Early immune response in post endoscopic retrograde cholangiopancreatography pancreatitis as a model for acute pancreatitis
Ivana Plavsic,Ivana Zitinic,Vera Tulic,Goran Poropat,Marinko Marusic,Goran Hauser
Ivana Plavsic,Vera Tulic,Department of Anesthesiology and Critical care medicine,Clinical Hospital Centre,Medical Faculty,University of Rijeka,Rijeka 51000,Croatia
Ivana Zitinic,Department of Emergency Medicine,Clinical Hospital Centre,Rijeka 51000,Croatia
Goran Poropat,Department of Internal Medicine,Division of Gastroenterology,Clinical Hospital Centre,Medical Faculty,Medical Faculty Rijeka,University of Rijeka,Rijeka 51000,Croatia
Marinko Marusic,Department of Internal Medicine,Division of Gastroenterology,Clinical Hospital Sv.Duh,Zagreb,Faculty of Health Studies,University of Rijeka,Rijeka 51000,Croatia
Goran Hauser,Department of Internal Medicine,Division of Gastroenterology,Clinical Hospital Centre,Medical Faculty,Faculty of Health Studies,University of Rijeka,Rijeka 51000,Croatia
Goran Hauser,Medical Faculty Osijek,University of J.J.Stossmayer,Osijek 31000,Croatia
Abstract
Key words:Innate immunity;Pancreatitis immunology;Post endoscopic retrograde cholangiopancreatography pancreatitis
INTRODUCTION
Acute pancreatitis (AP) is the most common gastrointestinal cause of morbidity and mortality,with a reported incidence that varies between 4.9 and 73.4 cases per 100000 worldwide[1].The most common cause of AP are gallstones,followed by alcohol abuse as an independent risk factor.
Endoscopic retrograde cholangiopancreatography (ERCP) is an invasive diagnostic and therapeutic technique,which carries certain complication risks.Acute pancreatitis is the most common one.According to the European Society of Gastrointestinal Endoscopy guidelines,the reported incidence of post-endoscopic pancreatitis (PEP) is 3.5% in unselected patients[2].
The severity of AP can be divided into mild,moderately severe or severe based on the presence or absence of persistent organ failure and local and systemic complications.In 90% of cases,PEP is of a mild or moderate severity[2].
Although,the prevalence of the severe form of PEP is reported to be low,Testoniet al[3]in their study reported that the overall and severe pancreatitis-related mortality was approximately double after ERCP in comparison with AP of other causes.Also,the length of hospital stay in severe cases was longer for post ERCP pancreatitis.
Treatment of AP regardless of the cause,is primarily supportive and implies a certain economic burden to the healthcare system worldwide.Even more,if it develops into a severe form[4].
More thorough clarification of the disease pathogenesis is needed,in order to find an adequate immune target to predict and consequently prevent the severe form of the disease[5].
CLINICAL PRESENTATION
Admission in hospital varies between patients who develop AP,therefore the exact time of injury is not known.In post-ERCP AP there is the opposite situation,the exact time of injury can be foreseen.Messmannet al.concluded that post-ERCP AP represents an adequate model for the evaluation of early immune response in AP.The researchers linked higher values of IL-6 and CRP with the development of AP after ERCP,and concluded that the severity of the disease is not only reflected by a higher,but also earlier peaking,IL-6 serum concentration[6].The role of IL-6 in predicting disease severity was also recognised in patients with AP[7,8].Time is a limit for IL-6,since most of the studies confirmed its effectiveness as a disease severity marker between 12-24 h after ERCP[9,10].Opposite to Il-6 and CRP values,amylase and lipase values were unselectively elevated in all patients after ERCP with an earlier peak in their higher values[6,10].Amylase and lipase are released into the systemic circulation due to a disturbance in transport and an increase in ductal permeability;however,they are not thought to be responsible for inducing further inflammation.They can't discriminate between patients with the potential to develop the mild or severe form of the disease[10].According to the present guidelines,use of the Cotton criteria is recommended and amylase values are evaluated after 24 h for the diagnosis of PEP[2].
Differences between the mild and severe form of PEP and non-ERCP were found,they are summarised in Table1.(With permission:Plavsicet al[5])
Testoniet al[3]reported that clinicians may overestimate the presence of truepancreatic acute damage in mild PEP,based on significant differences found in the dynamics of serum amylase values measured in patients with PEP and non- ERCP AP.Severe PEP was associated with a higher mortality rate and a longer hospital stay,although with no significant differences.
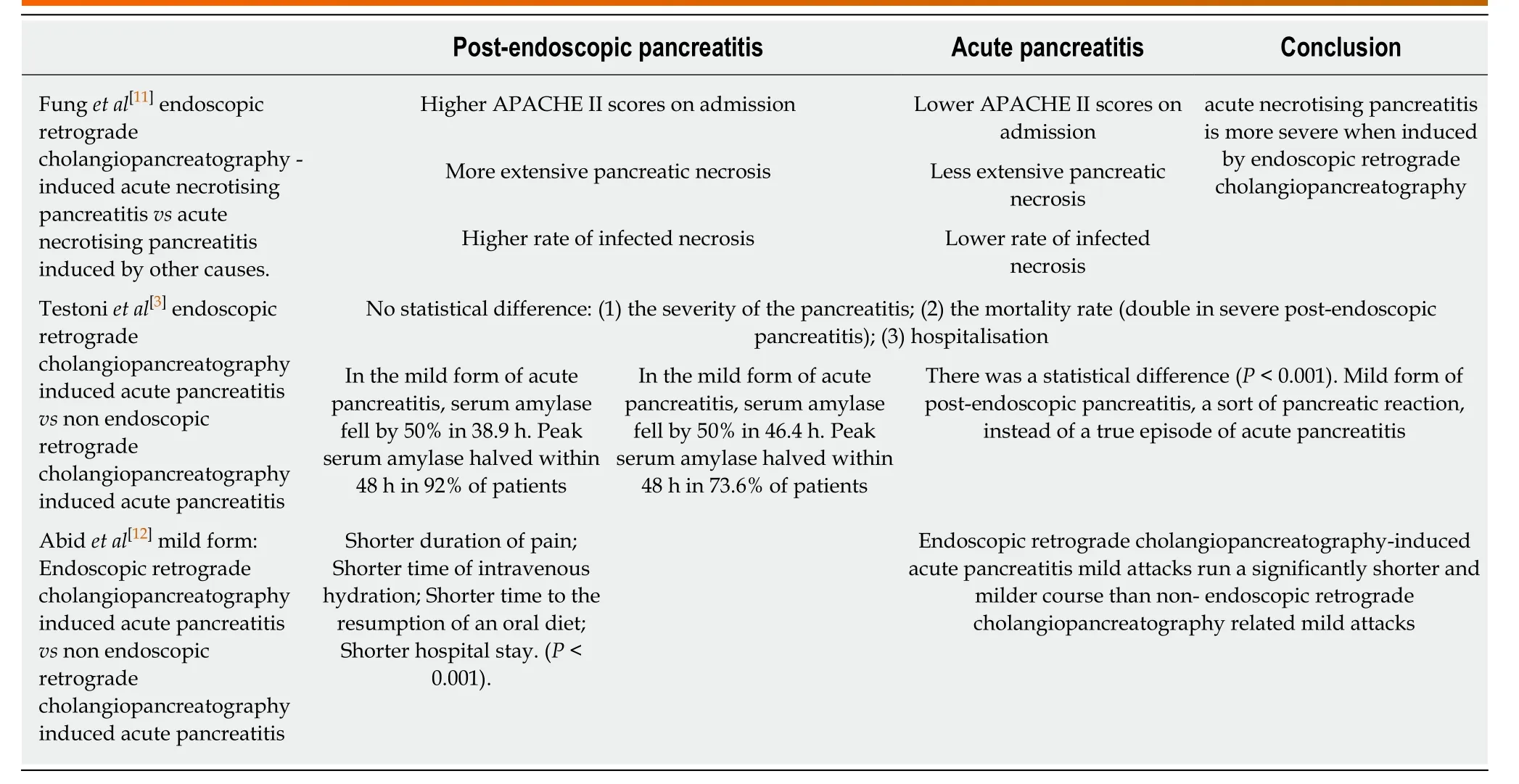
Table1 Differences in clinical presentation of post-endoscopic pancreatitis vsacute pancreatitis
IMMUNOLOGY
Disease immunology was extensively studied in both groups of patients and certain components of the immune system emerged as a potential disease severity marker.(Table2)
Systemic inflammatory response syndrome causes the activation of the compensatory anti-inflammatory response syndrome (CARS).Too strong a CARS,paradoxically leads to immunosuppression and a higher possibility of infection[22].A fall in the co-expression of HLA-DR on CD14+ monocytes is considered a standard laboratory indicator of a CARS[23]Analysis of this immune component is linked to the severe form of AP and immunosuppression.
Dysregulated host inflammatory response was included in the new sepsis definition by the Society for Critical Care Medicine and the European Society of Intensive Care in 2016.A recent review article analysed the role of the major innate lymphocyte population,Natural Killer (NK) cells,in the dysregulated host inflammatory response on infection.They concluded that NK cells appear to be critical for the elimination of pathogens during the early phase of sepsis and lead to the prevention of secondary infection during the immunosuppressive phase.This opinion suggests that they may be suitable as new immunotherapeutic agents[24].
Infection is considered to be the most important prognostic factor for disease severity in AP,regardless of the cause.In non-ERCP AP,infection is considered to be the secondary event,while in PEP it's considered to be the primary event[3].
CONCLUSION
It has been proven that innate immunity plays an immense role in AP and the imbalance of innate immunity may determine the severity of the disease early in the course of the disease[16,25,26].As Table2 shows,most of the studies that researched the role of immune cells in innate immunity,used patients with AP as the research subjects.Answers about the role of immune cells in patients with PEP are still insufficient.
On the contrary,the role of different cytokines in both groups of patients was extensively studied.

Table2 Role of immune components in predicting disease severity
Further investigation of innate immunity cells and their function in PEP is important.Especially,as already mentioned,the exact time of injury in PEP is known and therefore it may represent a good model for evaluation of the early immune response in AP[6,27].
 World Journal of Meta-Analysis2019年3期
World Journal of Meta-Analysis2019年3期
- World Journal of Meta-Analysis的其它文章
- PD-1/PD-L1 antagonists in gastric cancer:Current studies and perspectives
- Hepatic regeneration in Greek mythology
- Gastrointestinal stress ulcer prophylaxis in the intensive care unit,where is the data?
- Reproducibility and replicability of systematic reviews
- Higher dose of simethicone decreases colonic bubbles and increases prep tolerance and quality of bowel prep:Meta-analysis of randomized controlled trials
- Prospects for immunotherapy as a novel therapeutic strategy against hepatocellular carcinoma
