“Jianpi Tongwei Prescription”Acupoint Application Combined with Moxibustion for Gastric Retention in Elderly Patients with Nasal Feeding
Jing ZHAO, Ling TANG, Pei-Yao LI
1Beijing Daxing Integrated Traditional Chinese and Western Medicine Hospital, Beijing, China;
2Nursing Department, Dongfang Hospital, Beijing University of Chinese Medicine, Beijing, China;
3School of Nursing, Beijing University of Chinese Medicine, Beijing, China
Abstract
Key words: Acupoint application; Moxibustion; Gastric retention; Elderly patients; Nasal feeding
Introduction
With the development of China’s economy and change of life style, the proportion of the elderly population is increasing year by year. By the end of 2017, the number of elderly people over the age of 60 had reached 240 million, accounting for 17.3% of the total population. In the elderly, there are more and more people with abnormal power due to age-related dysphagia[1]and stroke, head trauma, neurodegenerative diseases and other diseases.Tube feeding diet has become the only long-term way to prolong the life of these elderly patients and maintain the nutrition supply. However, gastric retention caused by nasal feeding affects their quality of life, and is prone to complications such as aspiration and aspiration pneumonia. These will prolong hospital stay and even increase mortality[2]. We collected a total of 60 cases of elderly patients with gastric retention due to diseases of digestive tract system and nervous system from the department of internal medicine and rehabilitation of our hospital to explore the effect of “Jianpi Tongwei Prescription” acupoint application combined with moxibustion in the treatment of gastric retention in those patients with nasal feeding, and the report is as follows.
Materials and Methods
Patients
The study was approved by the medical ethics committee of Beijing Daxing Integrated Traditional Chinese and Western Medicine Hospital.
Inclusion criteria were (1) age >65 years, (2) indwelling nasogastric feeding tube with gastric retention, (3) patients with spleen and stomach qi deficiency syndrome.
Patients with the following conditions should be excluded: (1) mechanical obstruction of the digestive tract confirmed by gastroscopy, gastrointestinal angiography,abdominal CT and other examinations; (2) because of other diseases, such as poor control of diabetes, scleroderma,resulting in gastric disorders; (3) administration of morphine, atropine and other drugs that affect the smooth muscle function; (4) local skin spots, papules, erythema,bubble rash, exfoliating dermatitis or ulcerative dermatitis;(5) domperidone used in routine treatment.
According to the consensus of the operational standards of enteral nutrition support for nervous system diseases in China (2011 edition), combined with the actual situation and characteristics of elderly patients in this study, the diagnostic criteria for gastric retention are as follows: (1) indwelling nasal feeding tube due to difficulty in feeding caused by various reasons; (2) at least one examination suggesting the exclusion of intestinal obstruction, anastomotic stenosis and other mechanical factors, such as gastroscope,gastrointestinal contrast, upper abdominal CT, etc; (3) >4 hours after nasal feeding nutrition, >200 mL liquid being aspirated through the nasal feeding tube; (4) anhydrous electrolyte and acid-base balance disorder; (5) excluding other diseases that may cause gastric retention, such as poor control of diabetes, scleroderma, hypothyroidism, etc.; (6)without taking morphine, atropine and other drugs that affect the function of gastric smooth muscle.
Sixty patients with gastric retention after nasogastric feeding were selected as the study samples. The admission time of 60 patients was from March 2019 to November 2019. Random design was adopted: according to the visiting order, SPSS 19.0 statistical analysis software was used to randomly group all cases and generate serial numbers. Among them, 30 cases were included in the treatment group and the remaining 30 cases were included in the control group. In the control group, there were 14 males and 16 females, aged 65-82 years old, with an average age of (72.2±4.0) years. The course of disease ranged from 2 to 20 months, and the average course was(9.3±2.1) months. In the treatment group, There were 19 males and 11 females, aged 65-80 years old, with an average age of (74.0±3.0) years old. The course of disease ranged from 2 to 19 months, with an average (9.5±2.2)months. The data between the two groups showed no significant difference in gender (χ2=1.684, P>0.05),age (t=0.210, P>0.05), and course of disease (t=0.360,P>0.05), comparable.
Methods
The control group adopted conventional treatment methods: Domperidone (10 mg*30 tablets/box; Manu facturer: Xi’an Yangsen Pharmaceutical Co., LTD.), 10 mg/time, 3 times/d, for 21 days or until gastric retention<100 mL. The drug can be crushed and administered through the nasal feeding tube.
On the basis of the control group, patients in the treatment group was treated with traditional Chinese medicine (TCM) characteristic nursing “Jianpi Tongwei Prescription” acupoint application combined with moxibustion on Zusanli.
Preparaほon for acupoint applicaほon: Jianpi Tongwei Prescription granules was prepared for acupoint application. Jianpi Tongwei Prescription composes of Huangqi (Milkvetch Root) 20 g, Dangshen (Codonopsis Radix) 20 g, fried Baizhu (Atractylodes fricta) 20 g,Muxiang (Radix aucklandiae) 15 g, Dingxiang (Flos caryophylli) 10 g, Zhiqiao (Fructus aurantii)10 g, Houpu(Magnolia officinalis) 15 g, Jiangxiang (Dalbergia odorifera ) 10 g. Additionally, it is necessary to prepare 1 sheet of dressing, 1 rolling instrument, 1 treatment bowl,moderate amount of warm water, 1 pair of tape measure,1 pair of glove, 1 mask, and 1 microwave oven. Making process of a plaster patch was as follows: one dose of granules was taken and mixed with a small amount of water to turn into semi-solid state. The semi-solid mixture was added with 2 mL yellow rice wine, 4 mL honey, 2 mL sesame oil, and 2 mL vinegar to be made into a paste,put on supplementary material, using rolling machine to be made into a round plaster, 5 cm in diameter, 0.3 cm in thickness. The plaster fixed with the gauze was finally posted to the non-woven materials for preparation. During the whole making process, the nurse must wear a mask and gloves. When used for patients, the plaster needed to be heated in microwave oven on high temperature for 5 minutes, added with 2 drops of ginger juice.
Preparaほon for moxibusほon treatment: Tongrentang brand (smokeless moxibustion) moxa strip is 20 cm in length, 1.5 cm in diameter.
Specific methods: After applying “Jianpi Tongwei Prescription” to neiguan acupoint, moxibustion was performed on the top of the auxiliary material for 5 minutes. The burning end of the moxa strip was warm from the surface of the auxiliary material. Then find the Zusanli point and apply moxibustion on the top of the acupoint for 5 minutes. The distance between the burning end of moxa sticks and the skin can be controlled to make the skin surface warm. (Zusanli acupoint: located in the anterolateral side of the lower leg, when the dubi point 3 inches, tibial ridge outside a horizontal finger; Neiguan acupoint: located in the middle of the forearm, 2 inches on the horizontal wrist line) acupoint application, each time for 4 hours, once a day.
Routine treatment: Daily intake of calories was calculated according to the patient’s condition, and enteral nutrition perfusion was performed in different intervals.If residual amount <150 mL, nasal feeding could be continued. If the residual was >200 mL, nasal feeding was followed after 2 hours. If residual >400 mL, nasal feeding was suspended. Infusion speed and amount should be Controlled. The infusion speed was 5-10 mL/min, and 200-300 mL/time was insufficient to provide intravenous nutrition support as appropriate.
Observation indexes
According to the efficacy evaluation standard of TCM syndrome of the guiding principles of clinical research on new Chinese medicine (trial), the amount of gastric retention, classification of gastric retention after nasogastric feeding, score of major symptoms of gastroparesis, and change of TCM clinical syndrome score were compared before and after treatment.
Statistical analysis
SPSS 19.0 statistical software was used for data analysis.All the statistical test were conducted by bilateral test.When P≤0.05, the tested difference was considered statistically significant. Quantitative data of different groups were statistically described as mean±standard deviation (±s), and paired t-test was used to compare the difference before and after treatment groups, and group t-test was used to compare the difference between groups. The rank sum test was used to compare the changes before and after treatment. Qualitative data of different treatment groups were statistically described by frequency, and chi-square test was used for the changes before and after treatment in the two groups.
Results
Gastric retention reaction
gastric retention reaction was observed at 7, 14 and 21 days after treatment (Table 1). The treatment group had higher rate of mild gastric retention reaction, and lower rates of moderate and severe gastric retention reaction than the control group.
Gastrointestinal reactions
The incidence of gastrointestinal reactions in the treatment group was significantly lower than that in the control group regarding nausea and vomiting and abdominal distension (P<0.05), as shown in table 2.
Degree of TCM syndrome response
The degree of TCM symptom response: no gastrointestinal reaction rate in the treatment group was significantly higher than control group (P<0.05), moderate and severe gastrointestinal reaction rate was significantly lower than the control group (P<0.05). (Table 3)
Discussion
Early enteral nutrition is an important means of nutrition support treatment for critically ill patients. Some scholars report that the incidence of those patients with gastrointestinal intolerance is as high as 45%[3]. Studiesshow that deficiency syndrome, especially qi deficiency,is a common problem existing in elderly patients[4].Excess syndrome in elderly patients is often caused by deficiency syndrome. TCM syndrome of senile functional gastrointestinal disorder is mainly qi deficiency of the spleen and the stomach, which is different from deficiency due to qi stagnation and blood stasis caused by various surgeries and deficiency-cold in spleen and stomach.The disease mechanism of those patients is mainly characterized by spleen and stomach qi deficiency and qi stagnation of middle energizer, the root cause lies in qi deficiency, and the superficial cause lies in qi stagnation and indigestion, the syndrome belongs to deficiency in root, excess in surface, intermingled deficiency and excess. Ye Tianshi put forward the theories of “the stomach governing intake of food and absorbing nutrition,the spleen governing transportation and distribution of essence, the spleen suggesting healthy while the spleen qi is ascending, the stomach suggesting harmony while the stomach qi is descending” and “fu-organs should be treated with dredging method, stomach qi should be descending”, so the treatment method should be mainly tonifying the spleen qi, descending the stomach qi, so as to regulate qi activity of middle energizer.

Table 1 The degree of gastric retention reaction between two groups
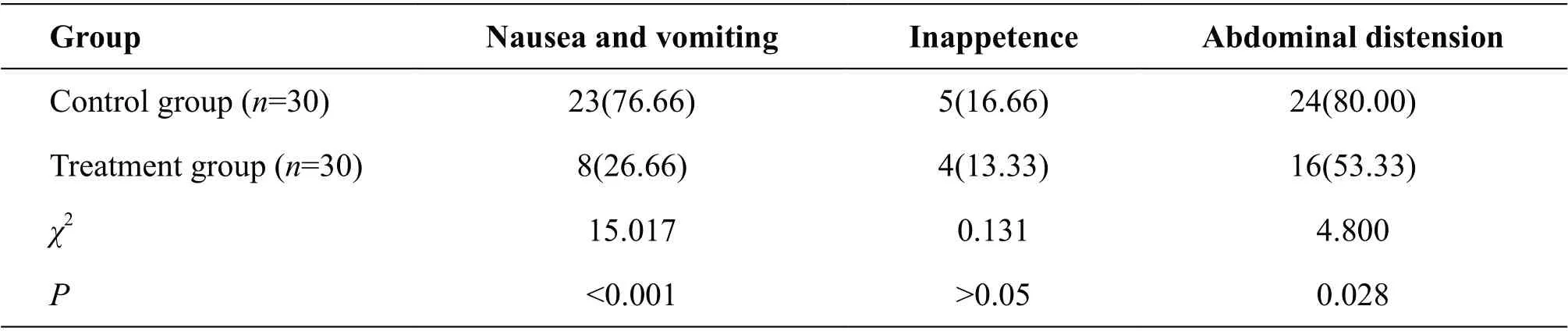
Table 2 Gastrointestinal reactions of two groups [n(%)]
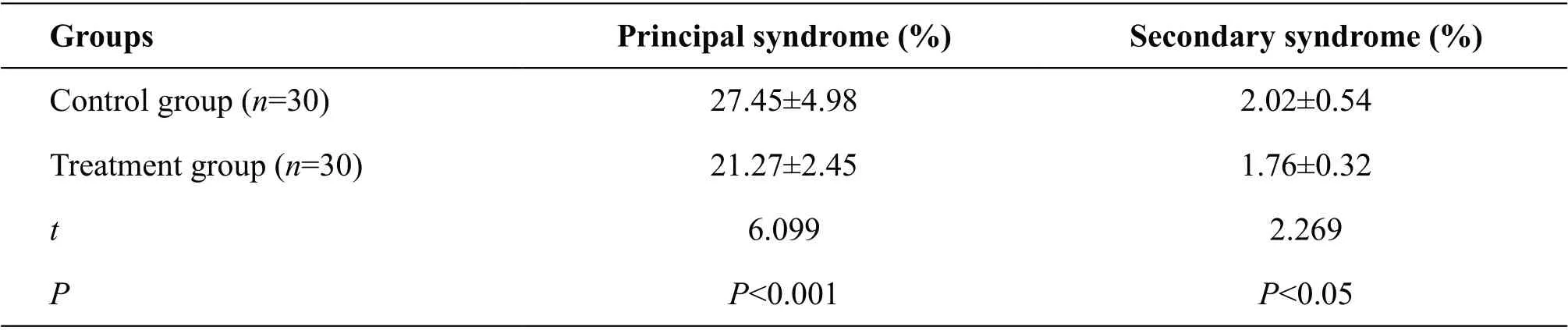
Table 3 TCM syndrome response level
In this study, acupoint application was used to induce the potency to the affected area through Neiguan acupoint on pericardium meridian (which is connected with Yinwei meridian) according to replenishing spleen qi and harmonizing stomach to qi stagnation as treatment methods, to treat gastrointestinal reactions such as nausea,vomiting and loss of appetite. Acupoint application gives direct stimulation to acupoint of patients by drug, make drug be absorbed through the skin to treat disease, playing dual role of drugs and acupoint[5-9]. Combined with moxibustion, it can strengthen spleen qi, promote qi flow.Zusanli acupoint is the joint point on the foot yangming stomach meridian to enhance gastrointestinal motility by moxibustion[10], for moxibustion has the functions of warming the meridians and regulating the stomach and intestines[11-15]. Moxibustion on Zusanli has the effect of strengthening the contraction of the gastrointestinal smooth muscle. Through the conduction and reflection of meridians, moxibustion can enhance gastrointestinal peristrosis, stimulate the secretion of digestive liquid to strengthen spleen, regulate qi, eliminate accumulation and guide stagnation, and promote the recovery of gastrointestinal function[16]. Relevant studies[17-20]have shown that moxibustion combined with acupoint massage is particularly effective in relieving gastrointestinal reactions, such as nausea, vomiting and abdominal distension. The results of this study were found that the effective rate of Jianpi Tongwei Prescription combined with moxibustion in the treatment of gastric retention in elderly patients with nasal feeding was higher than that of conventional treatment (51.2% vs. 23.3%, P<0.05), and the rate of no gastrointestinal reaction in the treatment group was significantly higher than that in the control group (P<0.05), moderate and severe gastrointestinal reactions were significantly lower than the control group(P<0.05).
To sum up, “Jianpi Tongwei Prescription” acupoint application combined with moxibustion for the treatment of gastric retention in elderly patients with nasal feeding may become an effective comprehensive method of TCM external treatment for those patients, which is worthy of clinical and regional promotion and application.
Declaration
All authors of the article declare they have no conflict of interest.
 Journal of Integrative Nursing2019年3期
Journal of Integrative Nursing2019年3期
- Journal of Integrative Nursing的其它文章
- Analysis of Adaptation Process of Evidence-Based Interventions by Taking Post-Stroke Dysphagia Screening As an Example
--Based on a Series of Empirical Studies - Construction of a Talent Cultivation Mode for Traditional Chinese Medicine Nursing Inheritance
- Five-Tone Therapy Plus Head and Face Massage Relieves Insomnia of Patients with Heart and Spleen Deficiency
- Correlation of Treatment Compliance, Treatment Attitude and Belief, and Quality of Life in Community Hypertensive Patients
- Investigation and Analysis on the Physical and Mental Health Status of Intern Nurses in a Hospital, Gansu Province
- Surrounding Needling with Fire Needle and Filiform Needle Plus Moxibustion in the Treatment of Lower Limb Herpes Zoster:One Case Report
