Multiple-Constraint-Aware RWA Algorithms Based on a Comprehensive Evaluation Model:Usein Wavelength-Switched Optical Networks
Hui Yang ,Yongli Zhao ,Shanguo Huang ,
Dajiang Wang 2,Xuping Cao 2,and Xuefeng Lin 2
(1.State Key Laboratory of Information Photonics and Optical Communications,Beijing University of Posts and Telecommunications,Beijing 100876,China;
2.ZTECorporation,Shenzhen 518057,China)
Abstract Because of explosive growth in Internet traffic and high complexity of heterogeneous networks,improving the routing and wavelength assignment(RWA)algorithm in underlying optical networks has become very important.Where there are multiple links between different the node pairs,a traditional wavelength-assignment algorithm may be invalid for a wavelength-switched optical networks(WSON)that has directional blocking constraints.Also,impairments in network nodes and subsequent degradation of optical signals may cause modulation failure in the optical network.In this paper,we propose an RWA algorithm based on a novel evaluation model for a WSON that has multiple constraints.The algorithm includes comprehensive evaluation model(CEM)and directional blocking constraint RWA based on CEM(DB-RWA).Diverse constraints are abstracted into various constraint conditions in order to better assign routing and wavelength.We propose using the novel CEM to optimize routing according to an assessed value of constraints on transmission performance.This eliminates the effects of physical transmission impairments in a WSON.DB-RWA based on CEM abstracts directional blocking conditions in multiple links between network nodes into directional blocking constraints.It also satisfies rigorous network specifications and provides flexibility,scalability,and first-fit rate for the backbone,especially in multiple links between WSON nodes.
Keyw ords RWA;WSON;multiple links between nodes pair;directional blocking constraint;comprehensive evaluation model
1 Introduction
T he Internet has become a critical piece of infrastructure in modern societies,and explosive growth in the number of Internet users has given rise to a corresponding explosion in Internet traffic.Over time,data packets have become the main type of traffic being transmitted over networks.An optical network carries not only fixed-bandwidth voice services but also variable-bandwidth services,mobile services,and multimedia services.Optical networks must support grid computing,file downloading,video-on-demand,storage-area networks,and other new applications.Meanwhile,demand is growing for capacity,responsiveness,resilience,quality,and different types of services.Underlying optical networks are ultrahigh-capacity,large-scale platforms that support synchronous optical network and synchronous digital hierarchy(SONET/SDH),multiprotocol label-switching transport profile(MPLS-TP),and optical transport network(OTN)for transporting data at different granularities.In large-scale commercial applications,wavelength-switched optical networks(WSONs)must satisfy the needs of network service providers,who face strong pressure to increase availability,improve reliability,and reduce bandwidth cost.
Nodes in a WSON—unlike nodes in other types of generalized multiprotocol label-switching(GMPLS)networks—are highly asymmetric in their switching capabilities,and compatibility of signal types and network components needs to be considered.Label assignment can also be nonlocal[1].In a WSON,wavelength continuity and resource availability constraints must be satisfied in order to determine optimal and cost-effective optical connections(paths)[1].Such determining of paths is referred to as routing and wavelength assignment(RWA).
To design a new WSON for complex contexts,multiple constraint conditions need to be applied to the evaluation model and RWAalgorithms.For redundancy and reliability in optical networks,most network operators place multiple optical fibers between the network nodes,especially in the backbone network or main part of an access or metro network.Therefore,application scenarios based on multiple links between network nodes have become the focus of attention of network operators.Traditionally,RWA algorithms have been used for only one link between network nodes;however,such algorithms are invalid for routing between different links and nodes[2].
Because there are impairments of varying degrees in a large-scale optical network,degradation can cause unacceptable bit error rates or even a complete failure to detect and demodulate the received signal.Therefore,optical impairments need to be taken into account in an RWA algorithm so that signals with acceptable quality can be propagated in the WSON.
Many studies have been done on quality of transmission(QoT)compensation as well as impairment-aware routing and wavelength assignment(IA-RWA)[3]-[5]based on path computation element(PCE)strategies and extended resource reservation protocol(RSVP)[6].Many traditional RWA algorithms have been studied only in one link field[7],[8].When there are multiple links between the network nodes,few traditional RWA algorithms can successfully compute the optimalpath,and few have been evaluated in terms of impairment assessment model[9].
In this paper,we describe a novel RWA algorithm based on a model for assessing multiple constraints in a WSON.The algorithm comprises a comprehensive evaluation model(CEM)and directional blocking RWA based on the CEM(DB-RWA).Diverse scenarios are abstracted into various constraint conditions so that routing and wavelength can be better assigned.We propose a novel CEM that optimizes routing based on a value derived from an assessment of constraints on transmission performance.The algorithm eliminates the effects of impairments in WSON transmission.
Directional blocking conditions are abstracted by DB-RWA based on CEM in multiple links between the network nodes into directional blocking constraints that satisfy the rigorous network specifications.DB-RWAbased on CEM provides scalability and flexibility for the backbone,especially in multiple links between WSON nodes.
2 Comprehensive Evaluation Model
When an optical signal is being transmitted in a fiber link and is passing through an optical device or cell,physical impairments—such as reduced signal strength;triggering noise;or changing time domain,frequency domain,or polarization properties—are ineluctable.Especially in a transparent or translucent light network,which lacks photoelectric regenerators,the effects of impairments accumulate as the optical signal is transmitted.When an impairment threshold is exceeded,quality of transmission is seriously affected.Transmission impairments can be linear or nonlinear.The effects of linear impairments of every wavelength are independent,and the effects of nonlinear impairments are not independent.An IVmodule is used to estimate the transmission quality of the chosen wavelength path so that the path meets QoTrequirements[10]-[12].Currently,the evaluation model most widely used is a multitarget constraint evaluation model.In this model,constraints are considered individually,and a light path is only eligible when it satisfies the thresholds for each target constraint.However,because this model ignores the interaction of factors,the estimation may be highly inaccurate.
In a comprehensive evaluation model,physicalimpairment is reflected in the error rate,which reflects a variety of impairments.This model uses a simulation and analytical fitting method to comprehensively evaluate physical impairments.It also uses bit error rate(BER)as a constraint when evaluating the QoTof a light path.Tolerance security reserve can be obtained from the BER.
Acomprehensive evaluation model takes into account the interaction of physical impairments.It requires much calculation;the modelis complex;and much information is acquired.However,the accuracy of the evaluation is greatly improved.A general way of implementing the model is through analytical and experimentalsimulation(fitting).By transforming the physicalimpairment into a BER,we can measure the quality of light transmission.
2.1 Sketch of Evaluation Model
BERis a key parameter for assessing systems that transmit digital data.BERis used to assess the fullend-to-end performance of a system that includes transmitter,receiver,and the medium in-between.BERallows the performance of a whole system in operation to be tested,which differs from testing individual component parts and hoping that they will operate satisfactorily when in place.The BERis the rate at which errors occur in a transmission system.This can be directly translated into the number of errors that occur in a string of bits.According to the principle of Gaussian noise distribution,Q-factor corresponds to BER.By evaluating Q-factor,the quality of a transmission system can be estimated.Q-factor is given by
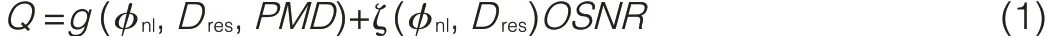
Where g()is the accumulated cost of each kind of impairment in the transmission,andζ()is the modeleffect caused by individual impairments such as dispersion,cross-phase modulation(XPM),and four-wave mixing(FWM).In normal circumstances,ζ()=1 when amplified spontaneous emission(ASE)noise plays a main role.As nonlinear effects increase,ζ()decreases below 1.This formula for evaluating transmission quality takes into account each kind of physical impairment,including residual dispersion,nonlinear phase shift,ASEnoise,and polarization mode dispersion(PMD)[13]-[15].The Q-factor cost of each physical impairment can be obtained by a semianalytical method in order to obtain the total performance index.
OSNRrefis the reference of the optical signal-to-noise ratio(obtained by experiment)when the BERrequirement is met,that is,when Q=Qref.The reference OSNRrefis a function of physicalimpairments,including residualdispersion,nonlinear phase shift,PMD,and crosstalk.The Q function can be?N
written as

We may assume that OSNRBtBis the OSNRwhen achieving Qrefin the back-to-back configuration.The Q-factor cost,taking into account various transmission impairments,is
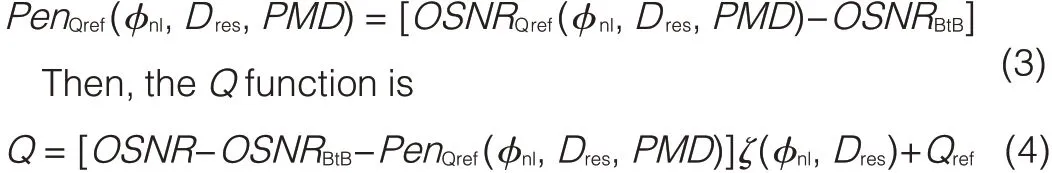
Because the combined effect of dispersion and nonlinear phase shift is not related to PMD and crosstalk,the Q function can be written as
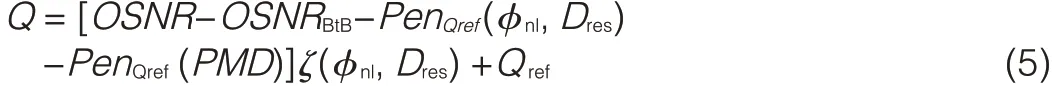
Thus,by obtaining the combined effects of dispersion and nonlinear phase shift,Q-factor costs of PMD,and other
impairments,we can work out the total Q function and BERof a transmission system.Q-factor costs can be obtained using a semianalytical method,that is,by collecting vast quantities of data from experiment(or simulation)about the relationship between a physicalimpairment and its Q-factor cost.The expression of the corresponding Q-factor cost can be obtained by polynomial regression.Finally,the regression formulas can be used to determine a performance index,such as Q-factor function or BER.
PenQrefis the OSNRcost when achieving Qrefat the current impairment.OSNRcost assumes a BER.The smallest OSNRB2Bcan be obtained with the B2B configuration that has no noise,dispersion,or nonlinear effects.If we want the same BERwhen there is dispersion or nonlinear effects,a higher OSNRis needed.The OSNRcost is the difference between these two values.
If we only consider dispersion,the cost is called dispersion cost.Likewise,if we only consider nonlinearity,the cost is called nonlinear effect cost.There is a complicated interaction between nonlinear effects,such as SPM,XPM and FWM,and dispersion.Also,there is no need to consider nonlinear phase noise for a phase-modulation system or QAM system.
2.2 Computation of Correction Factor
Usually,the correction factorζ(Dres,φnl)is a constant close to 1.Its value depends on span,optical power into the fiber,and residual dispersion.Span and optical power are the main factors affecting the correction factor,and residual dispersion has a minor effect on the correction factor.The correction factor can be expressed using Cure fitting when the influence of fiber span and opticalpower into fiber are taken into consideration:
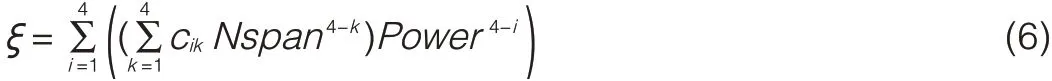
2.3 OSNR Cost of Residual Dispersion and Nonlinear Phase Shift
We can acquire the OSNRcost of residual dispersion and nonlinear phase shift by analyzing PenQref(Dres,φnl)under a fixed reference BER(or Q value)in a simulation or experiment.Much experimental data is needed for function fitting.Generally,the function can be obtained in two steps:
Step 1:When OSNRcost is less than 5 d B,fit each curve of residual dispersion and the cost to a binomialfunction:
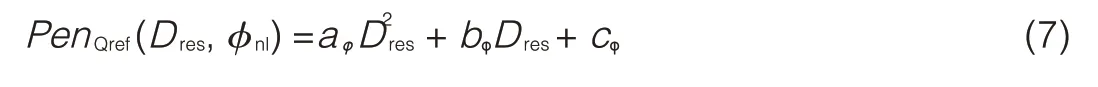
Step 2:The coefficients aφ,bφ,and cφshould be fitted to a two,three,or four order polynomial based onφnl.The OSNR cost is

2.4 Polarization Membrane Dispersion OSNR Cost
Polarization membrane dispersion in an optical fiber can be evaluated by the biggest group delay difference(DGD)probability statistical model.The independent cost of PMD can be determined by simulations in different DGD configurations.
3 DB-RWA based on CEM in Multiple Links Between Node Pairs
In the network topology,there are always more than one fiber link between the connected nodes.In a network where there are multiple links between adjacent nodes,finding a DB-RWA solution based on CEM is difficult.The network design must include route calculation,link assignment,and wavelength assignment.The design must also be capable of improving the algorithm complexity and time redundancy because of the larger network scale.The solution we propose can solve these problems.The procedures of the proposal are given in Fig.1.In a network environment where there are many fiber links between adjacent nodes,first we abstract a new network topology design according to the characteristics of the original network.The link information between the same hops is saved in the same structure so that it can be uniformly managed.Then,a KSPor other algorithm is used to calculate the path from source node to destination node.When the route is calculated,fiber and wavelength are assigned.
We abstract the multiple-link topology into a single-link topology.As a result,only the hops need to be calculated when calculating the route.There is no need to assign the specific link between adjacent nodes.This is done during backward wavelength assignment.
The most important part of the design is reflected in the wavelength allocation scheme(Table 1).The improved information structure ensures topology abstraction is achieved.Anormalrouting algorithm,such as D or KSP,can be used.In Table 1,
is the number of the fiber links between adjacent nodes

▼Table 1.Link and wavelength information
?M is the number of wavelengths in every fiber
?i is the i th wavelength,i=1,2,...,M
?j is the j th fiber,j=1,2,...,N
?aj,iis the occupancy of the i th wavelength in the j th fiber,0=occupied,1=available
?biis the number of available fibers with the i th wavelength
?ciis the occupancy of the i th wavelength.If the i th wavelength of any fiber is available,ci=1.If the i th wavelength of every fiber is occupied,ci=0.
We implemented and evaluated the proposed approach in the eighteen-node topology(Fig.2).The testbed has the same topology as the network topology,in which there are10 fiber links per hop,and each fiber link contains five wavelengths.In terms of traffic characteristics,uniformly distributed light path requests arrive at the network following a Poisson process.The holding time of the light path is exponentially distributed using unit mean.
For the directionless condition,if the traffic moves from node Ato K,the path derived using D algorithm is A-F-G-K.If the paths are calculated using KSPalgorithm,the first best path is A-F-G-K;the second best path is A-B-F-G-K;and the third best path is A-F-G-L-K.For the directionalcondition,we assume that link A-Fand link B-Fcan only exchange with link F-E.The three best paths cannot meet the directional limitation,but the path A-F-E-H-G-K can be used.As a result,we can try to find the RWA solution in the directional condition.
4 Simulation and Results
4.1 CEM Experimental Simulation System
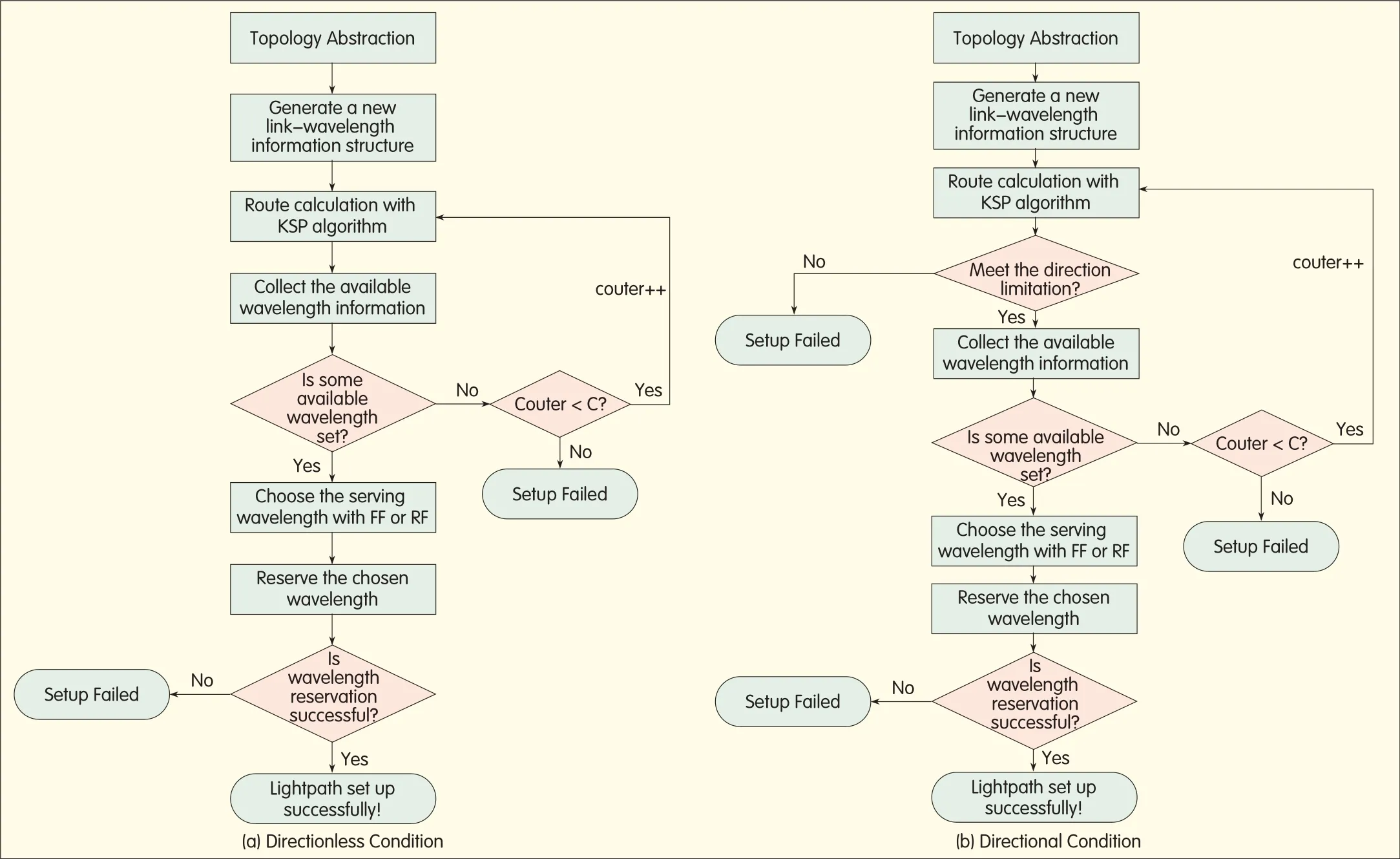
▲Figure 1.The procedures for DB-RWAin multiple links between the node pairs.
Because an analytical solution to OSNRcost of impairment cannot be obtained directly,a simulation or experimental fitting can be used to work out a second cost curve of impairment OSNRand obtain an approximate analytical solution.
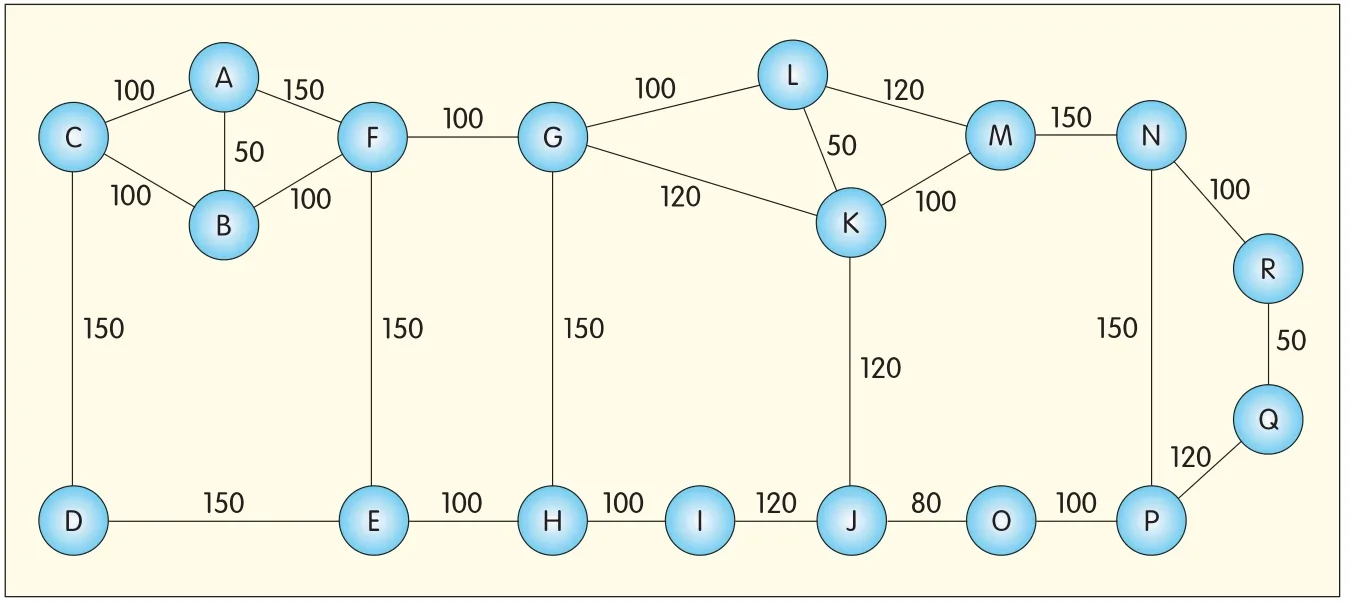
▲Figure 2.Network topology.
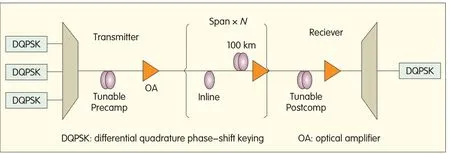
▲Figure 3.Structure of the simulation system.
In this simulation method,the structure of the simulation system in Fig.3 can be used.
At the transmitting terminal,the required number of wavelengths can be dispersed to emulate the physical impairment in the context of a single channel and multiple channels.After the optical multiplexer,the optical signal enters a dispersion compensating fiber(DCF)with predispersion compensation.Predispersion compensation depends on the value of dispersion parameters,span residual dispersion,and number of spans.Postdispersion compensation depends on the residual dispersion configuration of a span.The receiver performs decoding and judging based on the demux and demodulator and arrives at the BER.
In the simulation of OSNRcost curves,only one kind of impairment should generally be considered,and other impairments should be ignored.Other system parameters should be fixed.In simulation,parameters for the transmission fiber span,transmitting signal,in-span DCF,pre-DCF,and post-DCFare fixed.The fixed parameters of the transmission fiber span include fiber type,optical attenuation coefficient,optical fiber dispersion coefficient,span length,and nonlinear coupling coefficient.The fixed parameters of the transmitting signal are modulation format,signal rate,signal transmission power,symbol line code,duty cycle of optical pulse,rolling pressure coefficient,channel interval,and center wavelength.In-span DCFcontains dispersion coefficient,attenuation,and nonlinear coupling coefficient.The length of the compensation fiber depends on each segment's residual dispersion value.Pre-DCFand post-DCFmaintain the dispersion coefficient,nonlinear coupling coefficient,and fiber length(which is determined by compensation value).
When calculating the impairment OSNRcost curve,we can change the number of spans and the scheme for the span dispersion compensation in order to obtain more comprehensive data.
4.2DB-RWA-Based CEM Simulation and Results
We have implemented and evaluated the proposed approach in the eighteen-node topology(Fig.2).The testbed describes the same topology as the network topology in Fig.2,in which 10 fiber links per hop are assumed.Each fiber link contains five wavelengths.In terms of traffic characteristics,uniformly distributed light path requests arrive at the network following a Poisson process.The holding time of light path is exponentially distributed using unit mean.
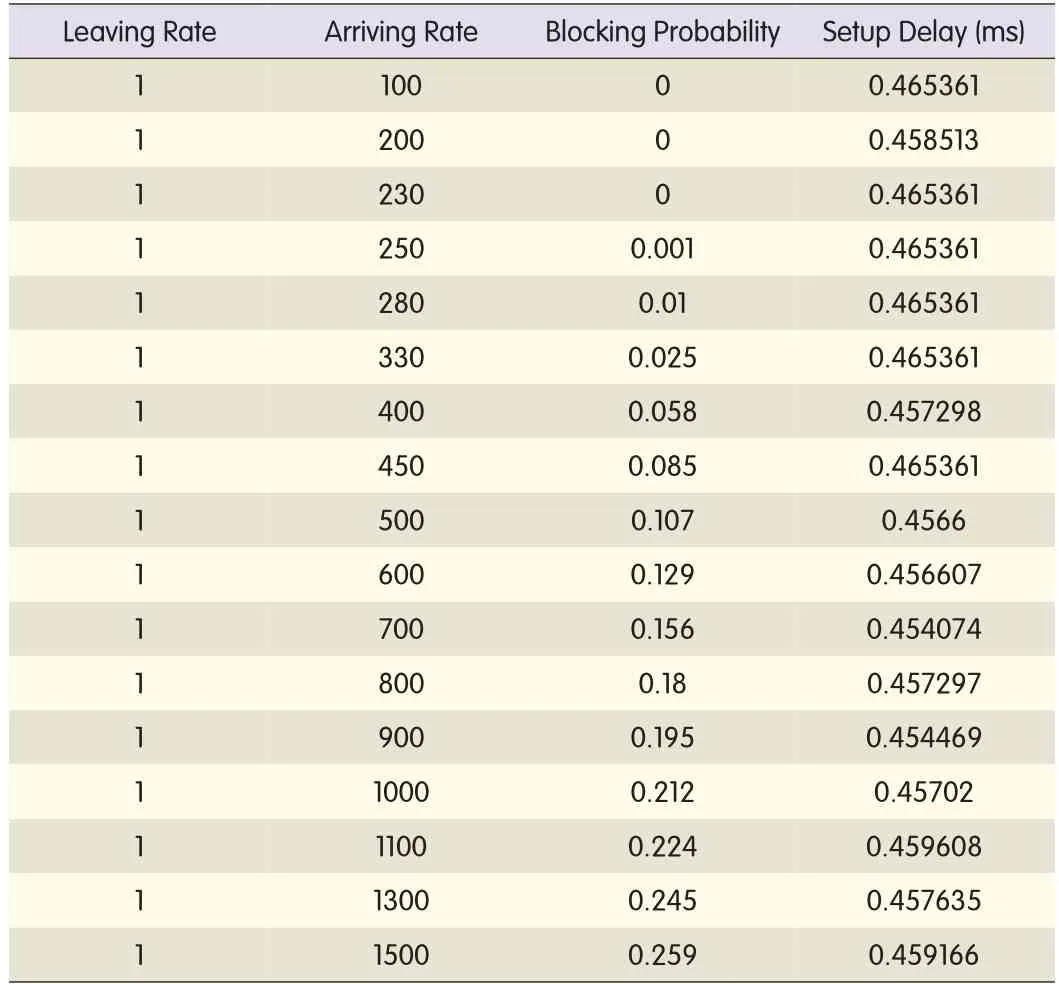
In the directionless condition,the simulation environment is independent of the direction limitation.The statistics are obtained for 100 to 1500 Erlangs.Table 2 shows the blocking rates and setup delays.
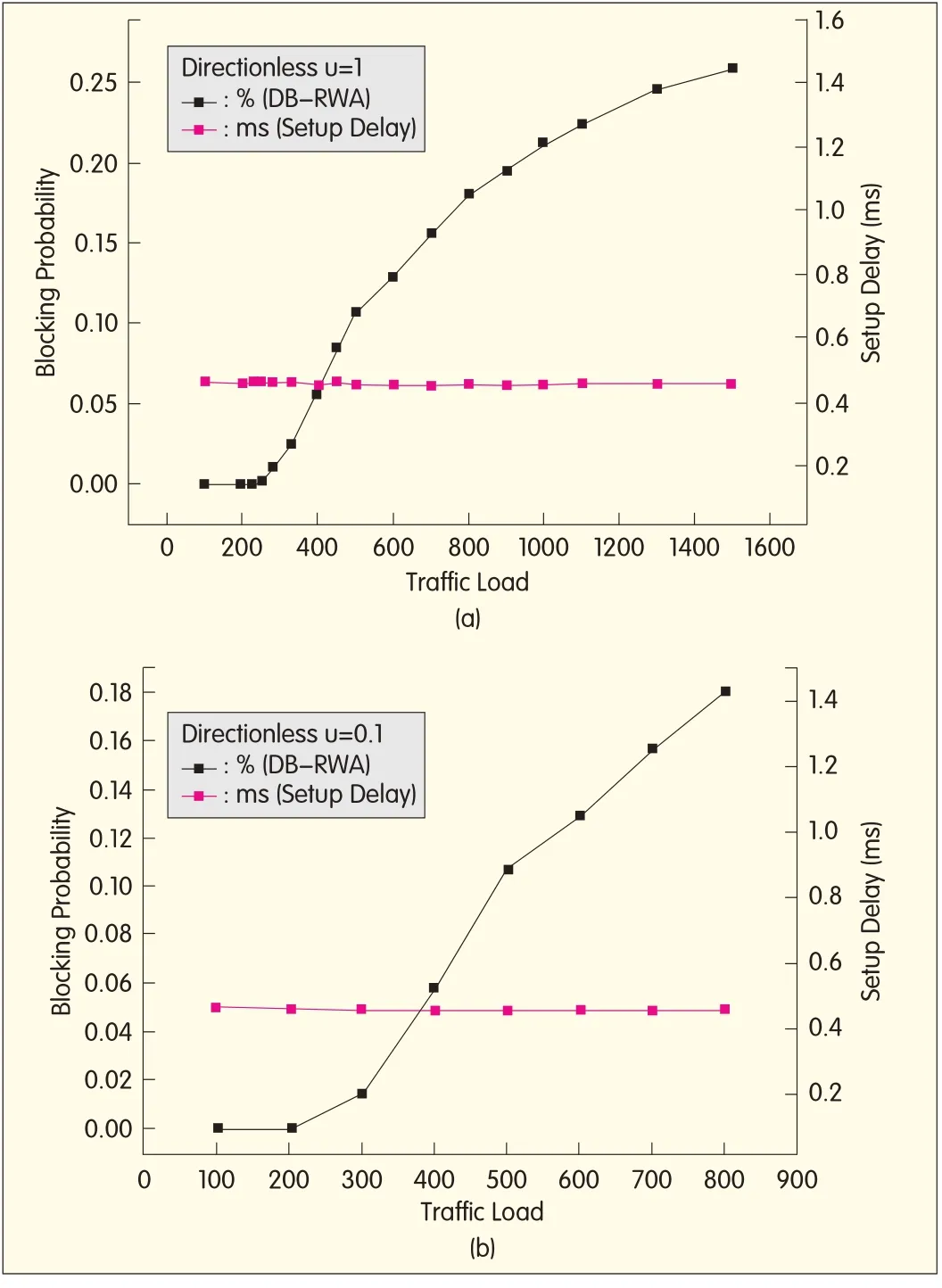
Fig.4(a)is based on the data in Table 2.
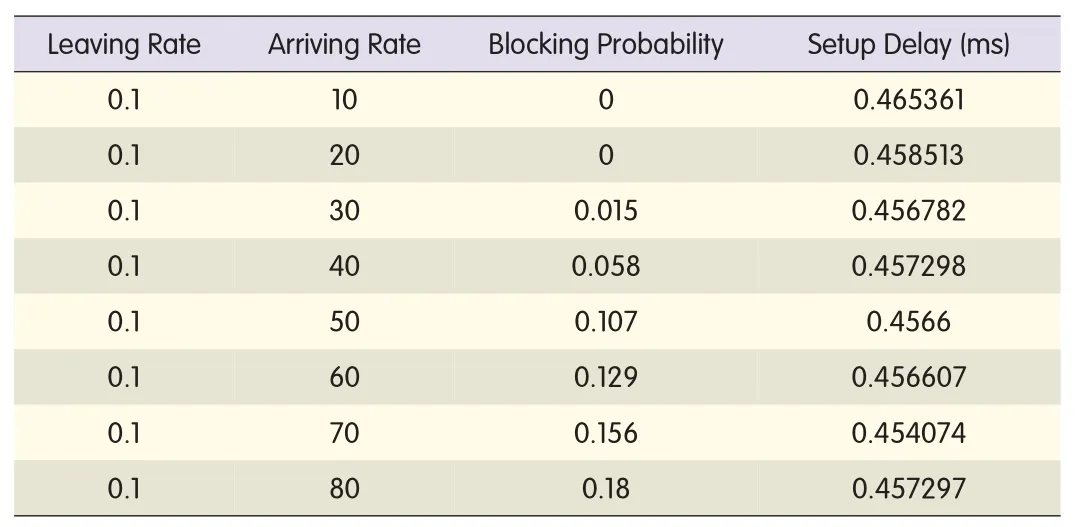
We assume the leaving rateμ=0.1 and the arriving rate ranges from 10 to 80services per second.The statistics areobtained for 100 to 800 Erlangs.The blocking rate and the setup delay are shown in Table 3.
▼Table 2.Blocking rate and setup delay when leaving rate is 1.
▲Figure 4.Blocking probabilityand setup delay when leaving rate is(a)1 and(b)0.1.
▼Table 3.The blocking rate and the setup delay when leaving rate is 0.1.
Fig.4(b)is based on the data in Table 3.As the traffic load increases,blocking probability increases.Fig.4(b)also confirms that the simulation is correct and reasonable.The setup delay is around 0.457 ms with smallfluctuation.The setup delay is calculated from the beginning of route calculation to the end of wavelength assignment.Because the K of the KSPalgorithm remains unchanged,the setup delay barely changes in different arriving-rate scenarios.
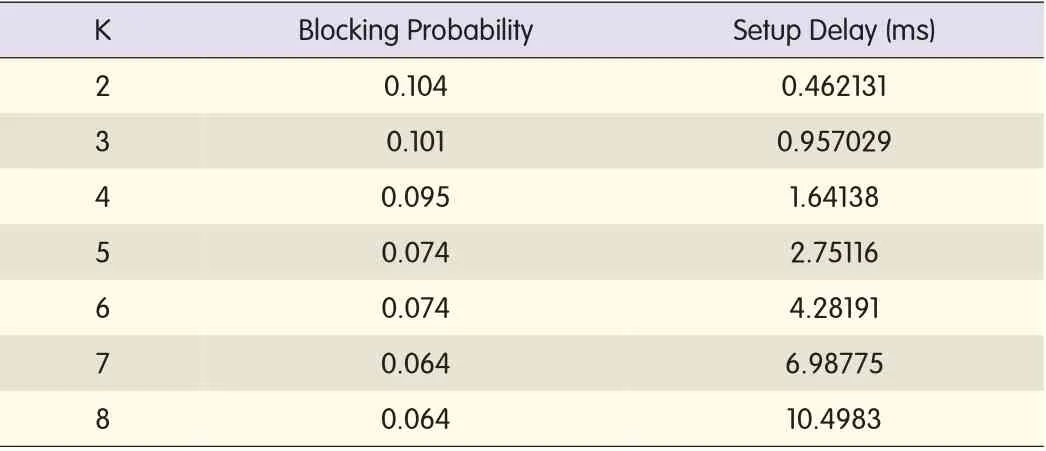
▼Table 4.Blocking rate and setup delay in directional condition
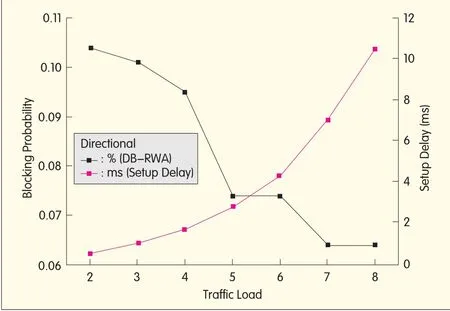
▲Figure 5.The setup delays with Kvalues.
In the directional condition,where the network is limited by direction,we assume the arriving rate remains at 40 services per second and the leaving rate remains 0.1.KSPalgorithm followed by the K-value is equalto 2,3,...,8.Table 4 and Fig.5 show the blocking probabilities and the setup delays.
Fig.5 shows the setup delays with K values.When K increases,the setup delay,which is determined by the complexity of the KSPalgorithm,gradually becomes longer.According to the data in Table 4,K increases,the probability of blocking reduction decreases.When the number of alternative paths increases,there is more chance a route will be chosen that has a lower chance of blocking.
5 Conclusion
In this paper,we have presented a novel CEM and DB-RWA algorithm based on CEM for use in a WSON with multiple constraints.Taking into account the interaction between physical impairments,a comprehensive evaluation model eliminates the effects of physical transmission impairments in a WSON.CEM improves the evaluation accuracy in the mathematicalmethod and reasonably obtains and calculates large amount of information.The implementation method and quality of light transmission are analytical and transform the physical impairment factor into a BERprice,especially in the transparent light network that lacks photoelectric regenerators.DB-RWA algorithm basedon CEM in multiple constraint conditions in WSON not only solves the problem of RWA in multiple links between network adjacent nodes but also substantially decreases the setup delay and cost of computation.With increasing scope in the multiple links between adjacent nodes in the network,time performance can be optimized.The simulations in both directional and directionless condition demonstrate that the network is optimized to for shorter routing time as the number of network nodes and links in adjacent nodes increases.An optimal path can be chosen for ultrahigh capacity with lower blocking probability.
Acknowledgment
This work was supported in part by 973 Program
(2010CB328204),NSFCproject(60932004)and RFDPProject(20090005110013).
- ZTE Communications的其它文章
- Introduction to ZTECommunications
- ZTEWins Contract to Provide LTEWireless Uifi Set to UNE
- ZTEPartners with KPNGroup Belgium to Deploy Packet-Switched Core Network
- Mobile Cloud for Personalized Any-Media Services
- Open Augmented Reality Standards:Current Activities in Standards-Development Organizations
- Field Transmission of 100Gand Beyond:Multiple Baud Ratesand Mixed Line Rates Using Nyquist-WDMTechnology

