Evaluation of Efficacy and Safety of Electro-acupuncture Precondition on Postoperative Cognitive Dysfunction (POCD)Following Knee Replacement in Elderly:A Randomized Controlled Trial
Zho Feiyi (趙非一), Zhng Zheyun (張浙元), Zho Yingxi (趙英俠),Yn Hixi (燕海霞), Xu Hong (許 紅)*
aShanghai Municipal Hospital of Traditional Chinese Medicine Affiliated to Shanghai University of Traditional Chinese Medicine,Shanghai 200071, China;
bHaiyan People's Hospital Affiliated to Zhejiang Pharmaceutical College, Jiaxing 314300, China
cCollege of Basic Medicine of Shanghai University of Traditional Chinese Medicine, Shanghai 201203, China
ABSTRACT
OBJECTIVE: To investigate that whether electro-acupuncture (EA) precondition can reduce the incidence of postoperative cognitive dysfunction (POCD) following knee replacement and its safety in elderly. METHODS: A total of 60 participants met the inclusion criteria were enrolled in a randomized controlled trial with the ratio of 1:1, with 30 cases in the treatment group and 30 cases in the control group. The participants in the treatment group were provided with real-EA therapy whereas participants in control group were provided with placebo-EA therapy. Interventions were offered 5 days prior to the surgery, once daily, and for a total of 5 days. The scores of Mini-Mental State Examination (MMSE), and contents of serumal inflammatory cytokines including interleukin 1β (IL-1β) and tumor necrosis factor-α (TNF-α) were observed at 24 hours prior- and posterior- to the surgery respectively for assessing the incidence of POCD among patients.Meanwhile, adverse effects were monitored and recorded. RESULTS: (1) After surgery, both treatment group and control group showed a significant decrease in MMSE global scores (P < 0.001, < 0.001, respectively), and the score in control group decreased more significantly than that in treatment group (P < 0.05); (2) Contents of serumal IL-1β and TNF-α were significantly increased in both groups after 24 hours posterior to the surgery (P < 0.001), and the contents in control group increased more significantly than that in treatment group (P < 0.001); (3) After surgery, the incidence of POCD was 20% in treatment group versus 36.67% in control group. There was no statistical difference between 2 groups (P > 0.05);(4) No serious adverse events were reported in this trial, except 1 patient from treatment group had a slight hematoma after receiving acupuncture. CONCLUSION: EA precondition might reduce cognitive impairments after 24 hours posterior to knee replacement surgery in elderly through inhibiting expression of inflammatory cytokines, including both IL-1β and TNF-α. However, there is insufficient evidence to support that EA precondition could reduce incidence of POCD.
KEYWORDS: Postoperative cognitive dysfunction; Electro-acupuncture; Precondition
As a global public health issue in the field of perioperative care, and with a high incidence ranging from 25% to 40% in elderly patients[1], postoperative cognitive dysfunction (POCD), is defined as a common neurological complication following prolonged surgery.Though POCD and delirium are often discussed together because both of them are brain dysfunction following surgery with high morbidity[2], there are still distinguishes between POCD and delirium which might not be neglected. Distinguished from delirium featuring acute change or fluctuation in consciousness and perception and that patients are often disoriented due to the decreased awareness of outside environment[3],POCD is characterized by deficits in memory, attention,concentration, and language comprehension, or even progressive personality changes in serious circumstances,but patients with POCD are oriented[1,3-6].
Many studies emphasize that due to the significant decline of patients' self-care ability and the heavy burden on both individual and the whole society, more attention should be paid to various impacts of POCD on the longterm life quality of patients. To illustrate, the influence of POCD on patient's postoperative life could be assessed from several aspects, including the patient's survival time,labor force status, and dependence on the medical security scheme and health care system[7].
Though the specific pathophysiology mechanism of POCD remains unclear, it is usually believed to be the result of a combination of numerous factors[8]. According to laboratory examination, agminated amyloid beta peptide (Aβ) similar to the typical feature of Alzheimer's disease is also found in patient with long-term POCD. The levels of preoperative plasma Aβ1-42 and Aβ1-40 are closely related to the incidence of POCD as well[9]. The pharmacological studies reveal that since different drugs can act on different cells and molecules among various brain regions, the choice of anesthetic agents therefore is responsible for incidence and prognosis POCD[10].In addition, systemic inflammatory response syndrome(SIRS) due to release of a large amount of inflammatory cytokines during and after the surgery was reported to play an important role in POCD. The inflammatory response of central nervous system (CNS), especially microglia, is deemed to affect the occurrence and development of POCD[11]. Hence, there are speculations that inhibition of expression of inflammatory cytokines might be an option in preventing and treating POCD,though more evidence resulting from larger sample size animal experiments and clinical trials is needed[12].It is worth mentioning that the relationship between endothelial cells and POCD has received increasing attention recently. In light of previous studies, many products activated by platelets and endothelial cells were reported as key biological markers in the development of POCD[13].
Angiotensin II receptor antagonists such as Candesartan, α-adrenoceptor agonists such as Dexmedetomidine, and free radical scavengers such as Edaravone are currently used as first-line drugs for POCD with satisfactory short-term efficacy as well[14]. However,potential risk of hypotension and bradycardia induced by Dexmedetomidine[15], angioedema and sacroiliac joint pain induced by Candesartan[16], and headache induced by Edaravone[17]can also limit the use of these medications in critical POCD patients or long-term use, which prompts patients to seek treatment from complementary and alternative medicine (CAM). Acupuncture, as a representative of CAM, is widely used in Asia and increasingly in Western countries, and showed satisfactory effects in the improvement of cognitive disorders caused by various diseases[18].
In previous literatures, some clinical trials regarding electro-acupuncture (EA) intervention for POCD were reported. However, since no placebo EA were set as effective control in the trial[19,20], decreased reliability and validity of the results seemed inevitable. To provide more credible evidence of EA on POCD, particularly investigate if EA precondition can reduce the incidence of POCD following knee replacement and its safety in elderly, in this study, a randomized, single-blind,placebo-controlled clinical trial with more intuitive and reliable detection techniques was conducted. In addition to method of placebo EA, both subjective assessment scale such as Mini-Mental State Examination (MMSE),and objective laboratory indicators such as content of serumal interleukin 1β (IL-1β) and tumor necrosis factor-α (TNF-α) were introduced in this trial in order to comprehensively evaluate the decline of postoperative cognitive function among patients, and address the defects of design in relevant previous studies. Meanwhile,adverse effects were monitored and recorded as well.
CLINICAL MATERIALS
Participants
A total of 60 elderly patients [aged 60-80 years old;American Society of Anesthesiologists (ASA) ranging from grade I to II] undergoing knee replacement surgery at either Shanghai Municipal Hospital of Tradition Chinese Medicine Affiliated to Shanghai University of Tradition Chinese Medicine or Haiyan People's Hospital Affiliated to Zhejiang Pharmaceutical College from March 2015 to February 2018 were selected. This study was approved by the ethics committees at both 2 hospitals mentioned above. All participants were required to sign informed consent before participating in the trial.
Inclusion criteria
(1) 60-80 years old; (2) Patients without cognitive dysfunction (MMSE27 points); (3) Did not take any psychoactive drugs within 4 weeks prior to the commencement of this trial; (4) Signed informed consent,voluntarily participated in this clinical trial, and pledged to cooperate with follow-up visits.
Exclusion criteria
(1) Individuals aged <60 or> 80 years old; (2) Those with cancer, severe hepatic and renal insufficiency, and primary diseases of hematopoietic system and endocrine system; (3) Patients with cognitive impairments caused by neurodegenerative diseases such as Parkinson disease,Alzheimer's disease, Vascular Dementia, Stroke or other psychiatric disorders, and other systemic chronic illness and medical condition (MMSE < 27 points); (4) Scores of Hamilton Anxiety Scale14 points, and (or) Hamilton Depression Scale18 points; (5) Pre-estimation of operation duration > 4 hours or intraoperative blood loss> 1000 mL; (6) Those participated in other clinical trials within the past 1 month; (7) Those with a tendency of skin infections and bleeding; (8) Patients who were deaf,blind and had disorders in communication.
Withdrawal and dropout criteria
(1) A serious adverse event related to the research occurred; (2) When a participant asked to withdraw from the trial for any reason at any time; (3) The treatment had to be interrupted due to the unforeseen reasons; (4)Participant accepted other treatments during this trial or didn't cooperate with the researcher.
RESEARCH METHODS
Participants and randomization
This was a single-centered, randomized, patientblinded, parallel-group and placebo-controlled trial with a 1:1 ratio to treatment and control group. Before the commencement of recruitment, the random numbers were generated by SPSS 21.0 statistical software, and these random sealed numbered were placed into 60 opaque envelopes. A total of 60 patients meeting the inclusion criteria were recruited by hospital-based advertisements from the outpatient clinic and wards of both Orthopedics Department and Rehabilitation Department in Shanghai Municipal Hospital Tradition Chinese Medicine and Haiyan People's Hospital. Those eligible patients were randomly allocated to the different groups through simple envelope method. Outcome assessments were conducted at 24 hours prior to surgery, and 24 hours posterior to surgery, respectively.
Intervention methods and courses
All patients received routine perioperative care of EA or placebo EA precondition 5 days prior to the surgery.
The treatment group (Real EA)
Acupoints: Sishencong (EX-HN1), Shenting(GV 24), Baihui (GV 20), bilateral Benshen (GB 13),bilateral Hegu (LI 4), and bilateral Taichong (LR 3).
Methods: Participants in treatment group were in dorsal position for needling at both head and extremities acupoints. Skin around acupoints was sterilized by 75% alcohol. Standard sterilized disposable needles(0.25 mm in diameter and 25 mm in length, stainless steels, Jiajian Medical Instrument Co., Ltd. China) were inserted horizontally into the acupoints of Sishencong(EX-HN1), Baihui (GV 20), Shenting (GV 24) and Benshen (GB 13), while acupoints of Hegu (LI 4) and bilateral Taichong (LR 3) were inserted perpendicularly with acupuncture needles of another specification (0.25 mm in diameter and 40 mm in length, Jiajian Medical Instrument Co., Ltd. China). Acupuncture depths were various according to different acupoints. Usually, needles were inserted into the skin to a depth of 10-30 mm due to the fatty tissues at the site of the acupoints and manipulated manually until the arrival of qi (an irradiating feeling considered to be indicative of effective needling) was achieved.The feelings of the arrival of qi were strengthened by acupuncturist through twisting or thrusting forward and backward the needles. After that, all of the needles were retained for further 30 minutes before removal.In addition, the needles inserted into Hegu (LI 4) and bilateral Taichong (LR 3) were connected to the EA instrument (Model: G6805-2; Shanghai Huayi Medicinal Instruments Co., Ltd. China) with dilatational wave, and the intensity was set according to the patient's tolerance.
The control group (Placebo EA)
Acupoints: Acupoints were as same as those in treatment group.
Methods: In light of previous insomnia-related,high-quality, randomized controlled trial[28], a noninvasive, placebo acupuncture approach (Streitberger Placebo-needle) was selected in the control group[29].Streitberger needle was a type of specially designed acupuncture needle with a blunt needlepoint. When the blunt needlepoint touched the skin, it would spring back into the needle sheath. The needles positioned at Hegu(LI 4) and bilateral Taichong (LR 3) were connected to the same model but modified EA instrument, but the instrument was not activated except the indicator light was flashing, so that the patients mistakenly believed that the EA instrument was working.
Patients in both groups were treated once a day consecutively for total five days. Meanwhile, they were informed that these 2 acupuncture approaches were commonly used in clinical practice and both of them were effective, and this trial was just to compare which acupuncture approach was much better for reducing the incidence of POCD. Patients' other questions about the treatment efficacy during the intervention course would not be answered by the acupuncturists.
Anesthesia methods
Both groups were given the same method of general anesthesia. When general anesthesia was performed, intravenous Fentanyl (2 μg/kg), Midazolam(0.04 mg/kg), Propofol (1 mg/kg), and Cisatracurium Besilate for Injection (0.2 mg/kg) were administered sequentially. Mask oxygen inhalation and artificially assisted breathing were provided as well. Endotracheal intubation was performed after the patient' muscles were relaxed, anesthesia machine was connected, and then mechanical ventilation and end-tidal carbon dioxide partial pressure monitoring were given. Intraoperative anesthesia was maintained by constant infusion of Remifentanil 0.2-0.5 μg/(kg·min) and Propofol 4-6 mg/(kg·h) to the end of surgery. During the surgery, blood pressure (BP)and heart rate (HR) were maintained within ± 20% of the baseline value, and bispectral index (BIS) was maintained at 40-60. After surgery, endotracheal tube was pulled out until the patient was awake.
Outcome measures
Primary outcomes
MMSE: MMSE is a commonly used, useful and economical clinical assessment tool to screen cognitive impairment[21]. Originally designed by Folstein, et al in 1975, MMSE includes the following seven domains:orientation to time, orientation to place, registration,attention and calculation, recall, language, repetition,and complex commands. Each domain contains at least 1 question, with 1 point for each question, and total 30 questions. According to the global scores, 27-30 points indicates interviewee without cognitive dysfunction;21-26 points indicates interviewee with mild cognitive dysfunction; 10-20 points indicates interviewee with moderate cognitive dysfunction; 0-9 indicates interviewee with severe cognitive dysfunction. POCD could be diagnosed if postoperative MMSE score is at least 2 points lower than preoperative MMSE score[22].
Secondary outcomes
Serumal IL-1β and TNF-α: IL-1β and TNF-α are main inflammatory cytokines produced by microglia, and can objectively show the level of systemic inflammatory response.
Statistical methods
SPSS 21.0 statistical software was used for statistical description and inference after the original data were inputted through Excel 2010. Measurement data in normal distribution were expressed as Mean ± Standard Deviation (Mean ± SD) and analyzed by paired t-test or 2 dependent samples t-test for inter-group comparisons and intra-group comparisons. The measurement data in abnormal distribution were analyzed by Wilcoxon ranksum test. The enumerations data were expressed by ratio and processed by Chi-square (χ2) test. Ranked data were analyzed by non-parametric test. The significance level was set at 0.05, 0.01 and 0.001 respectively.
Results and statistical analysis
Demographic and clinical characteristics
After baseline assessment, demographic and clinical characteristics of the participants were presented. See Table 1. As can be seen, baseline clinical characteristics were balanced between the 2 groups (P > 0.05).Meanwhile, there were no significant differences in demographic characteristics between 2 groups as well.
Efficacy
The results of global MMSE scores related to cognitive function changes, and content of serumal IL-1β and TNF-α which is relevant to systematic inflammation state changes are presented. See Table 2. Changes in global MMSE scores and content of serumal IL-1β and TNF-α revealed that significant decline in cognitive function while increasing release of inflammatory factors following the surgery occurred in both groups.
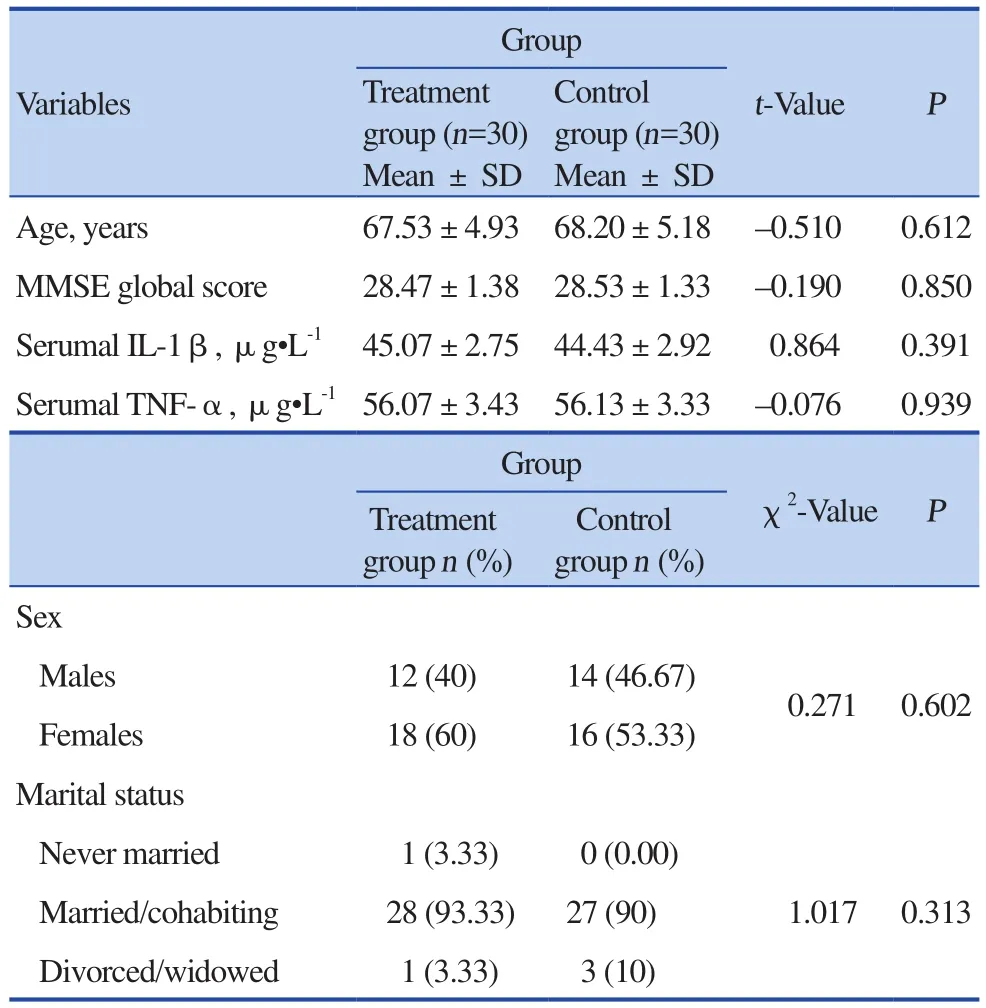
Table 1. Baseline balance test of participants'demographic and clinical characteristics
Compared with baseline, global MMSE scores in both treatment and control groups showed significant decreases after surgery (P < 0.001, P < 0.001,respectively). Moreover, decline in control group was more significant than that in treatment group (P < 0.05). It might be concluded that significant cognitive impairments occurred in both groups following the surgery.Furthermore, the cognitive dysfunction of patients who received placebo-EA were more severe than that of those who received real EA precondition.
Incidence of POCD in both groups was recorded.See Table 3. As can be seen, among 60 patients, 17 were diagnosed with POCD following knee replacement surgery, with an incidence of 28.33%. Of these, 6 were from the treatment group and 11 were from the control group. The incidence of POCD was 20% in treatmentgroup versus 36.67% in control group. Although there was no statistical difference in POCD incidence between 2 groups (P > 0.05), the incidence of POCD in patients receiving EA therapy was indeed much lower than that in patients receiving placebo-EA therapy.

Table 3. Incidence of POCD at 24 h posterior to the surgery
Inflammation levels: Compared with baseline,content of serumal IL-1β and TNFα in both groups increased significantly after 24 h posterior to the surgery(P < 0.001). Compared with treatment group, content of serumal serum IL-1β and TNFα increased more significantly in control group after surgery (P < 0.001).
SAFETY ASSESSMENT
No serious adverse events were reported in this trial, except 1 patient from treatment group had a slight hematoma after receiving acupuncture. That patient was treated with cold compress and recovered in 2 days. No one dropped out from this trial.
DISCUSSION
POCD is a common neurological complication following surgery in elderly patients. Epidemiological survey showed that, due to numerous factors involved in the perioperative period of major surgery, an average of 14% elderly experienced cognitive decline and mental confusion from a few weeks to three months after surgery[23]. Though POCD is usually reversible,there are some patients who will experience delays in rehabilitation and a low life quality because of POCD.The rate of disability and mortality might also increase within one year after surgery, which places a huge burden on both families and society. In addition, POCD may also accelerate the progression of Alzheimer's disease[24,25].Acupuncture, as a characteristic therapy of traditional Chinese medicine (TCM), due to its advantages including wide adaptability, safety and low cost, is popular in China and gradually being accepted by western countries.Previous studies have illustrated that acupuncture could play a role in brain protection through improving brain function, significantly reducing neurological deficits,and then promoting learning, memory, and other cognitive functions[26,27]. Hence, a randomized, singleblind, placebo-controlled clinical trial was conducted in our study in order to investigate if EA precondition can reduce the incidence of POCD after 24 hours posterior to knee replacement and its safety in elder patients.
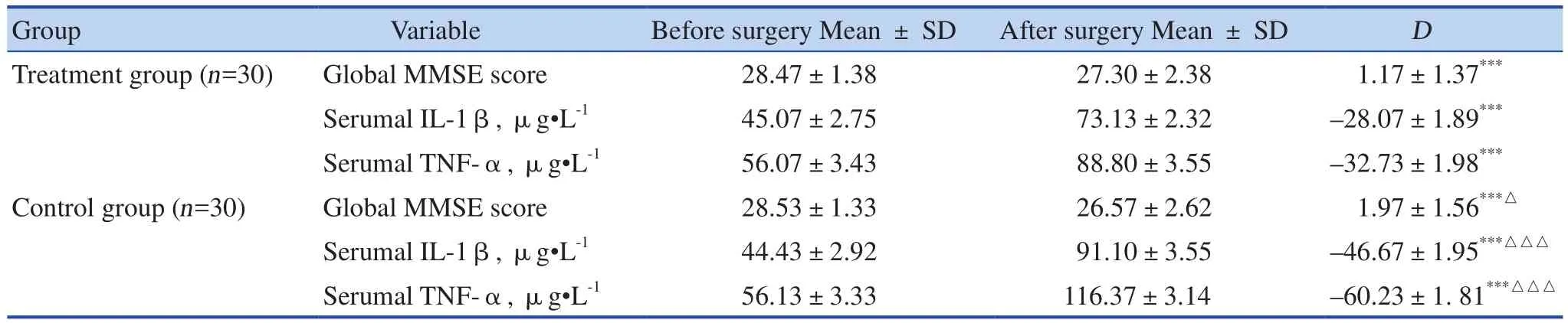
Table 2. Comparison of global MMSE scores, content of serumal IL-1β and TNF-α between 2 groups at 24 h before- and after- surgery (Mean ± SD)
According to the results, global MMSE scores in both treatment and control groups showed significant decreases after surgery. Moreover, decline in control group was more significant than that in treatment group.It suggested that cognitive function in elderly patients would be significantly impaired due to surgical trauma and usage of anesthetic agents in elderly patients undergoing knee replacement surgery whether or not they received EA precondition before. However, though the cognitive dysfunction seemed to be inevitable,EA precondition was proven to effectively reduce the severity of this kind of cognitive impairment. In addition, content of serumal IL-1β and TNF-α were significantly increased in both groups after 24 hours posterior to the surgery, and the score in control group increased more significantly than that in treatment group. Though the exact pathogenecis of POCD is still unclear, evidence is accumulating for a series of inflammatory responses[28,29]. It might be concluded that the protective effect of EA precondition on cognitive function might be achieved by inhibiting the expression of inflammatory factors following surgery.
There was no statistical difference in incidence of POCD between 2 groups, though the number of patients who received EA precondition was less than that of those who received placebo-EA precondition, which suggested that there was not enough evidence to support the efficacy of EA pretreatment on reduction of incidence of POCD.
In this study, "Head-Tri-Shen" including Sishencong(EX-HN1), Shenting (GV 24), and Benshen (GB 13)were selected as main acupoints combined with Baihui(GV 20), Hegu (LI 4), and Taichong (LR 3) as matching acupoints. Among 'Head-Tri-Shen', Shenting (GV 24) is the convergent acupoint of Governor Meridian, Bladder Meridian and Stomach Meridian. Since Governor Meridian links three yang meridians of hand and three yang meridians of foot to brain, Shenting (GV 24)can be viewed as a gathering place of qi and blood in Governor Meridian. Meanwhile, Bladder Meridian is derived from the mind and brain, and administrates the activities of mind and brain. Therefore, qi and blood in meridians will be regulated and delivered to brain through acupuncturing Shenting (GV 24). Sishencong (EX-HN1)is extraordinary acupoint with an effect in improving brain health and promoting intelligence as well. Benshen(GB 13) is the origin of qi in Gallbladder Meridian, and is also the pivot of meridian managing the open or close of three yang meridians. Regulating both Governor Meridian and Bladder Meridian can correct the imbalance of yin and yang of our body. In addition, Baihui (GV 20) is not only passed by Governor Meridian, but also is the convergence of various meridians. Regulation of yin and yang in zang-fu organs might be achieved by acupuncturing Baihui (DU 20)as well. Besides, Siguan acupoint consists of bilateral Hegu(LI 4) and Taichong (LR 3), which is a commonly used acupoint for tranquilizing and sedating the mind with a satisfactory curative effect in the treatment of neurologic and mental diseases. Animal studies showed that EA on Siguan acupoints could improve the learning and memory ability of Alzheimer's disease model rats through improving excitability of cerebral cortical, promoting cerebral circulation, and regulating signal transduction pathways[30]. Clinical trials also found that specific brain functional regions of elderly could be regulated by acupuncturing Siguan acupoint through activating frontal lobe and posterior cingulate cortex[31].
It should be noted that, in terms of no adverse events reported in this trial, and that no participants withdrew or dropped out from this trial, we believed that five consecutive days of EA precondition might be acceptable and safe for elder patients who is going to undergo knee replacement. Based on the results of present trial, EA precondition is worthy of clinical promotion in reducing the incidence of POCD.
LIMITATIONS
Both strengths and some methodological limitations were available in this trial, including the observation period is short, which may result in the statistical bias in outcome assessments. According to previous studies[23],POCD will occur at any time within 3 months following the surgery. Therefore, the ideal observation and outcome assessment period should be from the end of the surgery to 3 months posterior to surgery. In addition, the bias may also be caused due to the insufficient sample size.For further research, conducting a multi-centered,randomized, single-blind, placebo-controlled clinical trial with a larger sample and long-term observation of effects of acupuncture is warranted. Other laboratory examination indicators related to POCD such as IL-6,Bcl-2, Bax and s100β are also expected to be included as the object outcome, combined with self-reported outcome such as MMSE to provide more practical and stricter clinical research modalities in POCD clinical studies.
CONCLUSION
This trial provides evidence for the satisfactory short-term effects of EA precondition in reducing cognitive decline in elderly following knee replacement. It should be suggested that EA represents a safe and useful non-pharmacologic intervention option for prevention and treatment of POCD, though more evidence-based medicine evidence is still required.
STATEMENT OF INTERESTS CONFLICT
None of the authors have any conflicts of interests to declare in this study.
ACKNOWLEDGEMENTS
This study was financially supported by National Science & Technology Pillar Program during the Eleventh Five-Year Plan Period (2007BAI10B01-027); Project of Chinese Medicine Research Fund of Shanghai Municipal Health Bureau (No. 20134358)
 World Journal of Integrated Traditional and Western Medicine2019年1期
World Journal of Integrated Traditional and Western Medicine2019年1期
- World Journal of Integrated Traditional and Western Medicine的其它文章
- World Integrated Medicine Master Wu Yiling
- New Year's Message
- Effects of Acupoint Massage Combined with Psychological Nursing on Depression and Hope Level and Coping Style in Hospitalized Patients with Hepatocirrhosis
- The Method of Soothing the Liver in the Treatment of Acute Abdominal Pain
- Effects of Yigan Tiaozhi Decoction on Serum NO, Endotoxin and RBP4 in Patients with Nonalcoholic Fatty Liver Disease
- Clinical Comparison and Analysis of Decoction of Traditional Chinese Medicine Combined with Ear Acupoint Application and Simple Artificial Tears in the Treatment of Dry Eye Syndrome
