Assessing the reasons for increase in self-medication and control measures among student nurses in University of Benin Teaching Hospital, Edo State, Nigeria
Olaolorunpo OLORUNFEMI, Sarah Olayinka FALEKE, Omotayo Mercy OLORUNFEMI,Vitalis OKAFOR, Uche Gift EMIAREDepartment of Medical Surgical Nursing, School of Nursing,University of Benin Teaching Hospital, Benin-city, Edo State;Department of Medical Surgical Nursing, School of Post Basic ORL Nursing, National Ear Care Centre, Kaduna state;Department of Measurement and Evaluation, Staff School,University of Benin Teaching Hospita; School of Nursing,University of Benin Teaching Hospital, Benin-city, Edo State,Nigeria
ABSTRACT
Background: Self-medication among student nurses is the use of medicines without doctor’s prescription. This practice is a global phenomenon and potential contributor to human resistance to most drugs, associated with different types of health challenges. Despite the high knowledge on the complication of self-medication, studies showed that most student nurses still practice self-medication.
Aims: The aim of this study was to assess the reasons for increase in self-medication and and find ways on how to curbing the menace among student nurses in the School of Nursing, University of Benin Teaching Hospital, Edo State, Nigeria.
Materials and Methods: A descriptive cross-sectional survey was conducted with stratified simple random sampling technique to select ninety student nurses from three different levels in the School of Nursing, University of Benin Teaching Hospital in Benin City, Edo State.A self-structured questionnaire with open-type and Likert-type scale questions used as instrument to assess the reasons for increase in self-medication and the possible control measures. Data collected were analyzed using tables, percentages, means, standard deviation, and t-test for inferential statistics at 0.05 level of significance, through Statistical Package for the Social Sciences software.
Results: The result showed the reasons for increase in self-medication and how to reduce its occurrence. It also showed that the gender of the student nurses is statistically related to the reasons why they practice self-medication (t = 6.82, P ≤ 0.001).
Conclusion: Self-medication can be reduced among student nurses by empowering the law enforcement agencies against self-medication, improving the availability of essential and quality drugs in school clinics, and inclusion of all student nurses in National Health Insurance Scheme (NHIS) program, where they can enjoy the benefit of paying only 10% of the treatment charges.
Keywords: Knowledge, practice, self-medication, side effects, student nurses
INTRODUCTION
Self-medication is a human behavior in which an individual uses medications or any exogenous influence to selfadminister treatment for physical or psychological ailments or simply put as the self-consuming of medication without getting advice from a physician for either diagnosis or treatment; It is an important concern for health authorities at global level.[1-3]This is an integral and vital component of self-care; which include the use of medicines and medicinal products such as herbal and traditional products by individuals to treat self-recognized illnesses or symptoms,or continued use of medication prescribed by a physician for chronic or reoccurring diseases or symptoms.[4,5]Self-medication has been increasing in many developing and developed countries and has resulted in various side effects and complications.[6]Self-medication has become a common practice among those that have easy access to drugs, such as health workers, over those who do not have easy access to drugs, such as traders and teachers.[7-9]This practice results in wastage of resources, increases resistance to pathogens, and generally characterized with serious health hazards such as adverse drug reactions and prolonged suffering from side effects that result from irresponsible self-medication.[10,11]The indiscriminate consumption of drugs is associated with different disadvantages including decreasing clinical efficacy, an increase in treatment duration,and prolongation of recovery.[12,13]Self-medicating is not only with over-the-counter (OTC) medications but also with those medications sold under prescription, which induces the irrational use of medications.[14,15]In the case of drugs that require a prescription, it is very common for self-medication to be reused after a previous prescription or purchased directly from a pharmacy.[16]This reality is far from being a completely safe practice because self-medication can produce a series of health risks that in many cases may result in toxicity, side effects, adverse reactions, and in some cases intoxication or lack of effectiveness because they are used in situations where they are not indicated.[17,18]This practice is one of the leading causes of death and even suffering because of the serious health hazards it poses on people,despite of this drugs are still being misused in Nigeria.[19,20]In Nigeria, there are many unregistered medicine store/pharmacies from which people purchase drugs from unknown sources.[21]Self-medication, both in OTC and prescription drugs, is very common in Nigeria; previous studies have concentrated on general self-medication in Nigeria which is still on the high.[22,23]The researchers, in the course of clinical teaching in the hospital, have come across different student nurses suffering from the side effects that resulted from irresponsible self-medication in the University of Benin Teaching Hospital. we also found that no available studies examined the reason behind self-medication or proffer solutions to the problem. Based on this notice gap, this study will determine the reasons for increase in self-medication and the control measures.
MATERIALS AND METHODS
Research design and setting
A descriptive cross-sectional study was conducted with simple random sampling techniques to select respondents using a self-structured questionnaire, with open-ended and Likert scale questions. The research was carried out in the School of Nursing, University of Benin Teaching Hospital, Egor Local government located in Ugbowo, Benin-Lagos Road. It shares boundary with the University of Benin and Federal Government Girls’ College Road in Ugbowo Quarters, Benin City, Edo State.
The inclusion criteria were as follows: those who were willing to participate in the study and those who were current students at the school. The exclusion criterion was students who were under punishment or those who were preparing for nursing and midwifery council examination, which could limit their ability in participating in the study.
Sample size and sampling procedure
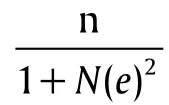
Data collection tools and procedure
Data collection instrument was a structured questionnaire consisting of questions made up of six parts: Section A:sociodemographic data of respondent with 5 items; Section B: knowledge of self-medication among nursing students. The mean score of ≥ 3.5 is rated as excellent knowledge, 3.0–3.4 is rated as very good knowledge, 2.0–2.9 is rated as good knowledge, and < 2.0 is rated as poor knowledge; Section C: practice of self-medication among nursing students with 3 items; Section D: effects of self-medication among nursing students with 6 items; Section E: reasons for increase in self-medication among nursing students with 24 items; and Section F: preventive measure of self-medication among nursing students with 9 items. To ensure reliability of the questionnaire, a pilot study was carried out among nursing students from Igbinedion School of Nursing, Okada, using test–retest method of reliability. Nearly 10% of the population questionnaire was administered and analyzed through Cronbach’s alpha the result of which, with the reliability of 0.89 obtained, shows that the test item is highly reliable.
Data obtained were coded and analyzed using the Statistical Package for Social Science (SPSS) version 21.00 statistical software (IBM Corp. released 2012. IBM SPSS statistics for Windows, version 21.0, Armonk, NY, USA). Variables and research questions were analyzed using descriptive mean,standard deviation, and the independentt-test for inferential statistics.
Ethical consideration
Ethical approval for this study was obtained from the University of Benin Teaching Hospital ethical committee where the study took place, with approval reference ADM/E22/A/VOL. VII/148300 on March 20, 2020. In line with the Belmont report, the researcher strived to do no harm to participants. Consent form was given to the participants to seek written consent, and verbal consent was also taken before data collection. Participants were not be exploited financially and physically, therefore their lecture time was not encroached; they took the questionnaires to the hostel and returned on the 2ndday, and data collection took place at the end of the class.
RESULTS
Table 1 shows that majority of the respondents (48.9%)were aged between 21 and 25 years. Nearly 13.3% of the respondents were male; 86.7% of the respondents were female; majority of the respondents (76.7%) were single; and 17.8% of the respondents were of Igbo, 11.1% Esan, 33.3% Benin, 11.1% Urhobo, 22.2% Yoruba, and 2% were of Hausa origin. Regarding the level of education, majority of the respondents (44.5%) were in 100 level.
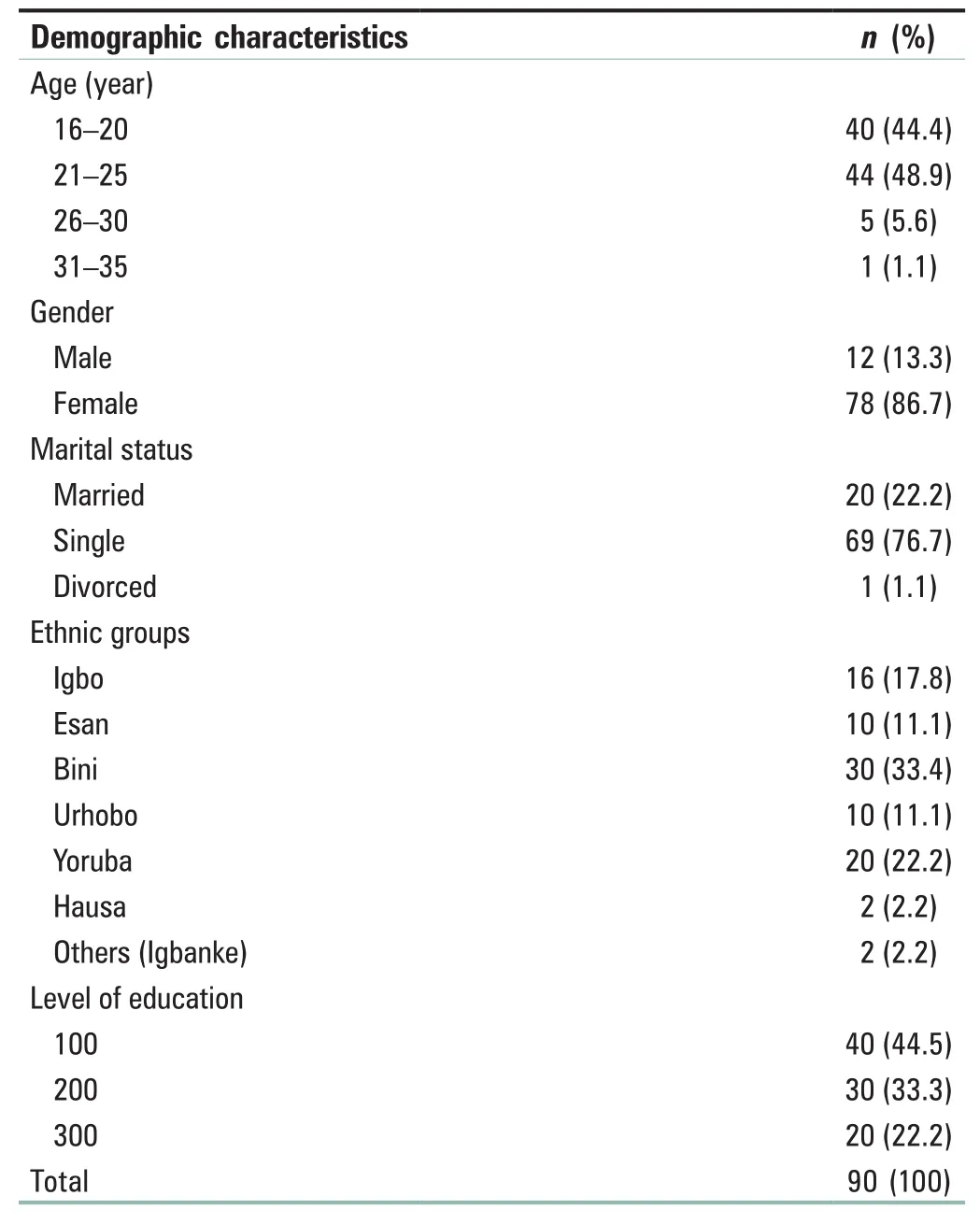
Table 1: Demographic characteristic of students nurses from the School of Nursing, University of Benin Teaching Hospital (n=90)
The knowledge of self-medication among students nurses is reported in Table 2: It shows that student nurses in the University of Benin Teaching Hospital have a good knowledge about self-medication with a ground mean score of 3.2 (1.7).
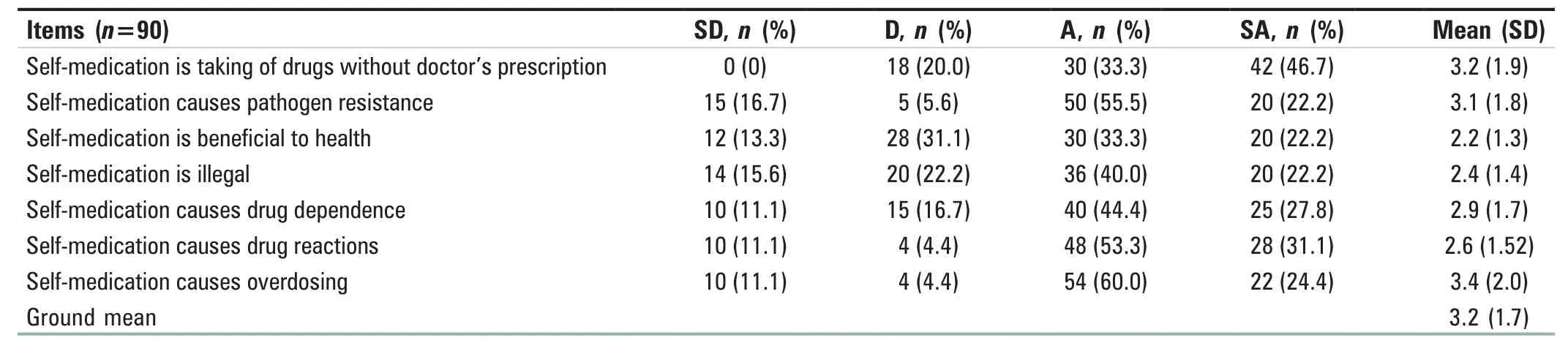
Table 2: Knowledge of self-medication among the School of Nursing students in the University of Benin Teaching Hospital
The practice of self-medication among student nurses is reported in Table 3: it shows that practicing self-medication involved all the participants (90 [100%]) and doing this on a regular basis involved 32 participants (35.5%). The effect of self-medication among the student nurses is reported in Table 4: it shows the major effects of self-medication, in which 80 (88.9%) agreed to drug addiction, 70 (77.8%) agreed to adverse drug reaction as an effect of self-medication,50 (55.6%) agreed to liver disease, 79 (87.8%) agree to peptic ulcer as an effect of self-medication, 72 (80.0%) agreed to drug resistance as an effect of self-medication, and 69 (76.7%)agreed to drug dependence as an effect of self-medication.
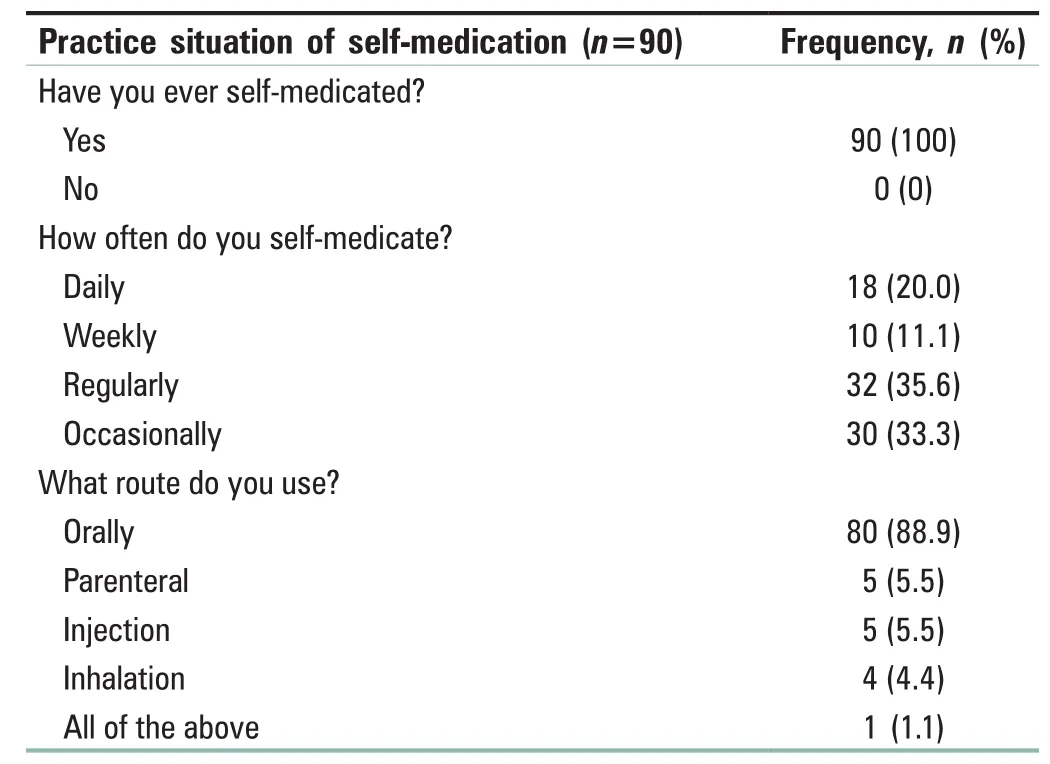
Table 3: Practice of self-medication among nursing students in the University of Benin Teaching Hospital
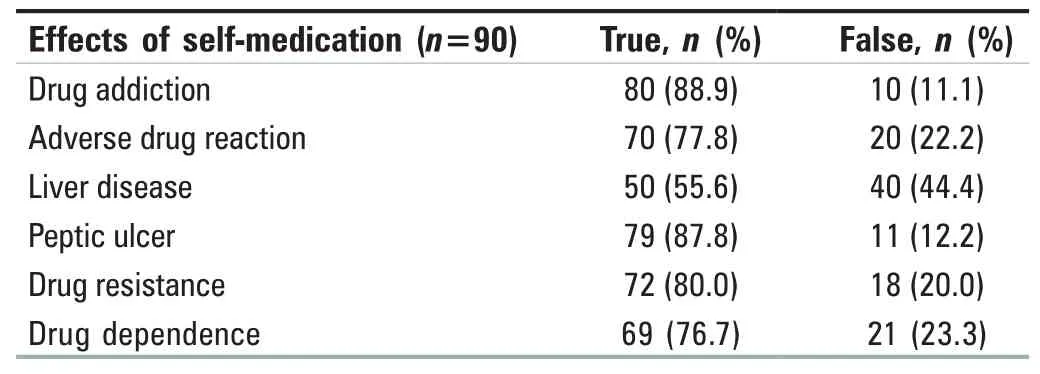
Table 4: Effects of self-medication among nursing students in the University of Benin Teaching Hospital
The reasons for increase in self-medication among student nurses are reported in Table 5: it shows that the participants agreed that the most reasons why student nurses practice self-medication are mild symptom of the diseases, ineffective drug in school clinics, and long waiting time with a mean score of 3.1 (1.8), and they believed that consulting a doctor is time consuming with a mean score of 3.3 (1.9). The participants also agreed that the major reasons why student nurses practice self-medication are: consulting a doctor is expensive,peer pressure, and emergency need of drug with a mean score of 2.9 (1.7), and they also identified the recent exclusion of student nurses from national health insurance scheme (NHIS)as a major causal factor. It was noted that the accessibility of drug literature on Internet, promote self-medication with mean score of 3.0 (1.7). The respondents also agreed the following as the reasons why student nurses practice self-medication: previous use of medication (2.1 [1.2]),ease of access to drug (2.1 [1.2]), easy to purchase OTC drug (2.7 [1.6]), familiarity with treatment (2.0 [1.2]), for hiding and denying mental illnesses (2.1 [1.2]), perceived self-medication to be harmless (2.4 [1.4]), availability of medication at home (2.1 [1.2]), cost-effective (2.4 [1.4]), and dissatisfaction by health-care system service (2.2 [1.3]).
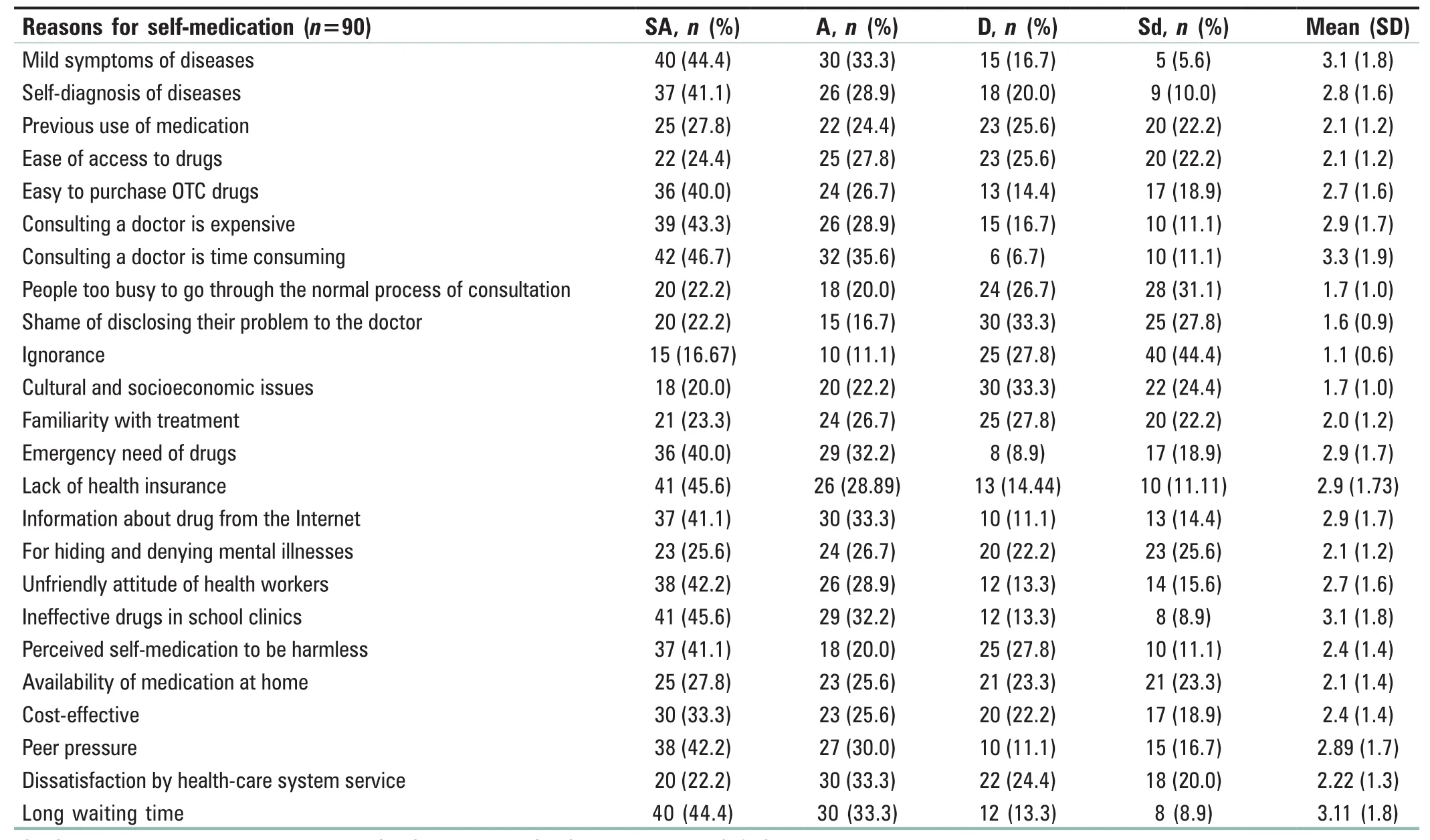
Table 5: Reasons for increase in self-medication among student nurses in the University of Benin Teaching Hospital
Moreover, this study identified the following as preventive measures of self-medication among nursing students [Table 6]:enforcement of laws to prevent self-medication (1.6 [0.9]),public enlightenment on the dangers (1.1 [0.6]), pharmacists must dispense drugs based on valid prescription (1.9 [1.1]),hospital managers should reduce or remove consultation fee for student nurses working in the hospital (1.6 [0.9]), reducing waiting time for doctor consultation (1.9 [1.1]), all student nurses should be included in the national health insurance scheme program of the country (1.9 [1.1]), provision of good and quality essential drugs in the school clinic (1.5 [0.9]),and information about drug on the Internet should be under control (1.2 [(0.7]).

Table 6: Preventive measures of self-medication among nursing students in the University of Benin Teaching Hospital
Furthermore,t-test analysis showed that there is a statistically significant difference between gender and the reasons for increase in self-medication among nursing students in the University of Benin Teaching Hospital (t= 6.82,P≤ 0.001).
DISCUSSION
This study showed that nursing students were knowledgeable about self-medication. This is in agreement with a study conducted in 2015 among medical students in Chitwan Medical College, Bharatpur, Nepal, where 75 students studying in the 1styear were selected for the study and found that more than half of the respondents have a good knowledge about self-medication regarding definition, adverse effects, and different types of drug.[24]It is also in line with the study carried out in 2016, which found that persons using self-medication have sufficient knowledge about medicines.[25,26]
This study also shows that student nurses practice self-medication regularly. This is in agreement with the study on the assessment of self-medication practices and its associated factors among undergraduates of a private university in Nigeria in 2018, and found that majority of the students practice self-medication and attribute it to the unfriendly attitude of health-care workers in the university clinic.[22]This is also in agreement with a doctoral dissertation in the University of Ghana in 2017 on self-medication perception and practice among pregnant women in Wa-municipality. Their study aim was to investigate the perception and practice of self-medication among pregnant women in Wa-Municipality and they found that easy accesses to nonprescribed medication is the main associated factor that had great influence in the practice of self-medication among pregnant women.[27]Moreover, the present study showed that the major perceived effects of self-medication among student nurses are drug addiction, adverse drug reaction,drug dependence, and liver disease. This is in agreement with a study carried out in 2016 on the analysis of analgesic,antipyretic, and nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drug use in pediatric prescriptions and found that paracetamol is an antipyretic and analgesic, which when used in large dose can cause liver problems (toxicity).[28]
In addition, this study identified the following reasons for self-medication: mild symptoms of the diseases, ineffective drugs in school clinics, long waiting time, consulting a doctor is time-consuming, consulting a doctor is expensive, peer pressure, emergency need of drugs, lack of health insurance,information about drugs from the Internet, previous use of medication, ease of access to drugs, easy to purchase OTC drugs, familiarity with treatment, for hiding and denying mental illnesses, perceived self-medication to be harmless,availability of medication at home, cost-effective, and dissatisfaction by health-care service. These findings are in agreement with a study carried out in Mansoura University,Egypt, on self-medication among university students in 2017 and found that the students practice self-medication because of their previous experiences, advice of family or friends,their health problems being considered as too trivial, time saving, nonavailability of transport, convenience, ability to self-manage the symptoms, urgency of the problem,unavailability of doctor, having sufficient information, lack of time, low-cost consultation, and lack of trust in medical doctors.[29]
Furthermore, this study also identified ways of reducing or eradicating self-medication among students as follows:enforcement of laws to prevent self-medication, public enlightenment on the dangers, pharmacist must dispense drugs based on valid prescription, reduction or removal of consultation fee for student nurses working in the hospital, reducing waiting time for doctor consultation,inclusion of student nurses under the health insurance scheme of the country, provision of good and quality essential drugs in the school clinic, and information about drug on the Internet should be under control.These findings are in conformity to the study carried out by Burnam-Fink, which reveals that health education of people about self-medication, patient waiting time, public enlightenment on dangers of self-medication through television, radio, and so on, are ways of preventing self-medication.[30]This is also in line with the research carried out by Gupta and Singh, 2016, after analyzing the data; it reveals that self-medication can be prevented through the prevention of supply of medicines without valid prescription, awareness and education regarding implication of self-medication, control of prescriber’s consultation fee, and enforcing strict rules regarding misleading pharmaceutical advertisement.[31]
Finally, this study shows that there is a significant relationship between gender of the student and the reasons for self-medication, which is in agreement with the study by Helal and Abou-ElWafa, 2017. They found that sex, having children, illicit drug use, and having a home pharmacy were statistically associated with self-medication among university students.[29]
Nevertheless, the researcher encountered some challenges during the course of this work. Some respondents were not honest enough while answering the questionnaire;also retrieving the questionnaire from the respondents was difficult as most of the respondents were slow in answering the questionnaire and said they are busy with their assignment, but after much explanation and persuasion by the researchers, they all cooperated.
CONCLUSION
This study revealed that majority of the student nurses had a good knowledge about self-medication, and they practiced self-medication. It also identified reasons for self-medication and its preventive measures. Based on the findings of the study, the researchers made the following recommendations: (1) hospital managers should encourage good interpersonal relationship between student nurses and other health personnel; (2) they should also re-consider inclusion of student nurses in the National Health Insurance Scheme that was said to have been removed since the last year in the country; (3) it is better to provide monthly incentive such as bursary to student nurses in other to alleviate their financial challenges; (4) seminars and workshop on the side effects and other complications associated with self-medication should be organized; and (5) the law enforcement agents should be strengthened to discipline err student.
Acknowledgments
The authors wish to sincerely thank all the student nurses in the School of Nursing, University of Benin Teaching Hospital,Benin-City, who participated in the study despite their tight academic schedule.
Financial support and sponsorship
Nil.
Con flicts of interest
There are no conflicts of interest.
 Journal of Integrative Nursing2020年4期
Journal of Integrative Nursing2020年4期
- Journal of Integrative Nursing的其它文章
- Nursing administration in the geriatric department in the epidemic of COVID-19
- Effect of mild moxibustion in improving the quality of life of patients with diabetic peripheral neuropathy
- An innovative approach of using online problem-based learning and case-based learning in teaching disaster nursing during the COVID-19 pandemic
- The impact of sleep quality on reported anxiety and fatigue among shift nurses: The mediating role of resilience
- Anxiety and perception among nurses toward the outbreak of COVID-19 in University of Uyo Teaching Hospital, Akwa Ibom State
- Construction of nursing standard of integrated traditional Chinese and Western medicine for patients with COVID-19 (mild and common) in Beijing based on Delphi method
