Reactive perforating collagenosis
Hang Zhang and Jian-Min Chang*
Department of Dermatology,Beijing Hospital,National Center of Gerontology,Beijing 100730,China.
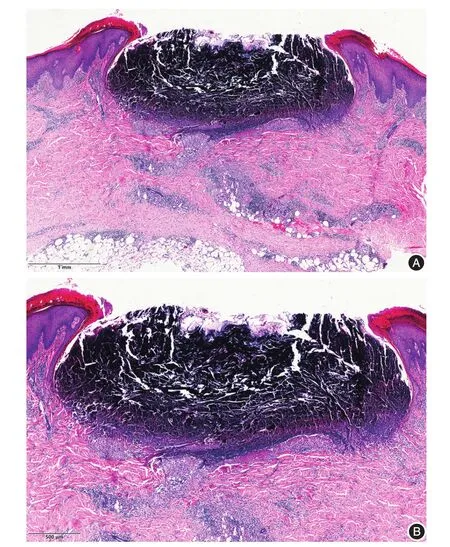
Figure 1 A cup-shaped depression is seen in the epidermis,and the necrotic epidermis and the collagen fibers penetrating upward is visible.Lymphocytes infiltrate in the superficial dermis,blood vessels and fat.A:H&E,× 40;B:H&E,× 100.
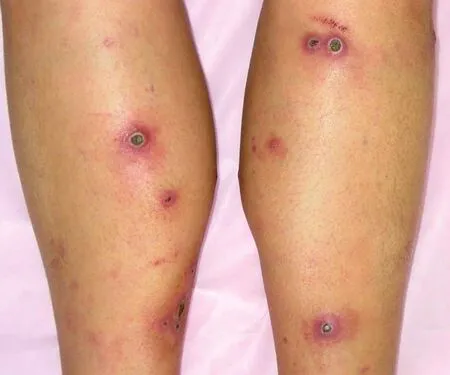
Figure 2 Scattered and symmetry distribution of bean-sized red papules on lower limbs,some have umbilical fossa,the center has a yellow-brown hard and thick crust,and the skin around the crust is red.
Histopathology
Histological features of reactive perforating collagenosis(RPC)vary according to stage of disease.The pathological manifestations of lesions that did not form an umbilical fossa in the early stages,degenerate collagen fibers accumulate in dermal papillae and epidermal hyperplasia may be seen.The upper epidermis is atrophied,and a thin layer of keratinized material is visible in the center.Typical acanthosis is visible on both sides of the lesion.In the late stage,epidermis cup-shaped depression can be seen in the epidermis,and it filled with columnar overlying keratin plug that consists of parakeratotic debris,denatured collagen fibers and inflammatory cells[1].The epidermis below is obviously thin.It is locally visible that degenerative collagen fibers pass through the epidermi vertically.The epidermis on both sides of the cup-shaped structure show acanthosis and hyperkeratosis,and infiltration of lymphoid cells is observed in the superficial dermis and around the blood vessels(Figure 1).Blue-stained collagen fibers are visible in the superficial dermis and epidermis in Masson staining.
Clinical features
RPC is a rare disorder in which abnormal collagen fibers extrude through the epidermis[2].It can be divided into inherited RPC and acquired RPC.The former is more rare,mainly seen in children.The latter is mainly seen in adults and often combined with systemic diseases,such as diabetes,chronic renal failure,particularly in patients undergoing dialysis.
The pathogenesis of RPC is not yet clear,it has a certain genetic predisposition and can be familyaggregated.Previous studies have demonstrated that immunoreactivities of transforming growth factor-β3,matrix met alloproteinase(MMP)-1 and tissue inhibitor of met alloproteinase-1 were significantly increased in the lesions of acquired RPC[3].
The disease occurs in the exposed area,usually in the limbs and back,as well as in the face and neck.The clinical manifestations are hard skin colored papules,and often at sites of superficial trauma,mosquito bites,hemorrhoids and after scratching[4].The center has umbilical fossa depressions,which are filled with keratinized substances.The crusts are not easy to remove,and scars and hypopigmentation can be left behind(Figure 2).Skin lesions can resolve spontaneously after 6-8 weeks,but are prone to recur.Itching symptoms are common,K?bner phenomenon is positive in some patients[5].Some autoimmune diseases are thought to be associated with this disease,such as systemic lupus erythematosus[6],vasculitis,dermatomyositis and Mikulicz disease.In addition,some malignant tumors,including lymphoma,thyroid cancer[7]and breast cancer[8],have also been reported as coexisting diseases.
The disease needs to be differentiated from amyloidosis,vasculitis and pruritus in the early stage.Late lesion needs to be distinguished from elastosis perforans sepiginosa,penetrating folliculitis,Kyrle disease,itching nodules,penetrating granuloma annulare and perforating psedoxanthoma elasticum.Histopathological examination can be identified.
There is no specific treatment for this disease.Ultraviolet light therapy,narrow-band UVB(NB-UVB),308 nm excimer laser[9],acitretin,cyclosporine,methotrexate,allopurinol,doxycycline,high-dose penicillin and compound glycyrrhizin tablets have been successfully reported.At the same time,effective treatment of combined systemic diseases is critical to the prognosis of acquired RPC.
- 國際皮膚性病學(xué)雜志的其它文章
- Paraneoplastic pemphigus comorbid with cardiac cancer and duodenal gastrointestinal stromal tumors:a rare case report
- Sun?protection knowledge and strategies of Chinese dermatologists:a nation?wide,questionnaire?based survey
- Initial presentation of acute myeloid leukemia in a patient with cutaneous myeloid sarcoma
- Persistent papules with adult?onset Still’s disease:a case report
- Primary vulvar melanoma in a 27?year?old pregnant woman:a case report and literature review
- Cutaneous plexiform schwannoma in the right thigh after trauma

