Comparison of Clinical Effects of Au-Pt Based and Ni-Cr Based Porcelain Crowns
Li-chun Wu *,Ye Shi ,and Teng Ma
1Department of Stomatology,Peking Union Medical College Hospital,Chinese Academy of Medical Sciences &Peking Union Medical College,Beijing 100730,China
2Department of Stomatology,First Hospital of Huairou District,Beijing 101500,China
CURRENTLY,porcelain fused to metal (PFM) crown/bridge has been widely used as a routine method in clinical prosthodontics treatment.It is in favor by both doctors and patients because it combines the strength of the cast metal with the esthetics of the porcelain crown.It can be divided into the noble metal ceramic crown and non-noble metal ceramic crown depending on the different materials of based metal.This research investigated the clinical effects of two different kinds of based metal of PFM crowns at the moment of immediate restoration and 36-month follow-up.
PATIENTS AND METHODS
Patients
During 2008 and 2009,a total of 64 patients underwent mouth rehabilitation using PFM crowns by Li-chun Wu in Peking Union Medical College Hospital.Of them,there were 28 men and 36 women.The age ranged from 18 to 65 years,averaging 39.7 years.Totally 131 teeth were rehabilitated,among which 59 were rehabilitated with Au-Pt alloy metal ceramic crown and 72 with Ni-Cr alloy metal ceramic crown.All the patients were with healthy periodontal status.
Materials
Au-Pt alloy consists of 86% Au and 11% Pt (Argen Corp.,CA,US).Ni-Cr alloy consists of 65% Ni and 22.5% Cr(Bego,Germany).The porcelain cement consists of feldspathic porcelain (Vita Corp.,Germany).
Clinical protocol
The patients decided the final prosthesis after we informed them of the advantages and disadvantages of the two different kinds of materials.Before the tooth preparation,a Vita 3D-master shade guide (Vita Corp.) was used for shade selection under the circumstance with natural lights.The actual preparation was as followed∶for the adequate thickness of the restoration,1.5 to 2.0 mm reduction was necessary on the occlusal and labial/buccal surface.The reduction on the proximal axial surface required less (1.5 mm),while that on the lingual surface required 0.5 to 1.0 mm.The subgingival margin was placed 0.5 to 0.8 mm below the gums.A 135 degrees shoulder being 1.0 to 1.5 mm in width on the labial/buccal surface was carefully prepared.After finishing the tooth surface preparation,we displaced gingiva to make a complete impression.A string was placed in the interproximal sulcus for 5 or 10 minutes.Then the impression was made with alginate material and filled with superstone.After impression,a temporary crown was cemented by zinc oxide eugenol (ZOE).After 7 days,we evaluated its proximal contact with adjacent teeth and occlusion.After adjustment and polishing,the final restoration was adhered by zinc polycarboxylate cement.
Standard
The following clinical parameters around the crown were recorded∶porcelain fracture,shade,marginal adaptation,gingival discoloration,and gingival status.All the parameters were divided into different grades (Table 1).
Statistical analysis
TheMann-Whitney Utest was used to detect differences between two groups by using SPSS 12.0 software.Results of the tests withP-values less than 0.05 were considered as significant.
RESULTS
The effects of Au-Pt based and Ni-Cr based porcelain crowns at the initial of restoration and 36-month of follow-up are shown in Table 2.
After 36 months of restoration,tooth rehabilitated by Au-Pt based or Ni-Cr based porcelain crowns did not occur porcelain fracture (P>0.05).Significant difference was found between Au-Pt alloy and Ni-Cr alloy groups in shade,marginal adaptation,gingival discoloration,as well as gingival status at 36 months of follow-up (allP<0.05),and the clinical effects of Au-Pt based porcelain crowns were better than those of Ni-Cr based porcelain crowns.
For teeth restored using porcelain fused to Au-Pt alloy crown,porcelain fracture,shade,marginal adaptation,gingival discoloration,and gingival status after 36 months of follow-up had no significant change compared with immediate restoration (allP>0.05).In the Ni-Cr alloy group,the clinical parameters regarding shade,gingival discoloration,and gingival status at the end of follow-up were worse than those at the initial of restoration (allP<0.05);however,other parameters had no significant difference (allP>0.05).

Table 1.Grading scale table of clinical parameters
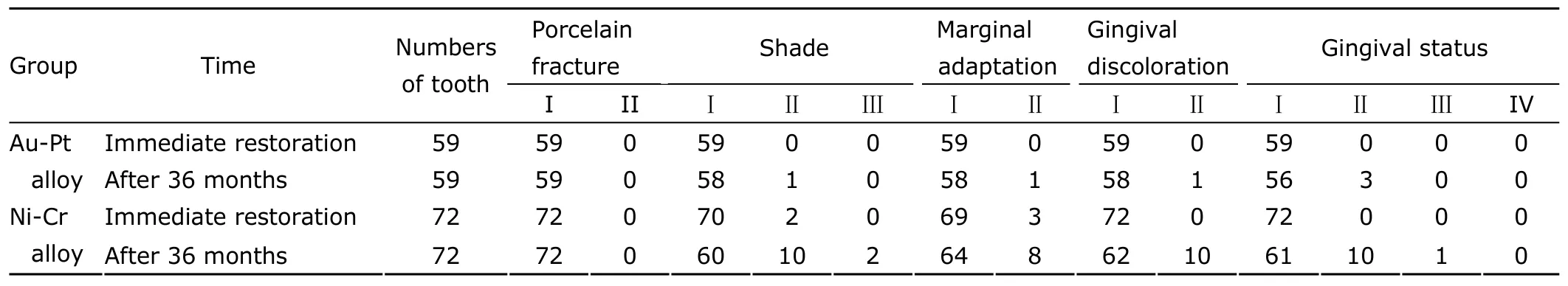
Table 2.Comparisons of clinical effects of two different kinds of metal based crown
DISCUSSION
PFM crown/bridge has been used for several decades.With the wide use of this method for restoration,the damage of gingival tissue caused by the crown has attracted more concern.The safety and bio-compatibility of the metal alloy have become the important issues for clinical application
No porcelain fracture occurred in tooth which was restored by two kinds of PFM crowns in this study,which meets the clinical standard.
The shade of the metal ceramic crown is the same as or similar to the natural teeth,which is the key to get a good aesthetic effect.This study showed that the shade of Au-Pt alloy ceramic crown was better than that of Ni-Cr alloy ceramic crown.The shade of Au-Pt alloy based PFM crown changes to light yellow after preoxidation,while the shade of Ni-Cr alloy based PFM crown changes to grayish black.The former is more similar to the color of natural teeth after applying the porcelain.Therefore,the gray color of Ni-Cr alloy needs to be masked with a layer of opaque and body,which affects the aesthetic effects.2,3
In this study,no gingival discoloration was observed in both the Au-Pt alloy and Ni-Cr alloy groups at the moment of immediate restoration.Only one case undergoing tooth rehabilitation with Au-Pt alloy ceramic crown had color change of cervical area 36 months after restoration;however,ten cases in Ni-Cr alloy group suffered from gingival discoloration at the same time.Therefore,Ni-Cr alloy metal ceramic crown was more prone to gingival discoloration.There are mainly two reasons.First,humoral contact with dental metallic materials will produce a corrosive effect on metal,resulting in the precipitation of the metal ion and its derivatives,which will cause harmful effects on the body tissue.Corrosion is closely related to the biocompatibility of the alloy.The precious metal such as Au-Pt alloy is not easily eroded by body fluids.4However,saliva and gingival crevicular fluid will cause the metal corrosion for Ni-Cr alloy.The metal iron and its derivatives will cause the cervical color change and gingivitis,even allergic reactions.5On the other hand,free gingival light transmitted should be taken into consideration for the optical point of view.The base metal of Ni-Cr alloy is present gray-black.If the ceramic neck is not thick enough,there will be metal color or decreasing transparency,which will make the gums appear blue-gray.
The marginal adaptation is the important index in evaluating the clinical effect of the prosthesis.In this study,the marginal adaptation of two groups after 36 months of restoration was significantly different (P<0.05).The statistics showed that Au-Pt alloy PFM would get a better marginal fitness than Ni-Cr alloy PFM.The Au-Pt alloy has good mechanical properties.It can meet the requirements of precision casting and good marginal adaptation.Schillinget al6thought that poor casting properties would lead to poor fitness.Casting shrinkage rate of Au-Pt alloy was 1.4%-1.6%,while that of Ni-Cr alloy was 2.0%-2.1%.Poor marginal adaptation was prone to cause gingivitis and gingival atrophy.7
In this study,the gingival status at the moment of prosthesis placement was not significantly different from 36 months of rehabilitation in the Au-Pt alloy group.However,there was significant difference in the Ni-Cr alloy group.Analyzing the reasons,when the margin of the Ni-Cr alloy base was not perfectly adaptable,the cement in the gap would get a larger contact area with the periodontal tissues,which would cause the increase of bacterial attachment.And the marginal gap of the crown would induce cement dissolution.The micro-gap could provide a protective environment for bacterial growth,which was easy to cause inflammation.8The margin of PMF consisted of metal base,opaque,and dentine porcelain.Among these components,the opaque is more likely to make plaque attach,causing gingivitis,for its coarse particles and large pore.9Furthermore,biocompatibility of Ni-Cr alloy was respectively poor.Cervical metal was prone to be eroded in the body fluids and released metal ions which would stimulate the gums.
Through observing the clinical effects on 131 teeth of 64 cases with two different kinds of PFM crowns for 36 months,we believe that the Au-Pt alloy metal ceramic crown has good biocompatibility and long-term effects.Compared with the Ni-Cr alloy metal ceramic crown,the Au-Pt alloy metal ceramic crown has the advantage of not only the less soft tissue damage such as gingival marginal change in color and inflammation but also the better esthetic effect.Nowadays it is welcomed by patients and dentists as an ideal prosthesis.
1.L?e H.The Gingival index,the plaque index and the retention index systems.J Periodontol 1967;38∶610-6.
2.Wang SP,Jin S,Wang SG,et al.Clinical uses of precious metal ceramic crowns.J Tianjin Med Univ 2007;13∶256-7.
3.Liu X,Liu WF,Xu L.Clinical evaluation of porcelainfused-to-three kinds of metal base crown.J Oral Sci Res 2002;18∶336-8.
4.Chen YQ.Oral biomaterials science.Beijing∶Beijing Chem Indus Press,2004.p.338-9.
5.Hu B,Zhang FQ.Electrochemical corrosion characteristics of Ni-Cr alloy in artificial saliva.Chin J Stomatol 2003;38∶140-2.
6.Schilling ER,Miller BH,Woody RD,et al.Marginal gap of crowns made with a phosphate-bonded investment and accelerated casting method.J Prosthet Dent 1999;81∶129-34.
7.Ma XX.Oral prosthodontics.Beijing∶Beijing People's Medical Publishing House,2006.p.129.
8.Pan DD,Zhang XY.Effect of porcelain fused metal crown on gingival health.Chin J Dent Mater Devices 2005;14∶83-92.
9.He R,Sun SX,Yu R.Clinical study of different marginal types in non-precious metal-ceramic crowns.Chin J Aesthet Med 2007;16∶1708-10.
 Chinese Medical Sciences Journal2012年3期
Chinese Medical Sciences Journal2012年3期
- Chinese Medical Sciences Journal的其它文章
- Hypercalcemia Appeared in a Patient with Glucagonoma Treated with Octreotide Acetate Long-acting Release
- Zinc Finger Protein-activating Transcription Factor Up-regulates Vascular Endothelial Growth Factor-A Expression in Vitro△
- Clinical Analysis of Placenta Previa Complicated with Previous Caesarean Section△
- Hipbone Biomechanical Finite Element Analysis and Clinical Study after the Resection of Ischiopubic Tumors△
- Accuracy Validation for Medical Image Registration Algorithms:a Review△
- Nucleotide-binding Oligomerization Domain-1 Ligand Induces Inflammation and Attenuates Glucose Uptake in Human Adipocytes△
