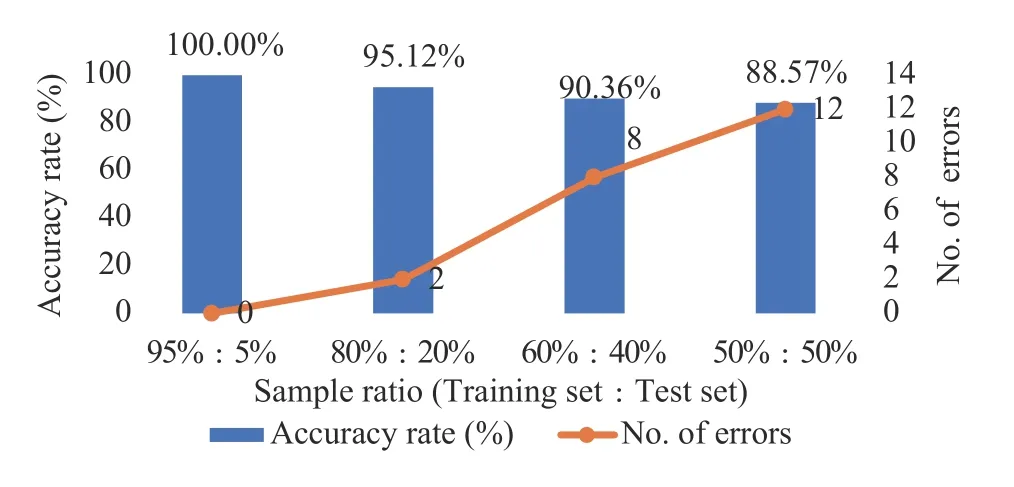
Figure5 Accuracy rate and number of errors of the blood transfusion index - TCM constitution correlation model with four different ratios
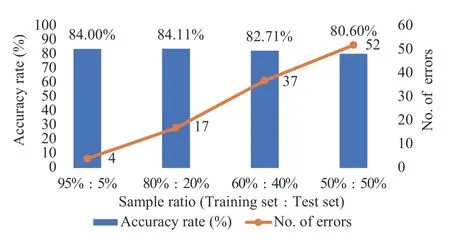
Figure6 Accuracy rate and number of errors of the urine routine index - TCM constitution correlation model with four different ratios
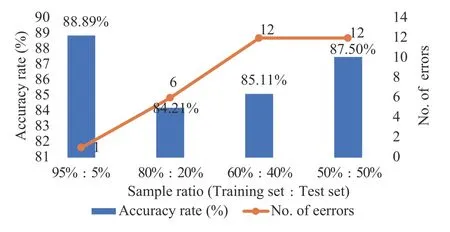
Figure7 Accuracy rate and number of errors of the blood routine index (female)- TCM constitution correlation model with four different ratios
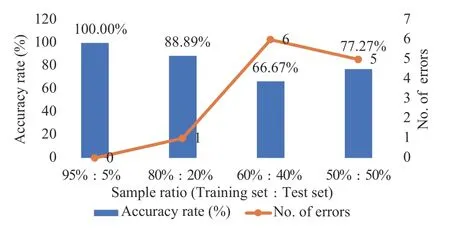
Figure8 Accuracy rate and number of errors of the blood routine index (male)- TCM constitution correlation model with four different ratios
5 Conclusions and Future Outlook
In this study, by applying the RBF neural network technology, we established correlation models between various physical examination indexes and TCM constitutions.Through the digitization of TCM constitution types and physical examination indexes,as well as an appropriate algorithm design and implementation, our sample data experiment showed that all six types of physical examination indexes, including blood routine, urine routine,blood lipid, renal function, and blood transfusion indexes, were related to TCM constitutions.The study has provided a novel approach for the quantitative analysis of TCM similar to that of western medicine, as well as an intelligent template for the integration of TCM and western medicine.In addition, the six types of physical examination index -TCM constitution correlation models established in this study demonstrated highly accurate predictions;therefore, they can be used as a new method for TCM constitution identification.
In the blood transfusion index - TCM constitution correlation model, there were cases where the prediction accuracy was 100%.This is likely because in the blood transfusion data selected in this study,all five indexes, including the preS1 antigen of the hepatitis B virus, the human immunodeficiency virus antibody, the treponema pallidum-specific antibody,the hepatitis C antibody, and the hepatitis C core antigen, were negative.In addition, owing to the limited number of samples, the distributions of the nine constitution types were uneven.Therefore, further research is required to verify the fact that the established renal function index - TCM constitution and the blood routine index (male)- TCM constitution correlation models achieved a constitution identification rate (prediction accuracy rate)of 100%, and whether all correlation models in the study will demonstrate reduced accuracy rates and larger errors with increasing sample numbers.
Acknowledgements
We thank for the funding support from the National Key Research and Development Project of China(No.2018YFC1707606), National Natural Science Foundation of China (No.81904324)and Youth Foundation of Sichuan Administration of Traditional Chinese Medicine (No.2016Q065).
Competing Interests
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
 Digital Chinese Medicine2020年1期
Digital Chinese Medicine2020年1期
- Digital Chinese Medicine的其它文章
- Instructions for Authors
- Discussion on Etiology and Pathogenesis of Corona Virus Disease 2019 from “Cold-dampness and Insidious Dryness”
- Clinical Intelligent Diagnosis Path Based on the Chief Complaint
- Effect of Electroacupuncture on Platelet-derived Growth Factor and the Ultrastructure of Mitochondria in Rats with Diabetic Gastroparesis
- Regularity of Wind-dispelling Medication Prescribed by LI Dong-Yuan: A Data Mining Technology-based Study
- Mechanism Prediction of Monotropein for the Treatment of Colorectal Cancer by Network Pharmacology Analysis
