Isolation and Identification of the Pathogen Causing Skin Ulcer Disease in Cynoglossus semilaevis Günther and Its Sensitivity to Chinese Herbal Medicine
Guisheng GAO, Yanying ZHANG, Qiumei SHI*, Guangping GAO, Hongsheng HAN, Xiaoyuan HUANG, Baofeng JIAO, Yaoyao CHANG
1. Key Laboratory of Preventive Veterinary Medicine of Hebei Province/College of Animal Science and Technology, Hebei Normal University of Science & Technology, Qinhuangdao 066600, China;
2. Qinhuangdao Liangfeng Marine Ecological Science and Technology Co., Ltd., Qinhuangdao 066600, China
In recent years, coastal industrial aquaculture is rapidly developing,but the benefit of the aquaculture industry has been greatly affected by disease epidemics. In previous studies, common bacterial diseases and their epidemiological characteristics in a circulating water aquaculture plant of Cynoglossus semilaevis Günther in Qinhuangdao City were investigated.The results show that skin ulcer is the most common bacterial disease in cir culating water aquaculture of C.semilaevis Günther, which poses a serious threat to the reproductive survival rate.At present, few systematic studies have been reported on diseases of C. semilaevis Günther, but Little is available on occurrence and pathogenesis of these diseases. In this study, skin ulcer disease in aquaculture of C. semilaevis Günther was investigated systematically, aiming at providing basis for further prevention and control of skin ulcer disease.
Clinical Symptoms and Pathological Changes in Cynoglossus semilaevis Günther infected with Skin Ulcer Disease
In April 2015, skin ulcer disease occurs in a coastal industrial aquaculture plant of C. semilaevis Günther in Qinhuangdao City. C. semilaevis Günther infected with skin ulcer disease exhibited skin ulcers, fin base swelling, fin end ulcers, local gill filament edema with telangiectasia and congestion, liver and pancreas swelling, renal tissue degeneration,necrosis and ulceration, red blood cell deposition and hemoglobin precipitation in spleen,gallbladder enlargement with telangiectasia,and large amounts of catarrhal mucus in intestines (Fig.1,Fig.2).
Pathogen Isolation
Liver, pancreas, kidney tissues and ascites of C. semilaevis Günther infected with skin ulcer disease were collected, inoculated to a nutrient agar plate, and incubated at 28 ℃for 24 h.Morphological observation results show that round translucent, pale yellow or light brown bacterial colonies were grown with smooth and moist surface and neat edges (Fig.3). The colonies were inoculated to a blood agar plate and incubated at 28 ℃for 12-24 h.As shown in Fig.4,completely transparent zones of hemolysis formed on the plate.As shown in Fig.5,the pathogen was a Gram-negative bacterium with blunt round ends, and individual cells were slightly curved.
Physiological and Biochemical Identification of the Pathogen
Three predominant strains were isolated from liver, pancreas, kidney tissues and ascites of C. semilaevis Günther infected with skin ulcer disease to detect the physiological and biochemical characteristics (Table 1).According to the results, these strains were positive to lipase, arginine dihydrolase, D-trehalose, D-maltose and β-galactosidase but negative to D-glucose,L-arabitol,D-mannitol,malonate,D-arabinitol, L-aspartate arylamidase,β-glucosidase, ornithine decarboxylase, 5-ketogluconate and lysine decarboxylase, indicating that culture,physiological and biochemical characteristics of the isolated strains were consistent with Vibrio harveyi. Therefore, the pathogen causing skin ulcer disease in C. semilaevis Günther was identified as V.harveyi.
Recurrent Infection of C.semilaevis Günther with the Pathogen
A strain isolated from liver and pancreas tissues was incubated with LB broth and inoculated to five healthy C. semilaevis Günther. A C. semilaevis Günther was used as the control,and other four individuals were injected with 0.3 ml of bacterial liquid (containing 2 ×106colonies/ml). At 12 h post-infection, experimental fish swam slowly with lassitude, gradual skin ulceration and loss of appetite, which died successively within 72 h, but the control fish exhibited no abnormal performance. Autopsy results showed gill congestion, organ adhesion and liver congestion, with similar symptoms to naturally infected C. semilaevis Günther.Strains were isolated from dead C.semilaevis Günther for culture and identification. According to the results, the original injection bacterium exhibited consistent morphological and biochemical characteristics with V. harveyi, indicating that the original injection bacterium was the pathogen causing skin ulcer disease in C.semilaevis Günther.
Detection of Outer Membrane Protein Gene (OMP)of the Pathogen
Genomic DNA of V. harveyi was extracted in accordance with the introductions of genomic DNA extraction kit(Fig.6). The results showed that genomic DNA of three V. harveyi strains was successfully extracted.Using genomic DNA of V. harveyi as a tem-plate, 933 bp specific band were amplified by PCR, which was consistent with the expected size (Fig.7),indicating that outer membrane protein gene(OMP) of V. harveyi was successfully amplified and detected.
The amplified OMP gene of V. harveyi was sequenced and submitted to GenBank. By using BLAST software, four reference strains published in GenBank were obtained for comparison and analysis of nucleotide homology. The results showed that OMP gene sequences of three V.harveyi strains shared 98.7%-100% homologies with reference strains. To be specific, OMP gene sequence of representative strain 3 shared 100% homology with reference strain JQ946883; OMP gene sequences of three representative strains shared 98.8%-99.4% homologies with each other(Fig.8).
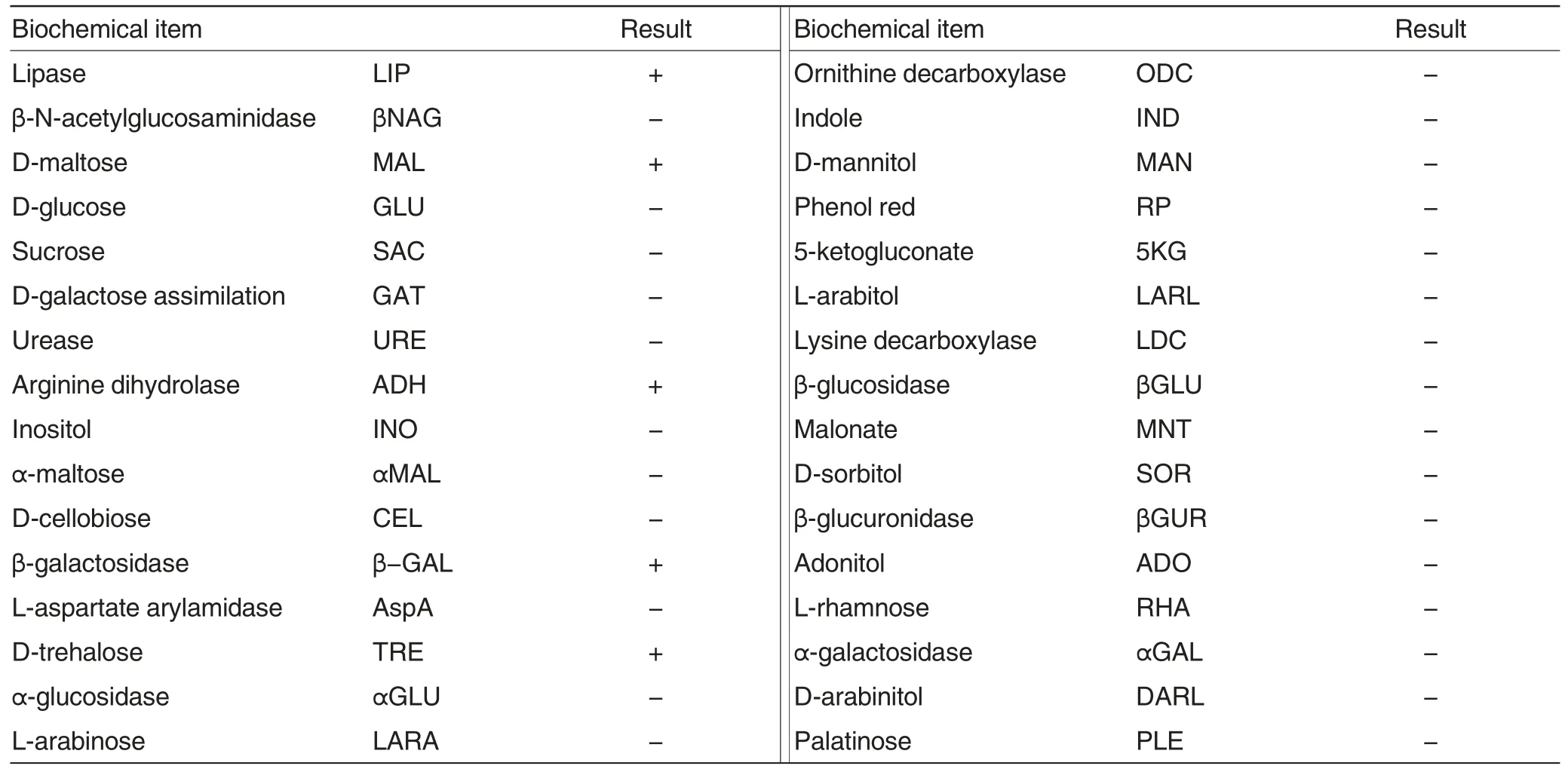
Table 1 Biochemical identification results
Sensitivity Test of the Pathogen to Chinese herbal medicine
As shown in Fig.9 and Table 2,among 12 single herbs used in this study,Galla Chinensis,Fructus Mume,Fructus Hippophae and Lignum Sappan exerted strong antibacterial effects against V.harveyi,among which Galla Chinensis had the highest antibacterial activity; Pericarpium Granati exerted no significant antibacterial effect against V. harveyi; Pericarpium Citri Reticulatae, Rhizoma Acori Graminei,Herba Houttuyniae, Herba Portulacae,Herba Andrographis,Eucalyptus globulus Labill. and Herba Menthae Heplocalycis had little effect on V.harveyi.
According to the results of sensitivity test of the pathogen to 12 single herbs, Galla Chinensis, Fructus Mume, Fructus Hippophae and Lignum Sappan, which exerted the strongest antibacterial effects, were prepared into prescription 1 (Galla Chinensis + Fructus Mume), prescription 2 (Galla Chinensis + Fructus Hip-pophae)and prescription 3(Galla Chinensis + Lignum Sappan) for sensitivity test. The results showed that prescription 1 (Galla Chinensis+Fructus Mume) exhibited the strongest antibacterial effect.
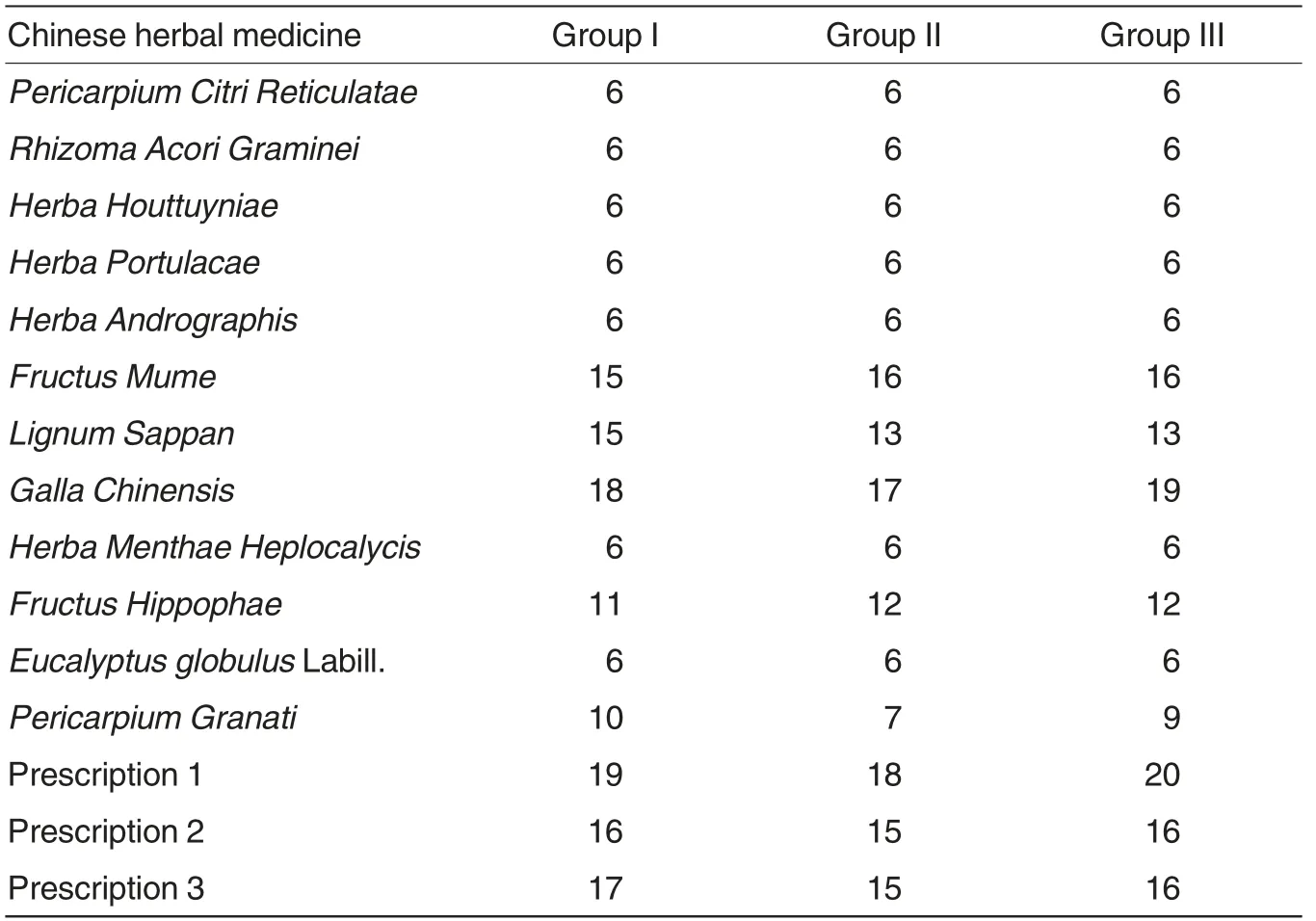
Table 2 Antibacterial circle diameter mm
Discussions
In the current aquaculture production, bacterial diseases are still the most important diseases endangering cultured fishes[1-4].According to the disease records from Key Laboratory of Preventive Veterinary Medicine of Hebei Province and existing researches,bacterial diseases of C. semilaevis Günther are mainly caused by Vibrio,and most pathogens belong to Gramnegative bacteria, such as V. harveyi,V.splendidus and V.anguillarum.Vibrio strains causing other flatfish diseases can also cause bacterial diseases in C. semilaevis Günther to some extent. In this study, V. harveyi is the main pathogen causing skin ulcer disease in C. semilaevis Günther.Statistics show that V. harveyi is the most important pathogen that causes diseases of maricultural animals[5],which can induce ulceration symptoms in Scophthalmus maximus[6], Fugu obscurus[7], Pseudosciaena crocea and other maricultural species, cause degeneration and necrosis of internal organs of diseased fishes[8-9], lead to physiological metabolic disorders of diseased fishes[10]and reduce their immunity and resistance to diseases,thereby causing the death of diseased individuals. In the present study, the pathogen causing skin ulcer disease in C. semilaevis Günther was identified as V.harveyi;all the three representative strains harbored OMP gene. According to the results of sensitivity test of the pathogen to Chinese herbal medicine, V. harveyi was strongly pathogenic to C. semilaevis Günther.Galla Chinensis, Fructus Mume,Fructus Hippophae and Lignum Sappan exerted strong antibacterial effects against V. harveyi; prescription 1(Galla Chinensis + Fructus Mume) exhibited the strongest antibacterial effect.
[1]LI NQ(李寧求),BAI JJ(白俊杰),WU SQ(吳淑琴), et al. Molecular classification of three kinds of pathogenic Vibrios in orange-spotted grouper, Epinephelus coioides(斜帶石斑魚3 種致病性弧菌的分子生物學(xué)鑒定)[J]. Journal of Fisheries of China (水產(chǎn)學(xué)報(bào)),2005,29(3):356-361.
[2]FAN WH(范文輝), WANG XH(王秀華),SHI CY(史成銀),et al.Identification and phylogenetic study of pathogenic bacteria causing ulcer disease of cultured turbot(Scophthalmus maximus)(養(yǎng)殖大菱鲆潰瘍癥病原菌的分離鑒定及系統(tǒng)發(fā)育分析)[J]. Acta Microbiologica Sinica(微生物學(xué)報(bào)),2005,45(5):665-670.
[3]WANG BK(王保坤),YU JH(余俊紅),LI J(李筠), et al. Isolation and identification of pathogen (Vibrio harveyi) from sea perch,Lateolabrax japonicus (花鱸弧菌病病原菌(哈維氏弧菌) 的分離與鑒定)[J]. Journal of Fishery Sciences of China(中國(guó)水產(chǎn)科學(xué)),2002,9(1):52-55.
[4]HUANG J(黃鈞),WEN HC(溫華成),SHI JG(施金谷),et al.Isolation and identification of pathogenic bacteria from Pelteobagrus fulvidraco ulcerative syndrome and its drug sensitive test (黃顙魚體表潰瘍病病原菌的分離鑒定與藥敏試驗(yàn))[J]. Guangxi Agricultural Sciences(南方農(nóng)業(yè)學(xué)報(bào)),2012,3(1):107-112.
[5]CHEN JX (陳吉祥), YANG H (楊慧),YANG XH (楊顯輝), et al. Cloning of hemolysin gene from a pathogenic Vibrio harveyi SF1 and its detection in diseased marine animals and marine environments (致病性哈維氏弧菌溶血素基因克隆及其檢測(cè))[J].Journal of FisherySciences of China (中國(guó)水產(chǎn)科學(xué)),2005,12(5):580-587.
[6]FAN WH (范文輝), HUANG J (黃捷),WANG XH (王秀華),et al.Identification and phylogenetic study of pathogenic bacteria causing ulcer disease of cultured turbot (Scophthalmus maximus)(養(yǎng)殖大菱鲆潰瘍癥病原菌的分離鑒定及系統(tǒng)發(fā)育分析)[J].Acta Microbiologica Sinica (微生物學(xué)報(bào)), 2005, 45(5):665-670.
[7]WANG B (王斌),YU LP (于蘭萍),HU L(胡亮), et al. Isolation and identification of bacteriosis pathogen from cultured Fugu obscurus with canker of skin(紅鰭東方鲀皮膚潰爛病病原菌的分離與鑒定) [J]. Journal of Fishery Sciences of China(中國(guó)水產(chǎn)科學(xué)),2008,15(2):352-358.
[8]MAO ZJ (毛芝娟), LIU GY (劉國(guó)勇),CHEN CF(陳昌福).Isolation and identification of pathogenic bacteria causing ulcerosis in large yellow croaker(Pseudosciaena crocea)(大黃魚潰瘍病致病菌的初步分離與鑒定) [J]. Journal of Anhui Agricultural University (安徽農(nóng)業(yè)大學(xué)學(xué)報(bào)),2002,29(2):178-181.
[9]XU XJ (徐曉津),XU B (徐斌),WANG J(王軍), et al. Histopathological studies on Pseudosciaena crocea artificially challenged with Vibrio harveyi(哈維氏弧菌人工感染大黃魚的組織病理學(xué)研究)[J].Journal of Xiamen University:Natural Science Edition(廈門大學(xué)學(xué)報(bào):自然科學(xué)版),2009,48(2):281-286.
[10]THOMPSON JR,RANDA MA,MARCELINO LA,et al.Diversity and dynamics of a North Atlantic coastal Vibrio community [J]. Applied and Environmental Microbiology, 2004, 70 (7):4103-4110.
 Agricultural Science & Technology2015年10期
Agricultural Science & Technology2015年10期
- Agricultural Science & Technology的其它文章
- Effects of Specific Gravity-based Seed Grading on Seed Germination,Seedling Emergence and Grain Yield of Hybrid Rice
- Effects of NaCl Stress on Seed Germination of Four Canavium album Raeuseh Cultivars
- Application Effects of Ultra-fine Powder Shaped Maize Seed Coating Agent in Spring Sowing areas in northeast China
- Breeding and Application of a Japonic Rice Cytoplasmic Male Sterility Line,E-Jing A
- Effect of Low Temperature and Sparse Light Conditions on Cold Tolerance of Different Rice Lines at Seedling Stage
- Molecular Marker Assisted Selection for Fusarium Wilt Resistance Breeding in Watermelon(Citrullus lanatus)
