Dermatofibrosarcoma metastases to the pancreas:A case report
Huai-Jie Cai,Jian-Hua Fang,Nan Cao,Wei Wang,Fan-Lei Kong,Xi-Xi Sun,Bin Huang
Huai-Jie Cai,Jian-Hua Fang,Nan Cao,Wei Wang,Fan-Lei Kong,The Fourth School of Clinical Medicine of Zhejiang Chinese Medical University,Hangzhou 310053,Zhejiang Province,China
Xi-Xi Sun,Bin Huang,Department of Ultrasound,Xixi Hospital Affiliated to Zhejiang Chinese Medical University,Hangzhou 310023,Zhejiang Province,China
Abstract
Key words:Pancreatic fibrosarcoma;Metastasis;Magnetic resonance imaging;Treatment;Case report
INTRODUCTION
A fibrosarcoma is a low-grade malignant tumor with a local recurrence rate of 60%[1].The incidence of distant metastases is <1%[2,3].When fibrosarcomas metastasize to the pancreas,there are no apparent clinical symptoms in the early stage;however,when the mass increases in size,there may be symptoms of compression,such as gastrointestinal obstruction,jaundice,and abdominal pain,as well as a series of clinical symptoms,such as cachexia,in the late stage.Generally speaking,pancreatic metastases of malignant tumors and primary pancreatic cancer have a higher degree of malignancy and often invade peripheral blood vessels,viscera,and other tissues,thus making radical surgery difficult.Palliative chemotherapy is often adopted clinically[4];however,this case illustrates that aggressive radical surgery is beneficial to long-term survival due to the low malignant characteristics of fibrosarcomas.Preoperative magnetic resonance imaging(MRI)can more accurately detect lesions and assess the extent of tumor invasion,thus enabling the development of a reasonable therapeutic schedule.At present,most of the treatment methods adopted involve surgical resection,while the effect of adjuvant chemotherapy is still uncertain.Due to the small number of cases,there is no universally recognized standard for imaging diagnosis and treatment.Hence,we report a case of a dermatofibrosarcoma with metastases to the pancreas with the imaging findings and treatment mode,in order to provide reference for scholars and clinicians.
CASE PRSENTATION
Chief complaint
A 45-year-old man was admitted to hospital due to recurrent epigastric pain for 10 d.
History of past illness
The 45-year-old male patient underwent a distal local dilation resection of a primary fibrosarcoma of the left chest wall in 2003,and a left pneumonectomy in 2017 for left pulmonary fibrosarcoma metastases.
Personal and family history
The family history was unremarkable.
Physical examination upon admission
No obvious abnormalities were noted on physical examination with the exception of slight tenderness in the upper abdomen.
Laboratory testing
No abnormalities were found on laboratory testing,including routine blood testing,liver function,blood amylase,and tumor markers.
Imaging examinations
A computed tomography(CT)scan of the upper abdomen suggested a soft tissue mass,4.8 cm × 3.0 cm in size,in the head of the pancreas,with an inhomogeneous density,unclear boundaries,and inhomogeneous enhancement(Figure 1A).Epigastric MRI showed that multiple masses of abnormal signals were visible in the pancreatic head and tail.The largest of which was located in the pancreatic head(approximately 4.8 cm in diameter),with an irregular shape that was hypointense on T1-weighted imaging(T1WI)(Figure 1B),slightly hyperintense on T2-weighted imaging(T2WI),and hyperintense on diffusion-weighted imaging(DWI)(Figure 1C).An enhanced MRI scan displayed progressive reinforcement at the edge of the mass,presenting spoke wheel-like enhancement(Figure 1D),and no significant expansion of the pancreatic duct.A CT scan and MRI revealed no local lymph node enlargement.The pathologic examination revealed that there were multiple fusiform interlobular tumors with abundant tumor cells interwoven within the matrix cells in the pancreas.The larger tumor(5 cm × 3 cm × 3 cm)was located in the pancreatic head.No tumor cells were found in the upper and lower margins or the bile duct margins.Immunohistochemical staining demonstrated the following in approximately 10% of tumor cells:Cytokeratin [-];CD117 [-];S-100 [-];desmin [-];smooth muscle actin [-];CD34 [+];vimentin [+];and Ki-67 [+](Figure 2).Thus,a final diagnosis of pancreatic fibrosarcoma was confirmed.
FINAL DIAGNOSIS
Pancreatic fibrosarcoma.
TREATMENT
A Whipple's procedure and distal pancreatectomy with splenectomy were performed under general anesthesia.Multiple lesions were observed in the pancreas during the operation.The size of the mass in the head of the pancreas was 5 cm × 3 cm × 3 cm.The mass had a tough consistency with yellow liquid inside.The largest mass in the tail of the pancreas was 3 cm × 2 cm in size and invaded the capsule of the spleen.Intraoperative frozen section suggested a mesenchymal spindle cell tumor in the tail of the pancreas,consistent with metastatic fibrosarcoma.No obvious abnormality was found in the retroperitoneal lymph nodes.Considering that the left lung had been excised,the patient was transferred to intensive care unit(ICU)for observation.
OUTCOME AND FOLLOW-UP
After the Whipple's procedure and distal pancreatectomy with splenectomy were performed,the patient uneventfully recovered,without a local recurrence or distant transfer at the 6-mo follow-up.
DISCUSSION
A fibrosarcoma is a slow,soft tissue tumor with low malignant potential that makes up 10% of soft tissue sarcomas.Soft tissue sarcomas comprise only 1% of tumors.Fibrosarcomas mainly manifest in soft tissues,such as the limbs,the head and neck,and the abdominal cavity(mainly in the peritoneum)[5].Dermatofibrosarcoma metastasis to the pancreas is extremely rare and was first reported by Atucha in 1960[6].
At present,the etiology of fibrosarcoma is unclear,but some scholars are of the opinion that this disease may be related to a history of the plague,trauma,radiation exposure,and a family history[7].This disease occurs most often in the elderly,and the incidence between males and females is not significantly different.Pancreatic tumors,in the early stages,often have no obvious clinical symptoms;however,when the mass enlarges,it can compress local tissues and result in gastrointestinal obstruction,jaundice,and abdominal pain[8].
In the current case,MRI of the masses were hypointense on T1WI and slightly hyperintense on T2WI.They were mainly characterized by T2WI signals with spoke wheel-like enhancement at the edges of the masses.The spoke wheel-likeenhancement of this case is consistent with the findings of Wanget al[9],who reported that such lesions usually exhibit peripheral enhancement and sometimes spoke wheel-like enhancement.The mechanism of enhancement has not been established.The enhancement may be related to the arrangement of collagen fibers within the tumor lesions,while the non-enhanced zone may be related to fibrous septations,cystic changes,or necrosis of the lesion.This disease should be distinguished from the following diseases.The first one is non-functional islet cell tumor(NFICE).Most NFICE patients have no clinical symptoms and are treated for compression.CT findings show that the tumor mass is large,at an average of 10 cm.The tumor density is not uniform,and liquefaction necrosis may occur,with some nodular calcification.MRI shows a sharp edge of the mass,hypointense on T1WI and hyperintense on T2WI,and obvious enhancement in the solid part of the mass.Solid false papilloma pseudopapillary tumor of the pancreas(SPTP)is also a differential diagnosis.SPTP,which is usually located in the head and tail of the pancreas,frequently occurs in young women.On CT,the mass presents a mixed density shadow,with hemorrhage and calcification within the tumor.MRI shows mixed signals in the mass,hypointense in the cystic part of T1WI,hyperintense in T2WI,and progressive moderate enhancement in the solid part.The third differential diagnosis is pancreatic cancer,which is a tumor with deficient blood supply.With CT enhancement,the tumor is not significantly strengthened and shows high malignancy and strong infiltration,and vague edges of the lesion,which often encroach on surrounding structures.It is worth mentioning that the enhanced CT scan of this case only showed irregular low-density masses in the head of pancreas,while the enhanced MRI suggested multiple signals of unequal soft tissue masses in the head and tail of the pancreas(Figure 3).Hence,MRI has a greater resolution of soft tissues.In the case of soft tissues,it is necessary to perform MRI enhancement before the operation.MRI enhancement provides more valuable information for surgeons to choose an optimal surgical approach.Although the spoke wheel-like enhancement of the mass is highly suggestive of a fibrosarcoma,it is ultimately confirmed by postoperative pathologic examination and immunochemical staining.The masses were generally not exquisite,having a fish-like appearance,in which the plane was pink and the cystic area was visible.The histologic characteristic was mainly the diffuse distribution of the tumor cells,which were interwoven with the matrix cells in which the blood vessels are abundant.At present,it is difficult to identify the sarcoma morphologically as a fibrosarcoma,but the expression of immunological markers,such as CD34,vimentin,and Ki-67,canhelp in the identification process.

Figure 1 lmaging findings of the head of the pancreas.
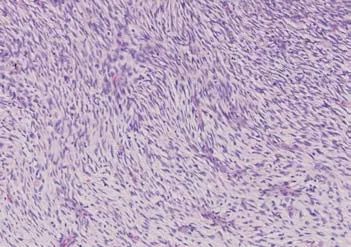
Figure 2 Postoperative pathologic photomicrograph showing a mesenchymal neoplasm in which the tumor and matrix cells were interwoven(HE staining,200×).
CT and MRI enhancement in this case suggested a pancreatic malignancy without metastases to the lymph nodes.A Whipple's procedure and distal pancreatectomy with splenectomy were performed.Unlike pancreatic metastases from breast cancer[10],aggressive surgery for a resectable fibrosarcoma of the pancreas was indicated[11,12].Debulking surgery prolongs long-term survival and controls local recurrence.Currently,radical surgery is considered the preferred treatment for localized fibrosarcomas[13].
When the tumor is transferred,it can be treated systemically,such as with chemotherapy and biological preparation;however,a fibrosarcoma is generally resistant to chemotherapy,the effect of which is still controversial,so that the patient does not receive further adjuvant chemotherapy.New research reveals that adjuvant chemotherapy may be beneficial[14],and the clinical trials of treatment,such as Oradin,have been shown to be effective.Based on phase 3 clinical trials,Oradin was a firstline treatment that has been classified by the United States as a high level or distant metastatic soft tissue sarcoma due to the good effect of Oradin combined with azithromycin in the second phase[15].
Generally,the severity of malignancy may be associated with the speed of metastasis.By comparison of the two metastatic events in this case,the second metastasis occurred faster.Hence,it is essential to have an increased clinical suspicion for a newly emerging fibrosarcoma.During the 6 months of follow-up,he recovered well without evidence of a local recurrence or newly distant metastases by abdominal CT re-evaluation;however,further long-term follow-up is needed.
CONCLUSION
Pancreatic fibrosarcoma is a rare malignant tumor of low malignant potential with a high local recurrence rate.It is essential to perform MRI enhancement before the operation and follow-up postoperatively.Surgery is the preferred treatment.Moreover,adjuvant chemotherapy also requires additional data for confirmation.
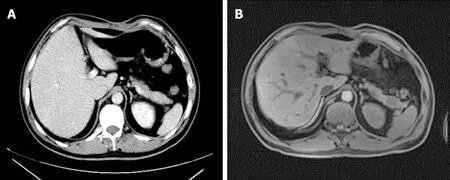
Figure 3 lmaging findings of the pancreatic tail.
 World Journal of Clinical Cases2019年20期
World Journal of Clinical Cases2019年20期
- World Journal of Clinical Cases的其它文章
- Clinical use of low-dose aspirin for elders and sensitive subjects
- Distribution and drug resistance of pathogenic bacteria in emergency patients
- Comparative analysis of robotic vs laparoscopic radical hysterectomy for cervical cancer
- Feasibility of laparoscopic isolated caudate lobe resection for rare hepatic mesenchymal neoplasms
- Soft tissue release combined with joint-sparing osteotomy for treatment of cavovarus foot deformity in older children:Analysis of 21 cases
- Clinical characteristics of sentinel polyps and their correlation with proximal colon cancer:A retrospective observational study
